Abstract
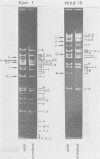
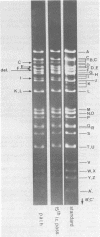
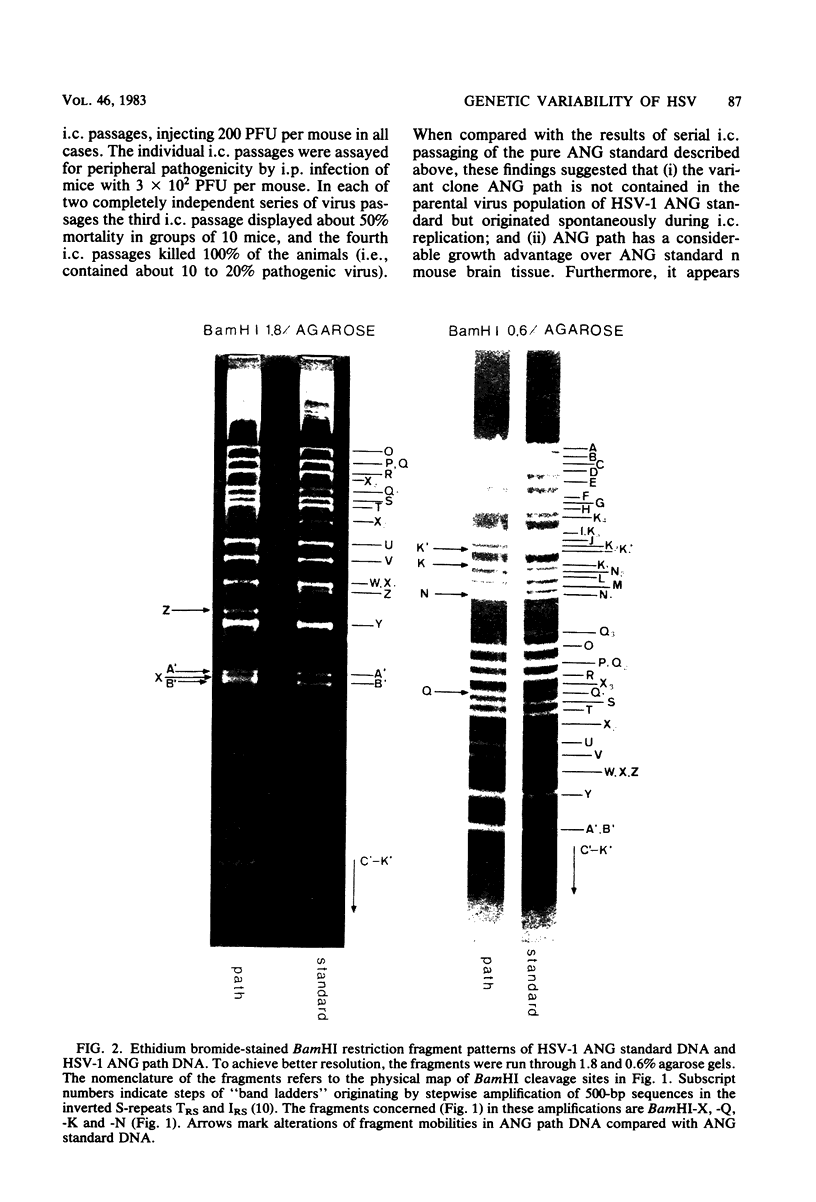
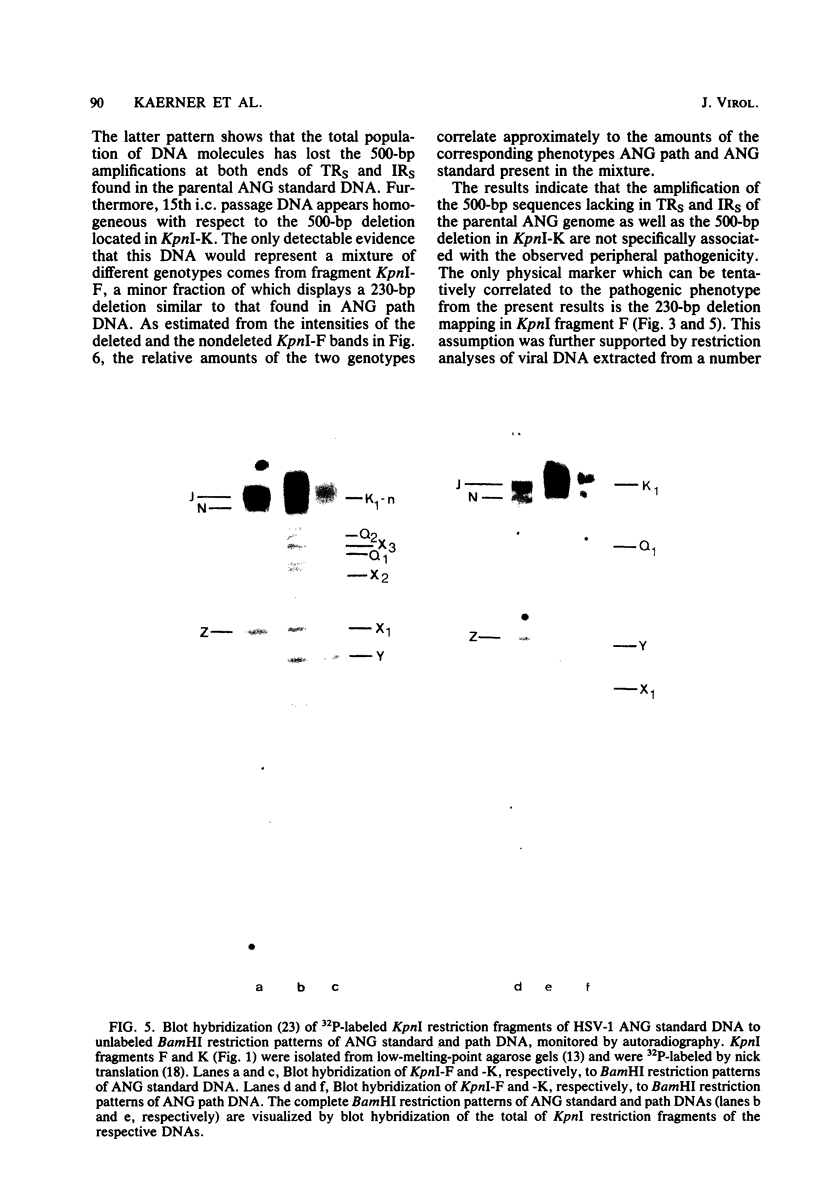
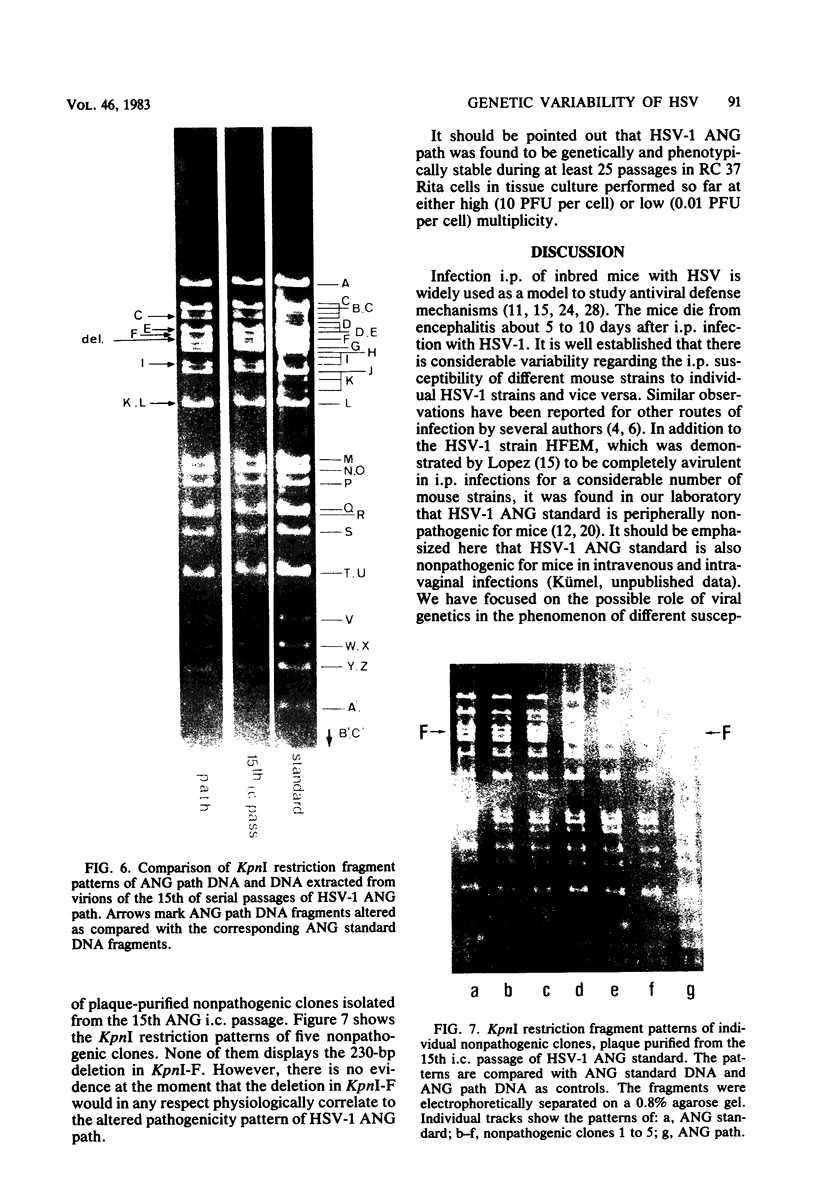
Herpes simplex virus type 1 ANG (HSV-1 ANG) is originally nonpathogenic for inbred mice upon intraperitoneal intravenous, or intravaginal inoculation. In contrast, mice died of encephalitis within 4 to 5 days after intracerebral inoculation with this strain. HSV-1 ANG was serially passaged in mouse brains. In two independent series, peripherally pathogenic virus variants had developed and accumulated in the virus progeny after 12 to 15 intracerebral passages. In mixed infections both nonpathogenic and pathogenic viruses replicated at the primary site of infection and spread to various organs. However, only the pathogenic phenotype could be recovered from the spinal cord and the brain. Comparison of the restriction enzyme cleavage patterns of pathogenic ANG and nonpathogenic ANG virus DNAs revealed distinct alterations in the S-segment (US) sequences bounded by coordinates 0.953 and 0.958 in the prototype orientation and by coordinates 0.862 to 0.867 in the IS orientation of the viral genome. However, it is not known whether these alterations are physiologically relevant to the observed changes in pathogenicity. When coinjected intraperitoneally at 50 to 100-fold excess, the nonpathogenic HSV-1 ANG protected mice against its own pathogenic variant as well as against other pathogenic HSV-1 strains. Pathogenic HSV-1 ANG proved to be genetically and phenotypically stable for at least 25 serial passages in tissue culture at either high or low multiplicity of infection.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Field H. J., Anderson J. R., Wildy P. Atypical patterns of neural infection produced in mice by drug-resistant strains of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1982 Mar;59(Pt 1):91–99. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-59-1-91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field H. J., Wildy P. The pathogenicity of thymidine kinase-deficient mutants of herpes simplex virus in mice. J Hyg (Lond) 1978 Oct;81(2):267–277. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400025109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halliburton I. W. Intertypic recombinants of herpes simplex viruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):1–23. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harbour D. A., Hill T. J., Blyth W. A. Acute and recurrent herpes simplex in several strains of mice. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jul;55(Pt 1):31–40. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward G. S., Frenkel N., Roizman B. Anatomy of herpes simplex virus DNA: strain differences and heterogeneity in the locations of restriction endonuclease cleavage sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1768–1772. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hill T. J., Field H. J., Blyth W. A. Acute and recurrent infection with herpes simplex virus in the mouse: a model for studying latency and recurrent disease. J Gen Virol. 1975 Sep;28(3):341–353. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-3-341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOHNSON R. T. THE PATHOGENESIS OF HERPES VIRUS ENCEPHALITIS. I. VIRUS PATHWAYS TO THE NERVOUS SYSTEM OF SUCKLING MICE DEMONSTRATED BY FLUORESCENT ANTIBODY STAINING. J Exp Med. 1964 Feb 1;119:343–356. doi: 10.1084/jem.119.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Maichle I. B., Ott A., Schröder C. H. Origin of two different classes of defective HSV-1 Angelotti DNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1979 Apr;6(4):1467–1478. doi: 10.1093/nar/6.4.1467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaerner H. C., Ott-Hartmann A., Schatten R., Schröder C. H., Gray C. P. Amplification of a short nucleotide sequence in the repeat units of defective herpes simplex virus type 1 Angelotti DNA. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):75–81. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.75-81.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Kochen M., Munk K., Hirt H. M., Mergenhagen S. E., Rosenstreich D. L. Differences in susceptibility to herpes simplex virus infection of inbred strains of mice. IARC Sci Publ. 1978;(24 Pt 2):783–788. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirschner H., Kochen M., Hirt H. M., Munk K. Immunological studies of hsv-infection of resistant and susceptible inbred strains of mice. Z Immunitatsforsch Immunobiol. 1978 Mar;154(2):147–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonsdale D. M., Brown S. M., Lang J., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Koprowski H., Warren K. G. Variations in herpes simplex virus isolated from human ganglia and a study of clonal variation in HSV-1. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1980;354:291–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1980.tb27973.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C. Genetics of natural resistance to herpesvirus infections in mice. Nature. 1975 Nov 13;258(5531):152–153. doi: 10.1038/258152a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C. Immunological nature of genetic resistance of mice to herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. IARC Sci Publ. 1978;(24 Pt 2):775–781. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopez C. Resistance to herpes simplex virus - type 1 (HSV-1). Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1981;92:15–24. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68069-4_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUSSELL W. C. A sensitive and precise plaque assay for herpes virus. Nature. 1962 Sep 8;195:1028–1029. doi: 10.1038/1951028a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schröeder C. H., Engler H., Kirchner H. Protection of mice by an apathogenic strain HSV-1 against lethal infection by a pathogenic strain of HSV-1. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):159–161. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skare J., Summers W. P., Summers W. C. Structure and function of herpesvirus genomes. I. comparison of five HSV-1 and two HSV-2 strains by cleavage their DNA with eco R I restriction endonuclease. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):726–732. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.726-732.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens J. G., Cook M. L. Restriction of herpes simplex virus by macrophages. An analysis of the cell-virus interaction. J Exp Med. 1971 Jan 1;133(1):19–38. doi: 10.1084/jem.133.1.19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson R. J., Vande Woude G. F. DNA sequence of an immediate-early gene (IEmRNA-5) of herpes simplex virus type I. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Feb 11;10(3):979–991. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.3.979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zawatzky R., Hilfenhaus J., Marcucci F., Kirchner H. Experimental infection of inbred mice with herpes simplex virus type 1. I. Investigation of humoral and cellular immunity and of interferon induction. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):31–38. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zisman B., Hirsch M. S., Allison A. C. Selective effects of anti-macrophage serum, silica and anti-lymphocyte serum on pathogenesis of herpes virus infection of young adult mice. J Immunol. 1970 May;104(5):1155–1159. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]