Abstract
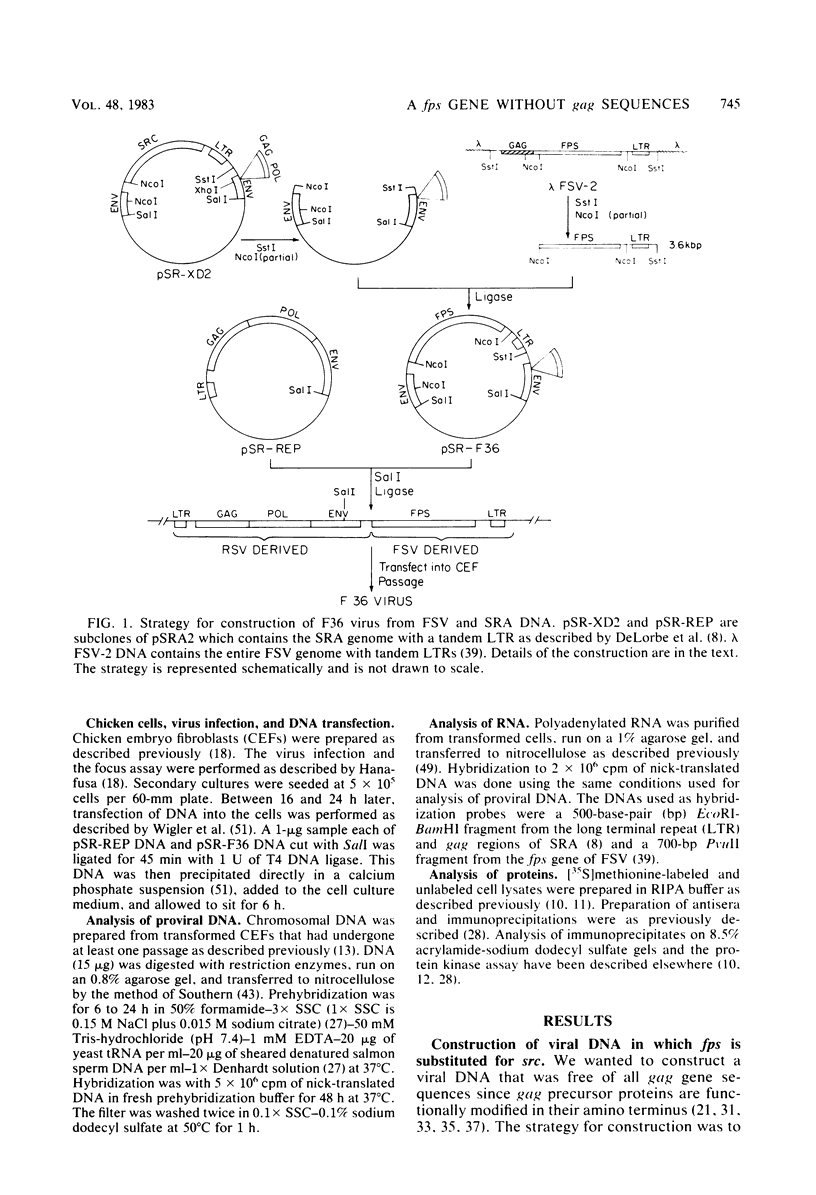
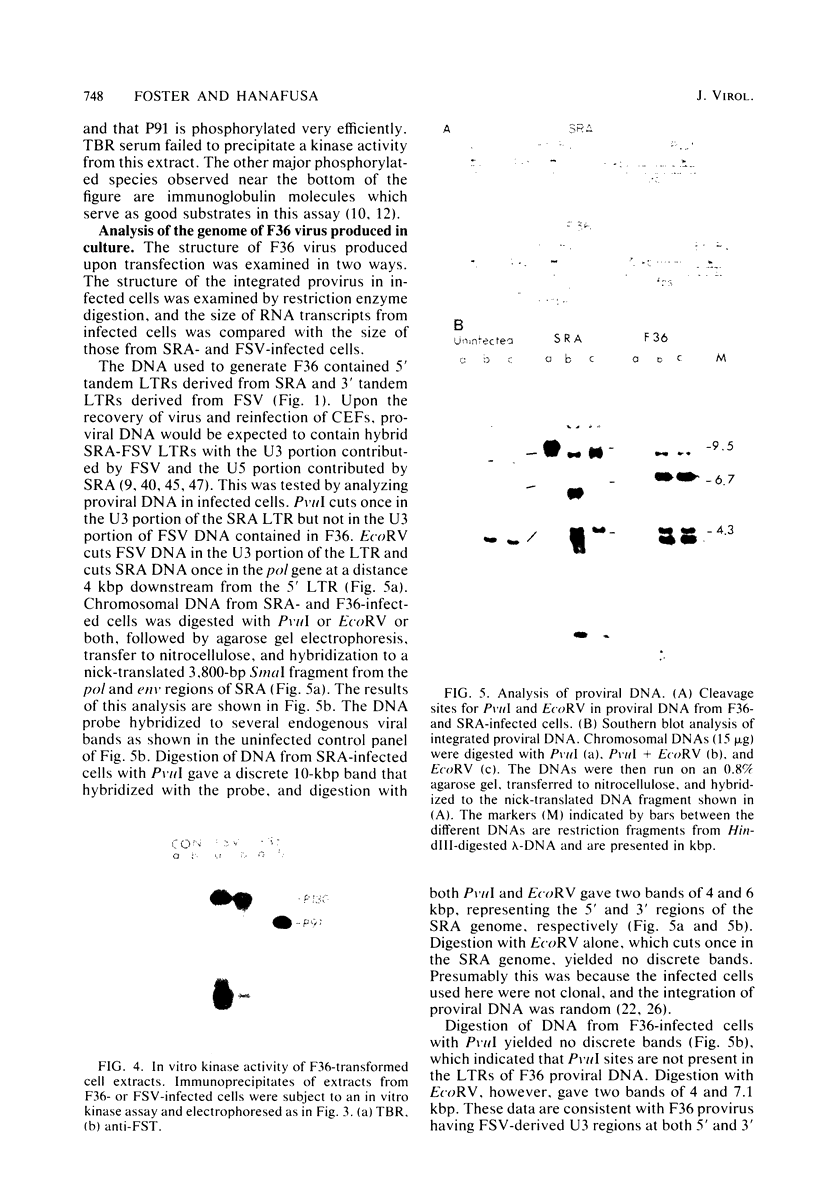
From molecularly cloned DNAs of Fujinami sarcoma virus (FSV) and the Schmidt-Ruppin-A strain of Rous sarcoma virus (SRA), viral DNA was constructed in which fps-specific sequences encoded in FSV replaced the src gene of SRA. A 3' fragment of FSV DNA, from an ATG methionine coding sequence 148 base pairs downstream from the gag-fps junction through the long terminal repeat, was joined to cloned SRA DNA at the translation start site for the src gene. The resultant DNA clone contained the splice acceptor site for src mRNA processing in SRA, but contained no src coding sequences from SRA nor any gag sequences from FSV. All genes for the replication of SRA were retained. Transfection of this cloned viral DNA genome into chicken embryo fibroblasts induced morphological transformation of the cells in culture. However, the morphology of the transformed cells was distinct from that observed in cells infected with wild-type FSV. The transformed cells produced a nondefective transforming virus called F36 which contained a hybrid FSV-SRA long terminal repeat. F36-infected cells produced a protein with the expected molecular weight of 91,000, which had an associated protein kinase activity and was immunoprecipitated by antibodies raised against fps gene determinants but not by antibodies raised against gag or src proteins. Injection of F36 virus into 8-day-old chicks produced tumors at the site of inoculation, detectable within 7 days. These results demonstrated that the gag portion of the gag-fps fusion protein of FSV is not required for transformation or tumorigenesis.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brugge J. S., Erikson R. L. Identification of a transformation-specific antigen induced by an avian sarcoma virus. Nature. 1977 Sep 22;269(5626):346–348. doi: 10.1038/269346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Hunter T. Four different classes of retroviruses induce phosphorylation of tyrosines present in similar cellular proteins. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 May;1(5):394–407. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.5.394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cross F. R., Hanafusa H. Local mutagenesis of Rous sarcoma virus: the major sites of tyrosine and serine phosphorylation of pp60src are dispensable for transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):597–607. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90392-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czernilofsky A. P., Levinson A. D., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Tischer E., Goodman H. M. Nucleotide sequence of an avian sarcoma virus oncogene (src) and proposed amino acid sequence for gene product. Nature. 1980 Sep 18;287(5779):198–203. doi: 10.1038/287198a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Wang E., Hanafusa H. Cytoplasmic localization of the transforming protein of Fujinami sarcoma virus: salt-sensitive association with subcellular components. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):782–791. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.782-791.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldman R. A., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H., Balduzzi P. C. Avian sarcoma virus UR2 encodes a transforming protein which is associated with a unique protein kinase activity. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):228–236. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.228-236.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster D. A., Hantzopoulos P., Zubay G. Resistance of adenoviral DNA replication to aphidicolin is dependent on the 72-kilodalton DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):679–686. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.679-686.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Stéhelin D. Avian leukemia viruses. Oncogenes and genome structure. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Jun 28;651(4):245–271. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(82)90014-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hampe A., Laprevotte I., Galibert F., Fedele L. A., Sherr C. J. Nucleotide sequences of feline retroviral oncogenes (v-fes) provide evidence for a family of tyrosine-specific protein kinase genes. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):775–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90282-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa T., Wang L. H., Anderson S. M., Karess R. E., Hayward W. S., Hanafusa H. Characterization of the transforming gene of Fujinami sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):3009–3013. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayward W. S. Size and genetic content of viral RNAs in avian oncovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):47–63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.47-63.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Krutzsch H. C., Oroszlan S. Myristyl amino-terminal acylation of murine retrovirus proteins: an unusual post-translational proteins modification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):339–343. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes S. H., Vogt P. K., Stubblefield E., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Integration of avian sarcoma virus DNA in chicken cells. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):208–221. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90539-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawai S., Hanafusa H. Genetic recombination with avian tumor virus. Virology. 1972 Jul;49(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/s0042-6822(72)80005-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Gonda T. J., Bishop J. M. Nucleotide sequence of the retroviral leukemia gene v-myb and its cellular progenitor c-myb: the architecture of a transduced oncogene. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):453–463. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90138-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee W. H., Bister K., Pawson A., Robins T., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Fujinami sarcoma virus: an avian RNA tumor virus with a unique transforming gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa H., Kawai S. A cellular protein is immunologically crossreactive with and functionally homologous to the Fujinami sarcoma virus transforming protein. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neel B. G., Wang L. H., Mathey-Prevot B., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H., Hayward W. S. Isolation of 16L virus: a rapidly transforming sarcoma virus from an avian leukosis virus-induced sarcoma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(16):5088–5092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.16.5088. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neil J. C., Breitman M. L., Vogt P. K. Characterization of a 105,000 molecular weight gag-related phosphoprotein from cells transformed by the defective avian sarcoma virus PRCII. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):98–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90530-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D., Gagnon J., Vogt V. M., Ripley S., Eisenman R. N. The NH2-terminal sequence of the avian oncovirus gag precursor polyprotein (Pr76gag). Virology. 1978 Dec;91(2):423–433. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90388-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pawson T., Guyden J., Kung T. H., Radke K., Gilmore T., Martin G. S. A strain of Fujinami sarcoma virus which is temperature-sensitive in protein phosphorylation and cellular transformation. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):767–775. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90553-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prywes R., Foulkes J. G., Rosenberg N., Baltimore D. Sequences of the A-MuLV protein needed for fibroblast and lymphoid cell transformation. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):569–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90389-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rettenmier C. W., Karess R. E., Anderson S. M., Hanafusa H. Tryptic peptide analysis of avian oncovirus gag and pol gene products. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):102–113. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.102-113.