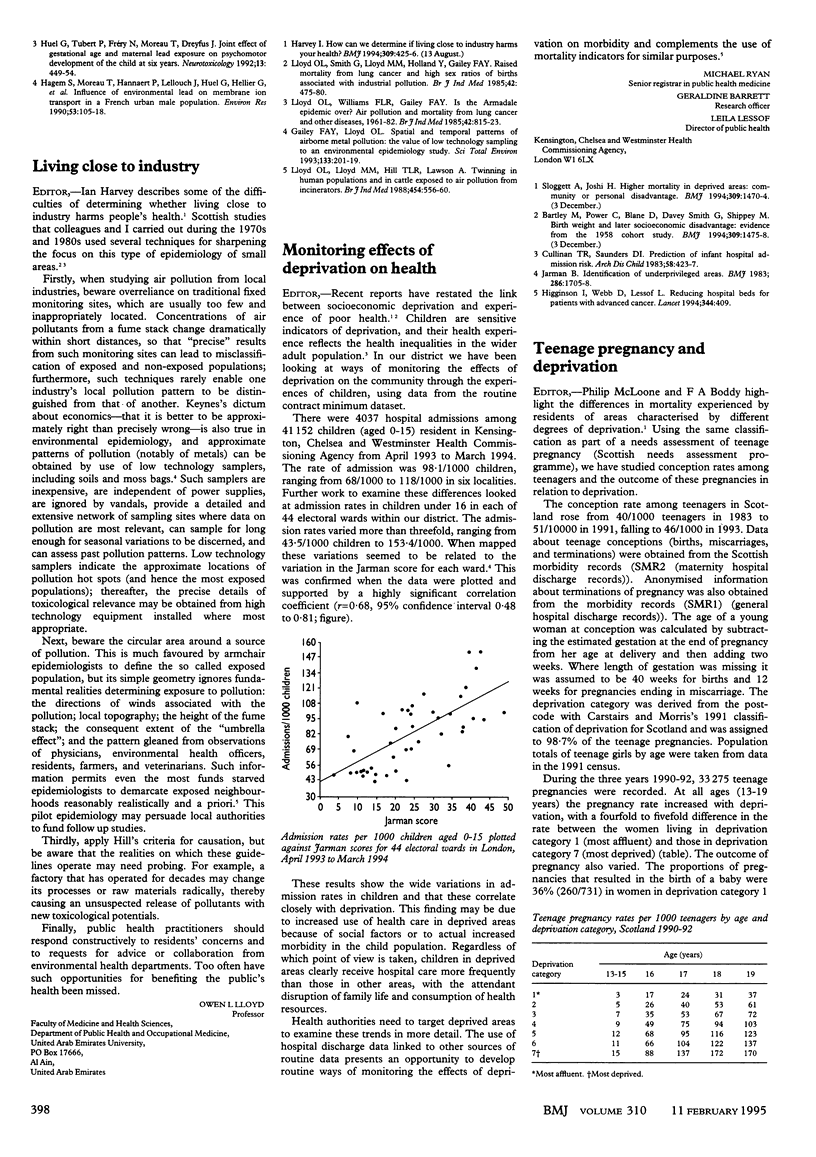
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hajem S., Moreau T., Hannaert P., Lellouch J., Huel G., Hellier G., Orssaud G., Claude J. R., Juguet B., Festy B. Influence of environmental lead on membrane ion transport in a French urban male population. Environ Res. 1990 Dec;53(2):105–118. doi: 10.1016/s0013-9351(05)80113-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones W., Gamble J. Epidemiological-environmental study of lead acid battery workers. I. Environmental study of five lead acid battery plants. Environ Res. 1984 Oct;35(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0013-9351(84)90110-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pocock S. J., Smith M., Baghurst P. Environmental lead and children's intelligence: a systematic review of the epidemiological evidence. BMJ. 1994 Nov 5;309(6963):1189–1197. doi: 10.1136/bmj.309.6963.1189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


