Abstract
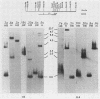
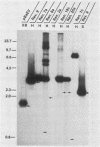
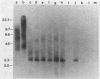
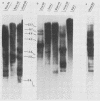
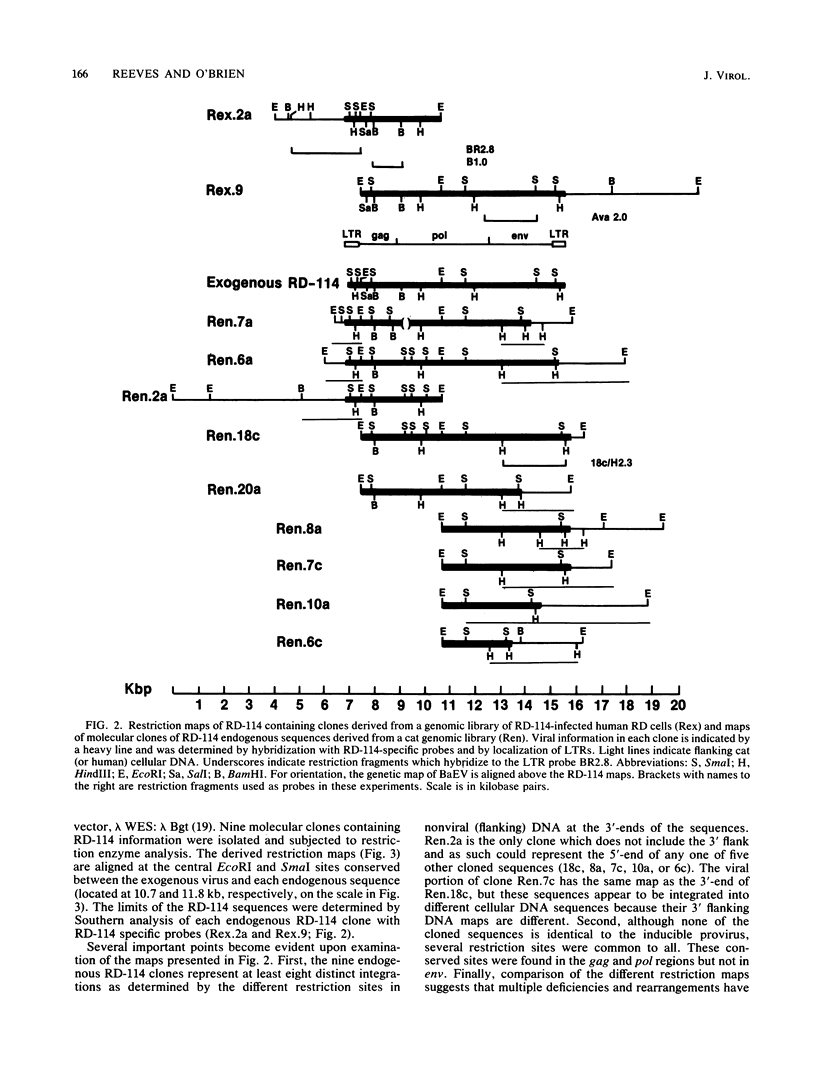
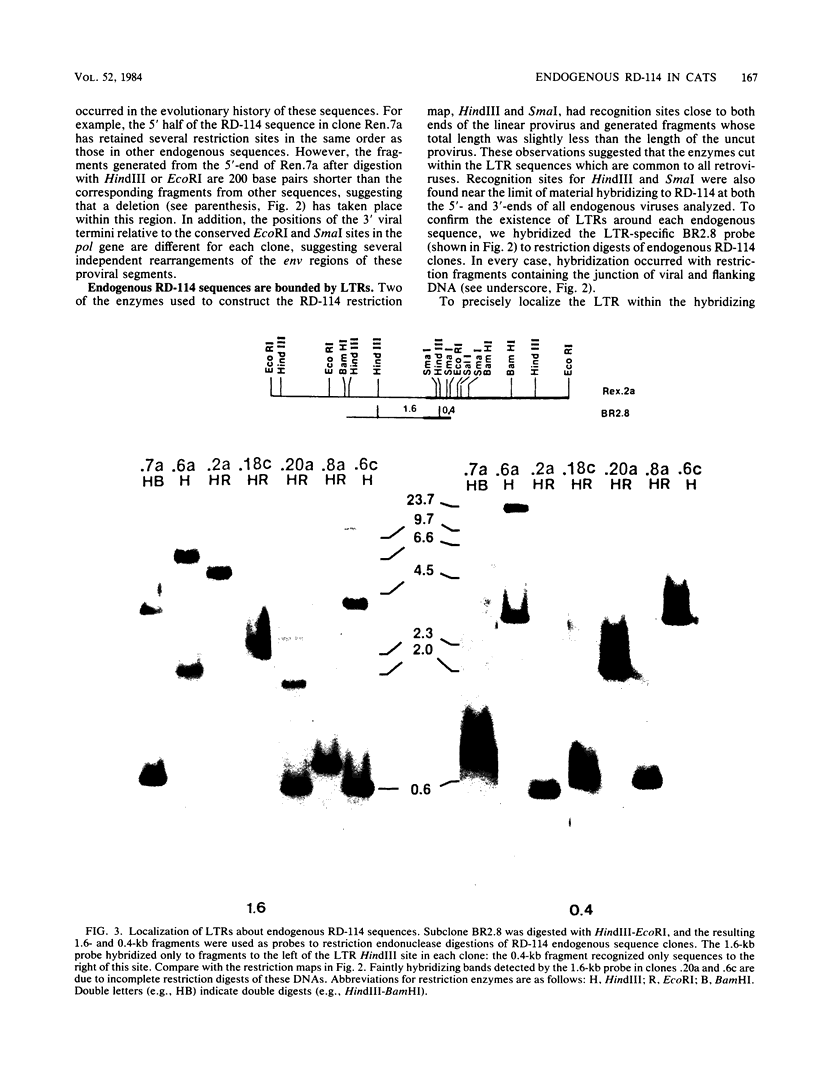
RD-114 is a replication-competent, xenotropic retrovirus which is homologous to a family of moderately repetitive DNA sequences present at ca. 20 copies in the normal cellular genome of domestic cats. To examine the extent and character of genomic divergence of the RD-114 gene family as well as to assess their positional association within the cat genome, we have prepared a series of molecular clones of endogenous RD-114 DNA segments from a genomic library of cat cellular DNA. Their restriction endonuclease maps were compared with each other as well as to that of the prototype-inducible RD-114 which was molecularly cloned from a chronically infected human cell line. The endogenous sequences analyzed were similar to each other in that they were colinear with RD-114 proviral DNA, were bounded by long terminal redundancies, and conserved many restriction sites in the gag and pol regions. However, the env regions of many of the sequences examined were substantially deleted. Several of the endogenous RD-114 genomes contained a novel envelope sequence which was unrelated to the env gene of the prototype RD-114 env gene but which, like RD-114 and endogenous feline leukemia virus provirus, was found only in species of the genus Felis, and not in other closely related Felidae genera. The endogenous RD-114 sequences each had a distinct cellular flank which indicates that these sequences are not tandem but dispersed nonspecifically throughout the genome. Southern analysis of cat cellular DNA confirmed the conclusions about conserved restriction sites in endogenous sequences and indicated that a single locus may be responsible for the production of the major inducible form of RD-114.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baluda M. A., Roy-Burman P. Partial characterization of RD114 virus by DNA-RNA hybridization studies. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):59–62. doi: 10.1038/newbio244059a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Battula N., Todaro G. J. Physical map of infectious baboon type C viral DNA and sites of integration in infected cells. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):709–718. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.709-718.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton C. V., Hodge H. M., Fine D. L. Comparative large-scale propagation of retroviruses from Old World (Mason-Pfizer monkey virus) and New World (squirrel monkey virus) primates. In Vitro. 1978 Feb;14(2):192–199. doi: 10.1007/BF02618222. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Sherr C. J., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: origin of feline leukemia virus. Science. 1975 Nov 28;190(4217):886–888. doi: 10.1126/science.52892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of C-type viral genes: inheritance of exogenously acquired viral genes. Nature. 1974 Dec 6;252(5483):456–459. doi: 10.1038/252456a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benveniste R. E., Todaro G. J. Evolution of type C viral genes: evidence for an Asian origin of man. Nature. 1976 May 13;261(5556):101–108. doi: 10.1038/261101a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner T. I., Todaro G. J. Carnivores have sequences in their cellular DNA distantly related to the primate endogenous virus, MAC-1. Virology. 1979 Apr 15;94(1):224–227. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90454-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J. W., Roach A., Mullins J. I., Burck K. B., Nicolson M. O., Gardner M. B., Davidson N. The U3 portion of feline leukemia virus DNA identifies horizontally acquired proviruses in leukemic cats. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Dec;78(12):7778–7782. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.12.7778. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M., Shure M., Davidson N., Rice N., Gilden R. V. Baboon endogenous virus genome. I. Restriction enzyme map of the unintegrated DNA genome of a primate retrovirus. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):28–39. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.28-39.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Rein A., Stephens R. M., O'Connell C., Gilden R. V., Shure M., Nicolson M. O., McAllister R. M., Davidson N. Baboon endogenous virus genome: molecular cloning and structural characterization of nondefective viral genomes from DNA of a baboon cell strain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5207–5211. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M., Rice N., Stephens R., O'Connell C. DNA sequence relationship of the baboon endogenous virus genome to the genomes of other type C and type D retroviruses. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):801–812. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.801-812.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fischinger P. J., Peebles P. T., Nomura S., Haapala D. K. Isolation of RD-114-like oncornavirus from a cat cell line. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):978–985. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.978-985.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frankel A. E., Gilbert J. H., Porzig K. J., Scolnick E. M., Aaronson S. A. Nature and distribution of feline sarcoma virus nucleotide sequences. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):821–827. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.821-827.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardner M. B., Rasheed S., Rongey R. W., Charman H. P., Alena B., Gilden R. V., Huebner R. J. Natural expression of feline type-C virus genomes, prevalence of detectable felv and RD-114 GS antigen, type-C particles and infectious virus in postnatal and fetal cats. Int J Cancer. 1974 Jul 15;14(1):97–105. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910140112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillespie D., Gillespie S., Gallo R. C., East J. L., Dmochowski L. Genetic origin of RD114 and other RNA tumour viruses assayed by molecular hybridization. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):51–54. doi: 10.1038/newbio244051a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirt B. Selective extraction of polyoma DNA from infected mouse cell cultures. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jun 14;26(2):365–369. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hohn B., Murray K. Packaging recombinant DNA molecules into bacteriophage particles in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3259–3263. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leder P., Tiemeier D., Enquist L. EK2 derivatives of bacteriophage lambda useful in the cloning of DNA from higher organisms: the lambdagtWES system. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):175–177. doi: 10.1126/science.322278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Livingston D. M., Todaro G. J. Endogenous type C virus from a cat cell clone with properties distinct from previously described feline type C virus. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):142–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90473-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann R., Mulligan R. C., Baltimore D. Construction of a retrovirus packaging mutant and its use to produce helper-free defective retrovirus. Cell. 1983 May;33(1):153–159. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90344-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAllister R. M., Nicolson M., Gardner M. B., Rongey R. W., Rasheed S., Sarma P. S., Huebner R. J., Hatanaka M., Oroszlan S., Gilden R. V. C-type virus released from cultured human rhabdomyosarcoma cells. Nat New Biol. 1972 Jan 5;235(53):3–6. doi: 10.1038/newbio235003a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neiman P. E. Measurement of RD114 virus nucleotide sequences in feline cellular DNA. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):62–64. doi: 10.1038/newbio244062a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Akhavi M., Gardner M. B., Stephenson J. R., Roy-Burman P. Differential expression of two distinct endogenous retrovisus genomes in developing tissues of the domestic cat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1980 Mar;64(3):587–594. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Gardner M. B., Stephenson J. R., Roy-Burman P. Endogenous RD-114 virus genome expression in malignant tissues of domestic cats. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):578–586. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.578-586.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niman H. L., Stephenson J. R., Gardner M. B., Roy-Burman P. RD-114 and feline leukaemia virus genome expression in natural lymphomas of domestic cats. Nature. 1977 Mar 24;266(5600):357–360. doi: 10.1038/266357a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien S. J., Nash W. G. Genetic mapping in mammals: chromosome map of domestic cat. Science. 1982 Apr 16;216(4543):257–265. doi: 10.1126/science.7063884. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okabe H., Gilden R. V., Hatanaka M. Extensive homology of RD114 virus DNA with RNA of feline cell origin. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):54–56. doi: 10.1038/newbio244054a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repaske R., O'Neill R. R., Steele P. E., Martin M. A. Characterization and partial nucleotide sequence of endogenous type C retrovirus segments in human chromosomal DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):678–682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Tseng J., Lee Y. K., Gilden R. V. Virus similar to RD114 virus in cat cells. Nat New Biol. 1973 Jul 11;244(132):56–59. doi: 10.1038/newbio244056a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soe L. H., Devi B. G., Mullins J. I., Roy-Burman P. Molecular cloning and characterization of endogenous feline leukemia virus sequences from a cat genomic library. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):829–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.829-840.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Benveniste R. E., Lieber M. M., Livingston D. M. Infectious type C viruses released by normal cat embryo cells. Virology. 1973 Oct;55(2):506–515. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90192-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watanabe S., Temin H. M. Encapsidation sequences for spleen necrosis virus, an avian retrovirus, are between the 5' long terminal repeat and the start of the gag gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5986–5990. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]