Full text
PDF





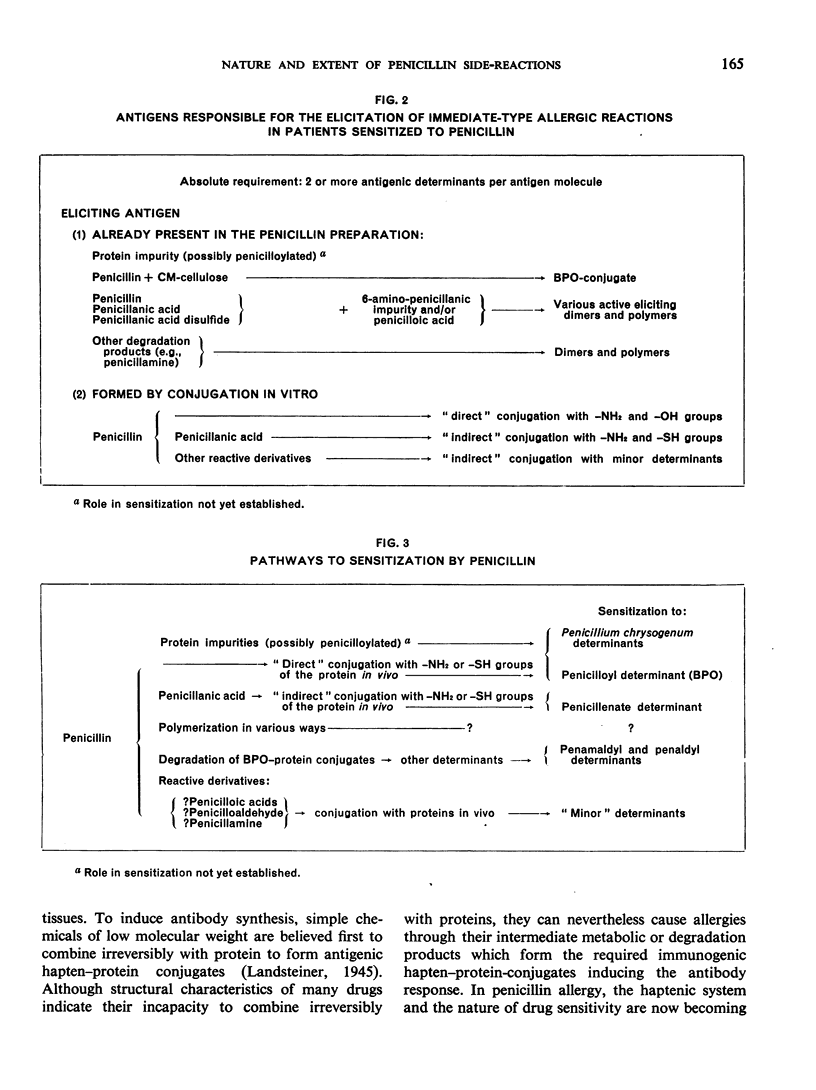

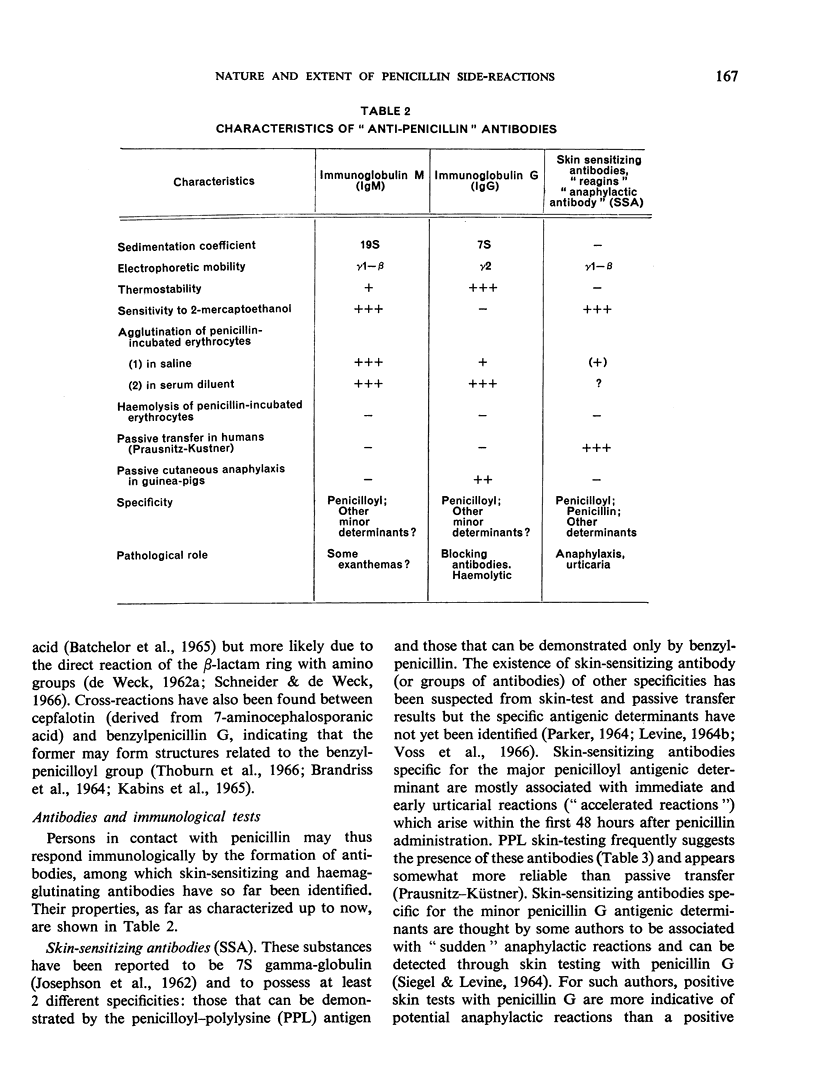










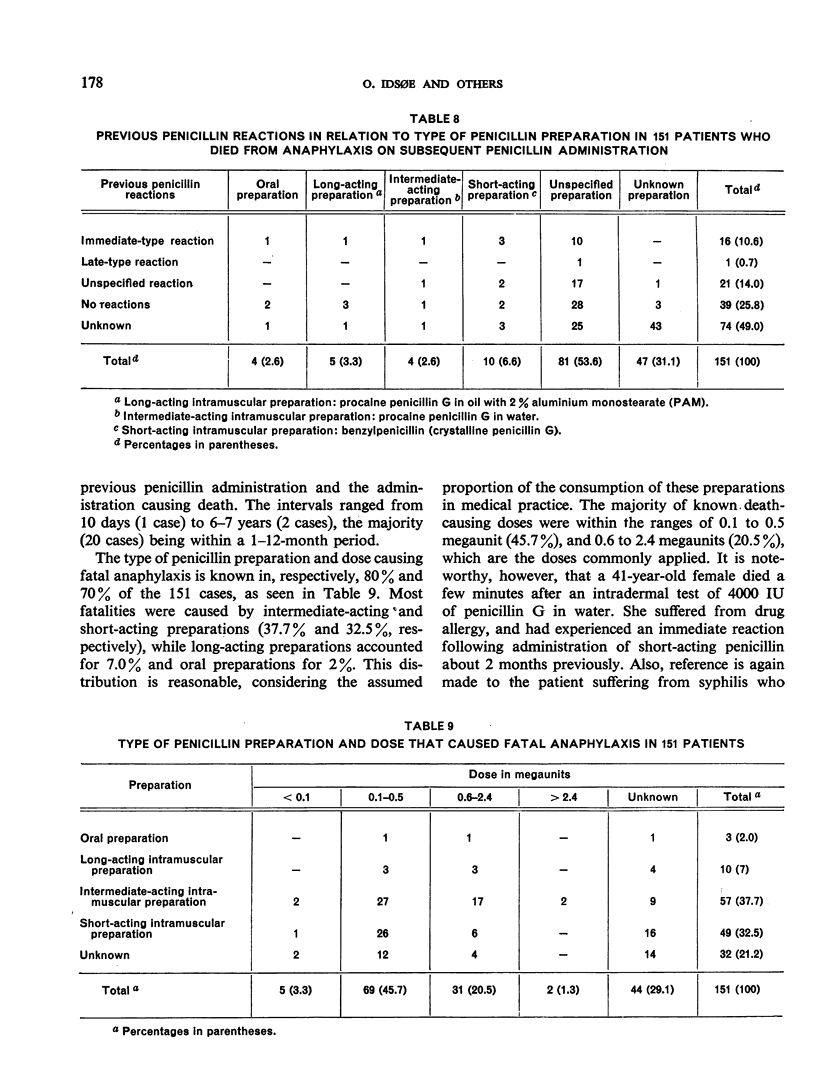










Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSEN N. A. Report on a survey of allergic reactions to penicillin. Med J Aust. 1959 Jun 20;1(25):827–830. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1959.tb88913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- APHENTOULES Th, ISOPOULOS G. [On a case of anaphylactic shock following the administration of a penicillin troche]. Hell Iatr. 1961 Mar;30:267–270. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ASKAROV U. A. [The main clinical manifestations of the side-effects of antibiotics]. Ter Arkh. 1959 Jul;31:32–43. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BATCHELOR R. C. L., HORNE G. O., ROGERSON H. L. An unusual reaction to procaine penicillin in aqueous suspension. Lancet. 1951 Aug 4;2(6675):195–198. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)91439-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECKER R. M. Penicillinase treatment of penicillin reactions. Practitioner. 1960 Apr;184:447–452. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEIDLEMAN B. KIDNEY DAMAGE FROM PENICILLIN SENSITIVITY. Med Trial Tech Q. 1964 Jun;10:39–44. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERGER A. J., EISEN B. Feasibility of skin testing for penicillin sensitivity; a study of one thousand cases. J Am Med Assoc. 1955 Sep 17;159(3):191–193. doi: 10.1001/jama.1955.02960200037007a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERTELSEN K., DALGAARD J. B. PENICILLINDODSFALD. 16 SECEREDE DANSKE TILFAELDE. Nord Med. 1965 Feb 25;73:173–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BJORNBERG A., SELSTAM J. Acute psychotic reaction after injection of procaine penicillin. A report of 33 cases. Acta Psychiatr Scand. 1960;35:129–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0447.1960.tb09472.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD E. M., BROUGHTON R. J., JAMES J. The acute oral toxicity of benzylpenicillin potassium. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 Jan 1;123:295–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN B. C., PRICE E. V., MOORE M. B., Jr PENICILLOYL-POLYLYSINE AS AN INTRADERMAL TEST OF PENICILLIN SENSITIVITY. JAMA. 1964 Aug 24;189:599–604. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070080005001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUDD M. A., PARKER C. W., NORDEN C. W. EVALUATION OF INTRADERMAL SKIN TESTS IN PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY. JAMA. 1964 Oct 19;190:203–205. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03070160027006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor F. R., Dewdney J. M., Feinberg J. G., Weston R. D. A penicilloylated protein impurity as a source of allergy to benzylpenicillin and 6-aminopenicillanic acid. Lancet. 1967 Jun 3;1(7501):1175–1177. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92838-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batchelor F. R., Dewdney J. M., Gazzard D. Penicillin allergy: the formation of the penicilloyl determinant. Nature. 1965 Apr 24;206(982):362–364. doi: 10.1038/206362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendixen G. Anafylaktisk shock. Ugeskr Laeger. 1966 Jul 14;128(28):807–811. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CAPUTI S., Jr An anaphylactic-type reaction attributed to penicillinase; report of a case. N Engl J Med. 1959 Feb 26;260(9):432–434. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195902262600907. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARTER E. S., Jr, COPE C. B. Anaphylaxis due to topical penicillin. J Allergy. 1954 May;25(3):270–271. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(54)90185-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHISHOLM D. R., ENGLISH A. R., MACLEAN N. A. Immunologic response of rabbits to 6-aminopenicillanic acid. J Allergy. 1961 Jul-Aug;32:333–342. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(61)90101-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COHEN S. B. BRAIN DAMAGE DUE TO PENICILLIN. JAMA. 1963 Dec 7;186:899–902. