Abstract
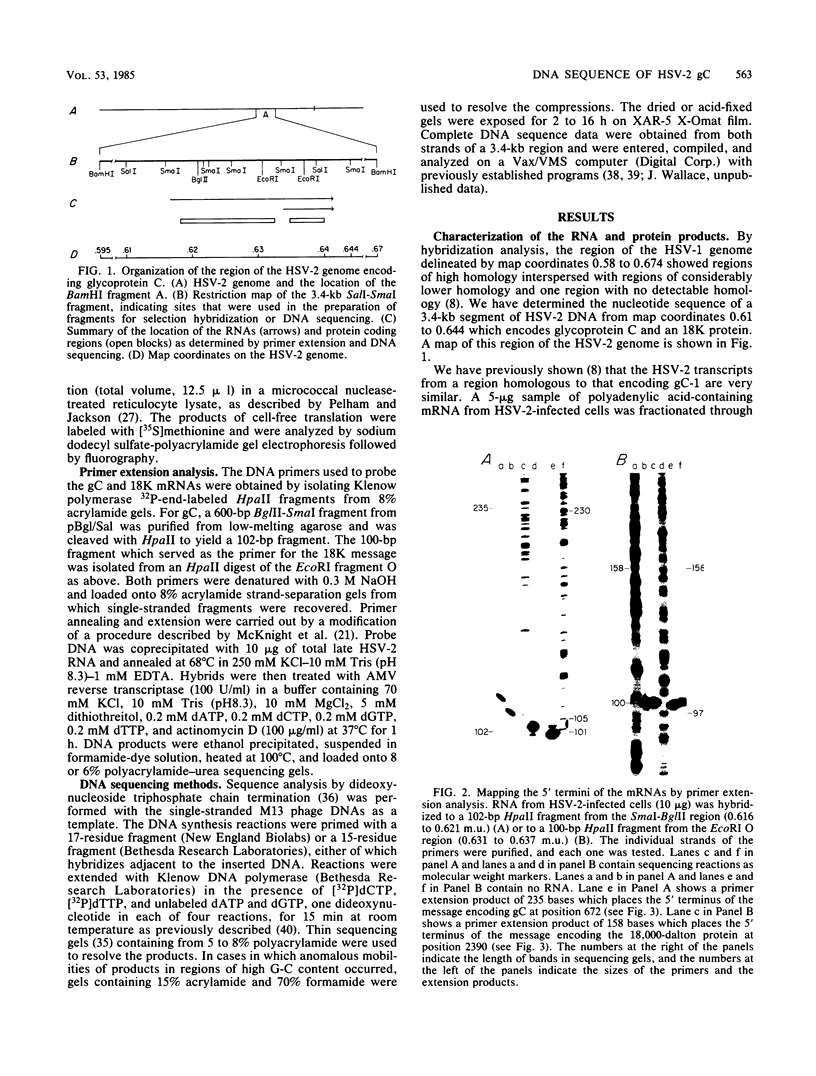
The gene encoding the glycoprotein C (gC) of herpes simplex virus type 1 maps to the region of the viral genome from 0.62 to 0.64. Recently, a herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein previously designated gF and now designated gC was mapped to a homologous location. Analysis of the herpes simplex virus type 2 mRNA species encoded in this region revealed a major transcript of 2.5 kilobases, a 0.73-kilobase transcript (the 5' ends of which were mapped by primer extension), and several minor species, all nearly identical to the herpes simplex virus type 1 pattern. A polypeptide of ca. 60,000 daltons was identified by in vitro translation of hybrid-selected mRNA. A smaller protein of ca. 20,000 daltons was also mapped to this region. The nucleotide sequence of a 3.4-kilobase segment of DNA encompassing gC was determined, and an open reading frame of 1,440 nucleotides specifying a 480-amino acid protein with properties consistent with that of a glycoprotein was identified. Comparative DNA sequence analysis showed regions of limited homology within the coding sequences for gC and a deletion which results in 31 fewer amino acids in the gC-2 near the amino terminus of the protein. The carboxy termini of gC-1 and gC-2 are very similar, as are the 20,000-dalton proteins.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Lewis J. B., Atkins J. F., Gesteland R. F. Cell-free synthesis of adenovirus 2 proteins programmed by fractionated messenger RNA: a comparison of polypeptide products and messenger RNA lengths. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jul;71(7):2756–2760. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.7.2756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson S. Shotgun DNA sequencing using cloned DNase I-generated fragments. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jul 10;9(13):3015–3027. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.13.3015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Harnish D., Killington R. A., Bacchetti S., Rawls W. E. Monoclonal antibodies to two glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):438–446. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.438-446.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balachandran N., Harnish D., Rawls W. E., Bacchetti S. Glycoproteins of herpes simplex virus type 2 as defined by monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):344–355. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.344-355.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Fox B. A., DeLuca N. A., Person S. Nucleotide sequence specifying the glycoprotein gene, gB, of herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):301–314. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90397-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassai E., Manservigi R., Corallini A., Terni M. Plaque dissociation of herpes simplex viruses: biochemical and biological characters of the viral variants. Intervirology. 1975;6(4-5):212–223. doi: 10.1159/000149476. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper K. G., Costa R. H., Lee G. T., Spear P. G., Wagner E. K. Molecular basis of the glycoprotein-C-negative phenotype of herpes simplex virus type 1 macroplaque strain. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):578–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.578-585.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Swain M., Galloway D., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 homology in the region between 0.58 and 0.68 map units. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):615–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.615-623.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenberg R. J., Ponce de Leon M., Pereira L., Long D., Cohen G. H. Purification of glycoprotein gD of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 by use of monoclonal antibody. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):1099–1104. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.1099-1104.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman H. M., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J., Seidel C. A., Cines D. B. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus 1 acts as a receptor for the C3b complement component on infected cells. Nature. 1984 Jun 14;309(5969):633–635. doi: 10.1038/309633a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Anderson K. P., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 HindIII fragment L encodes spliced and complementary mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):559–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.559-572.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Goldstein L. C., Lewis J. B. Identification of proteins encoded by a fragment of herpes simplex virus type 2 DNA that has transforming activity. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):530–537. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.530-537.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Swain M. A. Organization of the left-hand end of the herpes simplex virus type 2 BglII N fragment. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):724–730. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.724-730.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins F. J., Howett M. K. Characterization of mRNAs that map in the BglII N fragment of the herpes simplex virus type 2 genome. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.99-107.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. C., Spear P. G. O-linked oligosaccharides are acquired by herpes simplex virus glycoproteins in the Golgi apparatus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90083-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreil G. Transfer of proteins across membranes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:317–348. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.001533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manservigi R., Spear P. G., Buchan A. Cell fusion induced by herpes simplex virus is promoted and suppressed by different viral glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Gavis E. R., Kingsbury R., Axel R. Analysis of transcriptional regulatory signals of the HSV thymidine kinase gene: identification of an upstream control region. Cell. 1981 Aug;25(2):385–398. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90057-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKnight S. L., Kingsbury R. Transcriptional control signals of a eukaryotic protein-coding gene. Science. 