Abstract
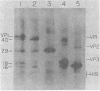
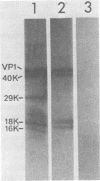
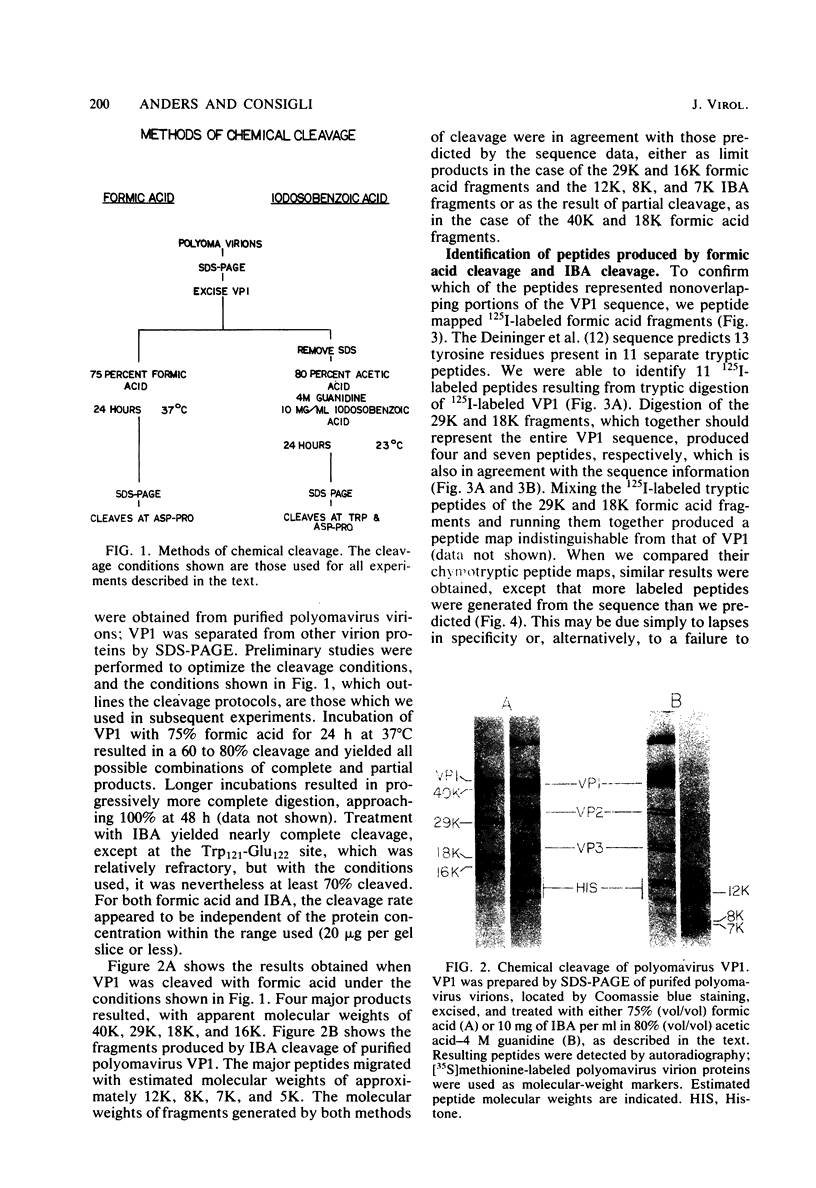
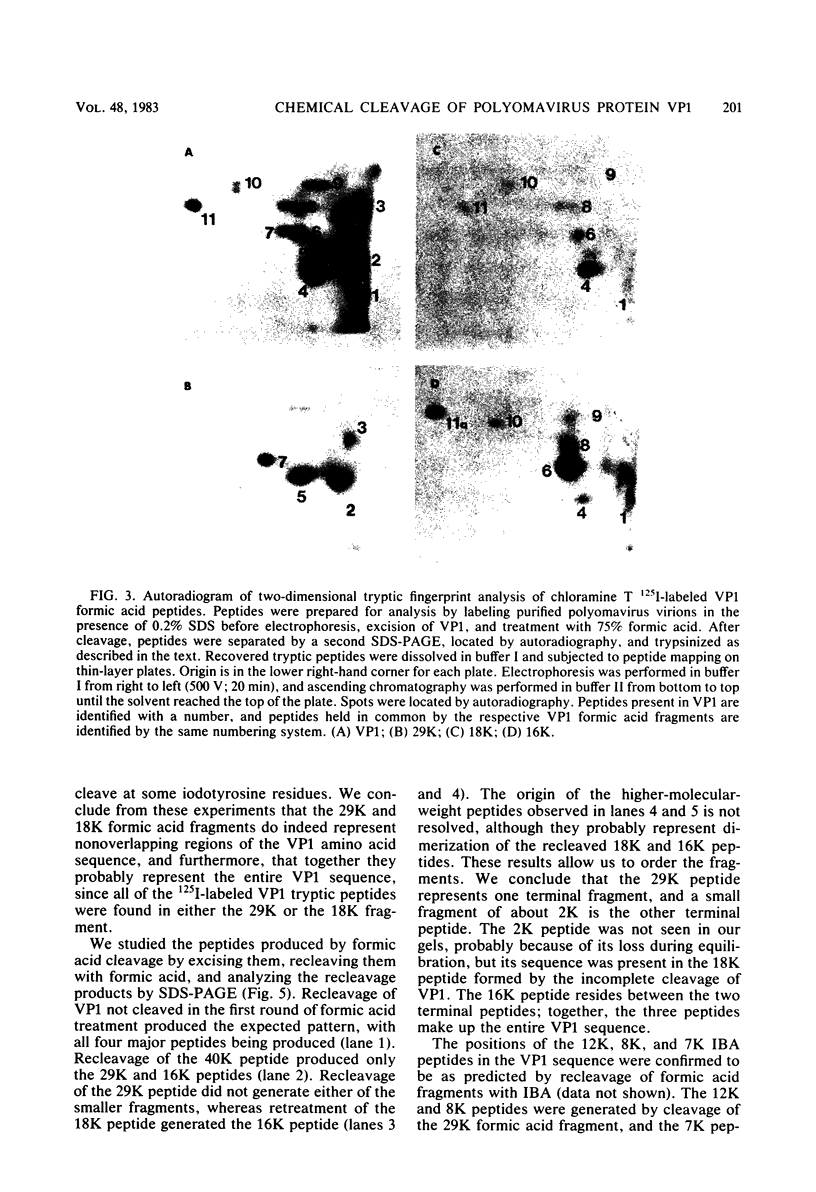
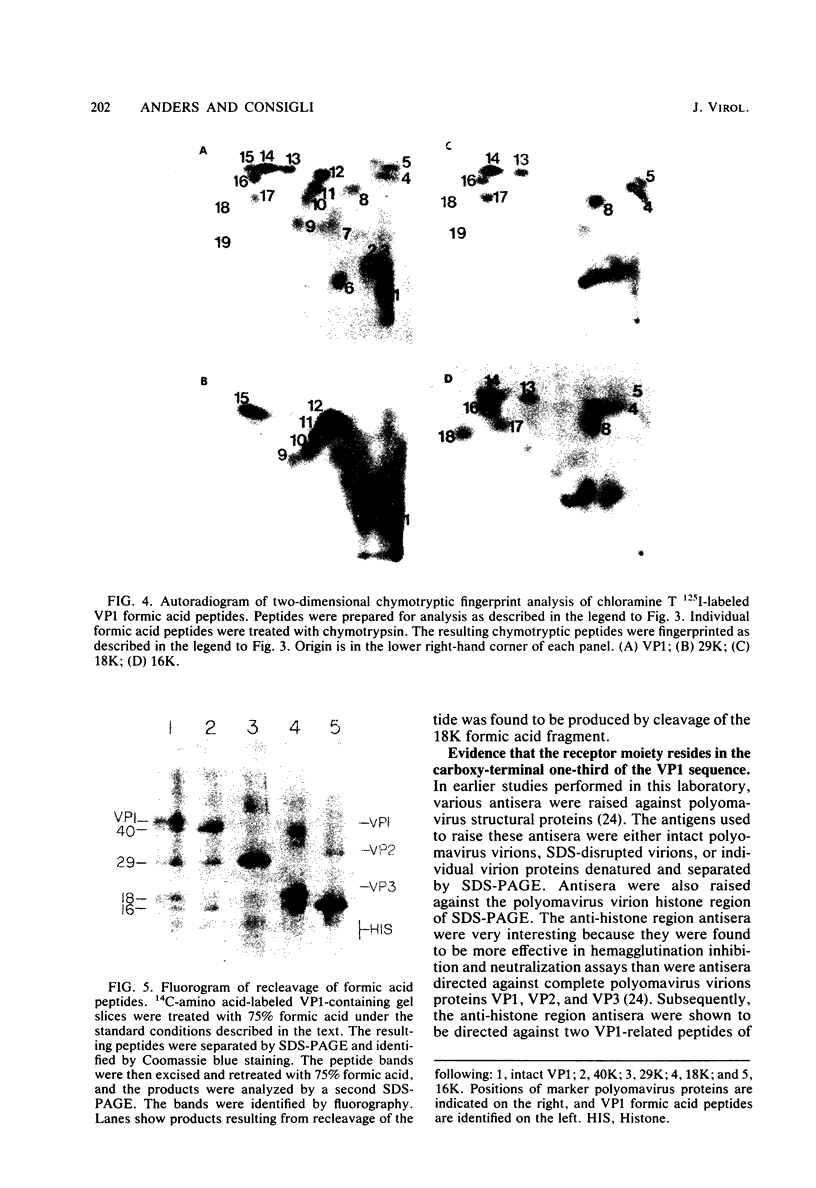
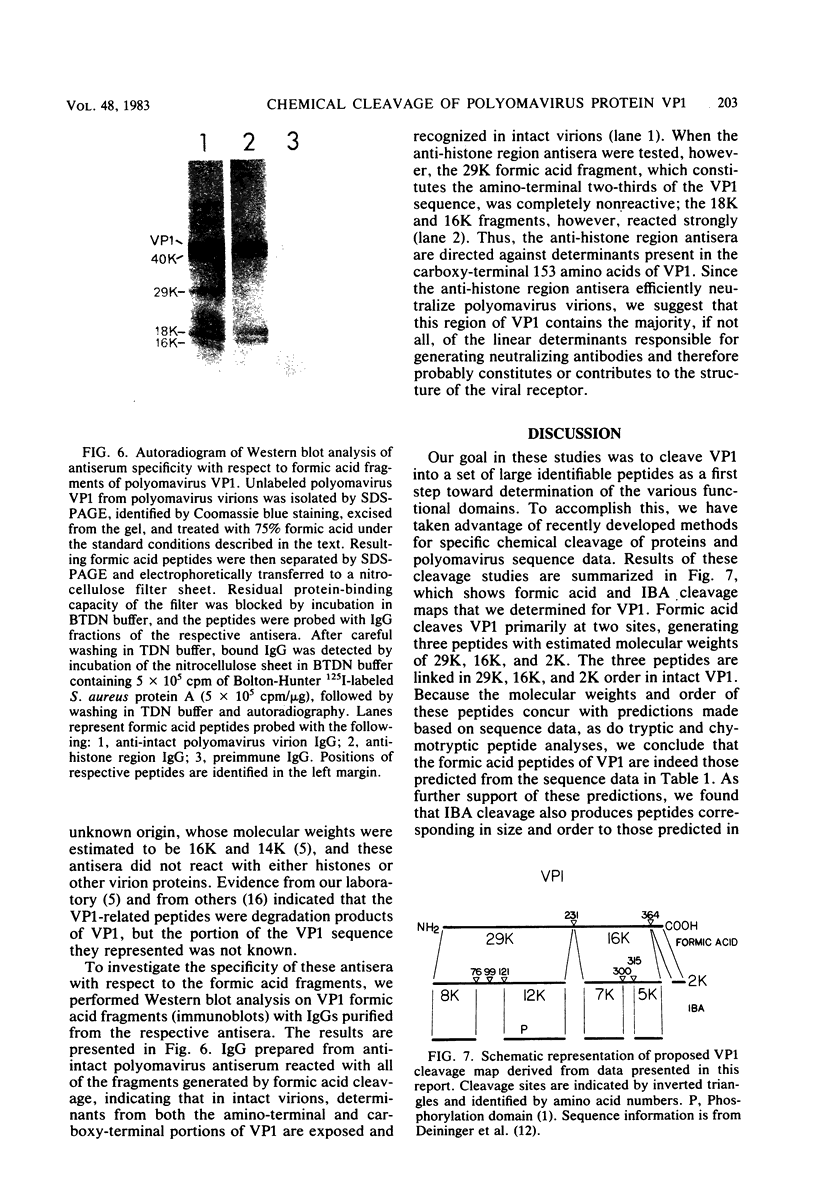
As a first step toward identifying the various functional regions of the polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1, we used recently developed methods for the chemical cleavage of proteins and the available polyomavirus sequence data to devise a scheme to produce large, identifiable peptides and generate a cleavage map of VP1. Formic acid (75%) was found to cleave VP1 at only two sites, producing three peptides of apparent molecular weights of 29,000, 16,000, and 2,000. The order of peptides in intact VP1 was determined by recleavage of partial products and was found to be 29,000, 16,000, and 2,000. Two-dimensional peptide mapping studies of 125I-labeled VP1 formic acid peptides established that the limit products of formic acid digestion contained mutually exclusive sets of labeled peptides when either trypsin or chymotrypsin was used and that together the formic acid peptides contained all of the 125I-labeled tryptic and chymotryptic peptides found in VP1. Iodosobenzoic acid (IBA) digestion produced four peptides separable by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, with apparent molecular weights of 12,000, 8,000, 7,000, and 5,000. The approximate positions of the IBA peptides in the VP1 sequence were determined by cleavage of formic acid fragments with IBA. The number of peptides produced, their respective sizes, and their order in the intact VP1 molecule agree with predictions made from available sequence data, both for formic acid cleavage and IBA cleavage. In addition, the numbers of 125I-labeled tryptic peptides produced from digestion of VP1 formic acid peptides also agree with predictions made from the sequence information. These data establish with reasonable certainty that the peptides produced by formic acid cleavage and IBA cleavage of VP1 are indeed those predicted. Antibodies raised against spontaneously produced, previously undefined polypeptides resulting from degradation of VP1 reacted exclusively with the formic acid peptides derived from the C-terminal