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03710100037008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLEMAN M., SIEGEL B. B. Studies in penicillin hypersensitivity. II. The significance of penicillin as a contaminant. J Allergy. 1955 May;26(3):253–261. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(55)90020-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- COLLART P., BOREL L. J., DUREL P. [Study of the effect of penicillin in late syphilis: persistence of Treponema pallidum following treatment. 2. Late syphilis--human]. Ann Inst Pasteur (Paris) 1962 Jun;102:693–704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CORICCIATI L., FRIGGERI L. [Acute necrosing epidemolysis caused by penicillin allergy (Lyell's syndrome)]. Minerva Dermatol. 1962 Apr;37:150–152. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciecierski L., Suchanek J. W sprawie odczynów alergicznych u chorych kiłowych leczonych penicylina. Przegl Dermatol. 1966 Mar-Apr;53(2):189–192. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WECK A. L., BLUM G. RECENT CLINICAL AND IMMUNOLOGICAL ASPECTS OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1965;27:221–256. doi: 10.1159/000229614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WECK A. L., EISEN H. N. Some immunochemical properties of penicillenic acid. An antigenic determinant derived from penicillin. J Exp Med. 1960 Dec 1;112:1227–1247. doi: 10.1084/jem.112.6.1227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WECK A. L. PENICILLIN ALLERGY: ITS DETECTION BY AN IMPROVED HAEMAGGLUTINATION TECHNIQUE. Nature. 1964 Jun 6;202:975–977. doi: 10.1038/202975a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE WECK A. L. Studies on penicillin hypersensitivity. II. The role of the side chain in penicillin antigenicity. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1962;21:38–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUREL P., BOREL L. J. Quelques problèmes posés par la syphilis nerveuse. Rev Prat. 1957 Sep 11;7(23):2519–passim. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson R. B., Jr, Segal B. L. Penicillin-induced immunohemolytic anemia. Arch Intern Med. 1966 Dec;118(6):575–579. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ETTINGER E., KAYE D. SYSTEMIC MANIFESTATIONS AFTER A SKIN TEST WITH PENICILLOYLPOLYLYSINE. N Engl J Med. 1964 Nov 19;271:1105–1106. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196411192712107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein E. Allergy to dermatologic agents. JAMA. 1966 Oct 31;198(5):517–520. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG S. M. Allergy from therapeutic products. Incidence, importance, recognition, and prevention. JAMA. 1961 Nov 25;178:815–818. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.03040470031007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG S. M., FEINBERG A. R. Allergy to penicillin. J Am Med Assoc. 1956 Mar 3;160(9):778–779. doi: 10.1001/jama.1956.02960440050014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FEINBERG S. M., FEINBERG A. R., MORAN C. F. Penicillin anaphylaxis, nonfatal and fatal reactions. J Am Med Assoc. 1953 May 9;152(2):114–119. doi: 10.1001/jama.1953.03690020006002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FINKE S. R., GRIECO M. H., CONNELL J. T., SMITH E. C., SHERMAN W. B. RESULTS OF COMPARATIVE SKIN TESTS WITH PENICILLOYL-POLYLYSINE AND PENICILLIN IN PATIENTS WITH PENICILLIN ALLERGY. Am J Med. 1965 Jan;38:71–82. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(65)90161-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FREEDMAN M. A. OXACILLIN--APPARENT HEMATOLOGIC AND HEPATIC TOXICITY. Rocky Mt Med J. 1965 Jan;62:34–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fellner M. J., Baer R. L., Ripps C. S., Hirschhorn K. Response of lymphocytes to penicillin: comparison with skin tests and circulating antibodies in man. Nature. 1967 Nov 25;216(5117):803–804. doi: 10.1038/216803a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox A. M. Anaphylactoid Shock Induced by Oral Penicillin and Resulting in Gerstmann's Syndrome. Br Med J. 1965 Jul 24;2(5455):206–208. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5455.206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GJESSING H. C. [Penicillin consumption in Norway. Venereal disease-penicillin consumption-complications]. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1960 Oct 15;80:977–980. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOULD J. C. Environmental penicillin and penicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Lancet. 1958 Mar 8;1(7019):489–493. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(58)90807-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRASREINER W. Vorzüge und Gefahren der lokalen oralen und intravaginalen Penicillintherapie. Dermatol Wochenschr. 1954;130(28):749–753. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREAVES A. B. Further observations on penicillinase. JAMA. 1961 Jun 17;176:951–953. doi: 10.1001/jama.1961.63040240017020b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREEN I., FINKEL M. Thrmbocytopenic purpura associated with sulfamethoxypyridazine administration. N Y State J Med. 1959 May 15;59(10):2034–2036. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUTHE T., IDSOE O., WILLCOX R. R. Untoward penicillin reactions. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(3):427–501. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HARRIS J., VAUGHAN J. H. Immunologic reactions to penicillin. J Allergy. 1961 Mar-Apr;32:119–127. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(61)90064-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERAUD G., STOFT H. CHOC ALLERGIQUE TR'ES GRAVE SECONDIARE 'A L'ADMINISTRATION RECTALE DE P'ENICILLINE; TROUBLES CARDIAQUES CONS'ECUTIFS. Presse Med. 1964 Nov 21;72:2931–2932. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HERXHEIMER H., STRESEMANN E. Protection against anaphylactic shock by ephedrine-theophylline combinations. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1960 May 1;125:265–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYMAN A., SHELDON W. H., EVANS L. D. Pathogenesis of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction; a review of clinical and experimental observations. Br J Vener Dis. 1952 Jun;28(2):50–60. doi: 10.1136/sti.28.2.50. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEYWORTH F. Treatment of penicillin anaphylaxis by controlled respiration; a case report. Postgrad Med J. 1958 Oct;34(396):550–passim. doi: 10.1136/pgmj.34.396.550. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIGGINS G. A., ROTHCHILD T. P. E. [Fatal anaphylactic shock from procaine penicillin]. N Engl J Med. 1952 Oct 23;247(17):644–646. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195210232471706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOCHLEITNER H. BEITRAG ZUR JARISCH-HERXHEIMER-REAKTION. Z Haut Geschlechtskr. 1965 Mar 1;38:158–161. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUMMEL K. [Quantitative studies on the attachment of polyvinlpyrrolidone to the erythrocyte surface. II. Further evaluation and discussion of results of the experiment]. Blut. 1963 Jul;9:215–237. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURIEZ C., AGACHE P., THOREUX M., MEUNIER-LALLIGIER A. Accidents neurologiques et cardiovasculaires graves chez des syphilitiques tertiaires en cours d'antibiothérapie. Bull Soc Fr Dermatol Syphiligr. 1958 Nov-Dec;15(5):574–577. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HURLEY H. J. A dental depot in penicillin hypersensitivity. Arch Dermatol. 1963 Mar;87:387–387. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1963.01590150103020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HYMAN A. L. Anaphylactic shock after therapy with penicillinase. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Feb 7;169(6):593–594. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.73000230003011a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huriez C., Vanoverschelde M. L'endémie syphilitique au Centre Régional de Prophylaxie de Lille (4.517 cas dépistés et traités ces 20 dernières années). Supériorité de l'association pénicilline-bismuth sur la pénicilline seule. Lille Med. 1965 Apr;10(4):348–355. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JOSEPHSON A. S., FRANKLIN E. C., OVARY Z. The characterization of antibodies to penicillin. J Clin Invest. 1962 Mar;41:588–593. doi: 10.1172/JCI104513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KABINS S. A., EISENSTEIN B., COHEN S. ANAPHYLACTOID REACTION TO AN INITIAL DOSE OF SODIUM CEPHALOTHIN. JAMA. 1965 Jul 12;193:165–166. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03090020079028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ H. I., GILL K. A., BAXTER D. L., MOSCHELLA S. L. INDIRECT BASOPHIL DEGRANULATION TEST IN PENICILLIN ALLERGY. JAMA. 1964 Apr 27;188:351–354. doi: 10.1001/jama.1964.03060300013002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERN R. A., WIMBERLEY N. A., Jr Penicillin reactions; their nature, growing importance, recognition, management and prevention. Am J Med Sci. 1953 Oct;226(4):357–375. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195310000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRAPIN D. Anaphylaxis with orally administered penicillin. N Engl J Med. 1962 Oct 18;267:820–820. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196210182671607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen E. A., Aastrup B. Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction in the treatment of early syphilis with penicillin and bismuth-arsphenamine. Br J Vener Dis. 1965 Sep;41(3):177–180. doi: 10.1136/sti.41.3.177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knudsen E. T., Robinson O. P., Croydon E. A., Tees E. C. Cutaneous sensitivity to purified benzylpenicillin. Lancet. 1967 Jun 3;1(7501):1184–1188. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92840-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunz M. L., Reisman R. E., Arbesman C. E. Evaluation of penicillin hypersensitivity by two newer immunological procedures. J Allergy. 1967 Sep;40(3):135–144. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(67)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEDFORD R. A., KOSIKOWSKI F. V. INACTIVATION OF PENICILLIN BY CHEESE. J Dairy Sci. 1965 May;48:541–543. doi: 10.3168/jds.s0022-0302(65)88280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEITES F. L. [Fatal complication in antibiotic therapy of a diabetic patient]. Probl Endokrinol Gormonoter. 1960 Jul-Aug;6:72–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE B. B., OVARY Z. Studies on the mechanism of the formation of the penicillin antigen. III. The N-(D-alpha-benzylpenicilloyl) group as an antigenic determinant responsible for hypersensitivity to penicillin G. J Exp Med. 1961 Dec 1;114:875–904. doi: 10.1084/jem.114.6.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE B. B., PRICE V. H. STUDIES ON THE IMMUNOLOGICAL MECHANISMS OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. II. ANTIGENIC SPECIFICITIES OF ALLERGIC WHEAL-AND-FLARE SKIN RESPONSES IN PATIENTS WITH HISTORIES OF PENICILLIN ALLERGY. Immunology. 1964 Sep;7:542–556. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE B. B. STUDIES ON ANTIGENICITY. THE EFFECT OF SUCCINYLATION OF EPSILON-AMINO GROUPS ON ANTIGENICITY OF BENZYLPENICILLOYL-POLY-L-LYSINE CONJUGATES IN RANDOM-BRED AND IN STRAIN 2 GUINEA PIGS. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1964 Aug-Sep;116:1127–1131. doi: 10.3181/00379727-116-29471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE B. B. THE PREPARATION OF PENICILLOYL-POLYLYSINES, SKIN TEST REAGENTS FOR THE CLINICAL EVALUATION OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY. J Med Chem. 1964 Sep;7:675–676. doi: 10.1021/jm00335a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEVINE M. I., PERRI J., ANTHONY J. J. A fatal anaphylactic reaction to oral penicillin. J Allergy. 1960 Nov-Dec;31:487–491. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(60)90082-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Fellner M. J., Levytska V. Benzylpenicilloyl specific serum antibodies to penicillin in man. I. Development of a sensitive hemagglutination assay method and haptenic specificities of antibodies. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):707–718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine B. B., Fellner M. J., Levytska V., Franklin E. C., Alisberg N. Benzylpenicilloyl-specific serum antibodies to penicillin in man. II. Sensitivity of the hemagglutination assay method, molecular classes of the antibodies detected, and antibody titers of randomly selected patients. J Immunol. 1966 Apr;96(4):719–726. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAHA G. E. Antibiotic therapy: complications and untoward effects. Am Pract Dig Treat. 