Abstract
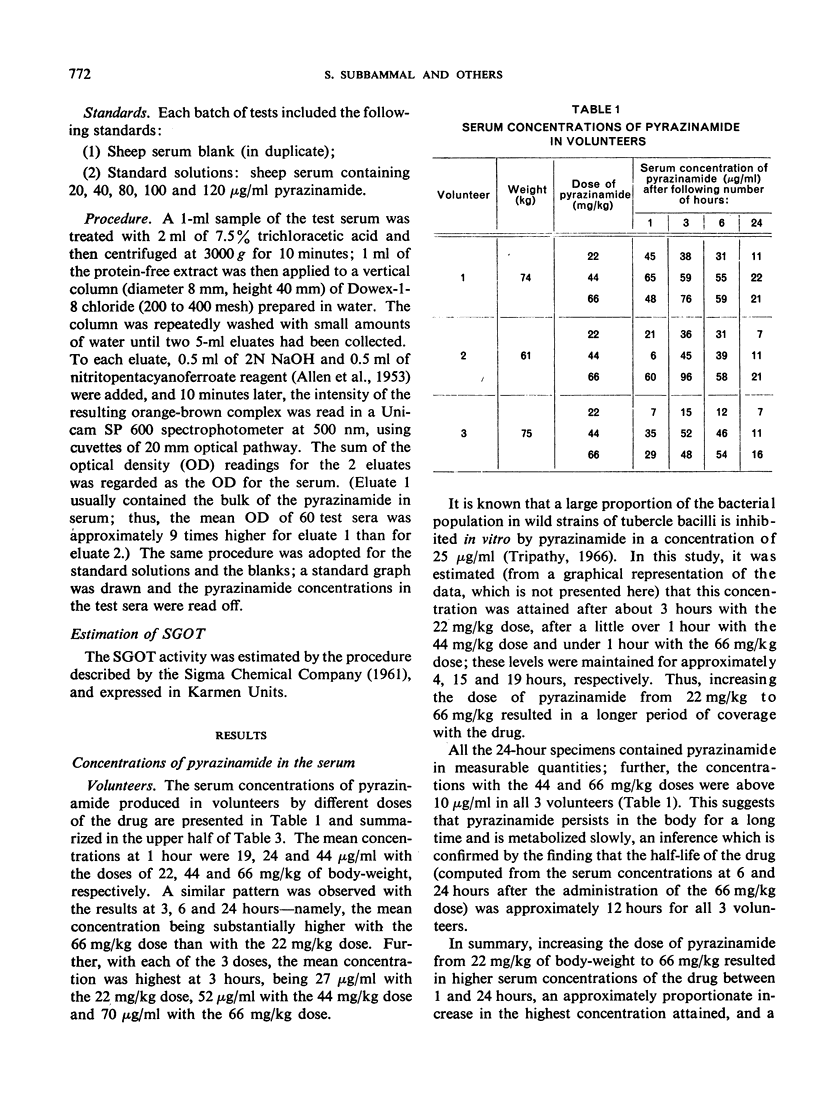
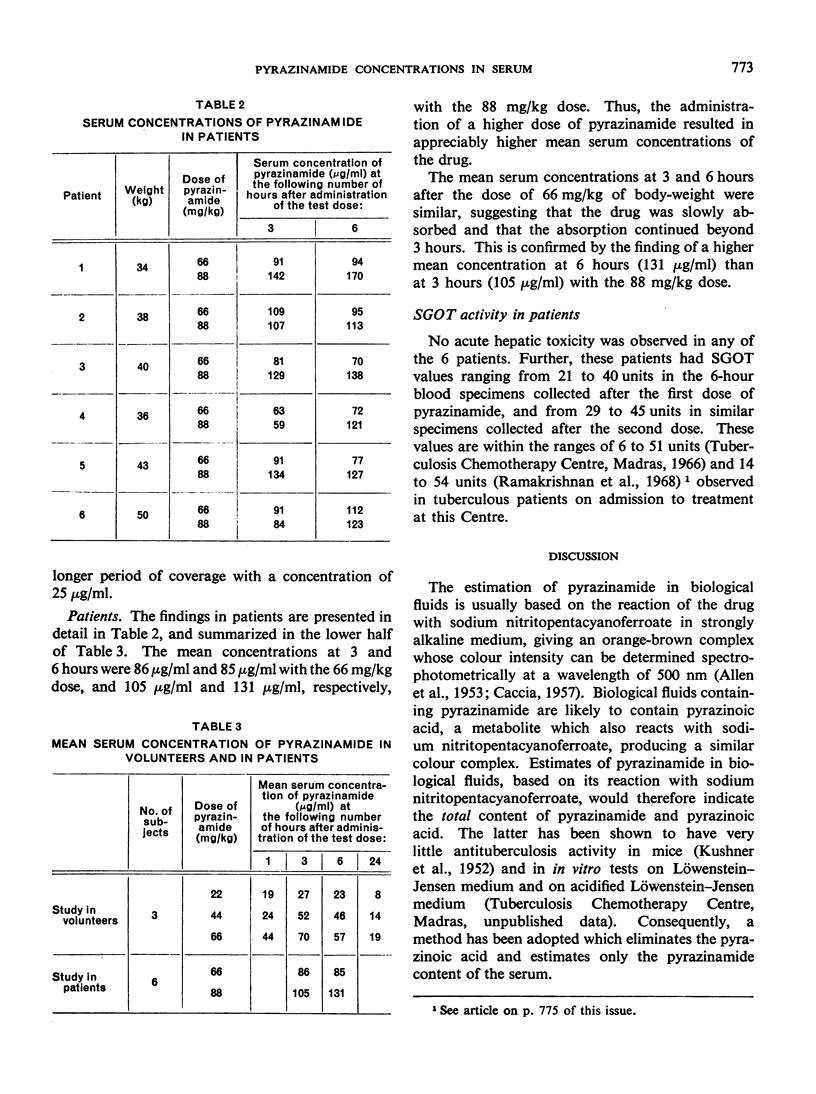
Serial concentrations of pyrazinamide in 3 volunteers showed that increasing the dose from 22 mg/kg of body-weight to 66 mg/kg resulted in substantially higher serum concentrations of the drug and a longer period of coverage (at a concentration of 25 μg/ml). Similarly, in a study based on 6 tuberculous patients, increasing the dose of pyrazinamide from 66 mg/kg to 88 mg/kg led to appreciably higher concentrations in the serum. In neither series of tests was any acute hepatic toxicity observed. The findings suggest that it would be interesting to study the effect of doses of about 90 mg/kg of pyrazinamide in once-weekly regimens of chemotherapy for the treatment of tuberculosis.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CACCIA P. A. Spectrophotometric determination of pyrazinamide blood concentrations and excretion through the kidneys. Am Rev Tuberc. 1957 Jan;75(1):105–110. doi: 10.1164/artpd.1957.75.1.105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDERMOTT W., ORMOND L., MUSCHENHEIM C., DEUSCHLE K., McCUNE R. M., Jr, TOMPSETT R. Pyrazinamide-isoniazid in tuberculosis. Am Rev Tuberc. 1954 Mar;69(3):319–333. doi: 10.1164/art.1954.69.3.319. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramakrishnan C. V., Janardhanam B., Krishnamurthy D. V., Stott H., Subbammal S., Tripathy S. P. Toxicity of pyrazinamide, administered once weekly in high dosage, in tuberculous patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1968;39(5):775–779. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VELU S., ANDREWS R. H., ANGEL J. H., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., JACOB P. G., NAIR C. N., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V. Streptomycin plus pyrazinamide in the treatment of patients excreting isonazid-resistant tubercle bacilli, following previous chemotherapy. Tubercle. 1961 Jun;42:136–147. doi: 10.1016/s0041-3879(61)80089-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