portion of VP1. These antibodies inhibited hemagglutination and neutralized polyomavirus virions. We interpret this to mean that at least some of the antigenic determinants of the receptor moiety reside in this portion of the VP1 sequence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anders D. G., Consigli R. A. Comparison of nonphosphorylated and phosphorylated species of polyomavirus major capsid protein VP1 and identification of the major phosphorylation region. J Virol. 1983 Oct;48(1):206–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.1.206-217.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittner M., Kupferer P., Morris C. F. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins and nucleic acids from slab gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl cellulose or nitrocellulose sheets. Anal Biochem. 1980 Mar 1;102(2):459–471. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Anders D. G., Trempy J., Consigli R. A. Differences in the subpopulations of the structural proteins of polyoma virions and capsids: biological functions of the multiple VP1 species. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):80–91. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.80-91.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Differential adsorption of polyoma virions and capsids to mouse kidney cells and guinea pig erythrocytes. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):679–683. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.679-683.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolen J. B., Consigli R. A. Separation of neutralizing and hemagglutination-inhibiting antibody activities and specificity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1980 Apr;34(1):119–129. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.1.119-129.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Lavialle C. A., Radonovich M. F., Salzman N. P. Stable association of viral protein VP1 with simian virus 40 DNA. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):432–437. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.432-437.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Lavialle C., Salzman N. P. Efficient transcription of a compact nucleoprotein complex isolated from purified simian virus 40 virions. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):371–381. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.371-381.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Winston V. D., Consigli R. A. Characterization of a DNA-protein complex and capsomere subunits derived from polyoma virus by treatment with ethyleneglycol-bis-N,N'-tetraacetic acid and dithiothreitol. J Virol. 1978 Jul;27(1):193–204. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.1.193-204.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J. N., Winston V. D., Consigli R. A. Dissociation of polyoma virus by the chelation of calcium ions found associated with purified virions. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):717–724. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.717-724.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brady J., Radonovich M., Lavialle C., Salzman N. P. Simian virus 40 maturation: chromatin modifications increase the accessibility of viral DNA to nuclease and RNA polymerase. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):603–611. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.603-611.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunk C. F., Leick V. Rapid equilibrium isopycnic CsC1 gradients. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Mar 18;179(1):136–144. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(69)90129-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deininger P., Esty A., LaPorte P., Friedmann T. Nucleotide sequence and genetic organization of the polyoma late region: features common to the polyoma early region and SV40. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):771–779. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90130-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietzschold B., Wiktor T. J., Macfarlan R., Varrichio A. Antigenic structure of rabies virus glycoprotein: ordering and immunological characterization of the large CNBr cleavage fragments. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):595–602. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.595-602.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Pickett R. A., 2nd, Hampton J., Lerner R. A. Radioiodination of proteins in single polyacrylamide gel slices. Tryptic peptide analysis of all the major members of complex multicomponent systems using microgram quantities of total protein. J Biol Chem. 1977 Sep 25;252(18):6510–6515. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Etchison D., Walter G. Subunit interactions in polyoma virus structure. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):783–796. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90499-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedmann T. Structural proteins of polyoma virus: proteolytic degradation of virion proteins by exogenous and by virion-associated proteases. J Virol. 1976 Nov;20(2):520–526. doi: 10.1128/jvi.20.2.520-526.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost E., Bourgaux P. Decapsidation of polyoma virus: identification of subviral species. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):245–255. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson W. Polyoma virus proteins: a description of the structural proteins of the virion based on polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and peptide analysis. Virology. 1974 Dec;62(2):319–336. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90395-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hare J. D., King V. L. Charge microheterogeneity of the major capsid protein of polyoma virus. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):456–464. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.456-464.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hewick R. M., Waterfield M. D., Miller L. K., Fried M. Correlation between genetic loci and structural differences in the capsid proteins of polyoma virus plaque morphology mutants. Cell. 1977 Jun;11(2):331–338. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90049-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon Cleavage at aspartyl-prolyl bonds. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:145–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahoney W. C., Hermodson M. A. High-yield cleavage of tryptophanyl peptide bonds by o-iodosobenzoic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Aug 21;18(17):3810–3814. doi: 10.1021/bi00584a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Center M. S., Consigli R. A. Origin of the polyoma virus-associated endonuclease. J Virol. 