Abstract
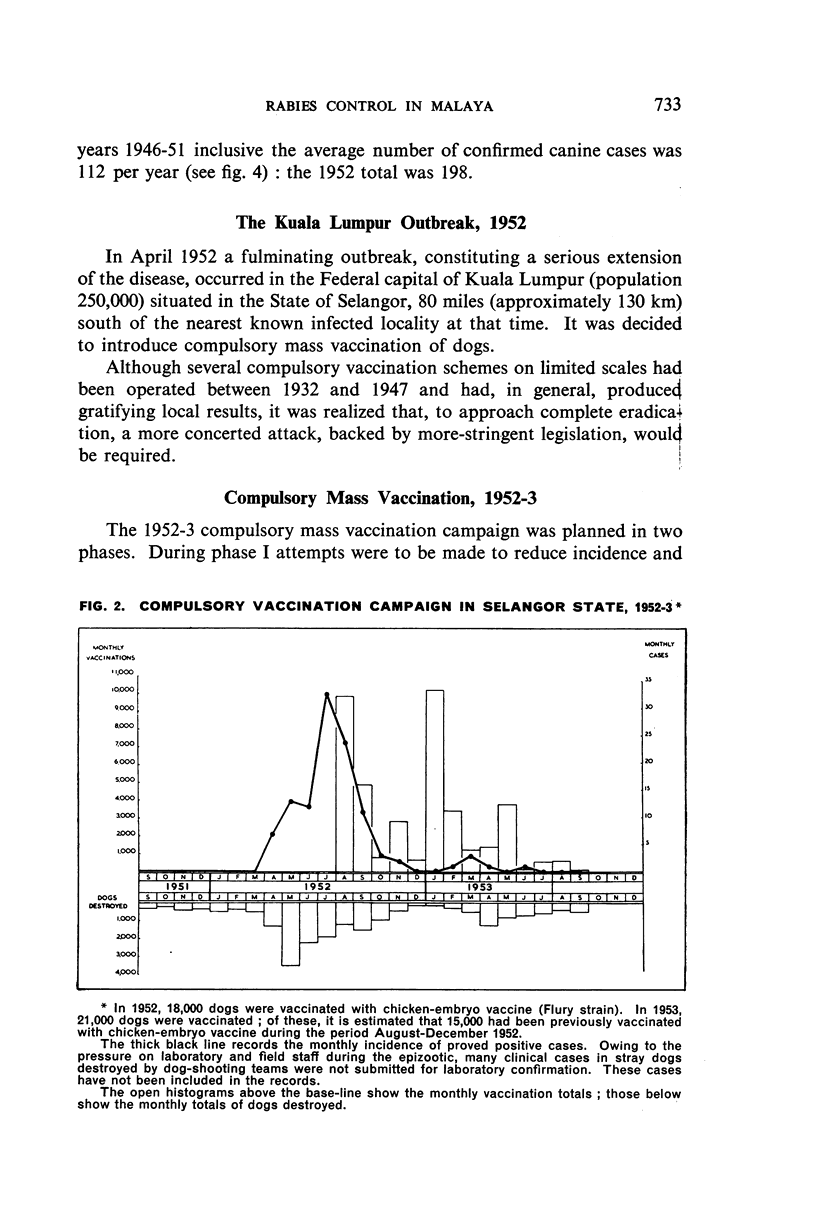
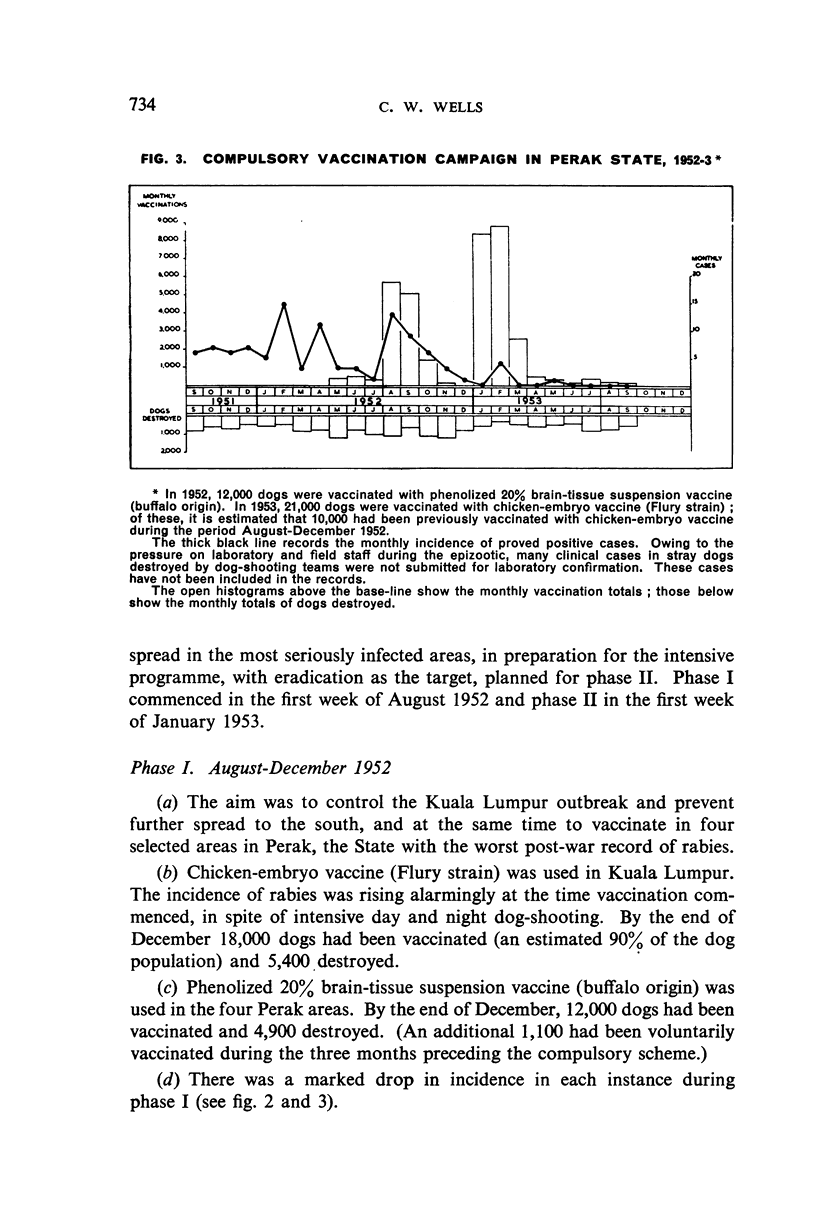
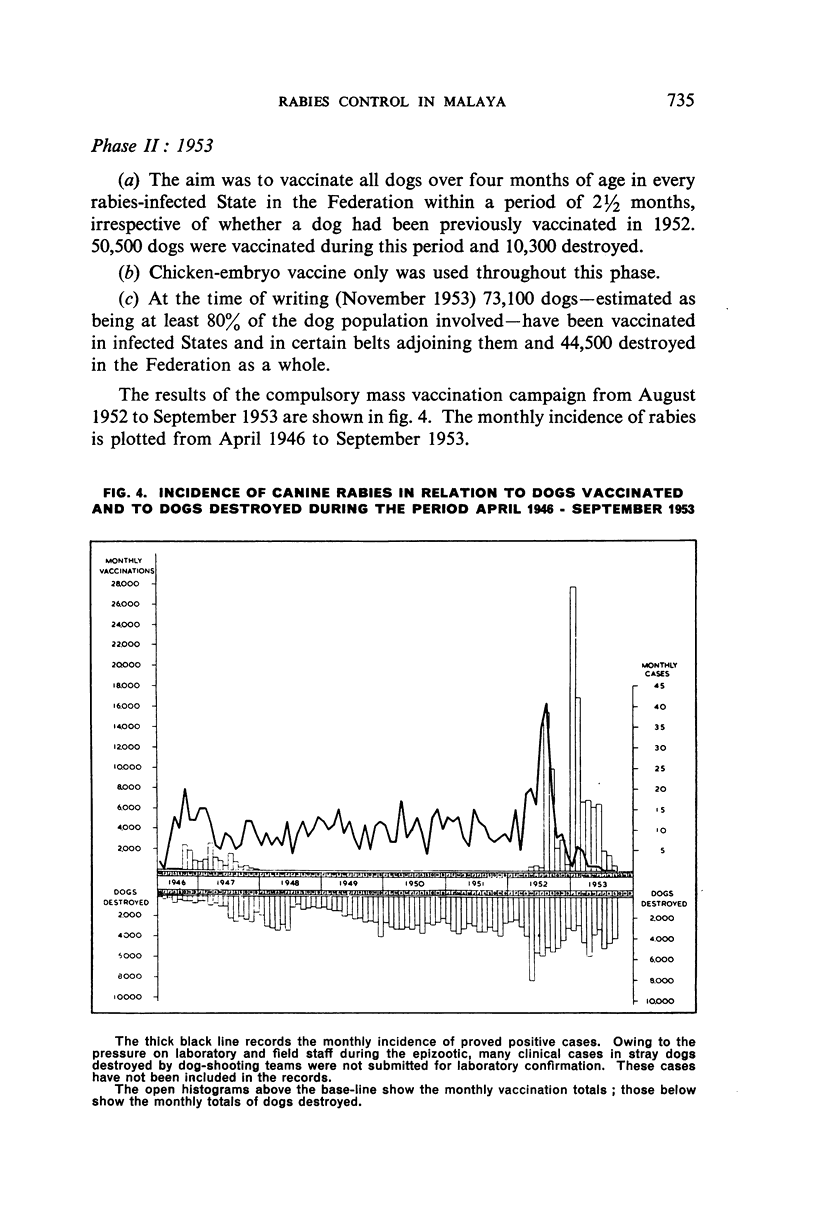
A fulminating extension of rabies—which has been enzootic in northern Malaya since 1924—occurred in Kuala Lumpur in April 1952. The outbreak was suppressed by the compulsory mass vaccination of dogs, stringent legislation, and intensive stray-dog destruction. Similar