Abstract
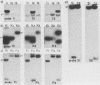
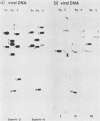
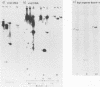
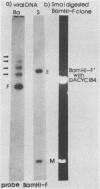
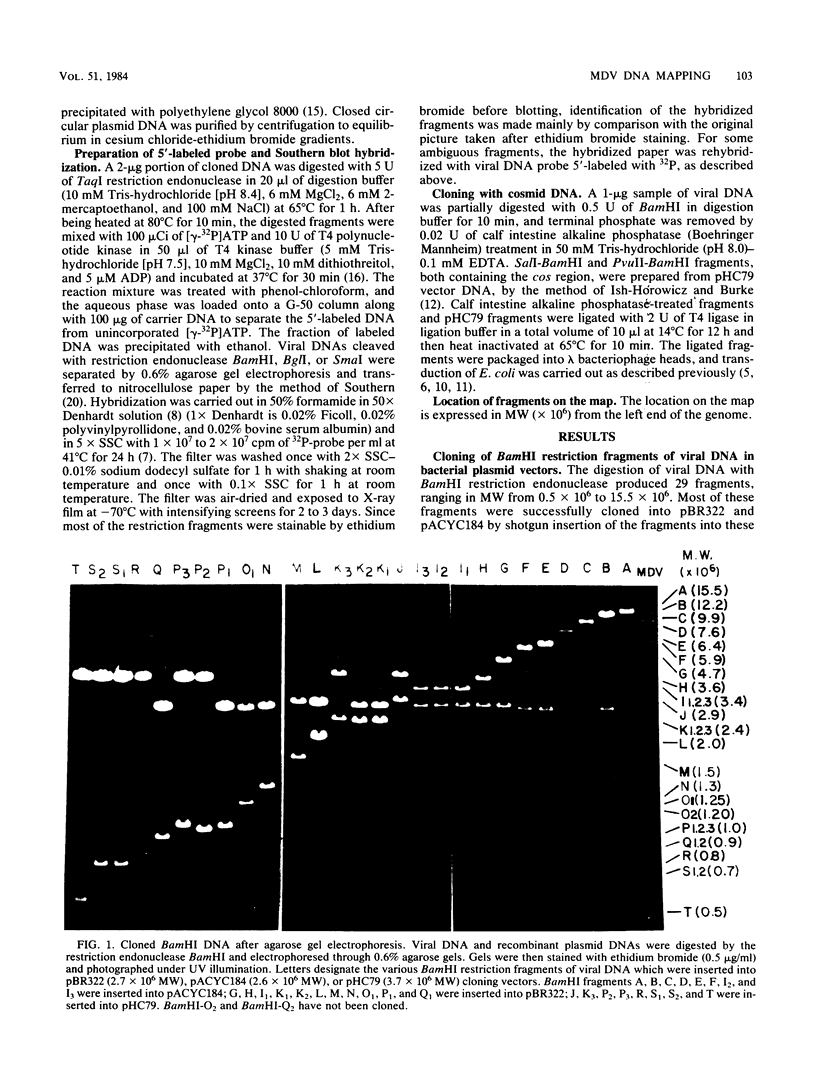
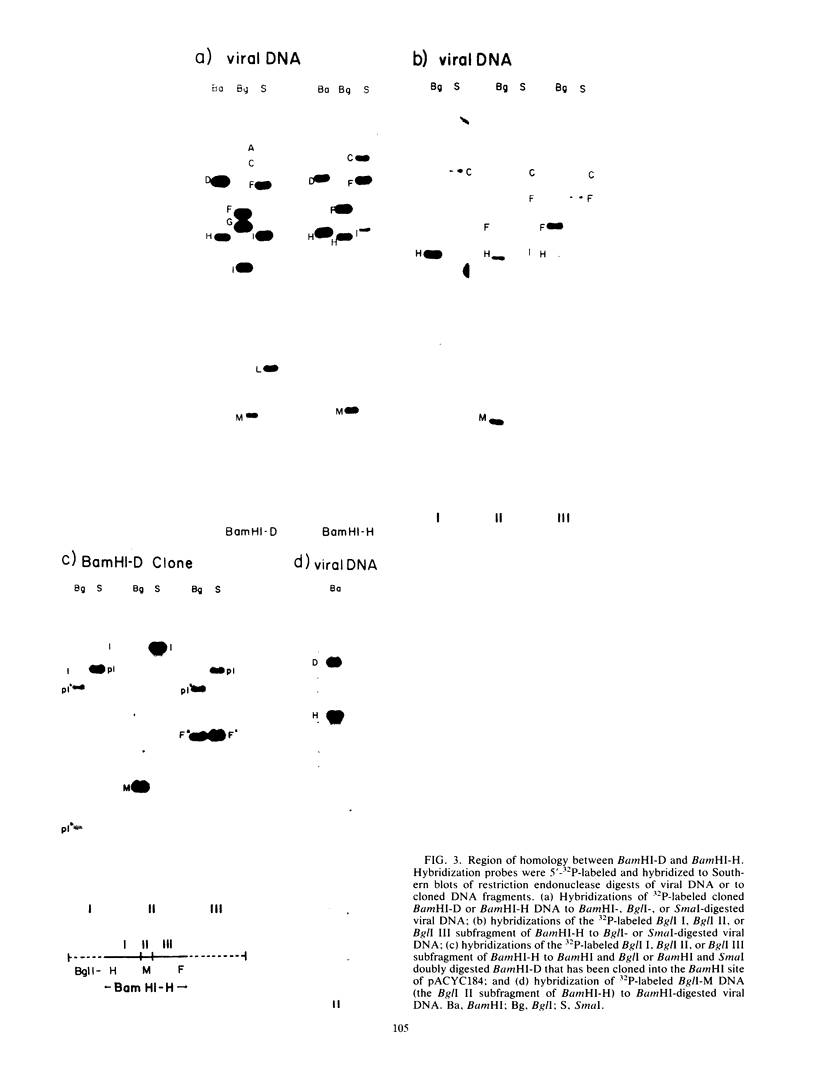
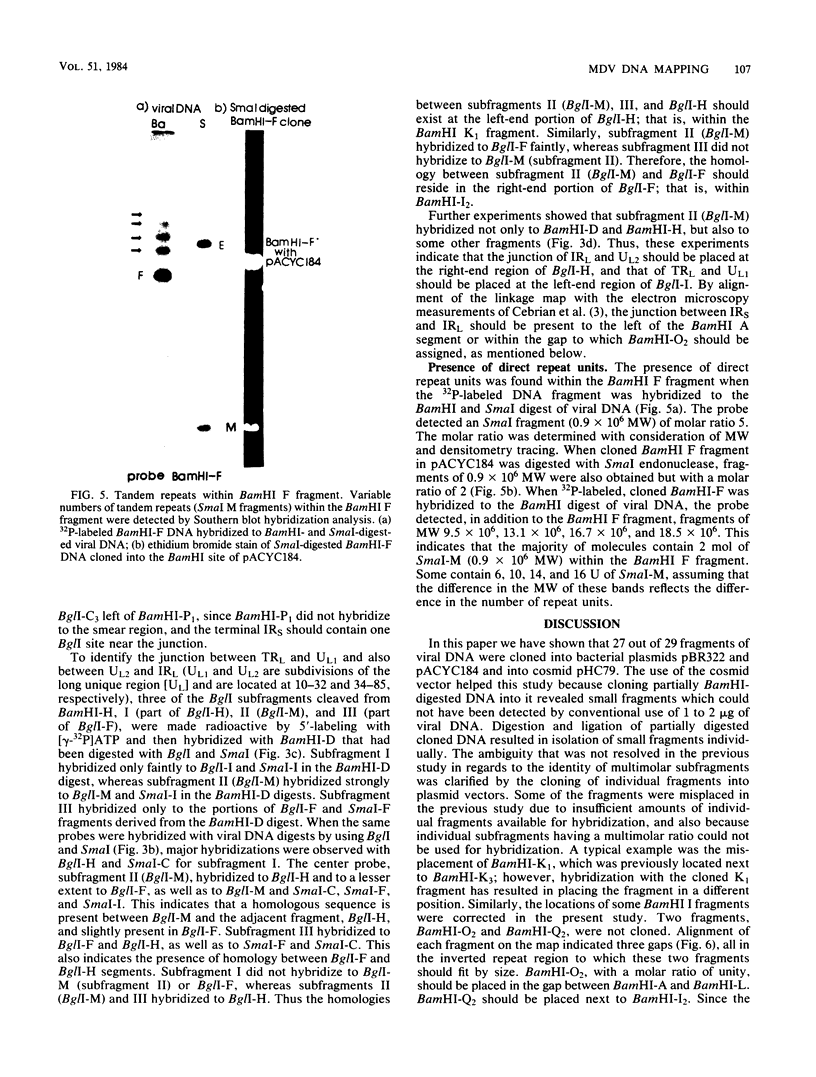
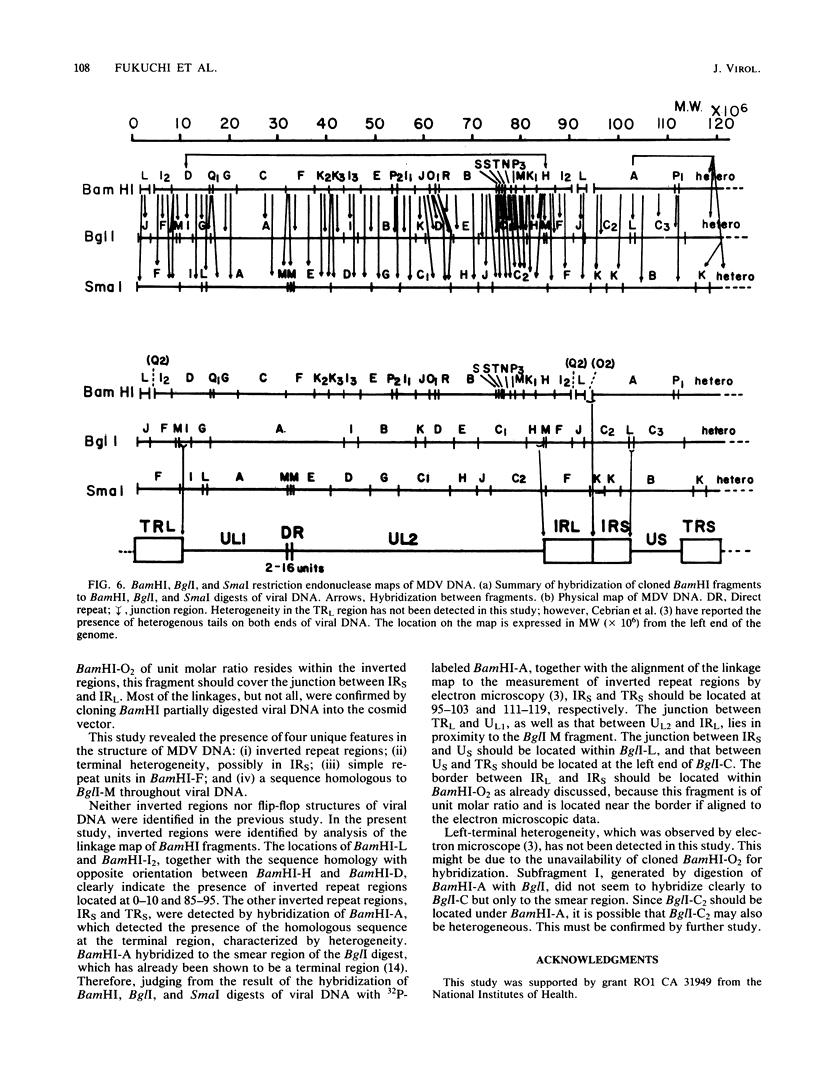
Purified virion DNA (120 X 10(6) molecular weight [MW]) of Marek's disease virus strain GA was cleaved with BamHI restriction endonuclease, and 27 out of the 29 fragments were cloned into bacterial plasmids. Restriction maps for BamHI, BglI, and SmaI endonucleases were constructed. The genomic structure of Marek's disease virus DNA was found to be similar to that of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. A long unique region (75 X 10(6) MW, located at 10 X 10(6) to 85 X 10(6) MW [10-85] from the left end of the genome), which was subdivided into segment 1 (22 X 10(6) MW, located at 10-32) and segment 2 (51 X 10(6) MW, located at 34-85) by direct repeats (32-34), was flanked by a long terminal region (10 X 10(6) MW, located at 0-10) and a long inverted region (10 X 10(6) MW, located at 85-95). A short unique region (8 X 10(6) MW, located at 103-111) was flanked by a short terminal region (8 X 10(6) MW, located at 111-119) and a short inverted region (8 X 10(6) MW, located at 95-103). The direct repeat fragments (0.9 X 10(6) could be isolated by cleavage with SmaI. The right terminal end was found to be heterogenous .
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bolivar F., Backman K. Plasmids of Escherichia coli as cloning vectors. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:245–267. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68018-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cebrian J., Kaschka-Dierich C., Berthelot N., Sheldrick P. Inverted repeat nucleotide sequences in the genomes of Marek disease virus and the herpesvirus of the turkey. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(2):555–558. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.2.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. N., Chang A. C., Hsu L. Nonchromosomal antibiotic resistance in bacteria: genetic transformation of Escherichia coli by R-factor DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Aug;69(8):2110–2114. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.8.2110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Brüning H. J. Plasmids useable as gene-cloning vectors in an in vitro packaging by coliphage lambda: "cosmids". Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):85–107. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90023-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J., Hohn B. Cosmids: a type of plasmid gene-cloning vector that is packageable in vitro in bacteriophage lambda heads. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4242–4246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawid I. B. DNA-DNA hybridization on membrane filters: a convenient method using formamide. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Jul 15;477(2):191–194. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90235-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Jacob R. J., Wadsworth S. C., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: evidence for four populations of molecules that differ in the relative orientations of their long and short components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Nov;72(11):4243–4247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.11.4243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B. In vitro packaging of lambda and cosmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:299–309. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68021-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ish-Horowicz D., Burke J. F. Rapid and efficient cosmid cloning. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):2989–2998. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.2989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee L. F., Kieff E. D., Bachenheimer S. L., Roizman B., Spear P. G., Burmester B. R., Nazerian K. Size and composition of Marek's disease virus deoxyribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):289–294. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.289-294.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. S., Tanaka A., Nonoyama M. Partial restriction map of Marek's disease virus DNA. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):185–190. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90005-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lis J. T. Fractionation of DNA fragments by polyethylene glycol induced precipitation. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):347–353. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65044-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okazaki W., Purchase H. G., Burmester B. R. Protection against Marek's disease by vaccination with a herpesvirus of turkeys. Avian Dis. 1970 May;14(2):413–429. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadsworth S., Jacob R. J., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA. II. Size, composition, and arrangement of inverted terminal repetitions. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1487–1497. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1487-1497.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]