1961 Jun;12:409–414. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARIE J., LEVEQUE B., DEBAUCHEZ C., BANGEMANN G. ACCIDENT H'EMORRAGIQUE ET N'ECROTIQUE LOCO-R'EGIONAL 'A LA SUITE D'UNE INJECTION DE BENZATHINE-P'ENICILLINE. Ann Pediatr (Paris) 1964 Nov 2;11:549–552. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTINEZ CORTES F. [Allergy to penicillin]. Gac Med Mex. 1960 Dec;90:991–998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MATHESON A., ELEGANT L. Penicillin reaction in children; a study of the value of the skin test in penicillin sensitization. J Allergy. 1955 Sep;26(5):415–424. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(55)90032-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCGOVERN J. P., DUKES C. D., WAGELIE R. G. SEROLOGIC STUDIES ON PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY IN HUMAN BEINGS. Ann Allergy. 1964 May;22:252–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOHR C. F., HAHN R. Therapeutic paradox (?) in cardiovascular syphilis. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1952 Jan;36(1):82–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE J. A., WOODY R. H. Reactions to intramuscular benzathine penicillin G. GP. 1960 Dec;22:100–102. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MURPHY E. S., MIRELES M. Shock, liver necrosis, and death after penicillin injection. Arch Pathol. 1962 May;73:355–362. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magnusson B., Hersle K. Patch test methods. 3. Influence of adhesive tape on test response. Acta Derm Venereol. 1966;46(4):275–278. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks J. H., Williams D. K. Anaphylactoid shock induced by oral ampicillin in a woman with Addison's disease. Practitioner. 1966 Jul;197(177):85–87. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matner T., Leonhardi G. Hauttestung auf urticarielle Penicillin-Uberempfindlichkeit. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol. 1966;227(1):349–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00502858. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. W., DEWECK A. L., KERN M., EISEN H. N. The preparation and some properties of penicillenic acid derivatives relevant to penicillin hypersensitivity. J Exp Med. 1962 Apr 1;115:803–819. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.4.803. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. W., SHAPIRO J., KERN M., EISEN H. N. Hypersensitivity to penicillenic acid derivatives in human beings with penicillin allergy. J Exp Med. 1962 Apr 1;115:821–838. doi: 10.1084/jem.115.4.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PARKER C. W., THIEL J. A., MITCHELL S. THE IMMUNOGENICITY OF HAPTEN-POLYLYSINE CONJUGATES. A COMPARISON OF D AND L POLYMERS. J Immunol. 1965 Feb;94:289–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PELTONEN T., SAARIMAA H., SAARIMAA A. PENICILLINOEVERKAENSLIGHET. Nord Med. 1963 Oct 31;70:1196–1197. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PETERS G. A., HENDERSON L. L., PRICKMAN L. E. Anaphylactic reactions to penicillin: case reports with certain immunologic observations. Ann Allergy. 1957 Mar-Apr;15(2):135–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- POPPER M. UNINTENTIONAL INTRAVASCULAR INJECTION OF PENICILLIN. Public Health Rep. 1964 Jul;79:610–612. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petz L. D., Fudenberg H. H. Coombs-positive hemolytic anemia caused by penicillin administration. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jan 27;274(4):171–178. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196601272740401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Putkonen T., Salo O. P., Mustakallio K. K. Febrile Herxheimer reaction in different phases of primary and secondary syphilis. Br J Vener Dis. 1966 Sep;42(3):181–184. doi: 10.1136/sti.42.3.181. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RABINOVICH P. D. SLUCHA I ANAFILAKTICHESKOGO SHOKA PRI ZAKAPYVANII PENITSILLINA V NOS. Sov Med. 1963 Jul;27:138–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISCH M. Penicillinase therapy; clinical report of severe reactions. J Am Med Assoc. 1959 Feb 7;169(6):594–595. doi: 10.1001/jama.1959.73000230004011b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REISMAN R. E., ROSE N. R., WITEBSKY E., ARBESMAN C. E. Penicillin allergy and desensitization. J Allergy. 