Abstract
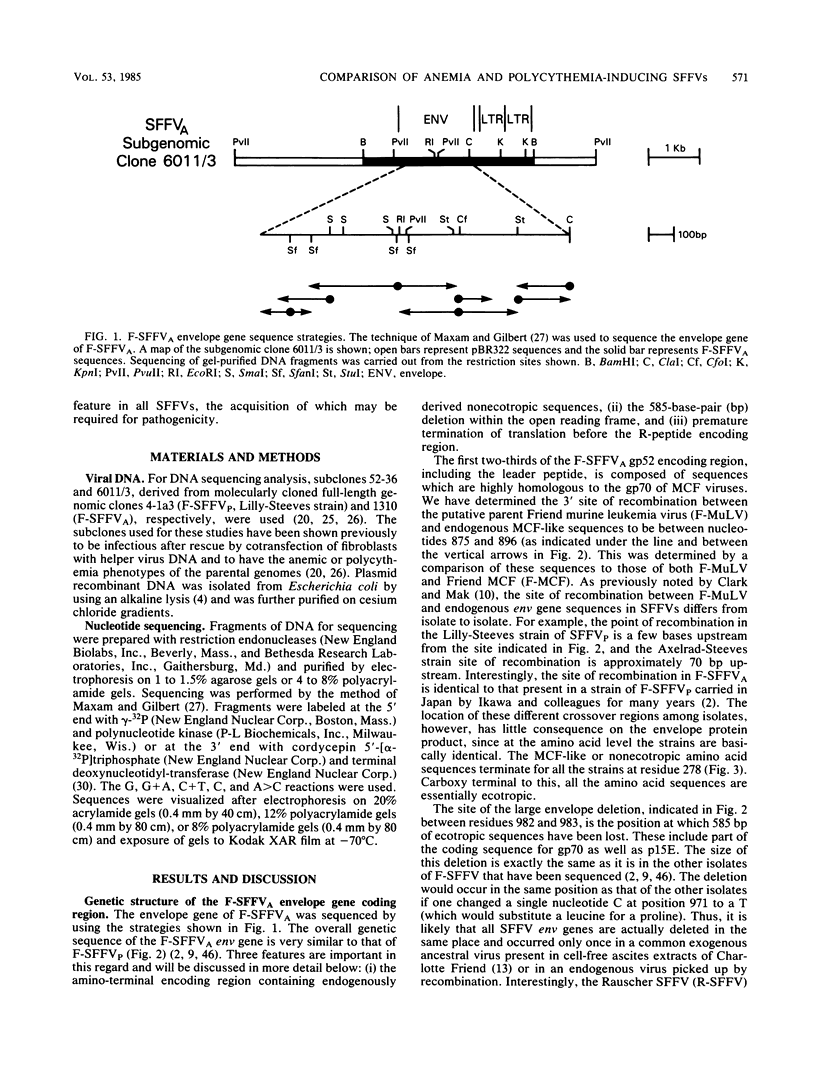
A nucleotide sequence analysis carried out on the envelope gene of the anemia-inducing strain of the Friend spleen focus-forming virus (F-SFFVA) reveals that its product has some unique features in common with previously described polycythemia-inducing strains of F-SFFV (F-SFFVP). (i) It contains an amino terminus that is highly related to the gp70 of mink cell focus-inducing viruses, (ii) it is a fusion protein containing the amino terminus of gp70 and the carboxy terminus of p15E, and (iii) it lacks the R-peptide normally found at the carboxy end of the p15E region. Although the envelope genes of F-SFFVA and F-SFFVP are quite similar overall, they do show sequence variation, particularly at the 3' end in the p15E-related region. These variations may contribute to previously observed differences in the response of F-SFFVP- and F-SFFVA-infected erythroid cells to regulatory hormone or to differences in the way the envelope glycoproteins are processed. The long terminal repeat regions of F-SFFVA and the Lilly-Steeves strain of F-SFFVP were also sequenced and compared with each other and with a previously published sequence of another F-SFFVP long terminal repeat. The sequences were found to be reasonably similar to each other but different from their ecotropic parent, Friend murine leukemia virus, as a result of a deletion of one copy of the direct tandem repeat in the enhancer regions. The observation that all SFFVS have this common change in the long terminal repeat enhancer region raises the possibility that it is required for pathogenicity.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Adachi A., Sakai K., Kitamura N., Nakanishi S., Niwa O., Matsuyama M., Ishimoto A. Characterization of the env gene and long terminal repeat of molecularly cloned Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus DNA. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.813-821.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amanuma H., Katori A., Obata M., Sagata N., Ikawa Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of the gene for the specific glycoprotein (gp55) of Friend spleen focus-forming virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3913–3917. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3913. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Boswell B. A., Kabat D. Molecular cloning of biologically active Rauscher spleen focus-forming virus and the sequences of its env gene and long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.695-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birnboim H. C., Doly J. A rapid alkaline extraction procedure for screening recombinant plasmid DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Nov 24;7(6):1513–1523. doi: 10.1093/nar/7.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., Van Griensven L. J., Vogt M., Verma I. M. Genome organization of retroviruses IX. Analysis of the genomes of Friend spleen focus-forming (F-SFFV) and helper murine leukemia viruses by heteroduplex-formation. Virology. 1980 Apr 15;102(1):234–239. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90088-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Mak T. W. Complete nucleotide sequence of an infectious clone of Friend spleen focus-forming provirus: gp55 is an envelope fusion glycoprotein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):5037–5041. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.5037. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Mak T. W. Fluidity of a retrovirus genome. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):759–765. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.759-765.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Mak T. W. Nucleotide sequences of the murine retrovirus Friend SFFVp long terminal repeats: identification of a structure with extensive dyad symmetry 5' to the TATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3315–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dresler S., Ruta M., Murray M. J., Kabat D. Glycoprotein encoded by the Friend spleen focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):564–575. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.564-575.