1975 Jan;17(1):127–131. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.1.127-131.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMillen J., Consigli R. A. Immunological reactivity of antisera to sodium dodecyl sulfate-derived polypeptides of polyoma virions. J Virol. 1977 Mar;21(3):1113–1120. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.3.1113-1120.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayment I., Baker T. S., Caspar D. L., Murakami W. T. Polyoma virus capsid structure at 22.5 A resolution. Nature. 1982 Jan 14;295(5845):110–115. doi: 10.1038/295110a0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renart J., Reiser J., Stark G. R. Transfer of proteins from gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and detection with antisera: a method for studying antibody specificity and antigen structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jul;76(7):3116–3120. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.7.3116. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. L., Consigli R. A. Transient inhibition of polyoma virus synthesis by Sendai virus (parainfluenza I). I. Demonstration and nature of the inhibition by inactivated virus. J Virol. 1972 Dec;10(6):1091–1097. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.6.1091-1097.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Griffin B. E. Polyoma virus DNA: complete nucleotide sequence of the gene which codes for polyoma virus capsid protein VP1 and overlaps the VP2/VP3 genes. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.619-630.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter G., Deppert W. Intermolecular disulfide bonds: an important structural feature of the polyoma virus capsid. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 1):255–257. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Heuverswyn H., van de Voorde A., Fiers W. Nucleotide sequence of the simian virus 40 Hind II + III restriction fragment J and the total amino acid sequence of the major structural protein VP1. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Nov 15;91(2):415–430. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12694.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]