Abstract
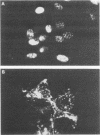
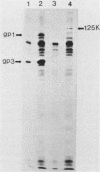
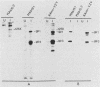
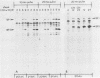
Two monoclonal antibodies were prepared against varicella-zoster virus proteins. One of the monoclonal antibodies (10.2) reacted only with the nuclei of infected cells and immunoprecipitated one nonglycosylated late viral protein (125,000 molecular weight). The other monoclonal antibody (19.1) with neutralizing activity, reacted with membrane antigens of infected cells and with the varicella-zoster virus envelope and immunoprecipitated two late major viral glycoproteins (gp1 and gp3). Synthesis of the 125,000-molecular-weight protein, gp1, and gp3 began at 20 to 22 h postinfection, 2 h after the peak of viral DNA synthesis, and continued until 29 h postinfection, when the first progeny virus appeared in infected cells. Pulse-chase experiments showed that during pulse-labeling, only gp1 was detected, whereas during the chase period, gp1 as well as gp3 was detected in infected cells. Under nonreducing conditions, gp3 migrated in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis as a 130,000-molecular-weight protein as compared with the 62,000-molecular-weight species obtained when gels were resolved under reducing conditions. This finding indicates that gp3 is a dimer that is disulfide linked.
Full text
PDF
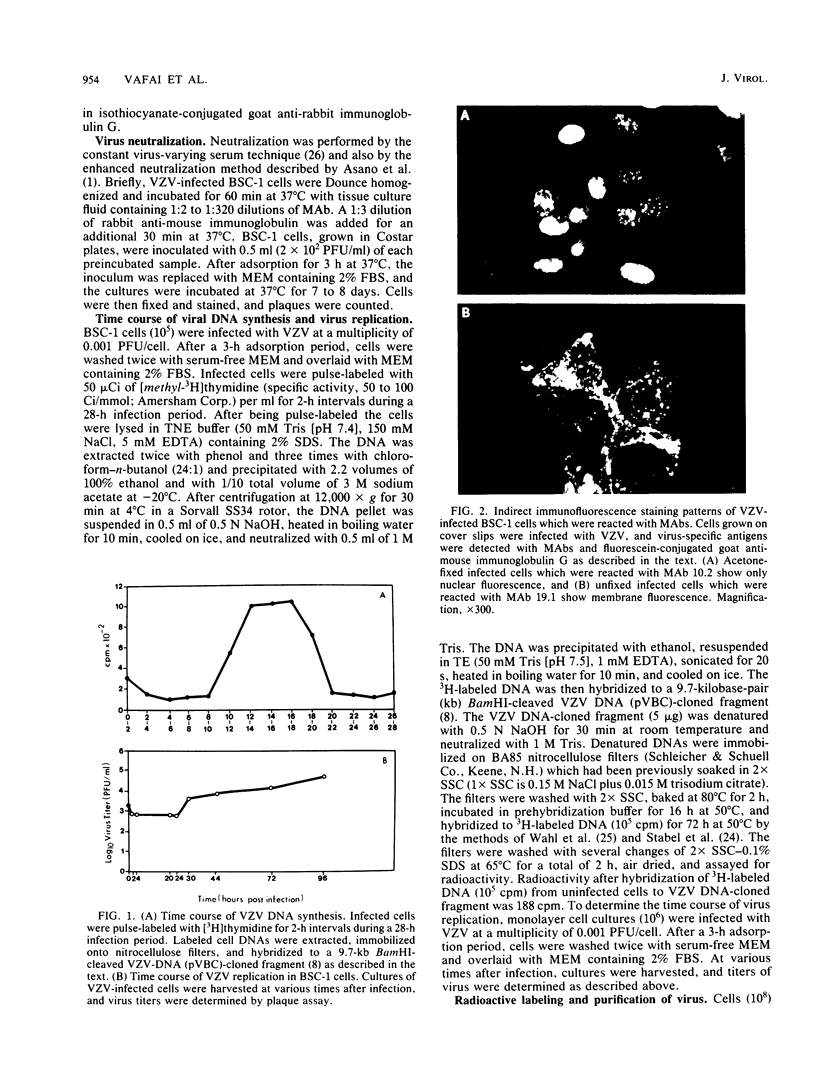
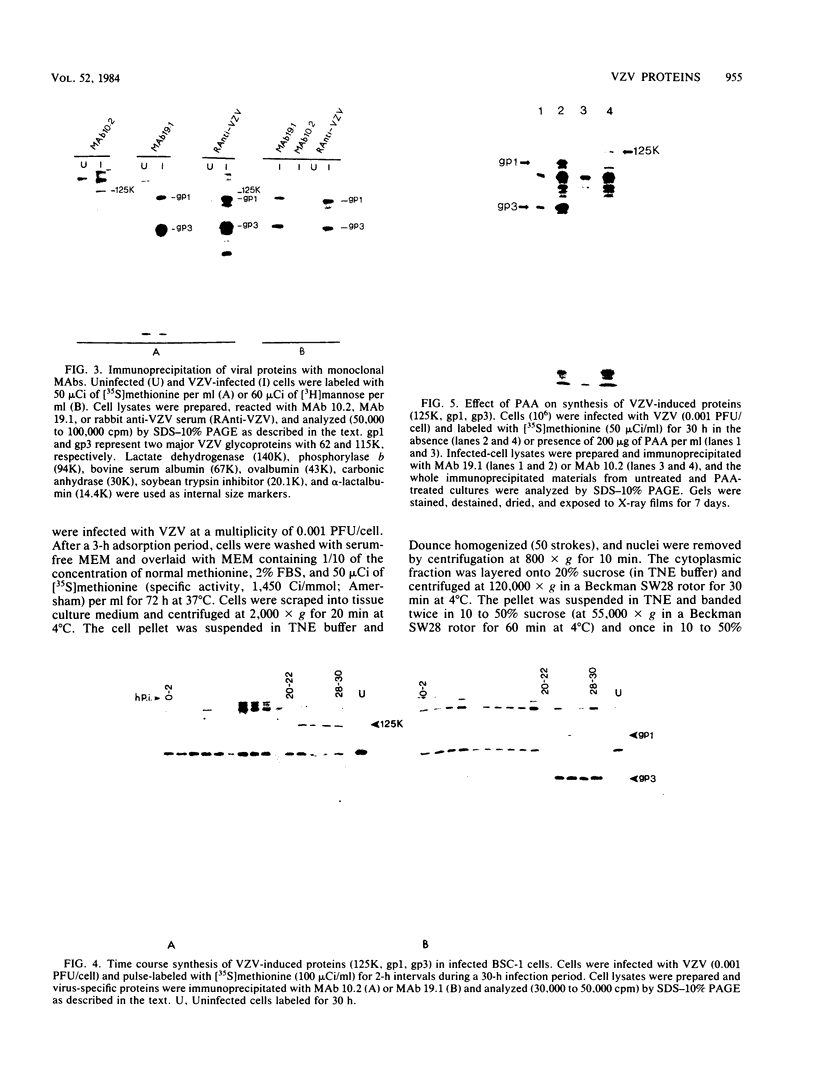



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano Y., Albrecht P., Vujcic L. K., Quinnan G. V., Jr, Takahashi M. Evaluation of humoral immunity to varicella-zoster virus by an enhanced neutralization test and by the fluorescent antibody to membrane antigen test. Arch Virol. 1983;75(3):225–228. doi: 10.1007/BF01315277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano Y., Takahashi M. Studies on the polypeptides of varicella-zoster (V-Z) virus. 1. Detection of varicella-zoster virus polypeptides in infected cells. Biken J. 1979 Sep;22(3):81–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Long D., Eisenberg R. J. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins gD and gC of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):429–439. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.429-439.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen G. H., Vaughan R. K., Lawrence W. C. Deoxyribonucleic acid synthesis in synchronized mammalian KB cells infected with herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1971 Jun;7(6):783–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.6.783-791.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conley A. J., Knipe D. M., Jones P. C., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. VII. Characterization of a temperature-sensitive mutant produced by in vitro mutagenesis and defective in DNA synthesis and accumulation of gamma polypeptides. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):191–206. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.191-206.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Shtram Y., Friedmann A., Wellish M., Devlin M., Cohen A., Fraser N., Becker Y. Extraction of cell-associated varicella-zoster virus DNA with triton X-100-NaCl. J Virol Methods. 1982 May;4(4-5):263–275. doi: 10.1016/0166-0934(82)90073-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Vafai A., Shtram Y., Becker Y., Devlin M., Wellish M. Varicella-zoster virus DNA in human sensory ganglia. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):478–480. doi: 10.1038/306478a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilden D. H., Wroblewska Z., Kindt V., Warren K. G., Wolinsky J. S. Varicella-zoster virus infection of human brain cells and ganglion cells in tissue culture. Arch Virol. 