Abstract
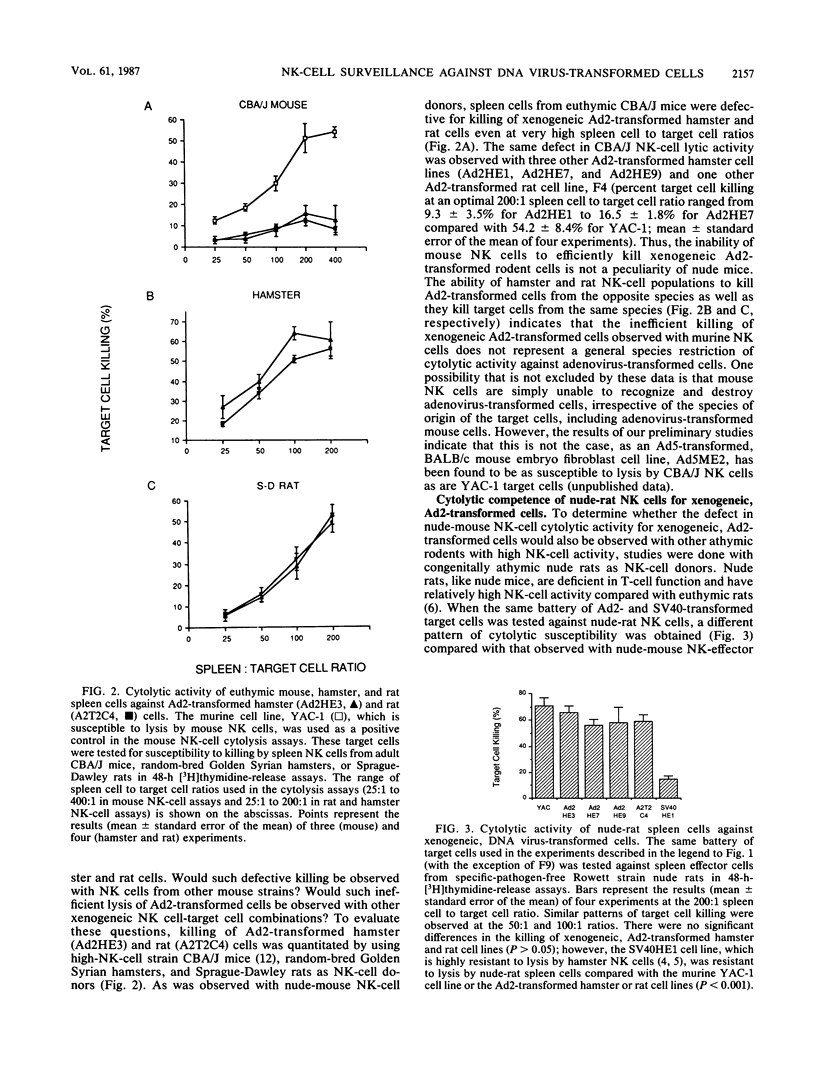
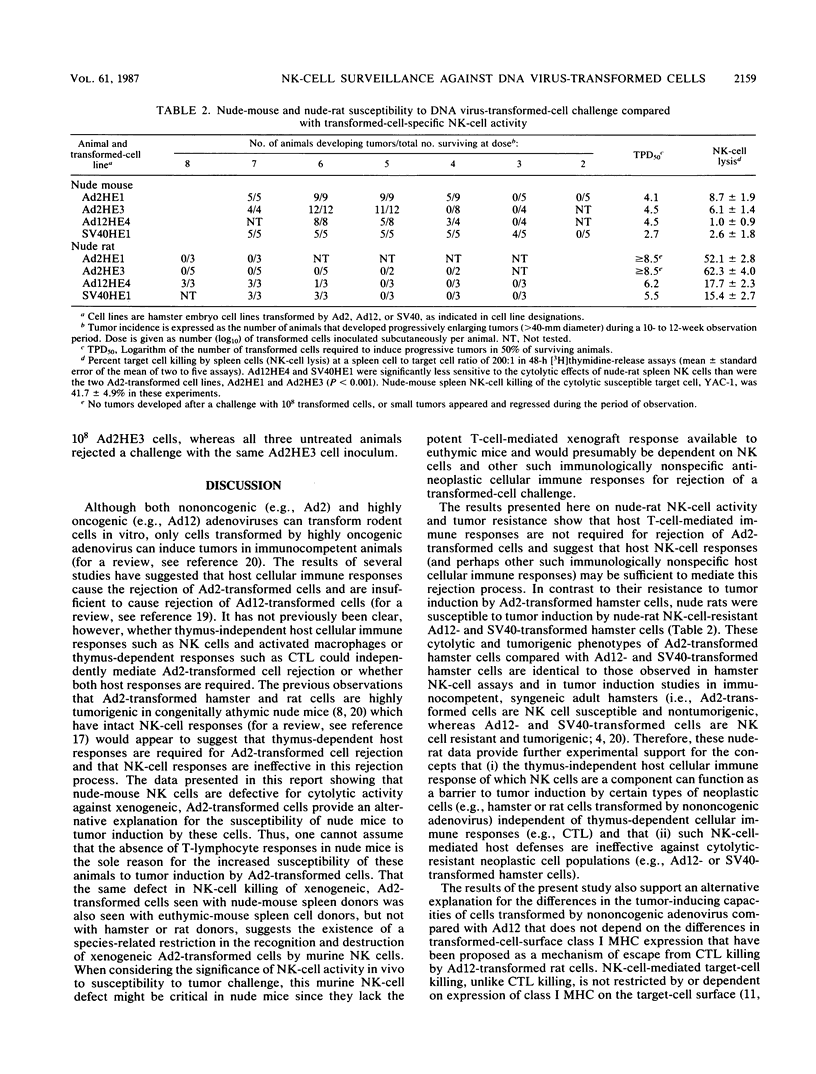
Adenovirus type 2 (Ad2)-transformed hamster and rat cells are susceptible to lysis by natural killer (NK) cells from the host of origin and are nontumorigenic in immunocompetent hamsters and rats, respectively. These NK-cell-susceptible, virus-transformed cells are, however, highly tumorigenic in athymic (nude) mice--animals with intact NK-cell responses. In vitro lysis of these xenogeneic, Ad2-transformed cells by nude-mouse NK cells was found to be defective. In contrast, Ad2-transformed hamster and rat cells were highly susceptible to lysis by nude-rat NK cells. Furthermore, xenogeneic, Ad2-transformed hamster cells were nontumorigenic in nude rats unless the NK-cell responses of the challenged animals were compromised. The results of the nude-rat studies show that thymus-dependent, cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-mediated, host cellular immune responses are not essential for rejection of xenogeneic cells transformed by nononcogenic Ad2. The data suggest instead that immunologically nonspecific host cellular immune responses, such as those mediated by NK cells, are sufficient for rejection of Ad2-transformed cells. These results indicate that biologically important differences exist in the NK-cell-mediated defenses mounted by nude mice and nude rats against transformed cells that may account for the different patterns of tumor induction by various neoplastic cell types in these athymic animals.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bernards R., Schrier P. I., Houweling A., Bos J. L., van der Eb A. J., Zijlstra M., Melief C. J. Tumorigenicity of cells transformed by adenovirus type 12 by evasion of T-cell immunity. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):776–779. doi: 10.1038/305776a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berstine E. G., Hooper M. L., Grandchamp S., Ephrussi B. Alkaline phosphatase activity in mouse teratoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Dec;70(12):3899–3903. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.12.3899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bloom E. T., Korn E. L. Quantification of natural cytotoxicity by human lymphocyte subpopulations isolated by density: heterogeneity of the effector cells. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Mar 25;58(3):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90360-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Hibbs J. B., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr DNA virus-transformed hamster cell--host effector cell interactions: level of resistance to cytolysis correlated with tumorigenicity. Int J Cancer. 