Abstract
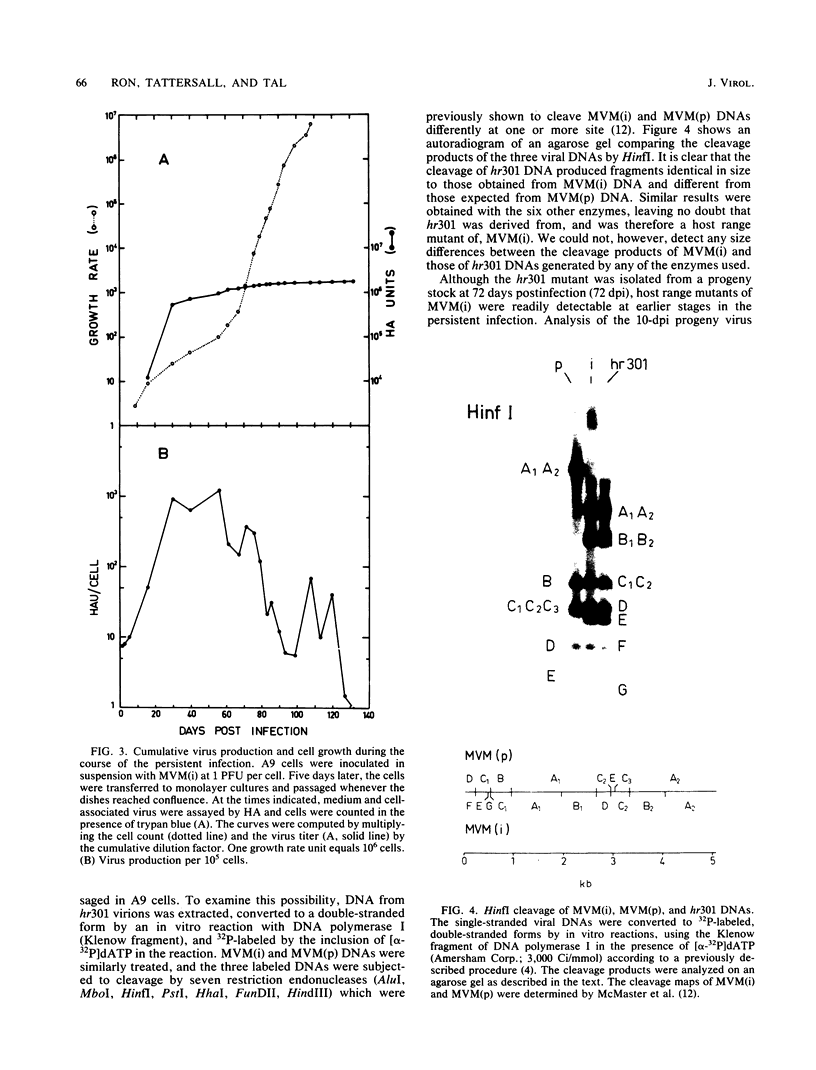
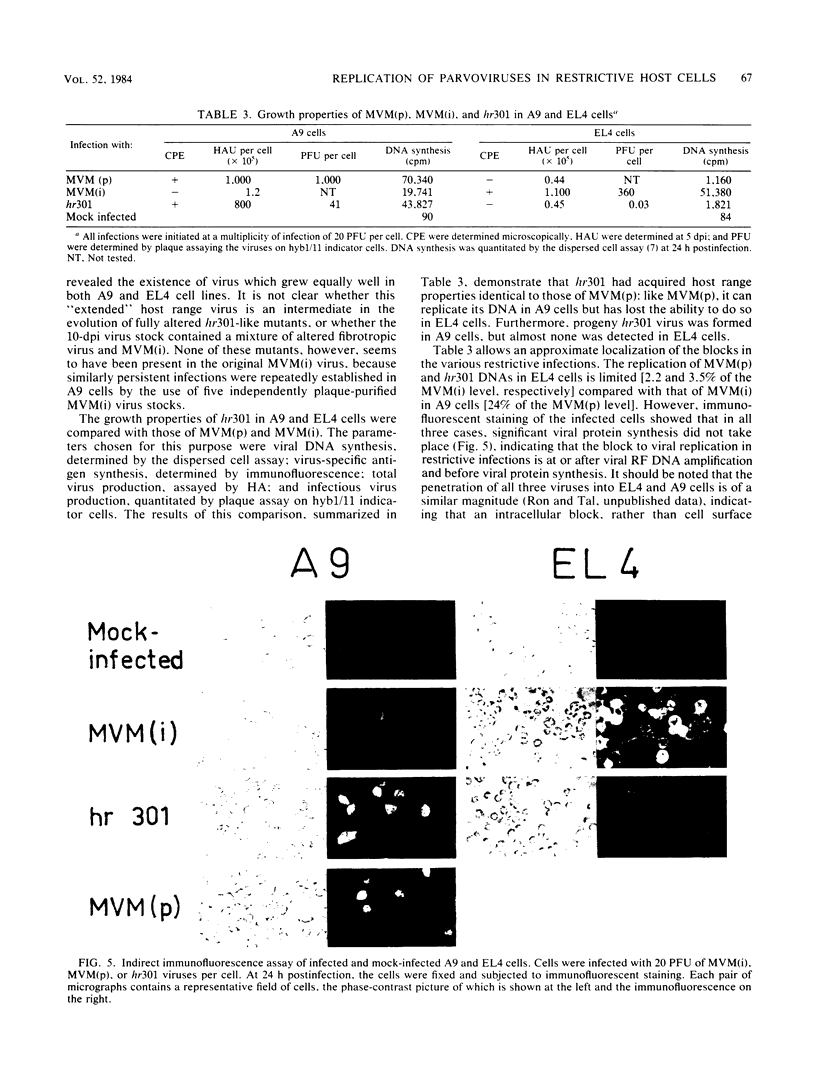
Minute virus of mice (i), the lymphotropic strain of minute virus of mice, established a persistent infection in normally restrictive L cells. The carrier state, which lasted 150 days, exhibited three clearly distinguishable stages. During the early stage (days 1 to 10 postinfection), small amounts of virus were formed. A "crisis" then developed that lasted 50 to 60 days and was characterized by massive cell lysis and high titers of virus. This was followed by a 70- to 80-day period in which small but stable quantities of virus were produced. Virus shed by the carrier culture during the latter phase had acquired an altered host range, namely, it had lost its ability to replicate in T-lymphocyte cell lines and had adapted to growth in L cells. Virus isolated at this time from a single plaque in L cells, designated hr301, was shown to possess similar host range properties. No differences, however, could be found between the DNAs of minute virus of mice (i) and of hr301 by restriction enzyme analysis, suggesting that the mutation that affected the viral host range did not involve an extensive region of the viral genome.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astell C. R., Thomson M., Merchlinsky M., Ward D. C. The complete DNA sequence of minute virus of mice, an autonomous parvovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Feb 25;11(4):999–1018. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.4.999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonnard G. D., Manders E. K., Campbell D. A., Jr, Herberman R. B., Collins M. J., Jr Immunosuppressive activity of a subline of the mouse EL-4 lymphoma. Evidence for minute virus of mice causing the inhibition. J Exp Med. 1976 Jan 1;143(1):187–205. doi: 10.1084/jem.143.1.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourguignon G. J., Tattersall P. J., Ward D. C. DNA of minute virus of mice: self-priming, nonpermuted, single-stranded genome with a 5'-terminal hairpin duplex. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):290–306. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.290-306.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins J. L., Patek P. Q., Cohn M. In vivo surveillance of tumorigenic cells transformed in vitro. Nature. 1982 Sep 9;299(5879):169–171. doi: 10.1038/299169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampton E. G. H-1 virus growth in synchronized rat embryo cells. Can J Microbiol. 1970 Apr;16(4):266–268. doi: 10.1139/m70-049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. THREE DEGREES OF GUANYLIC ACID--INOSINIC ACID PYROPHOSPHORYLASE DEFICIENCY IN MOUSE FIBROBLASTS. Nature. 1964 Sep 12;203:1142–1144. doi: 10.1038/2031142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lavi S., Etkin S. Carcinogen-mediated induction of SV40 DNA synthesis in SV40 transformed Chinese hamster embryo cells. Carcinogenesis. 1981;2(5):417–423. doi: 10.1093/carcin/2.5.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather J. P. Establishment and characterization of two distinct mouse testicular epithelial cell lines. Biol Reprod. 1980 Aug;23(1):243–252. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod23.1.243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathews J. H., Vorndam A. V. Interferon-mediated persistent infection of Saint Louis encephalitis virus in a reptilian cell line. J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):177–186. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-177. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Beard P., Engers H. D., Hirt B. Characterization of an immunosuppressive parvovirus related to the minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):317–326. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.317-326.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchlinsky M. J., Tattersall P. J., Leary J. J., Cotmore S. F., Gardiner E. M., Ward D. C. Construction of an infectious molecular clone of the autonomous parvovirus minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):227–232. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.227-232.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohanty S. B., Bachmann P. A. Susceptibility of fertilized mouse eggs to minute virus of mice. Infect Immun. 1974 Apr;9(4):762–763. doi: 10.1128/iai.9.4.762-763.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shevach E. M., Stobo J. D., Green I. Immunoglobulin and theta-bearing murine leukemias and lymphomas. J Immunol. 1972 May;108(5):1146–1151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siegl G., Gautschi M. The multiplication of parvovirus Lu3 in a synchronized culture system. I. Optimum conditions for virus replication. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;40(1):105–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01242642. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalholz B. A., Tattersall P. Interaction of minute virus of mice with differentiated cells: strain-dependent target cell specificity is mediated by intracellular factors. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):937–943. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.937-943.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Bratton J. Reciprocal productive and restrictive virus-cell interactions of immunosuppressive and prototype strains of minute virus of mice. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):944–955. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.944-955.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P., Cawte P. J., Shatkin A. J., Ward D. C. Three structural polypeptides coded for by minite virus of mice, a parvovirus. J Virol. 1976 Oct;20(1):273–289. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.1.273-289.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tattersall P. Replication of the parvovirus MVM. I. Dependence of virus multiplication and plaque formation on cell growth. J Virol. 1972 Oct;10(4):586–590. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.4.586-590.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toolan H. W. Lack of oncogenic effect of the H-viruses for hamsters. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):1036–1036. doi: 10.1038/2141036a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toolan H. W., Ledinko N. Inhibition by H-1 virus of the incidence of tumors produced by adenovirus 12 in hamsters. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):475–478. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90226-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toolan H. W., Rhode S. L., 3rd, Gierthy J. F. Inhibition of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced tumors in Syrian hamsters by prior infection with H-1 parvovirus. Cancer Res. 1982 Jul;42(7):2552–2555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]