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saule S., Sergeant A., Torpier G., Raes M. B., Pfeifer S., Stehelin D. Subgenomic mRNA in OK10 defective leukemia virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):71–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.71-82.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz A. M., Oroszlan S. In vivo modification of retroviral gag gene-encoded polyproteins by myristic acid. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):355–361. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.355-361.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz D. E., Tizard R., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of Rous sarcoma virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):853–869. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Trowbridge I. S., Cooper J. A., Scolnick E. M. The transforming proteins of Rous sarcoma virus, Harvey sarcoma virus and Abelson virus contain tightly bound lipid. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):465–474. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Hanafusa H. Nucleotide sequence of Fujinami sarcoma virus: evolutionary relationship of its transforming gene with transforming genes of other sarcoma viruses. Cell. 1982 Oct;30(3):787–795. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90283-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Molecular cloning of the Fujinami sarcoma virus genome and its comparison with sequences of other related transforming viruses. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1007–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1007-1016.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotohno K., Temin H. M. Spontaneous variation and synthesis in the U3 region of the long terminal repeat of an avian retrovirus. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):163–171. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.163-171.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. P., Theilen G. H. Transmissible feline fibrosarcoma. Nature. 1969 Mar 15;221(5185):1074–1075. doi: 10.1038/2211074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeya T., Hanafusa H. Structure and sequence of the cellular gene homologous to the RSV src gene and the mechanism for generating the transforming virus. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):881–890. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90073-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Structure, variation and synthesis of retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):1–3. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90353-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Beveren C., Galleshaw J. A., Jonas V., Berns A. J., Doolittle R. F., Donoghue D. J., Verma I. M. Nucleotide sequence and formation of the transforming gene of a mouse sarcoma virus. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):258–262. doi: 10.1038/289258a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Feldman R., Shibuya M., Hanafusa H., Notter M. F., Balduzzi P. C. Genetic structure, transforming sequence, and gene product of avian sarcoma virus UR1. J Virol. 1981 Oct;40(1):258–267. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.1.258-267.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. H., Snyder P., Hanafusa T., Hanafusa H. Evidence for the common origin of viral and cellular sequences involved in sarcomagenic transformation. J Virol. 1980 Jul;35(1):52–64. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.1.52-64.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. R., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. The size and genetic composition of virus-specific RNAs in the cytoplasm of cells producing avian sarcoma-leukosis viruses. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):983–992. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90163-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wigler M., Pellicer A., Silverstein S., Axel R., Urlaub G., Chasin L. DNA-mediated transfer of the adenine phosphoribosyltransferase locus into mammalian cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Witte O. N., Dasgupta A., Baltimore D. Abelson murine leukaemia virus protein is phosphorylated in vitro to form phosphotyrosine. Nature. 1980 Feb 28;283(5750):826–831. doi: 10.1038/283826a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]