1962 Mar-Apr;33:178–187. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(62)90007-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDZKI E., LUKASIAK B., LESZCZYNSKI W. PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY AND HAEMAGGLUTINATING ANTIBODIES IN WORKERS AT A PENICILLIN FACTORY. Acta Allergol. 1965;20:206–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1965.tb03371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RYTEL M. W., KLION F. M., ARLANDER T. R., MILLER L. F. DETECTION OF PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY WITH PENICILLOYL-POLYLYSINE. JAMA. 1963 Dec 7;186:894–898. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03710100032007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SABLAN R. G., BEST W. C. FEBRILE RESPONSE IN THE JARISCH-HERXHEIMER REACTION; OBSERVATIONS IN 52 PATIENTS WITH SYPHILIS. Arch Dermatol. 1964 Sep;90:293–295. doi: 10.1001/archderm.1964.01600030043009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHAMBERG I. L. Syphilis and Sisyphus. Br J Vener Dis. 1963 Jun;39:87–97. doi: 10.1136/sti.39.2.87. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOENWETTER A. H., SIBER E. N. PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY, ACUTE PERICARDITIS, AND EOSINOPHILIA. JAMA. 1965 Feb 22;191:672–673. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080080062023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUEMMELFEDER N., KLEIN H. J., STUETTGEN G. LUES II UND TOEDLICHE PENICILLIN-ANAPHYLAXIE. Med Welt. 1965 Apr 3;14:693–695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUPPLI R. [Clinical aspects and therapy of side-effects of penicillin]. Praxis. 1963 Jan 17;52:70–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHUPPLI R. [On the relation between penicillin allergies and fungus infections]. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1962 Feb 16;87:333–335. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1111758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J., KLOPSTOCK A., VARDINON N. THE ROLE OF THE COMPLEMENT IN THE BASOPHILE CELLS TEST. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1965;26:142–152. doi: 10.1159/000229565. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ J., KLOPSTOCK A., ZIKERT-DUVDEVANI P., HOENIG S. DETECTION OF HYPERSENSITIVITY BY INDIRECT RAT MAST CELLS DEGRANULATION. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1965;26:333–339. doi: 10.1159/000229586. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHWARTZ R. H., VAUGHAN J. H. IMMUNOLOGIC RESPONSIVENESS OF MAN TO PENICILLIN. JAMA. 1963 Dec 28;186:1151–1157. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.63710130002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCIPLE G. W., KNOX J. M., MONTGOMERY C. H. Incidence of penicillin reactions after an antihistaminic simultaneously administered parenterally. N Engl J Med. 1959 Nov 26;261:1123–1125. doi: 10.1056/NEJM195911262612207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELDON W. H., HEYMAN A. Morphologic changes in syphilitic lesions during the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1949 May;33(3):213–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELLEY W. B., COMAISH J. S. NEW TEST FOR PENICILLIN ALLERGY: FLUOROMETRIC ASSAY OF HISTAMINE RELEASE. JAMA. 1965 Apr 5;192:36–40. doi: 10.1001/jama.1965.03080140042010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHELLEY W. B. Indirect basophil degranulation test for allergy to penicillin and other drugs. JAMA. 1963 Apr 20;184:171–178. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03700160047006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGAL S. Allergic reactions to antibiotics. N Y State J Med. 1955 Aug 15;55(16):2303–2314. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGAL S., STEINHARDT R. W., GERBER R. Fatal and near-fatal penicillin anaphylaxis; three new cases with a note on prevention. J Allergy. 1953 Jan;24(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(53)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIEGEL B. B. Hidden contacts with penicillin. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;21:703–713. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SLOANE M. B. Recapitulation of local antibiotic therapy. J Med Soc N J. 1956 Sep;53(9):450–453. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SONNTAG W. M., MARCUS S. PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY DEMONSTRATED BY PASSIVE CUTANEOUS ANAPHYLAXIS IN THE RAT. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;23:238–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STEWART G. T. Cross-allergenicity of penicillin G and related substances. Lancet. 1962 Mar 10;1(7228):509–510. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(62)91481-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkany I. Lymphocyte transformation in drug hypersensitivity. Lancet. 1967 Apr 8;1(7493):743–745. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)91362-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C. H., De Weck A. L. A new chemical spect of penicillin allergy: the direct reaction of penicillin with epsilon-amino-groups. Nature. 1965 Oct 2;208(5005):57–59. doi: 10.1038/208057a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C. H., de Weck A. L. Chemische Aspekte der Penicillin-Allergie: Die direkte Penicilloylierung von epsilon-Aminogruppen durch Penicilline bei pH 7,4. Helv Chim Acta. 1966 Jul 11;49(5):1695–1706. doi: 10.1002/hlca.19660490532. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skog E., Gudjónsson H. On the allergic origin of the Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction. Acta Derm Venereol. 1966;46(2):136–143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith J. W., Johnson J. E., Cluff L. E. Studies on the epidemiology of adverse drug reactions. II. An evaluation of penicillin allergy. N Engl J Med. 1966 May 5;274(18):998–1002. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196605052741804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steenfeldt-Foss O. W. Allergiske og toksiske reaksjoner på penicillinbehandling. Oversikt og kasuistikk. Tidsskr Nor Laegeforen. 1965 May 15;85(10):834–838. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. T. Allergenic residues in penicillins. Lancet. 1967 Jun 3;1(7501):1177–1183. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(67)92839-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson M. A., Chanmougan D., Schwartz R. S. Immunohemolytic anemia due to antipenicillin antibodies. Report of a case. N Engl J Med. 1966 Jan 27;274(4):178–181. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196601272740402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIEL J. A., MITCHELL S., PARKER C. W. THE SPECIFICITY OF HEMAGGLUTINATION REACTIONS IN HUMAN AND EXPERIMENTAL PENICILLIN HYPERSENSITIVITY. J Allergy. 1964 Sep-Oct;35:399–424. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(64)90067-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THIERS H., MOULIN G., MATTA K., GUEIDON LES INCIDENTS ET ACCIDENTS IMPUTABLES 'A UNE ALLERGIE 'A LA P'ENICILLINE AU COURS DU TRAITEMENT AMBULATOIRE DE L'INFECTION SYPHILITIQUE. J Med Lyon. 1964 Dec 20;45:2169–2171. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMAS J. W. Constitutional reaction to penicillinase used in the treatment of a penicillin reaction. South Med J. 1959 Apr;52(4):451–455. doi: 10.1097/00007611-195904000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TRINCA J. C., KEEN T. E. Penicillinase in penicillin reactions. Med J Aust. 1960 Dec 17;47(2):973–976. doi: 10.5694/j.1326-5377.1960.tb23978.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUFT L., GREGORY D. C., GREGORY J. Evaluation of skin testing methods employed in the diagnosis of penicillin allergy. Am J Med Sci. 1955 Oct;230(4):370–379. doi: 10.1097/00000441-195510000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thoburn R., Johnson J. E., 3rd, Cluff L. E. Studies on the epidemiology of adverse drug reactions. IV. The relationship of cephalothin and penicillin allergy. JAMA. 1966 Oct 24;198(4):345–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VALLERY-RADOT P., DOMART A., WOLFROMM R., HAZARD J. [Method of desensitization by subintrant doses in a subject sensitized to penicillin]. Sem Hop. 1960 May 12;36:1383–1385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANARSDEL P. P., Jr, O'ROURKE T. K., HORAN J. D., KUMASAKA Y. Serum hemagglutinating antibodies in penicillin allergy. JAMA. 1963 Aug 17;185:584–587. doi: 10.1001/jama.1963.03060070052024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VANARSDEL P. P., Jr, TOBE A. D., PASNICK L. J. ASSOCIATION OF HEMAGGLUTINATING ANTIBODIES WITH SKIN SENSITIVITY IN PENICILLIN ALLERGY. J Allergy. 