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans L., Nunn M., Duesberg P. H., Troxler D., Scolnick E. RNAs of defective and nondefective components of Friend anemia and polycythemia virus strains identified and compared. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):823–835. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.087. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIEND C. Cell-free transmission in adult Swiss mice of a disease having the character of a leukemia. J Exp Med. 1957 Apr 1;105(4):307–318. doi: 10.1084/jem.105.4.307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonda M. A., Kaminchick J., Oliff A., Menke J., Nagashima K., Scolnick E. M. Heteroduplex analysis of molecular clones of the pathogenic Friend virus complex: Friend murine leukemia virus, Friend mink cell focus-forming virus, and the polycythemia- and anemia-inducing strains of Friend spleen focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):306–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.306-314.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Kost T. A., Koury M. J., Krantz S. B. Erythroid bursts produced by Friend leukaemia virus in vitro. Nature. 1978 Nov 30;276(5687):506–508. doi: 10.1038/276506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Krantz S. B. Helper virus is not required for in vitro erythroid transformation of hematopoietic cells by Friend virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5287–5291. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Krantz S. B. In vitro expression of erythroid differentiation induced by Friend polycythaemia virus. Nature. 1975 Feb 27;253(5494):731–732. doi: 10.1038/253731a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Troxler D. Polycythemia- and anemia-inducing erythroleukemia viruses exhibit differential erythroid transforming effects in vitro. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90545-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horoszewicz J. S., Leong S. S., Carter W. A. Friend leukemia: rapid development of erythropoietin-independent hematopoietic precursors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Jan;54(1):265–267. doi: 10.1093/jnci/54.1.265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaminchik J., Hankins W. D., Ruscetti S. K., Linemeyer D. L., Scolnick E. M. Molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA of the anemia-inducing strain of spleen focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):922–931. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.922-931.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laimins L. A., Gruss P., Pozzatti R., Khoury G. Characterization of enhancer elements in the long terminal repeat of Moloney murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):183–189. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.183-189.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao S. K., Axelrad A. A. Erythropoietin-independent erythroid colony formation in vitro by hemopoietic cells of mice infected with friend virus. Int J Cancer. 1975 Mar 15;15(3):467–482. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Ruscetti S. K., Evans L. H., Scolnick E. M. Envelope gene sequences which encode the gp52 protein of spleen focus-forming virus are required for the induction of erythroid cell proliferation. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):223–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.223-233.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Ruscetti S. K., Menke J. G., Scolnick E. M. Recovery of biologically active spleen focus-forming virus from molecularly cloned spleen focus-forming virus-pBR322 circular DNA by cotransfection with infectious type C retroviral DNA. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):710–721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.710-721.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Ruscetti S. K., Scolnick E. M., Evans L. H., Duesberg P. H. Biological activity of the spleen focus-forming virus is encoded by a molecularly cloned subgenomic fragment of spleen focus-forming virus DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1401–1405. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson J. S. The anatomy and taxonomy of protein structure. Adv Protein Chem. 1981;34:167–339. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60520-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rommelaere J., Faller D. V., Hopkins N. Characterization and mapping of RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides derived from the genomes of Akv and MCF murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):495–499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychoudhury R., Wu R. Terminal transferase-catalyzed addition of nucleotides to the 3' termini of DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):43–62. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S. K., Feild J. A., Scolnick E. M. Polycythaemia- and anaemia-inducing strains of spleen focus-forming virus differ in post-translational processing of envelope-related glycoproteins. Nature. 1981 Dec 17;294(5842):663–665. doi: 10.1038/294663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Davis L., Feild J., Oliff A. Friend murine leukemia virus-induced leukemia is associated with the formation of mink cell focus-inducing viruses and is blocked in mice expressing endogenous mink cell focus-inducing xenotropic viral envelope genes. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):907–920. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Wolff L. Spleen focus-forming virus: relationship of an altered envelope gene to the development of a rapid erythroleukemia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;112:21–44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69677-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Clarke S., Boswell B., Kabat D. Heterogeneous metabolism and subcellular localization of a potentially leukemogenic membrane glycoprotein encoded by Friend erythroleukemia virus. Isolation of viral and cellular processing mutants. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jan 10;257(1):126–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruta M., Kabat D. Plasma membrane glycoproteins encoded by cloned Rauscher and Friend spleen focus-forming viruses. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):844–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.844-853.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F. Acylation of viral spike glycoproteins: a feature of enveloped RNA viruses. Virology. 1982 Jan 15;116(1):327–338. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90424-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas R. V., Compans R. W. Glycosylation and intracellular transport of spleen focus-forming virus glycoproteins. Virology. 1983 Mar;125(2):274–286. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(83)90201-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Srinivas R. V., Compans R. W. Membrane association and defective transport of spleen focus-forming virus glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Dec 10;258(23):14718–14724. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tambourin P. E., Wendling F., Jasmin C., Smadja-Joffe F. The physiopathology of Friend leukemia. Leuk Res. 1979;3(3):117–129. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(79)90009-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiher H., König M., Gruss P. Multiple point mutations affecting the simian virus 40 enhancer. Science. 1983 Feb 11;219(4585):626–631. doi: 10.1126/science.6297005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Hubbert N., Ruscetti S. Structural analysis of the spleen focus-forming virus envelope gene product. Virology. 1984 Mar;133(2):376–385. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Koller R., Ruscetti S. Monoclonal antibody to spleen focus-forming virus-encoded gp52 provides a probe for the amino-terminal region of retroviral envelope proteins that confers dual tropism and xenotropism. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):472–481. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.472-481.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Scolnick E., Ruscetti S. Envelope gene of the Friend spleen focus-forming virus: deletion and insertions in 3' gp70/p15E-encoding region have resulted in unique features in the primary structure of its protein product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4718–4722. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4718. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



