Abstract
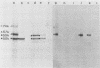
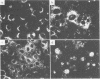
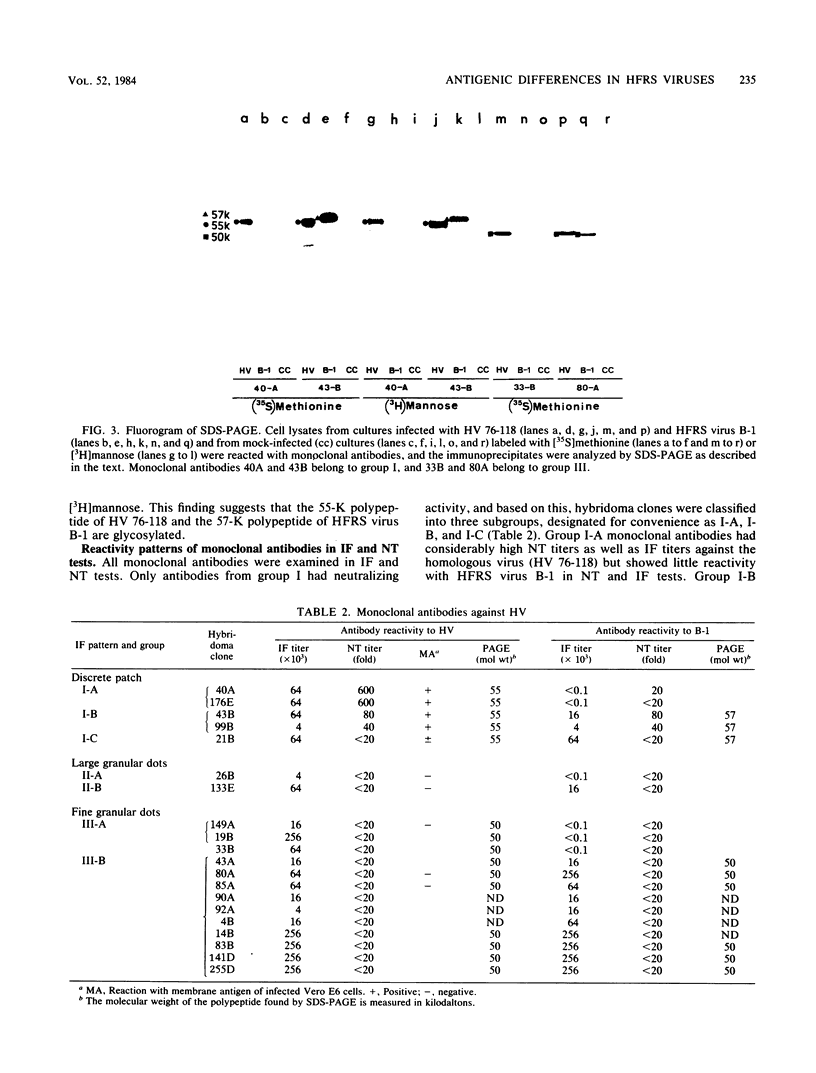
Hantaan virus (HV) 76-118, isolated from Apodemus agrarius coreae in Korea, and hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) virus B-1, isolated from a rat in Japan, were examined for polypeptide compositions and for differences in immune responses in rats. In immunoprecipitation experiments, a major polypeptide of ca. 50 kilodaltons (K) was detected with antisera against HV 76-118 in cell extracts from Vero E6 cells infected with HFRS virus B-1, whereas three major polypeptides of 74 K (glycosylated), 57 K (glycosylated), and 50 K were detected with antisera against HFRS virus B-1. On the other hand, two polypeptides with molecular weights of 55,000 (glycosylated) and 50,000 were detected with either antiserum in cell extracts infected with HV 76-118. In neutralizing antibody tests with antisera prepared in rats, a remarkable difference in antibody titer (5 to 30 times higher to the homologous virus than to the heterologous virus) was observed between the two viruses. However, this difference was not so marked (1 to 4 times higher to the homologous virus) in the immunofluorescent antibody test. Twenty hybrid cell lines producing mouse monoclonal antibodies against HV 76-118 were isolated by fusion of spleen cells from BALB/c mice immunized against HV (strain 76-118) with mouse myeloma cells. The specificity of these monoclonal antibodies was established by immunofluorescent antibody, neutralizing antibody, and fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen tests and by analysis with sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. These hybrid cell lines were classified into three groups based principally on the IF staining pattern of the HV-infected cells: (i) antibodies which showed a discrete patch pattern in the cytoplasm by the immunofluorescent antibody test, reacting with the membrane antigen of infected cells and immunoprecipitating a 55-K glycoprotein from HV 76-118-infected cell lysates and a 57-K glycoprotein from the heterologous (strain B-1) HFRS virus-infected cell lysates. Among these, depending on the neutralizing antibody activity and the reaction with the heterologous antigen, three subgroups designated I-A, I-B, and I-C were established; (ii) antibodies which showed large granular dots in the cytoplasm, neither having neutralizing antibody activity nor immunoprecipitating any antigen; (iii) antibodies which showed defined granular dots throughout the cytoplasm, reacting with a 50-K polypeptide of both virus strains. These antibodies also classified into two subgroups based on the reactivity with the B-1 strain.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 400 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brummer-Korvenkontio M., Vaheri A., Hovi T., von Bonsdorff C. H., Vuorimies J., Manni T., Penttinen K., Oker-Blom N., Lähdevirta J. Nephropathia epidemica: detection of antigen in bank voles and serologic diagnosis of human infection. J Infect Dis. 1980 Feb;141(2):131–134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/141.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen M. S., Casals J., Hsiung G. D., Kwei H. E., Chin C. C., Ge H. C., Hsiang C. M., Lee P. W., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Epidemic hemorrhagic fever in Hubei Province, The People's Republic of China: a clinical and serological study. Yale J Biol Med. 1981 Jan-Feb;54(1):41–55. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franko M. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Lee P. W., Gajdusek D. C. Monoclonal antibodies specific for Hantaan virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):4149–4153. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.4149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- French G. R., Foulke R. S., Brand O. A., Eddy G. A., Lee H. W., Lee P. W. Korean hemorrhagic fever: propagation of the etiologic agent in a cell line of human origin. Science. 1981 Mar 6;211(4486):1046–1048. doi: 10.1126/science.6110243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friman G., French G. R., Hambraeus L., Beisel W. R., Ilbäck N. G. Serum antibodies reactant with Korean haemorrhagic fever agent in Scandinavian epidemic (endemic) nephropathy (nephropathia epidemica) demonstrated by immunofluorescence utilizing an in vitro antigen source. Scand J Infect Dis. 1981;13(2):89–93. doi: 10.3109/inf.1981.13.issue-2.02. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goding J. W. Antibody production by hybridomas. J Immunol Methods. 1980;39(4):285–308. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90230-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura T., Morita C., Komatsu T., Sugiyama K., Arikawa J., Shiga S., Takeda H., Akao Y., Imaizumi K., Oya A. Isolation of virus causing hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) through a cell culture system. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1983 Feb;36(1):17–25. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.36.17. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W. Korean hemorrhagic fever. Prog Med Virol. 1982;28:96–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Johnson K. M. Isolation of the etiologic agent of Korean Hemorrhagic fever. J Infect Dis. 1978 Mar;137(3):298–308. doi: 10.1093/infdis/137.3.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H. W., Lee P. W., Lähdevirta J., Brummer-Korventkontio M. Aetiological relation between Korean haemorrhagic fever and nephropathia epidemica. Lancet. 1979 Jan 27;1(8109):186–187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Amyx H. L., Gajdusek D. C., Yanagihara R. T., Goldgaber D., Gibbs C. J., Jr New hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome-related virus in rodents in the United States. Lancet. 1982 Dec 18;2(8312):1405–1405. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Goldgaber D., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C., Yanagihara R. T., Svedmyr A., Hlaca D., Vesenjak-Hirjan J., Gligic A. Other serotypes of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome viruses in Europe. Lancet. 1982 Dec 18;2(8312):1405–1406. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Svedmyr A., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Antigenic difference between European and East Asian viruses causing haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Lancet. 1981 Aug 1;2(8240):256–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee P. W., Svedmyr A., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Nyström K. Antigenic difference between European and East Asian viruses causing haemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. Lancet. 1981 Aug 1;2(8240):256–257. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90505-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopetegui P., Matsunaga Y., Okuno T., Ogino T., Yamanishi K. Expression of varicella-zoster virus-related antigens in biochemically transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):1181–1186. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-1181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCormick J. B., Sasso D. R., Palmer E. L., Kiley M. P. Morphological identification of the agent of Korean haemorrhagic fever (Hantaan virus)as a member of the Bunyaviridae. Lancet. 1982 Apr 3;1(8275):765–768. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91812-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmaljohn C. S., Hasty S. E., Harrison S. A., Dalrymple J. M. Characterization of Hantaan virions, the prototype virus of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome. J Infect Dis. 1983 Dec;148(6):1005–1012. doi: 10.1093/infdis/148.6.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Song G., Hang C. S., Qui X. Z., Ni D. S., Liao H. X., Gao G. Z., Du Y. L., Xu J. K., Wu Y. S., Zhao J. N. Etiologic studies of epidemic hemorrhagic fever (hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome). J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):654–659. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.654. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Svedmyr A., Lee H. W., Berglund A., Hoorn B., Nyström K., Gajdusek D. C. Epidemic nephropathy in Scandinavia is related to Korean haemorrhagic fever. Lancet. 1979 Jan;1(8107):100–100. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(79)90083-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAMURA M. OCCURRENCE OF EPIDEMIC HEMORRHAGIC FEVER IN OSAKA CITY: FIRST CASES FOUND IN JAPAN WITH CHARACTERISTIC FEATURE OF MARKED PROTEINURIA. Biken J. 1964 Oct;7:79–94. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tkachenko E. A., Dzagurova T. K., Leshchinskaya E. V., Zagidulin I. M., Ustjugova I. M., Gasanova T. A., Rezapkin G. V., Miasnikov J. A. Serological diagnosis of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome in European region of U.S.S.R. Lancet. 1982 Dec 18;2(8312):1407–1407. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91311-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White J. D., Shirey F. G., French G. R., Huggins J. W., Brand O. M., Lee H. W. Hantaan virus, aetiological agent of Korean haemorrhagic fever, has Bunyaviridae-like morphology. Lancet. 1982 Apr 3;1(8275):768–771. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(82)91813-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamanishi K., Dantas J. R., Takahashi M., Yamanouchi T., Domae K., Kawamata J., Kurata T. Isolation of hemorrhagic fever with renal syndrome (HFRS) virus from a tumor specimen in a rat. Biken J. 1983 Dec;26(4):155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]