1963 Nov-Dec;34:526–534. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(63)90094-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VIDAL J., FOURCADE J., GUIN J. J., MARTY J. C. [Fatal anaphylactic shock following an intramuscular injection of penicillin]. Montp Med. 1960 Dec;58:325–327. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Voronina L. A. Povyshennaia chuvstvitel'nost' k penitsillinu i streptomitsinu u meditsinskikh rabotnikov. Vrach Delo. 1965 Apr;4:127–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WAGELIE R. G., DUKES C. D., MCGOVERN J. P. ANTIGENICITY AND CROSS-REACTIVITY OF 6-AMINOPENICILLANIC ACID AND PENICILLIN G. J Allergy. 1963 Nov-Dec;34:489–497. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(63)90090-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATANABE T. Infective heredity of multiple drug resistance in bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1963 Mar;27:87–115. doi: 10.1128/br.27.1.87-115.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATSON K. C., JOUBERT S. M., BENNETT M. A. The occurrence of haemagglutinating antibody to penicillin. Immunology. 1960 Jan;3:1–10. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WATTIEZ P. La réaction d'Herxheimer dans le traitement de la syphilis congénitale par la pénicilline. Acta Paediatr Belg. 1954;8(1):43–48. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEINGAERTNER L. ZUR POLYMORPHIE ALLERGISCH BEDINGTER HAUTERSCHEINUNGEN BEI PENICILLINBEHANDLUNG. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 1964 Jun 5;89:1115–1124. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1111264. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS L. R. Anaphylactic reaction from topical penicillin; report of a case. J Allergy. 1953 Sep;24(5):407–410. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(53)90040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEISS R. C., CREPEA S. B. Development of sensitivity to penicillinase following its use in penicillin reaction. J Allergy. 1959 Jul-Aug;30(4):337–341. doi: 10.1016/0021-8707(59)90041-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELCH H., LEWIS C. N., WEINSTEIN H. I., BOECKMAN B. B. Severe reactions to antibiotics; a nationwide survey. Antibiotic Med Clin Ther (New York) 1957 Dec;4(12):800–813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WELCH H., LEWIS C. N., WEINSTEIN H. I., BOECKMAN B. B. Severe reactions to antibiotics; a nationwide survey. Antibiot Annu. 1957;5:296–309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WILLCOX R. R. INFLUENCE OF PENICILLIN ALLERGIC REACTIONS ON VENEREAL DISEASE CONTROL PROGRAMMES. Br J Vener Dis. 1964 Sep;40:200–209. doi: 10.1136/sti.40.3.200. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WIRTH L. On anaphylactic shock due to penicillin. Mil Med. 1963 Mar;128:245–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Westerman G., Corman A., Stelos P., Nodine J. H. Adverse reactions to penicillin. JAMA. 1966 Oct 10;198(2):173–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEAGER L. B., KVINGE V. E. PENICILLIN SKIN TEST PROCEDURE AND PREVENTION OF PENICILLIN REACTIONS. J Lancet. 1965 Mar;85:126–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YEH F. Peripheral gangrene and hemorrhagic purpura due to penicillin sensitivity: report of a fatal case. Chin Med J. 1958 Jun;76(6):599–601. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YOBS A. R., OLANSKY S., ROCKWELL D. H., CLARK J. W., Jr DO TREPONEMES SURVIVE ADEQUATE TREATMENT OF LATE SYPHILIS? Arch Dermatol. 1965 Apr;91:379–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de WECK A. Newer developments in penicillin immunochemistry. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1963;22:245–252. doi: 10.1159/000229368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de WECK A. [Studies of penicillin allergy. IV. Skin tests in penicillin allergy]. Dermatologica. 1962;125:283–301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


