Abstract
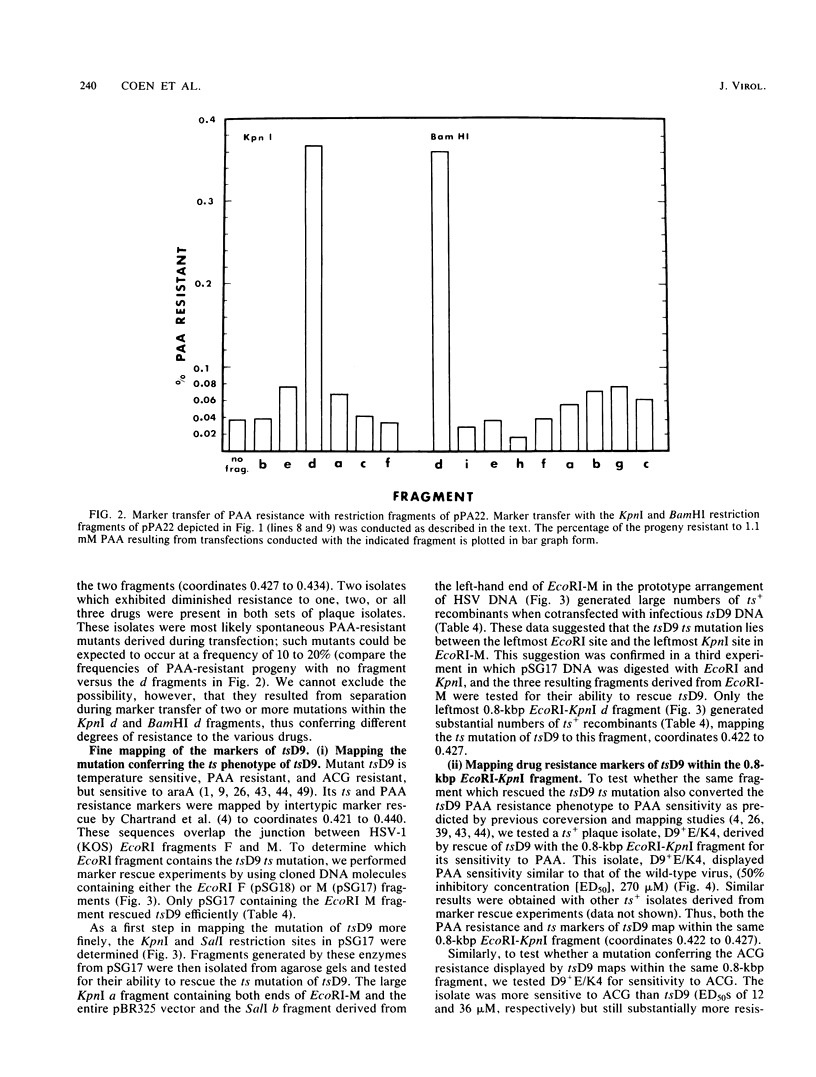
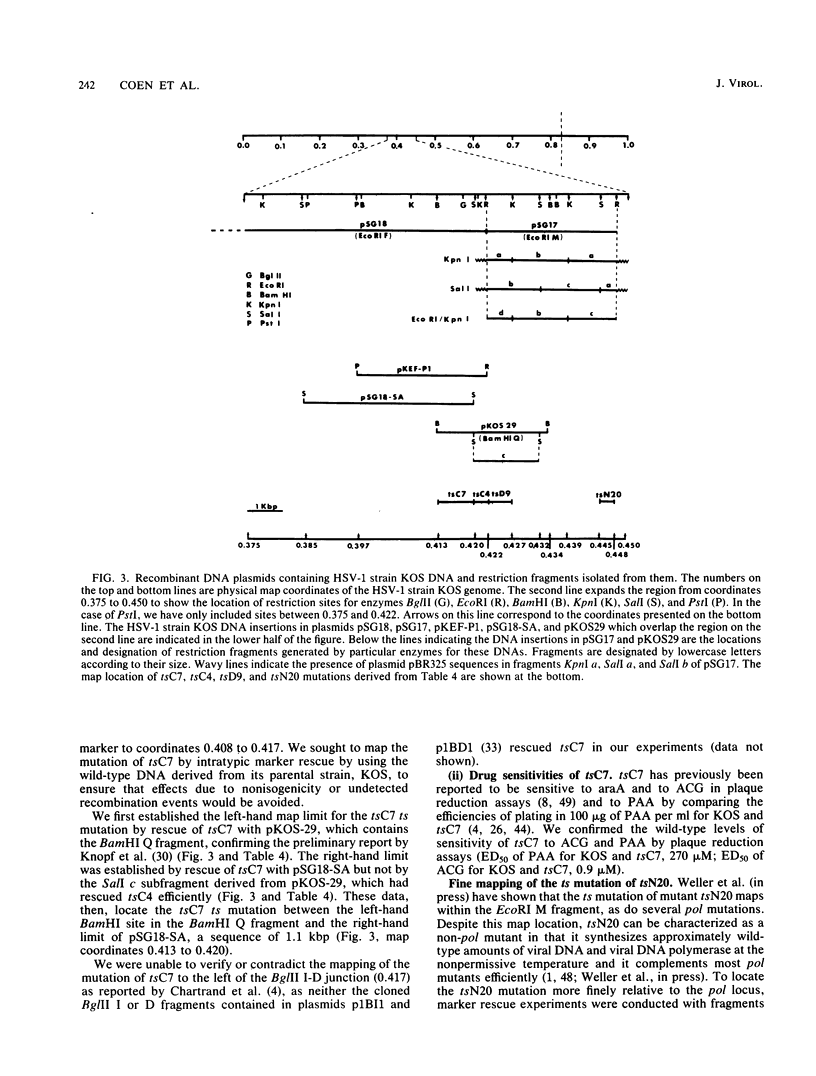
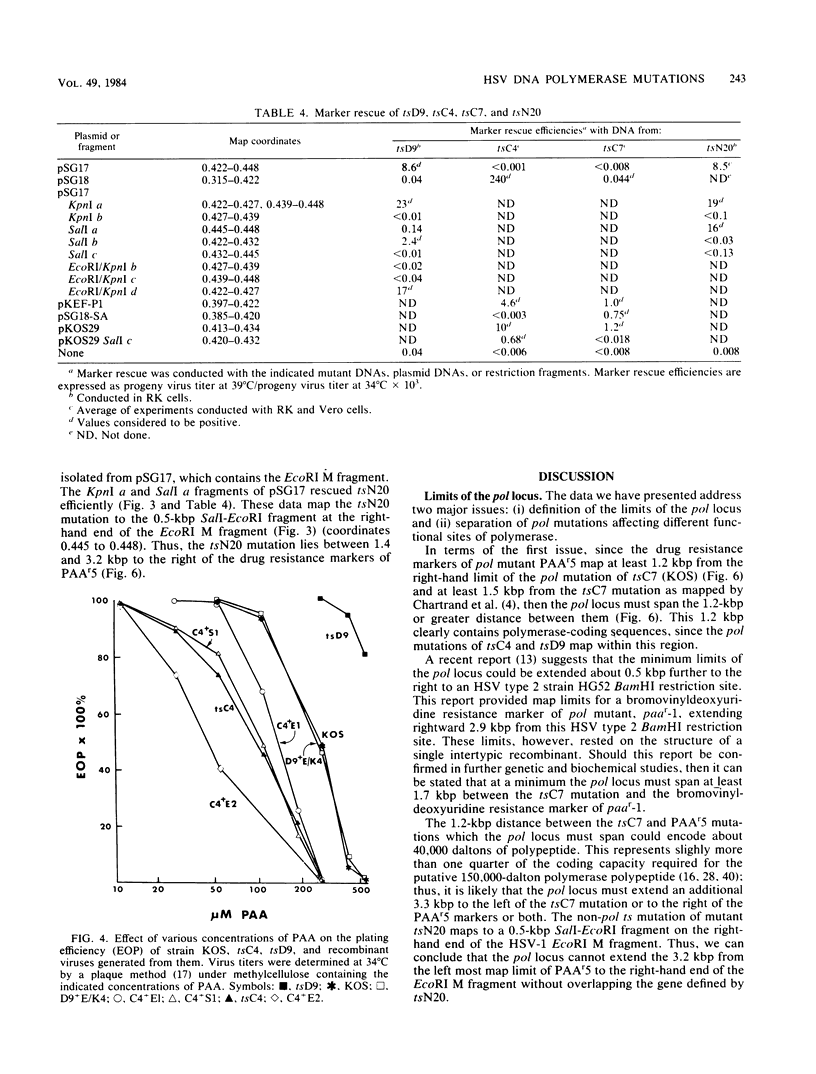
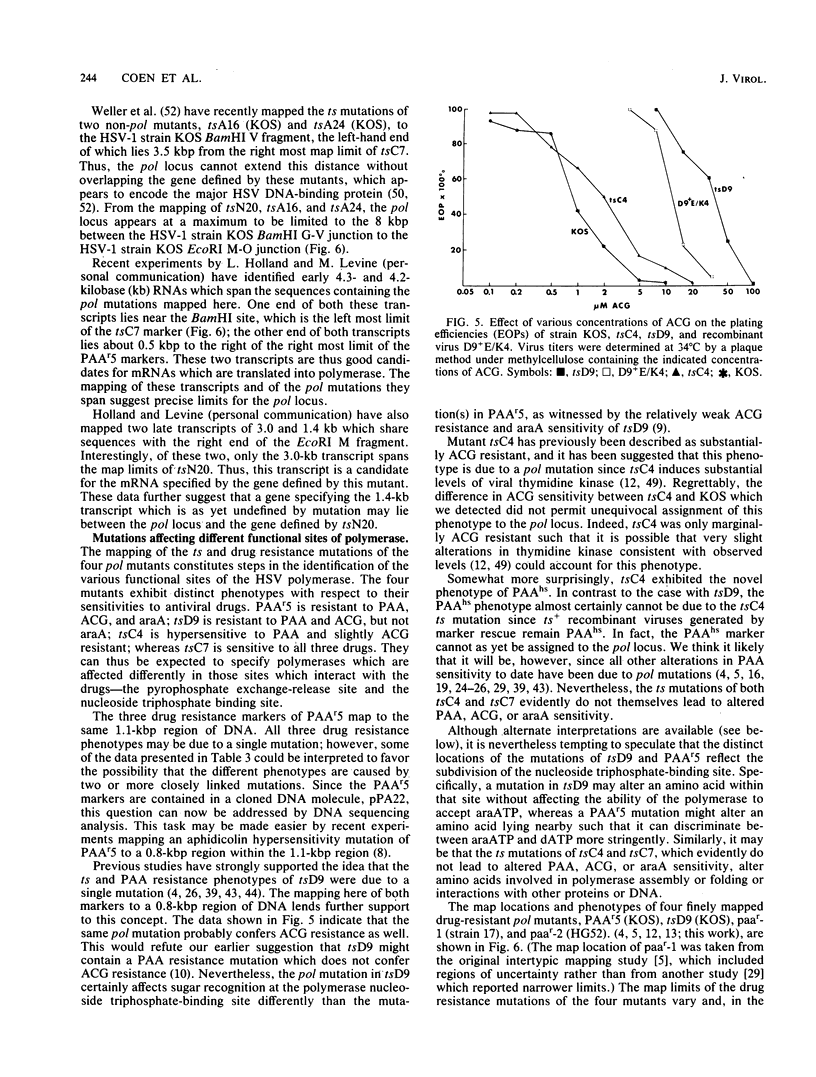
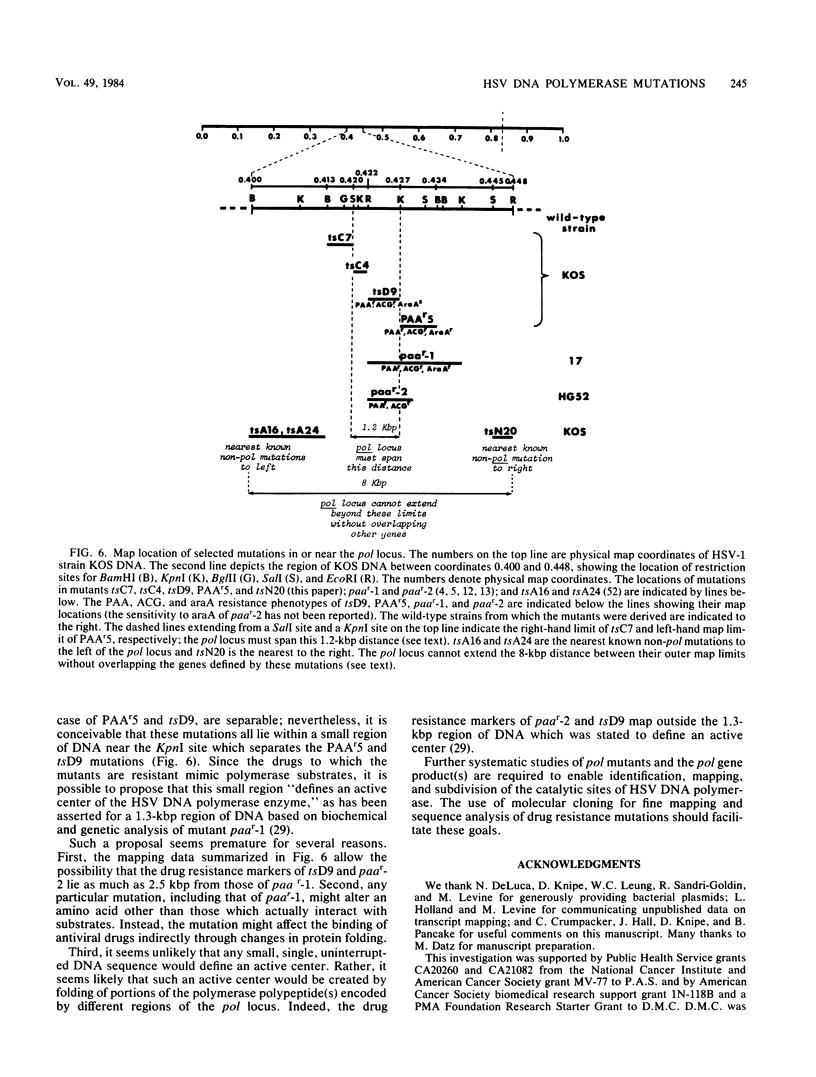
Mutations in five phenotypically distinct mutants derived from herpes simplex virus type 1 strain KOS which lie in or near the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase (pol) locus have been fine mapped with the aid of cloned fragments of mutant and wild-type viral DNAs to distinct restriction fragments of 1.1 kilobase pairs (kbp) or less. DNA sequences containing a mutation or mutations conferring resistance to the antiviral drugs phosphonoacetic acid, acyclovir, and arabinosyladenine of pol mutant PAAr5 have been cloned as a 27-kbp Bg+II fragment in Escherichia coli. These drug resistance markers have been mapped more finely in marker transfer experiments to a 1.1-kbp fragment (coordinates 0.427 to 0.434). In intratypic marker rescue experiments, temperature-sensitive (ts), phosphonoacetic acid resistance, and acyclovir resistance markers of pol mutant tsD9 were mapped to a 0.8-kbp fragment at the left end of the EcoRI M fragment (coordinates 0.422 to 0.427). The ts mutation of pol mutant tsC4 maps within a 0.3-kbp sequence (coordinates 0.420 to 0.422), whereas that of tsC7 lies within the 1.1-kbp fragment immediately to the left (coordinates 0.413 to 0.420). tsC4 displays the novel phenotype of hypersensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid; however, the phosphonoacetic acid hypersensitivity phenotype is almost certainly not due to the mutation(s) conferring temperature sensitivity. The ts mutation of mutant tsN20--which does not affect DNA polymerase activity--maps to a 0.5-kbp fragment at the right-hand end of the EcoRI M fragment (coordinates 0.445 to 0.448). The mapping of the mutations in these five mutants further defines the limits of the pol locus and separates mutations differentially affecting catalytic functions of the polymerase.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aron G. M., Purifoy D. J., Schaffer P. A. DNA synthesis and DNA polymerase activity of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1975 Sep;16(3):498–507. doi: 10.1128/jvi.16.3.498-507.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. III. Derivatives of plasmid pBR322 carrying unique Eco RI sites for selection of Eco RI generated recombinant DNA molecules. Gene. 1978 Oct;4(2):121–136. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(78)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyer H. W., Roulland-Dussoix D. A complementation analysis of the restriction and modification of DNA in Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):459–472. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90288-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Crumpacker C. S., Schaffer P. A., Wilkie N. M. Physical and genetic analysis of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase locus. Virology. 1980 Jun;103(2):311–326. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Stow N. D., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of paar mutations of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 by intertypic marker rescue. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):265–276. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.265-276.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewell D. B., Helinski D. R. Supercoiled circular DNA-protein complex in Escherichia coli: purification and induced conversion to an opern circular DNA form. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Apr;62(4):1159–1166. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.4.1159. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Furman P. A., Aschman D. P., Schaffer P. A. Mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene conferring hypersensitivity to aphidicolin. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Aug 11;11(15):5287–5297. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.15.5287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Furman P. A., Gelep P. T., Schaffer P. A. Mutations in the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene can confer resistance to 9-beta-D-arabinofuranosyladenine. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):909–918. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.909-918.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A., Furman P. A., Keller P. M., St Clair M. H. Biochemical and genetic analysis of acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1. Am J Med. 1982 Jul 20;73(1A):351–360. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(82)90122-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coen D. M., Schaffer P. A. Two distinct loci confer resistance to acycloguanosine in herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2265–2269. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Chartrand P., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine--genetic and physical analysis. Virology. 1980 Aug;105(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90165-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crumpacker C. S., Schnipper L. E., Kowalsky P. N., Sherman D. M. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to adenine arabinoside and E-5-(2-bromovinyl)-2'-deoxyuridine: a physical analysis. J Infect Dis. 1982 Aug;146(2):167–172. doi: 10.1093/infdis/146.2.167. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. W., Thomas M., Cameron J., St John T. P., Scherer S., Padgett R. A. Rapid DNA isolations for enzymatic and hybridization analysis. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):404–411. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65051-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derse D., Bastow K. F., Cheng Y. Characterization of the DNA polymerases induced by a group of herpes simplex virus type I variants selected for growth in the presence of phosphonoformic acid. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10251–10260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Benyesh-Melnick M. Spectrum of human cytomegalovirus complement-fixing antigens. J Immunol. 1967 Dec;99(6):1106–1114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dugaiczyk A., Boyer H. W., Goodman H. M. Ligation of EcoRI endonuclease-generated DNA fragments into linear and circular structures. J Mol Biol. 1975 Jul 25;96(1):171–184. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90189-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., Coen D. M., St Clair M. H., Schaffer P. A. Acyclovir-resistant mutants of herpes simplex virus type 1 express altered DNA polymerase or reduced acyclovir phosphorylating activities. J Virol. 1981 Dec;40(3):936–941. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.3.936-941.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., St Clair M. H., Fyfe J. A., Rideout J. L., Keller P. M., Elion G. B. Inhibition of herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase activity and viral DNA replication by 9-(2-hydroxyethoxymethyl)guanine and its triphosphate. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):72–77. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.72-77.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furman P. A., de Miranda P., St Clair M. H., Elion G. B. Metabolism of acyclovir in virus-infected and uninfected cells. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1981 Oct;20(4):518–524. doi: 10.1128/aac.20.4.518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldin A. L., Sandri-Goldin R. M., Levine M., Glorioso J. C. Cloning of herpes simplex virus type 1 sequences representing the whole genome. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):50–58. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.50-58.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J., Moss H., Jamieson A. T., Timbury M. C. Herpesvirus proteins: DNA polymerase and pyrimidine deoxynucleoside kinase activities in temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):65–73. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-65. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay J., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 that are resistant to phosphonoacetic acid induce altered DNA polymerase activities in infected cells. J Gen Virol. 1976 Apr;31(1):145–148. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-31-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Watson D. H. Herpes simplex virus resistance and sensitivity to phosphonoacetic acid. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):584–600. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.584-600.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jofre J. T., Schaffer P. A., Parris D. S. Genetics of resistance to phosphonoacetic acid in strain KOS of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1977 Sep;23(3):833–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.23.3.833-836.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knipe D. M., Ruyechan W. T., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. III. Fine mapping of a genetic locus determining resistance to phosphonoacetate by two methods of marker transfer. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):698–704. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.698-704.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W., Kaufman E. R., Crumpacker C. Physical mapping of drug resistance mutations defines an active center of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase enzyme. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):746–757. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.746-757.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knopf K. W. Properties of herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase and characterization of its associated exonuclease activity. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Jul;98(1):231–244. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13181.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krokan H., Schaffer P., DePamphilis M. L. Involvement of eucaryotic deoxyribonucleic acid polymerases alpha and gamma in the replication of cellular and viral deoxyribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1979 Oct 2;18(20):4431–4443. doi: 10.1021/bi00587a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leinbach S. S., Reno J. M., Lee L. F., Isbell A. F., Boezi J. A. Mechanism of phosphonoacetate inhibition of herpesvirus-induced DNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1976 Jan 27;15(2):426–430. doi: 10.1021/bi00647a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locker H., Frenkel N. BamI, KpnI, and SalI restriction enzyme maps of the DNAs of herpes simplex virus strains Justin and F: occurrence of heterogeneities in defined regions of the viral DNA. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):429–441. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.429-441.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mao J. C., Robishaw E. E., Overby L. R. Inhibition of DNA polymerase from herpes simplex virus-infected wi-38 cells by phosphonoacetic Acid. J Virol. 1975 May;15(5):1281–1283. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.5.1281-1283.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison D. A. Transformation and preservation of competent bacterial cells by freezing. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:326–331. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68023-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North T. W., Cohen S. S. Aranucleosides and aranucleotides in viral chemotherapy. Pharmacol Ther. 1979;4(1):81–108. doi: 10.1016/0163-7258(79)90016-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostrander M., Cheng Y. C. Properties of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 DNA polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 19;609(2):232–245. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(80)90234-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parris D. S., Dixon R. A., Schaffer P. A. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 ts mutants by marker rescue: correlation of the physical and genetic maps. Virology. 1980 Jan 30;100(2):275–287. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90519-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J. Nonstructural proteins of herpes simplex virus. I. Purification of the induced DNA polymerase. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):618–626. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.618-626.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G. Fine-structure mapping of herpes simplex virus type 1 temperature-sensitive mutations within the short repeat region of the genome. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):150–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.150-161.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Benyesh-Melnick M. DNA polymerase induction by DNA-negative temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1975 Dec;68(2):374–386. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90280-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Lewis R. B., Powell K. L. Identification of the herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase gene. Nature. 1977 Oct 13;269(5629):621–623. doi: 10.1038/269621a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Herpes simplex virus DNA polymerase as the site of phosphonoacetate sensitivity: temperature-sensitive mutants. J Virol. 