Abstract
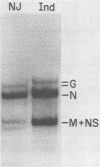
The nucleotide sequence of the mRNA encoding the glycoprotein from the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus (VSV) was determined from a cDNA clone containing the entire coding region. The sequence of 12 5'-terminal noncoding nucleotides present in the mRNA but not in the cDNA clone was determined from a primer extended to the 5' terminus of the mRNA. The mRNA is 1,573 nucleotides long (excluding polyadenylic acid) and encodes a protein of 517 amino acids. Only six nucleotides occur between the translation termination codon and the polyadenylic acid. Short homologies between the untranslated termini of this mRNA and the mRNAs of the Indiana serotype were found. The predicted protein sequence was compared with that of the glycoprotein of the Indiana serotype of VSV and with the glycoprotein of rabies virus, using a computer program which determines optimal alignment. An amino acid identity of 50.9% was found for the two VSV serotypes. Approximately 20% identity was found between the rabies virus and VSV New Jersey glycoproteins. The positions and sizes of the transmembrane domains, the signal sequences, and the glycosylation sites are identical in both VSV serotypes. Two of five serine residues which were possible esterification sites for palmitate in the glycoprotein from the Indiana serotype are changed to glycine residues in the glycoprotein from the New Jersey serotype. Because the glycoprotein of the New Jersey serotype does not contain esterified palmitate, we suggest that one or both of these residues are the probable esterification sites in the glycoprotein from the Indiana serotype.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anilionis A., Wunner W. H., Curtis P. J. Structure of the glycoprotein gene in rabies virus. Nature. 1981 Nov 19;294(5838):275–278. doi: 10.1038/294275a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown E., Prevec L. Proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. IV. A comparison of tryptic peptides of the vesicular stomatitis group of rhabdoviruses. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):7–21. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cartwright B., Brown F. Serological relationships between different strains of vesicular stomatis virus. J Gen Virol. 1972 Sep;16(3):391–398. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-16-3-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doel T. R., Brown F. Tryptic peptide analysis of the structural proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Gen Virol. 1978 Feb;38(2):351–361. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-38-2-351. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doolittle R. F. Similar amino acid sequences: chance or common ancestry? Science. 1981 Oct 9;214(4517):149–159. doi: 10.1126/science.7280687. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franze-Fernandez M. T., Banerjee A. K. In vitro RNA transcription by the New Jersey serotype of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Characterization of the mRNA species. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):179–187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.179-187.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallione C. J., Greene J. R., Iverson L. E., Rose J. K. Nucleotide sequences of the mRNA's encoding the vesicular stomatitis virus N and NS proteins. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):529–535. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.529-535.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Greenawalt J. W., Wagner R. R. Defective T particles of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Preparation, morphology, and some biologic properties. Virology. 1966 Oct;30(2):161–172. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90092-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley J. M., Emerson S. U., Wagner R. R. The glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus is the antigen that gives rise to and reacts with neutralizing antibody. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1231–1235. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1231-1235.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancios L., Lyles D. S. The interactionof antiody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. I. Analysis of neutralizing epitopes with monoclonal antibodies. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):157–167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lefrancois L., Lyles D. S. The interaction of antibody with the major surface glycoprotein of vesicular stomatitis virus. II. Monoclonal antibodies of nonneutralizing and cross-reactive epitopes of Indiana and New Jersey serotypes. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):168–174. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90126-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGeoch D. J., Dolan A., Pringle C. R. Comparisons of nucleotide sequences in the genomes of the New Jersey and Indiana serotypes of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):69–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.69-77.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reading C. L., Penhoet E. E., Ballou C. E. Carbohydrate structure of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 25;253(16):5600–5612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Flamand A., Clark H. F., Obijeski J. F., Roy P., Bishop D. H. Detection of homologous RNA sequences among six rhabdovirus genomes. J Virol. 1974 Jan;13(1):250–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.13.1.250-252.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K. Complete intergenic and flanking gene sequences from the genome of vesicular stomatitis virus. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):415–421. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90515-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rose J. K., Doolittle R. F., Anilionis A., Curtis P. J., Wunner W. H. Homology between the glycoproteins of vesicular stomatitis virus and rabies virus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):361–364. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.361-364.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlesinger M. J., Malfer C. Cerulenin blocks fatty acid acylation of glycoproteins and inhibits vesicular stomatitis and Sindbis virus particle formation. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):9887–9890. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt M. F., Schlesinger M. J. Fatty acid binding to vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein: a new type of post-translational modification of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):813–819. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90321-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Webster R. G., Laver W. G., Air G. M., Schild G. C. Molecular mechanisms of variation in influenza viruses. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):115–121. doi: 10.1038/296115a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zilberstein A., Snider M. D., Porter M., Lodish H. F. Mutants of vesicular stomatitis virus blocked at different stages in maturation of the viral glycoprotein. Cell. 1980 Sep;21(2):417–427. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90478-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]