1978;56(1-2):105–117. doi: 10.1007/BF01317286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Edmond B. J., Friedrichs W. E. Immunogenic glycoproteins of laboratory and vaccine strains of Varicella-Zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1044–1053. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1044-1053.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Edwards D. P., Friedrichs W. E., Weigle K. A., McGuire W. L. Monoclonal antibodies against three major glycoproteins of varicella-zoster virus. Infect Immun. 1983 Apr;40(1):381–388. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.1.381-388.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Edwards D. P., Weigle K. A., Friedrichs W. E., McGuire W. L. Varicella-zoster virus-specific gp140: a highly immunogenic and disulfide-linked structural glycoprotein. Virology. 1984 Jan 15;132(1):138–146. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90098-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C., Friedrichs W. E. Immunoprecipitable polypeptides specified by varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1982 Apr 15;118(1):86–95. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90322-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grose C. The synthesis of glycoproteins in human melanoma cells infected with varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1980 Feb;101(1):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):584–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.584-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Continuous cultures of fused cells secreting antibody of predefined specificity. Nature. 1975 Aug 7;256(5517):495–497. doi: 10.1038/256495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okuno T., Yamanishi K., Shiraki K., Takahashi M. Synthesis and processing of glycoproteins of Varicella-Zoster virus (VZV) as studied with monoclonal antibodies to VZV antigens. Virology. 1983 Sep;129(2):357–368. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90175-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shemer Y., Leventon-Kriss S., Sarov I. Isolation and polypeptide characterization of varicella-zoster virus. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):133–140. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90228-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Okuno T., Yamanishi K., Takahashi M. Polypeptides of varicella-zoster virus (VZV) and immunological relationship of VZV and herpes simplex virus (HSV). J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):255–269. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiraki K., Takahashi M. Virus particles and glycoprotein excreted from cultured cells infected with varicella-zoster virus (VZV). J Gen Virol. 1982 Aug;61(Pt 2):271–275. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-61-2-271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stabel S., Doerfler W., Friis R. R. Integration sites of adenovirus type 12 DNA in transformed hamster cells and hamster tumor cells. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):22–40. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.22-40.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff M. H. The proteins of varicella-zoster-virus. Med Microbiol Immunol. 1978 Nov 17;166(1-4):21–28. doi: 10.1007/BF02121130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska Z., Devlin M., Reilly K., van Trieste H., Wellish M., Gilden D. H. The production of varicella Zoster virus antiserum in laboratory animals. Brief report. Arch Virol. 1982;74(2-3):233–238. doi: 10.1007/BF01314717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]