Abstract
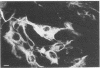
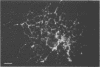
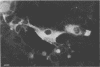
By using cell-type-specific markers and neural cultures derived from various areas of the nervous system, it has been possible to identify various interactions between OC43 virus and mouse oligodendrocytes, neurons, astrocytes, and fibroblasts. Neurons derived from dorsal root ganglia produced viral antigen and infectious virus. Astrocytes and fibroblasts both produced viral antigen but not infectious virus. Oligodendrocytes produced neither infectious virus nor viral antigen. Human embryo brain cells, including astrocytes, were susceptible to OC43 infection but did not produce infectious virus.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Antanitus D. S., Choi B. H., Lapham L. W. Immunofluorescence staining of astrocytes in vitro using antiserum to glial fibrillary acidic protein. Brain Res. 1975 May 23;89(2):363–367. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(75)90729-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bignami A., Eng L. F., Dahl D., Uyeda C. T. Localization of the glial fibrillary acidic protein in astrocytes by immunofluorescence. Brain Res. 1972 Aug 25;43(2):429–435. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(72)90398-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burks J. S., DeVald B. L., Jankovsky L. D., Gerdes J. C. Two coronaviruses isolated from central nervous system tissue of two multiple sclerosis patients. Science. 1980 Aug 22;209(4459):933–934. doi: 10.1126/science.7403860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins A. R., Tunison L. A., Knobler R. L. Mouse hepatitis virus type 4 infection of primary glial cultures from genetically susceptible and resistant mice. Infect Immun. 1983 Jun;40(3):1192–1197. doi: 10.1128/iai.40.3.1192-1197.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubois-Dalcq M. E., Doller E. W., Haspel M. V., Holmes K. V. Cell tropism and expression of mouse hepatitis viruses (MHV) in mouse spinal cord cultures. Virology. 1982 Jun;119(2):317–331. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90092-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eng L. F., Vanderhaeghen J. J., Bignami A., Gerstl B. An acidic protein isolated from fibrous astrocytes. Brain Res. 1971 May 7;28(2):351–354. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(71)90668-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes J. C., Klein I., DeVald B. L., Burks J. S. Coronavirus isolates SK and SD from multiple sclerosis patients are serologically related to murine coronaviruses A59 and JHM and human coronavirus OC43, but not to human coronavirus 229E. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):231–238. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.231-238.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Temperature-sensitive mutants of mouse hepatitis virus produce a high incidence of demyelination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):4033–4036. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.4033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Clements G. B., Brown S. M. Differential susceptibility of human neural cell types in culture to infection with herpes simplex virus. Brain. 1983 Mar;106(Pt 1):101–119. doi: 10.1093/brain/106.1.101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy P. G., Lisak R. P., Raff M. C. Cell type-specific markers for human glial and neuronal cells in culture. Lab Invest. 1980 Oct;43(4):342–351. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Dubois-Dalcq M., Haspel M. V., Claysmith A. P., Lampert P. W., Oldstone M. B. Selective localization of wild type and mutant mouse hepatitis virus (JHM strain) antigens in CNS tissue by fluorescence, light and electron microscopy. J Neuroimmunol. 1981 Mar;1(1):81–92. doi: 10.1016/0165-5728(81)90010-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knobler R. L., Haspel M. V., Oldstone M. B. Mouse hepatitis virus type 4 (JHM strains). induced fatal central nervous system disease. I. genetic control and murine neuron as the susceptible site of disease. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):832–843. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.832. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. T., Autilio L. A. The lipid composition of purified bovine brain myelin. J Neurochem. 1966 Apr;13(4):213–222. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1966.tb06794.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearson J., Mims C. A. Selective vulnerability of neural cells and age-related susceptibility to OC43 virus in mice. Arch Virol. 1983;77(2-4):109–118. doi: 10.1007/BF01309260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Fields K. L., Hakomori S. I., Mirsky R., Pruss R. M., Winter J. Cell-type-specific markers for distinguishing and studying neurons and the major classes of glial cells in culture. Brain Res. 1979 Oct 5;174(2):283–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90851-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raff M. C., Mirsky R., Fields K. L., Lisak R. P., Dorfman S. H., Silberberg D. H., Gregson N. A., Leibowitz S., Kennedy M. C. Galactocerebroside is a specific cell-surface antigenic marker for oligodendrocytes in culture. Nature. 1978 Aug 24;274(5673):813–816. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiner L. P. Pathogenesis of demyelination induced by a mouse hepatitis. Arch Neurol. 1973 May;28(5):298–303. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1973.00490230034003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wroblewska Z., Kennedy P. G., Wellish M. C., Lisak R. P., Gilden D. H. Demonstration of JC virus by immunofluorescence in multiple cell types in experimentally infected adult human brain cell cultures. J Neurol Sci. 1982 May;54(2):189–196. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(82)90181-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Fields K. L. Antibodies to neurofilament, glial filament, and fibroblast intermediate filament proteins bind to different cell types of the nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jan;88(1):115–126. doi: 10.1083/jcb.88.1.115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]