1977 Nov;24(2):470–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.2.470-477.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purifoy D. J., Powell K. L. Temperature-sensitive mutants in two distinct complementation groups of herpes simplex virus type 1 specify thermolabile DNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1981 May;54(Pt 1):219–222. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-54-1-219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao R. N., Rogers S. G. Plasmid pKC7: a vector containing ten restriction endonuclease sites suitable for cloning DNA segments. Gene. 1979 Sep;7(1):79–82. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(79)90044-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinke C. M., Drach J. C., Shipman C., Jr, Weissbach A. Differential inhibition of mammalian DNA polymerases alpha, beta and gamma and herpes simplex virus-induced DNA polymerase by the 5'-triphosphates of arabinosyladenine and arabinosylcytosine. IARC Sci Publ. 1978;(24 Pt 2):999–1005. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffer P. A., Carter V. C., Timbury M. C. Collaborative complementation study of temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):490–504. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.490-504.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnipper L. E., Crumpacker C. S. Resistance of herpes simplex virus to acycloguanosine: role of viral thymidine kinase and DNA polymerase loci. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2270–2273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spang A. E., Godowski P. J., Knipe D. M. Characterization of herpes simplex virus 2 temperature-sensitive mutants whose lesions map in or near the coding sequences for the major DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):332–342. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.332-342.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogelstein B., Gillespie D. Preparative and analytical purification of DNA from agarose. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Feb;76(2):615–619. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.2.615. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weller S. K., Lee K. J., Sabourin D. J., Schaffer P. A. Genetic analysis of temperature-sensitive mutants which define the gene for the major herpes simplex virus type 1 DNA-binding protein. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):354–366. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.354-366.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