1982 Dec 15;30(6):795–803. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300619. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook J. L., Walker T. A., Lewis A. M., Jr, Ruley H. E., Graham F. L., Pilder S. H. Expression of the adenovirus E1A oncogene during cell transformation is sufficient to induce susceptibility to lysis by host inflammatory cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6965–6969. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eager K. B., Williams J., Breiding D., Pan S., Knowles B., Appella E., Ricciardi R. P. Expression of histocompatibility antigens H-2K, -D, and -L is reduced in adenovirus-12-transformed mouse cells and is restored by interferon gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5525–5529. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5525. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H., McDougall J. K., Chen L. B. In vitro traits of adenovirus-transformed cell lines and their relevance to tumorigenicity in nude mice. Cell. 1977 Apr;10(4):669–678. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90100-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H., Paraskeva C. A study to determine the reasons for differences in the tumorigenicity of rat cell lines transformed by adenovirus 2 and adenovirus 12. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):703–713. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H. Viral DNA in transformed cells. II. A study of the sequences of adenovirus 2 DNA IN NINE LINES OF TRANSFORMED RAT CELLS USING SPECIFIC FRAGMENTS OF THE VIRAL GENOME;. J Mol Biol. 1974 Oct 15;89(1):49–72. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90162-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Bakacs K. K., Kiessling R., Klein G. Intra- and interspecies reactivity of human and mouse natural killer (NK) cells. J Immunol. 1978 Jul;121(1):6–12. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Holden H. T. Natural cell-mediated immunity. Adv Cancer Res. 1978;27:305–377. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60936-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R. Natural killer cells: their roles in defenses against disease. Science. 1981 Oct 2;214(4516):24–30. doi: 10.1126/science.7025208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kasai M., Iwamori M., Nagai Y., Okumura K., Tada T. A glycolipid on the surface of mouse natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1980 Mar;10(3):175–180. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830100304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Klein E., Wigzell H. "Natural" killer cells in the mouse. I. Cytotoxic cells with specificity for mouse Moloney leukemia cells. Specificity and distribution according to genotype. Eur J Immunol. 1975 Feb;5(2):112–117. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830050208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kindred B. Nude mice in immunology. Prog Allergy. 1979;26:137–238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Cook J. L. A new role for DNA virus early proteins in viral carcinogenesis. Science. 1985 Jan 4;227(4682):15–20. doi: 10.1126/science.3843807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Cook J. L. Presence of allograft-rejection resistance in simian virus 40-transformed hamster cells and its possible role in tumor development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2886–2889. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2886. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lewis A. M., Jr, Cook J. L. The interface between adenovirus-transformed cells and cellular immune response in the challenged host. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:1–22. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schrier P. I., Bernards R., Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Expression of class I major histocompatibility antigens switched off by highly oncogenic adenovirus 12 in transformed rat cells. 1983 Oct 27-Nov 2Nature. 305(5937):771–775. doi: 10.1038/305771a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheil J. M., Gallimore P. H., Zimmer S. G., Sopori M. L. Susceptibility of Adenovirus 2-transformed rat cell lines to natural killer (NK) cells: direct correlation between NK resistance and in vivo tumorigenesis. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1578–1582. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern P., Gidlund M., Kimura A., Grönvik K. O., Wigzell H. Murine embryonal carcinoma cells: universal targets for mammalian NK cells? Int J Cancer. 1981 May 15;27(5):679–688. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910270515. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Jong W. H., Steerenberg P. A., Ursem P. S., Osterhaus A. D., Vos J. G., Ruitenberg E. J. The athymic nude rat. III. Natural cell-mediated cytotoxicity. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1980 Oct;17(2):163–172. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(80)90084-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


