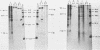Abstract
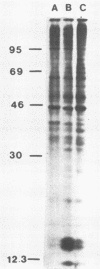
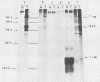
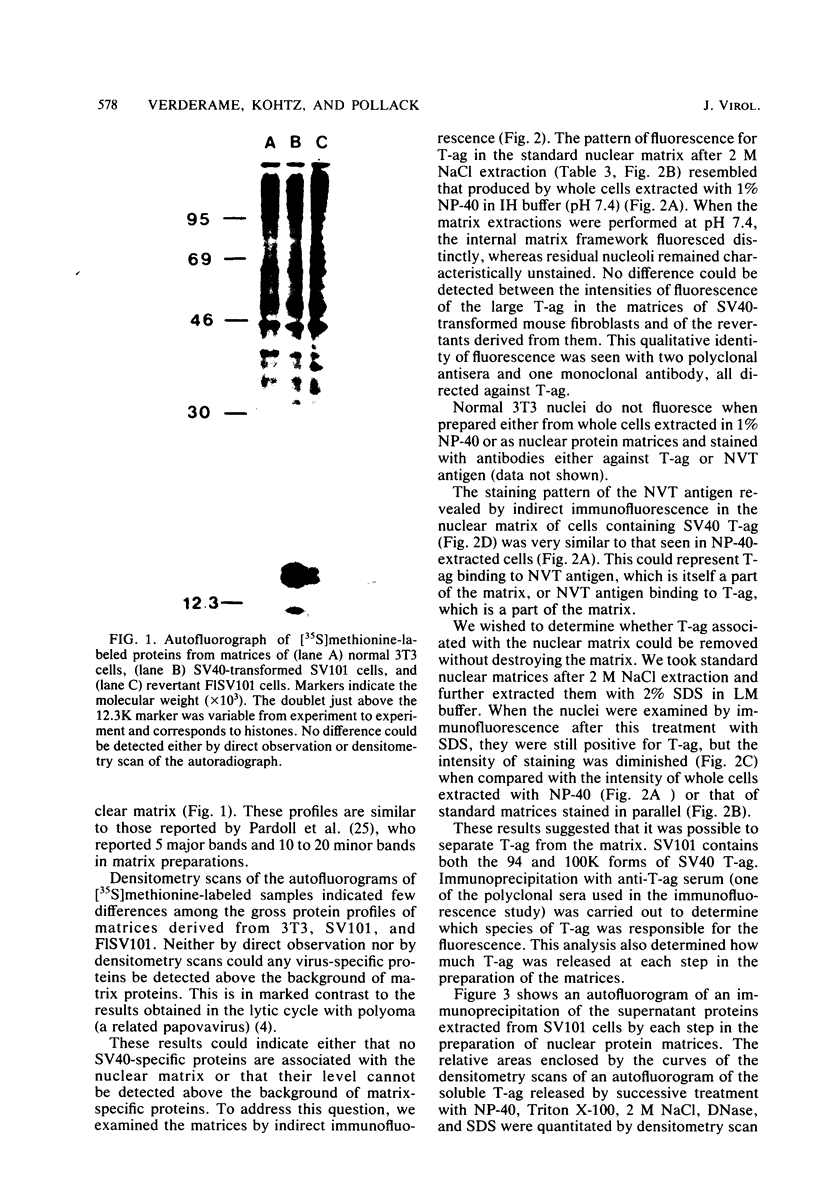
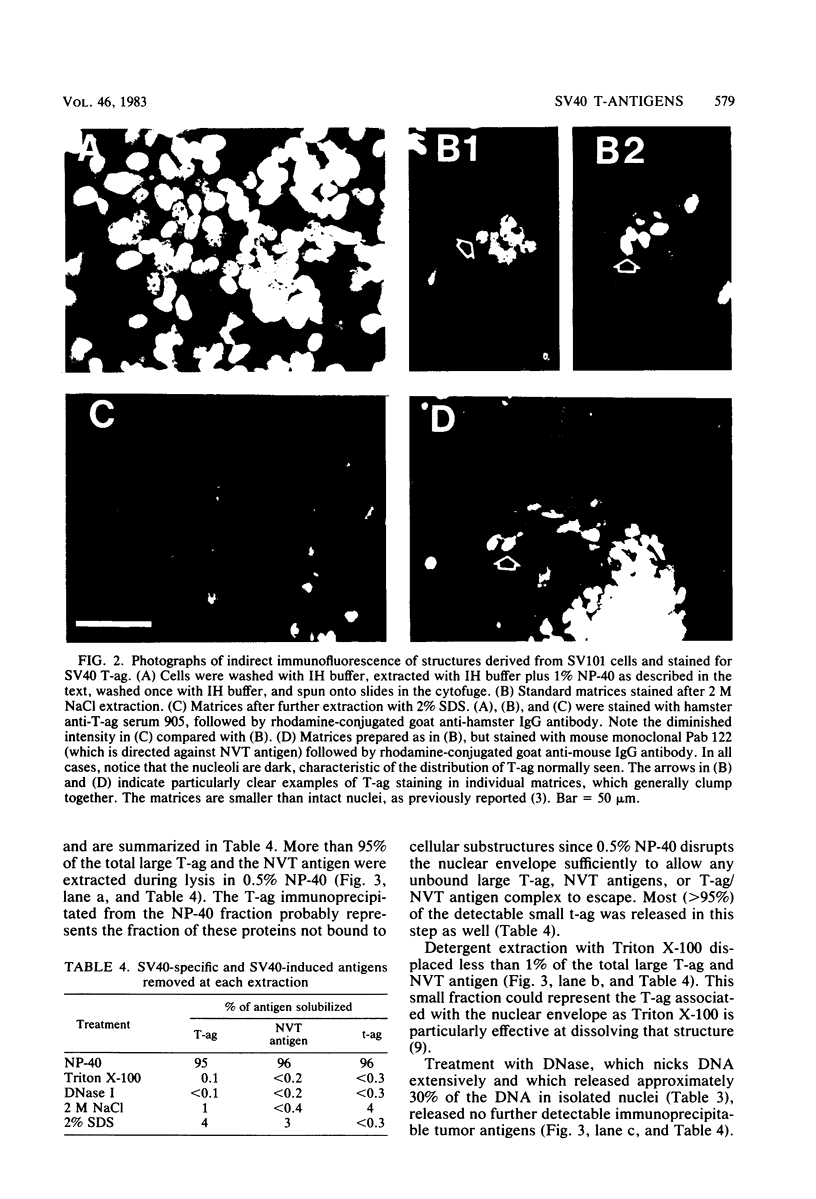
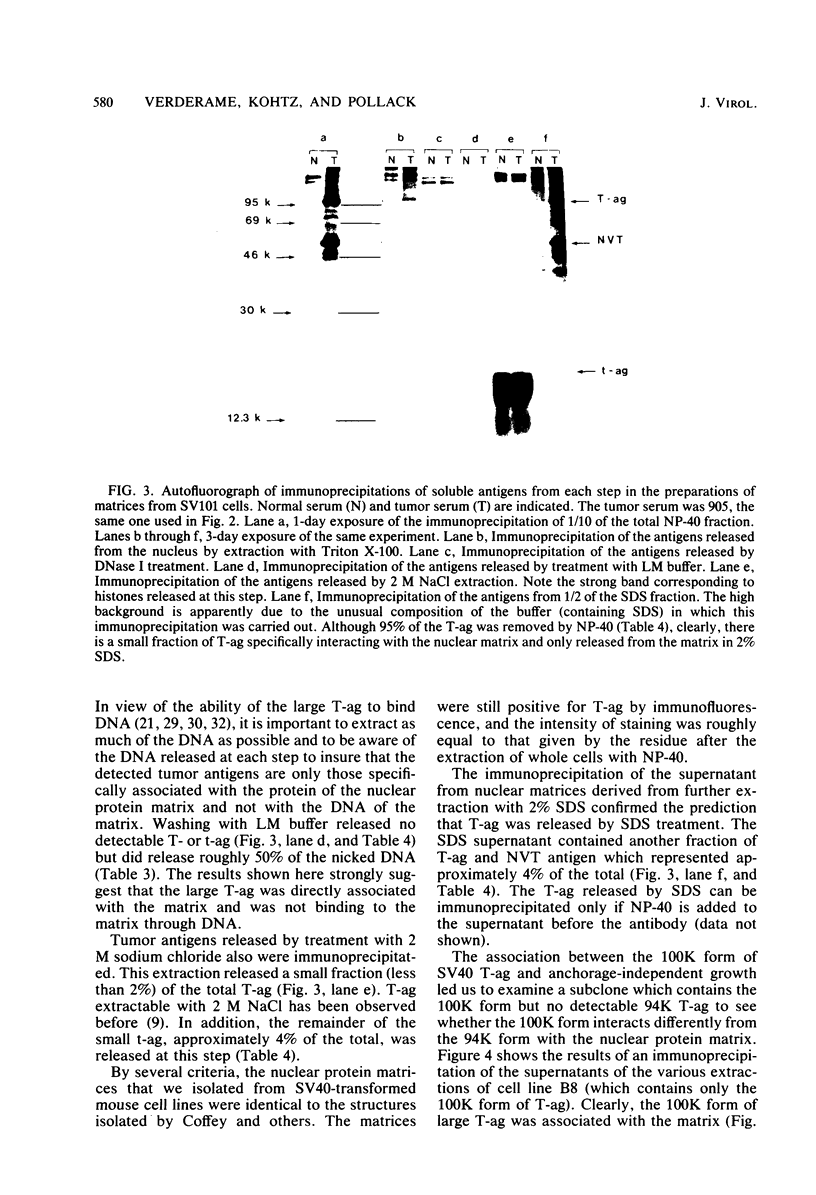
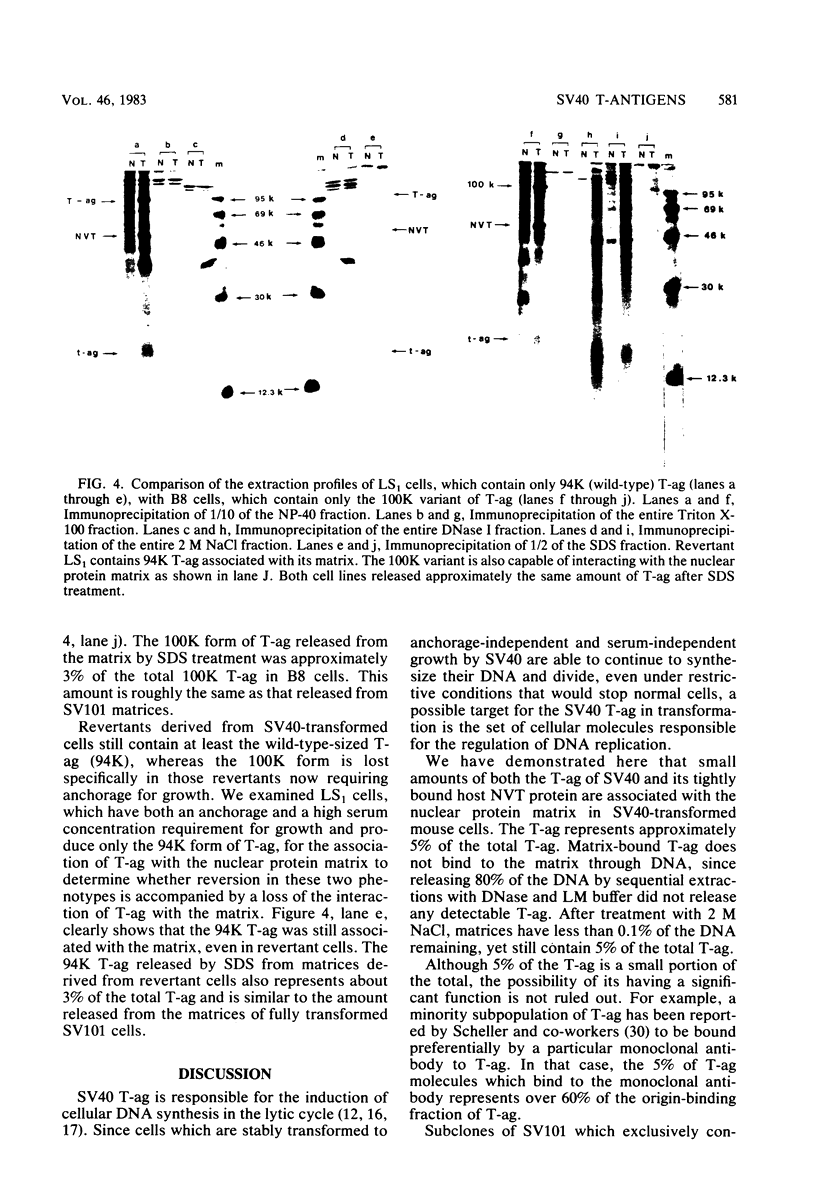
A small fraction of the 94,000-molecular-weight multifunctional large T-antigen of simian virus 40 was associated with the nuclear protein matrix derived from simian virus 40-transformed mouse cells. The interaction between this fraction of T-antigen and the matrix was largely or entirely independent of nuclear DNA. Similar amounts of T-antigen were retained by the nuclei of transformed and revertant cell lines. A 100,000-molecular-weight variant of T-antigen, which has been found to correlate specifically with anchorage-independent growth, was present in the nuclear protein matrix of a transformed cell line. A T-antigen-containing revertant selected for the reacquisition of a high serum requirement and an anchorage requirement for growth retained T-antigen in association with its matrix.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen S. L., Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Phosphorylation of nuclear matrix proteins in isolated regenerating rat liver nuclei. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Mar 7;75(1):111–116. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURTON K. A study of the conditions and mechanism of the diphenylamine reaction for the colorimetric estimation of deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochem J. 1956 Feb;62(2):315–323. doi: 10.1042/bj0620315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear matrix. Isolation and characterization of a framework structure from rat liver nuclei. J Cell Biol. 1977 Jun;73(3):616–637. doi: 10.1083/jcb.73.3.616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berezney R., Coffey D. S. Nuclear protein matrix: association with newly synthesized DNA. Science. 