1982 Jul 23;217(4557):316–324. doi: 10.1126/science.6283634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norrild B., Pedersen B. Effect of tunicamycin on the synthesis of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins and their expression on the cell surface. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):395–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.395-402.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olofsson S., Sjöblom I., Lundström M., Jeansson S., Lycke E. Glycoprotein C of herpes simplex virus type 1: characterization of O-linked oligosaccharides. J Gen Virol. 1983 Dec;64(Pt 12):2735–2747. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-12-2735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Para M. F., Zezulak K. M., Conley A. J., Weinberger M., Snitzer K., Spear P. G. Use of monoclonal antibodies against two 75,000-molecular-weight glycoproteins specified by herpes simplex virus type 2 in glycoprotein identification and gene mapping. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1223–1227. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1223-1227.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peake M. L., Nystrom P., Pizer L. I. Herpesvirus glycoprotein synthesis and insertion into plasma membranes. J Virol. 1982 May;42(2):678–690. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.2.678-690.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira L., Dondero D., Norrild B., Roizman B. Differential immunologic reactivity and processing of glycoproteins gA and gB of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 made in Vero and HEp-2 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5202–5206. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizer L. I., Cohen G. H., Eisenberg R. J. Effect of tunicamycin on herpes simplex virus glycoproteins and infectious virus production. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):142–153. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.142-153.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ricciardi R. P., Miller J. S., Roberts B. E. Purification and mapping of specific mRNAs by hybridization-selection and cell-free translation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4927–4931. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roizman B., Norrild B., Chan C., Pereira L. Identification and preliminary mapping with monoclonal antibodies of a herpes simplex virus 2 glycoprotein lacking a known type 1 counterpart. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):242–247. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90447-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doolittle R. F., Anilionis A., Curtis P. J., Wunner W. H. Homology between the glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):361–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.361-364.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Welch W. J., Sefton B. M., Esch F. S., Ling N. C. Vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein is anchored in the viral membrane by a hydrophobic domain near the COOH terminus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3884–3888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Coulson A. R. A rapid method for determining sequences in DNA by primed synthesis with DNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1975 May 25;94(3):441–448. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90213-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreier P. H., Cortese R. A fast and simple method for sequencing DNA cloned in the single-stranded bacteriophage M13. J Mol Biol. 1979 Mar 25;129(1):169–172. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90068-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Further procedures for sequence analysis by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1978 Mar;5(3):1013–1016. doi: 10.1093/nar/5.3.1013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staden R. Sequence data handling by computer. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977 Nov;4(11):4037–4051. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.11.4037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain M. A., Galloway D. A. Nucleotide sequence of the herpes simplex virus type 2 thymidine kinase gene. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1045–1050. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1045-1050.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J. DNA sequence of the Herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein D gene. Gene. 1983 Dec;26(2-3):307–312. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(83)90203-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Weis J. H., Salstrom J. S., Enquist L. W. Herpes simplex virus type-1 glycoprotein D gene: nucleotide sequence and expression in Escherichia coli. Science. 1982 Oct 22;218(4570):381–384. doi: 10.1126/science.6289440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wenske E. A., Bratton M. W., Courtney R. J. Endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H sensitivity of precursors to herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoproteins gB and gC. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):241–248. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.241-248.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zezulak K. M., Spear P. G. Mapping of the structural gene for the herpes simplex virus type 2 counterpart of herpes simplex virus type 1 glycoprotein C and identification of a type 2 mutant which does not express this glycoprotein. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):741–747. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.741-747.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Showalter S. D., Bladen S. V., Heilman C. J., Jr, Hampar B. Herpes simplex virus type 2 glycoprotein gF and type 1 glycoprotein gC have related antigenic determinants. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):185–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.185-192.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zweig M., Showalter S. D., Simms D. J., Hampar B. Antibodies to a synthetic oligopeptide that react with herpes simplex virus type 1 and 2 glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):430–436. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.430-436.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]