measures are being employed in the current campaign, the aim of which is the complete eradication of the disease.
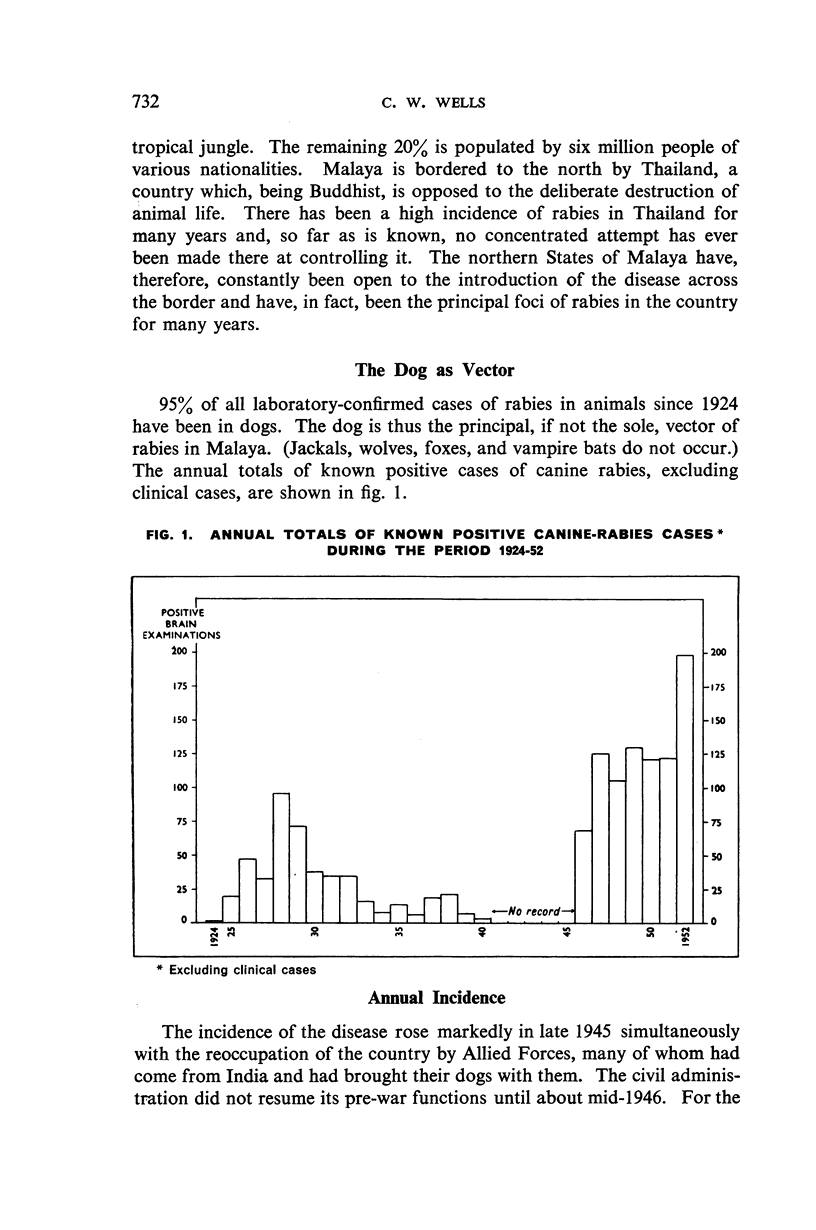
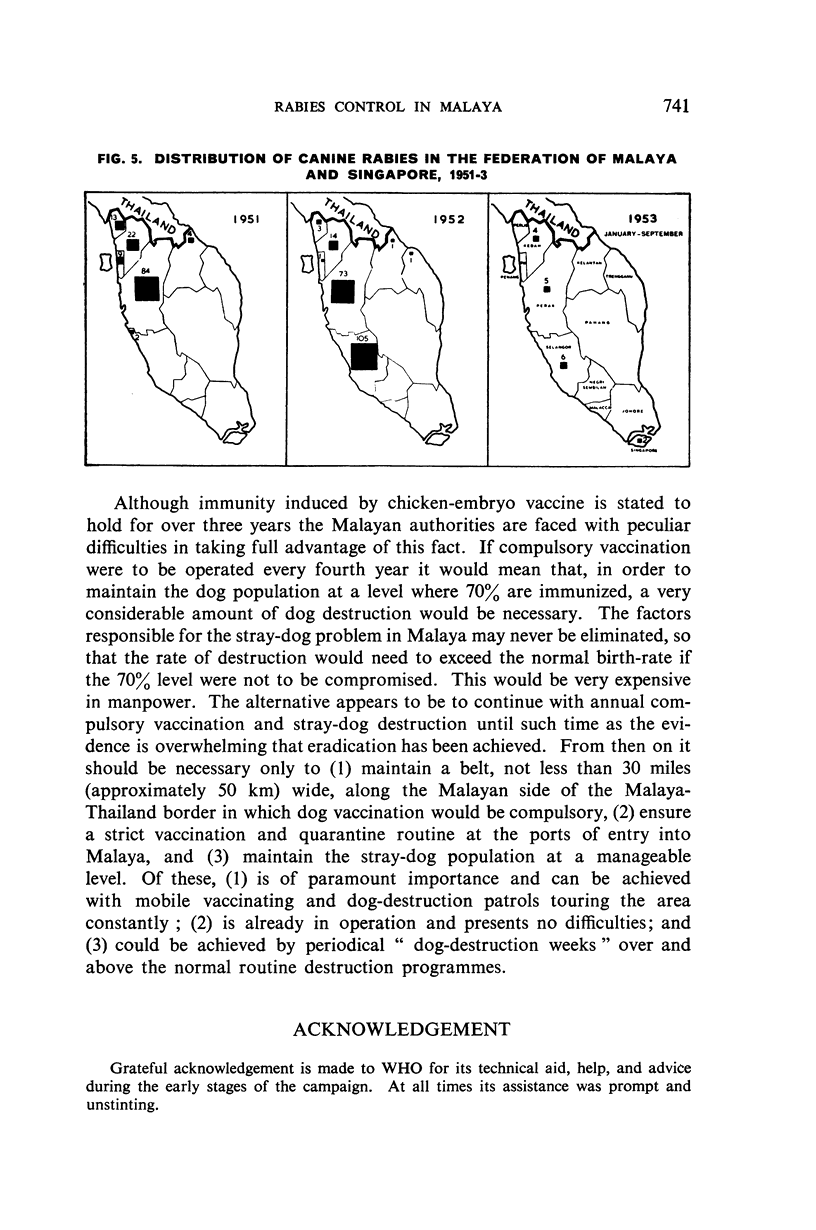
From an average annual incidence of 112 confirmed canine cases prior to 1952—when a total of 198 cases was reported—the incidence fell to 15 cases (all in unvaccinated dogs) for the period January-November 1953, during the last 5½ months of which no case in either animals or man was reported. It is considered that the extensive publicity campaign and strict enforcement of the control measures have contributed measurably to the present improved position.
Statistics relating to confirmed cases in dogs previously vaccinated with (a) phenolized 20% brain-tissue suspension vaccine (buffalo origin) and (b) chicken-embryo vaccine (Flury strain) are quoted and their probable significance in favour of the latter under Malayan conditions is discussed. The hypothesis that the development of rabies may, in many instances, have been blocked by the vaccine is advanced.
The plan for a pan-Federation compulsory vaccination campaign in 1954, to consolidate the 1952-3 improvements, is outlined.
Full text
PDF