Abstract
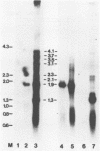
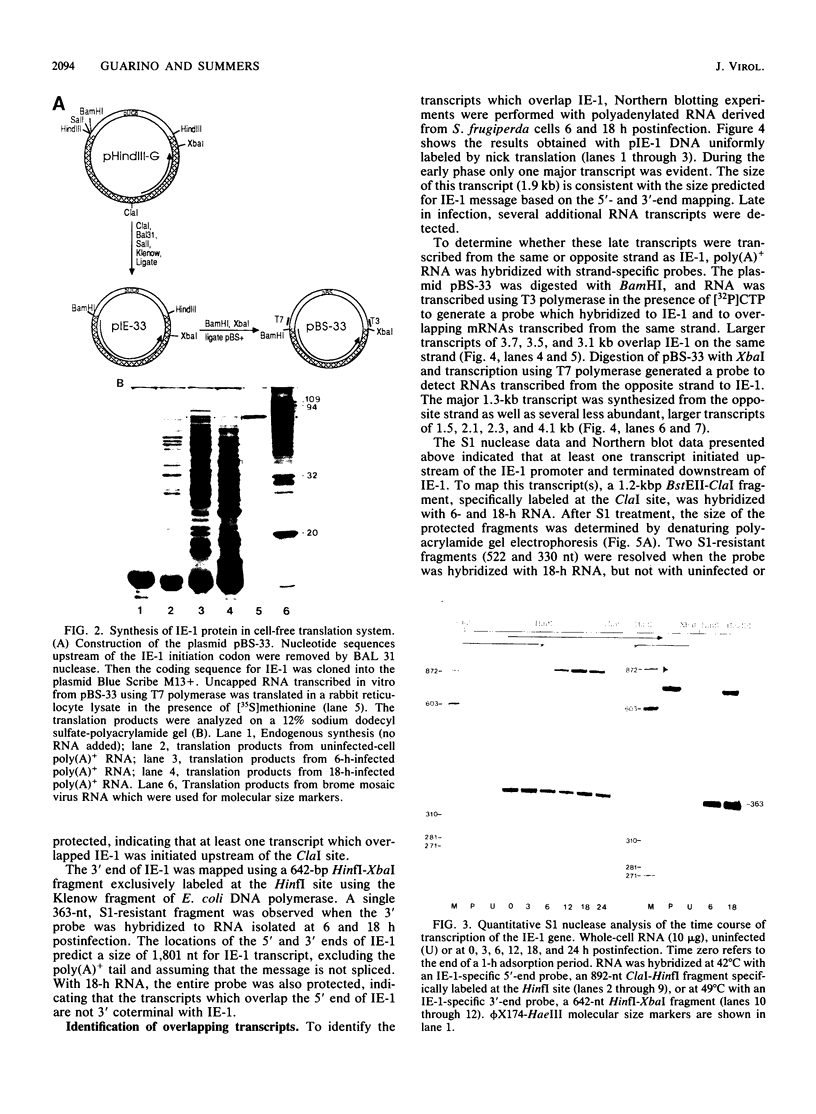
The nucleotide sequence of a trans-activating regulatory gene (IE-1) of the baculovirus Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus has been determined. This gene encodes a protein of 581 amino acids with a predicted molecular weight of 66,856. A DNA fragment containing the entire coding sequence of IE-1 was inserted downstream of an RNA promoter. Subsequent cell-free transcription and translation directed the synthesis of a single peptide with an apparent molecular weight of 70,000. Quantitative S1 nuclease analysis indicated that IE-1 was maximally synthesized during a 1-h virus adsorption period and that steady-state levels of IE-1 message were maintained during the first 24 h of infection. Northern blot hybridization indicated that several late transcripts which overlap the IE-1 gene were transcribed from both strands. The precise locations of the 5′ and 3′ ends of these overlapping transcripts were mapped using S1 nuclease. The overlapping transcripts were grouped in two transcriptional units. One unit was composed of IE-1 and overlapping γ transcripts which initiated upstream of IE-1 and terminated downstream of IE-1. The other unit, transcribed from the opposite strand, consisted of γ transcripts with coterminal 5′ ends and extended 3′ ends. The shorter, more abundant transcripts in this unit overlapped 30 to 40 bases of IE-1 at the 3′ end, while the longer transcripts overlapped the entire IE-1 gene. Transcription of several early A. californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genes, in addition to 39K, was shown to be trans-activated by IE-1, indicating that IE-1 may have a central role in the regulation of β-gene expression.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Androphy E. J., Lowy D. R., Schiller J. T. Bovine papillomavirus E2 trans-activating gene product binds to specific sites in papillomavirus DNA. Nature. 1987 Jan 1;325(6099):70–73. doi: 10.1038/325070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baer R., Bankier A. T., Biggin M. D., Deininger P. L., Farrell P. J., Gibson T. J., Hatfull G., Hudson G. S., Satchwell S. C., Séguin C. DNA sequence and expression of the B95-8 Epstein-Barr virus genome. Nature. 1984 Jul 19;310(5974):207–211. doi: 10.1038/310207a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beard P., Faber S., Wilcox K. W., Pizer L. I. Herpes simplex virus immediate early infected-cell polypeptide 4 binds to DNA and promotes transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(11):4016–4020. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.11.4016. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Bolen J. B., Radonovich M., Salzman N., Khoury G. Stimulation of simian virus 40 late gene expression by simian virus 40 tumor antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2040–2044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen E. Y., Howley P. M., Levinson A. D., Seeburg P. H. The primary structure and genetic organization of the bovine papillomavirus type 1 genome. Nature. 1982 Oct 7;299(5883):529–534. doi: 10.1038/299529a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Fine-structure mapping and functional analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants in the gene encoding the herpes simplex virus type 1 immediate early protein VP175. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):189–203. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.189-203.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erlandson M. A., Gordon J., Carstens E. B. Size and map locations of early transcription products on the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus genome. Virology. 1985 Apr 15;142(1):12–23. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90418-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esche H., Lübbert H., Siegmann B., Doerfler W. The translational map of the Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus (AcNPV) genome. EMBO J. 1982;1(12):1629–1633. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01365.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. Temporal regulation of baculovirus RNA: overlapping early and late transcripts. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):392–400. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.392-400.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friesen P. D., Miller L. K. The regulation of baculovirus gene expression. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1986;131:31–49. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-71589-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. D., Carstens E. B. Phenotypic characterization and physical mapping of a temperature-sensitive mutant of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus defective in DNA synthesis. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):69–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90148-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Gonzalez M. A., Summers M. D. Complete Sequence and Enhancer Function of the Homologous DNA Regions of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):224–229. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.224-229.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Functional mapping of a trans-activating gene required for expression of a baculovirus delayed-early gene. J Virol. 1986 Feb;57(2):563–571. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.2.563-571.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarino L. A., Summers M. D. Interspersed Homologous DNA of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Enhances Delayed-Early Gene Expression. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):215–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.215-223.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. M., Alwine J. C. Activation of the SV40 late promoter: direct effects of T antigen in the absence of viral DNA replication. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):381–389. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90231-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis J. B., Mathews M. B. Control of adenovirus early gene expression: a class of immediate early products. Cell. 1980 Aug;21(1):303–313. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90138-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Doerfler W. Mapping of Early and Late Transcripts Encoded by the Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus Genome: Is Viral RNA Spliced? J Virol. 1984 May;50(2):497–506. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.2.497-506.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lübbert H., Doerfler W. Transcription of overlapping sets of RNAs from the genome of Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus: a novel method for mapping RNAs. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):255–265. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.255-265.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rankin C., Ladin B. F., Weaver R. F. Physical mapping of temporally regulated, overlapping transcripts in the region of the 10K protein gene in Autographa californica nuclear polyhedrosis virus. J Virol. 1986 Jan;57(1):18–27. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.1.18-27.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlins D. R., Milman G., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Sequence-specific DNA binding of the Epstein-Barr virus nuclear antigen (EBNA-1) to clustered sites in the plasmid maintenance region. Cell. 1985 Oct;42(3):859–868. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90282-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. B., Thimmappaya B., Dhar R., Subramanian K. N., Zain B. S., Pan J., Ghosh P. K., Celma M. L., Weissman S. M. The genome of simian virus 40. Science. 1978 May 5;200(4341):494–502. doi: 10.1126/science.205947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisman D., Sugden B. trans activation of an Epstein-Barr viral transcriptional enhancer by the Epstein-Barr viral nuclear antigen 1. Mol Cell Biol. 1986 Nov;6(11):3838–3846. doi: 10.1128/mcb.6.11.3838. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sodroski J. G., Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A. Trans-acting transcriptional activation of the long terminal repeat of human T lymphotropic viruses in infected cells. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):381–385. doi: 10.1126/science.6330891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Yang Y. C., Howley P. M. Transactivation of a bovine papilloma virus transcriptional regulatory element by the E2 gene product. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):183–191. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80114-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Ormondt H., Maat J., De Waard A., Van der Eb A. J. The nucleotide sequence of the transforming HpaI-E fragment of adenovirus type 5 DNA. Gene. 1978 Dec;4(4):309–328. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90048-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vlak J. M., Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Hybridization Selection and In Vitro Translation of Autographa californica Nuclear Polyhedrosis Virus mRNA. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):762–771. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.762-771.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weaver R. F., Weissmann C. Mapping of RNA by a modification of the Berk-Sharp procedure: the 5' termini of 15 S beta-globin mRNA precursor and mature 10 s beta-globin mRNA have identical map coordinates. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 10;7(5):1175–1193. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.5.1175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]