1975 Jul 25;189(4199):291–293. doi: 10.1126/science.1145202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler-White A. J., Humphrey G. W., Pigiet V. Association of polyoma T antigen and DNA with the nuclear matrix from lytically infected 3T6 cells. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):37–46. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90152-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COOPERSTEIN S. J., LAZAROW A. A microspectrophotometric method for the determination of cytochrome oxidase. J Biol Chem. 1951 Apr;189(2):665–670. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen S., Verderame M., Lo A., Pollack R. Nonlytic simian virus 40-specific 100K phosphoprotein is associated with anchorage-independent growth in simian virus 40-transformed and revertant mouse cell lines. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Nov;1(11):994–1006. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.11.994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comings D. E., Okada T. A. Nuclear proteins. III. The fibrillar nature of the nuclear matrix. Exp Cell Res. 1976 Dec;103(2):341–360. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(76)90271-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W. Simian virus 40 (SV40)-specific proteins associated with the nuclear matrix isolated from adenovirus type 2-SV40 hybrid virus-infected HeLa cells carry SV40 U-antigen determinants. J Virol. 1978 Apr;26(1):165–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.1.165-178.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Jay G., DeLeo A. B., Khoury G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection by monoclonal antibody in mouse and human cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1695–1699. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerace L., Blobel G. The nuclear envelope lamina is reversibly depolymerized during mitosis. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):277–287. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90409-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gershon D., Sachs L., Winocour E. The induction of cellular DNA synthesis by simian virus 40 in contact-inhibited and in x-irradiated cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Sep;56(3):918–925. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.3.918. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacherio D., Hager L. P. A poly(dT)-stimulated ATPase activity associated with simian virus 40 large T antigen. J Biol Chem. 1979 Sep 10;254(17):8113–8116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gurney E. G., Harrison R. O., Fenno J. Monoclonal antibodies against simian virus 40 T antigens: evidence for distinct sublcasses of large T antigen and for similarities among nonviral T antigens. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):752–763. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.752-763.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hand R. Functions of T antigens of SV40 and polyomavirus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 31;651(1):1–24. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(81)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Dulbecco R. Induction of DNA synthesis by SV40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Aug;56(2):736–740. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.2.736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henry P., Black P. H., Oxman M. N., Weissman S. M. Stimulation of DNA synthesis in mouse cell line 3T3 by Simian virus 40. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Oct;56(4):1170–1176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.4.1170. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jackson D. A., McCready S. J., Cook P. R. RNA is synthesized at the nuclear cage. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):552–555. doi: 10.1038/292552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Jay F. T., Chang C., Friedman R. M., Levine A. S. Tumor-specific transplantation antigen: use of the Ad2+ND1 hybrid virus to identify the protein responsible for simian virus 40 tumor rejection and its genetic origin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jul;75(7):3055–3059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.7.3055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jay G., Khoury G., DeLeo A. B., Dippold W. G., Old L. J. p53 transformation-related protein: detection of an associated phosphotransferase activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2932–2936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jessel D., Landau T., Hudson J., Lalor T., Tenen D., Livingston D. M. Identification of regions of the SV40 genome which contain preferred SV40 T antigen-binding sites. Cell. 1976 Aug;8(4):535–545. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(76)90222-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Hoeffler W. K. SV40 large T shares an antigenic determinant with a cellular protein of molecular weight 68,000. Nature. 1980 Nov 13;288(5787):167–170. doi: 10.1038/288167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPE J. H., ROWE W. P. DETECTION OF SPECIFIC ANTIGEN IN SV40-TRANSFORMED CELLS BY IMMUNOFLUORESCENCE. J Exp Med. 1964 Aug 1;120:121–128. doi: 10.1084/jem.120.2.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pardoll D. M., Vogelstein B., Coffey D. S. A fixed site of DNA replication in eucaryotic cells. Cell. 1980 Feb;19(2):527–536. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90527-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prives C., Gilboa E., Revel M., Winocour E. Cell-free translation of simian virus 40 early messenger RNA coding for viral T-antigen. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):457–461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S. I., Ferguson J., Davis R. W., Stark G. R. T antigen binds to simian virus 40 DNA at the origin of replication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1605–1609. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scheller A., Covey L., Barnet B., Prives C. A small subclass of SV40 T antigen binds to the viral origin of replication. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):375–383. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90154-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TODARO G. J., GREEN H. Quantitative studies of the growth of mouse embryo cells in culture and their development into established lines. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:299–313. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tegtmeyer P., Schwartz M., Collins J. K., Rundell K. Regulation of tumor antigen synthesis by simain virus 40 gene A. J Virol. 1975 Jul;16(1):168–178. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.1.168-178.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R., Robbins A. Enzymatic activities associated with a purified simian virus 40 T antigen-related protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):610–614. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tjian R. The binding site on SV40 DNA for a T antigen-related protein. Cell. 1978 Jan;13(1):165–179. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90147-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Green H. High frequency of SV40 transformation of mouse cell line 3T3. Virology. 1966 Apr;28(4):756–759. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90261-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Pollack R. Isolation and characterization of revertant cell lines. IV. Direct selection of serum-revertant sublines of SV40-transformed 3T3 mouse cells. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Oct;82(2):189–198. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040820207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Pollack R. Isolation and characterization of revertant cell lines. VI. Susceptibility of revertants to retransformation by simian virus 40 and murine sarcoma virus. J Virol. 1974 Dec;14(6):1404–1410. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.6.1404-1410.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel A., Pollack R. Isolation and characterization of revertant cell lines. VII. DNA synthesis and mitotic rate of serum-sensitive revertants in non-permissive growth conditions. J Cell Physiol. 1975 Feb;85(1):151–162. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040850116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]