Abstract
Abate is a larvicide for Aedes aegypti, a vector of yellow fever, dengue, and haemorrhagic fever. It is less toxic than malathion or DDT. Tests in human volunteers had previously indicated it would be safe to add to drinking-water where the mosquito often breeds.
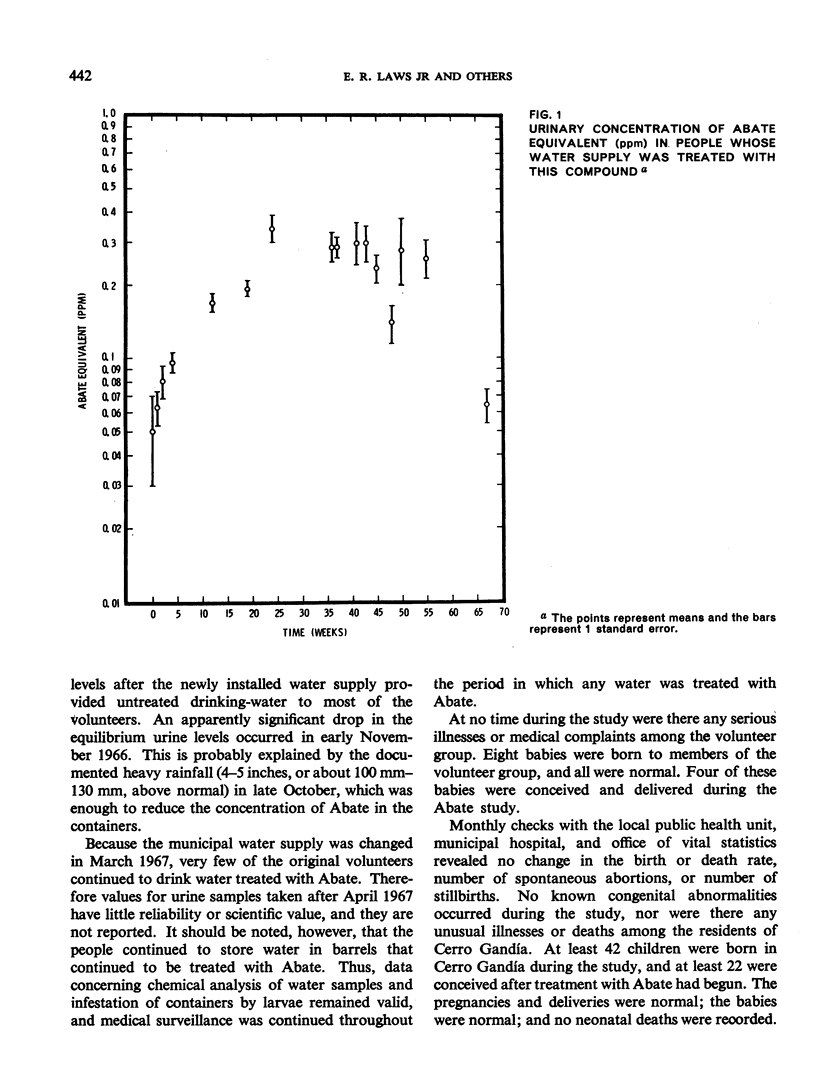
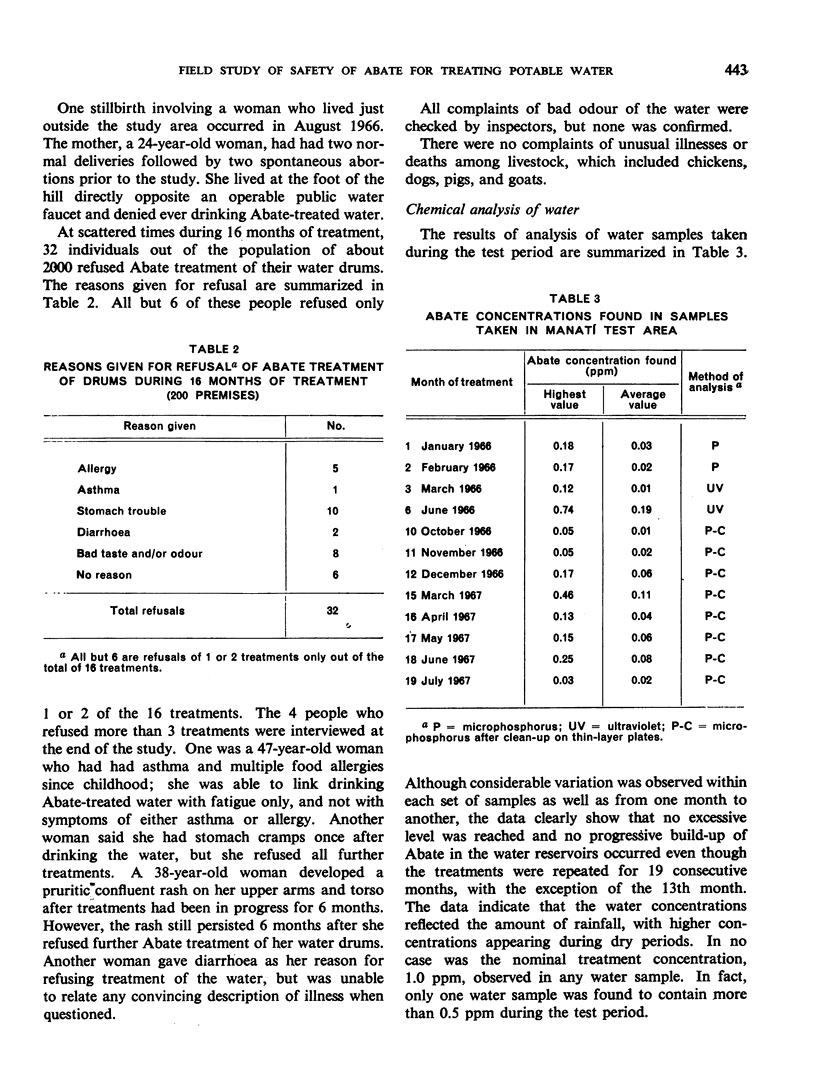
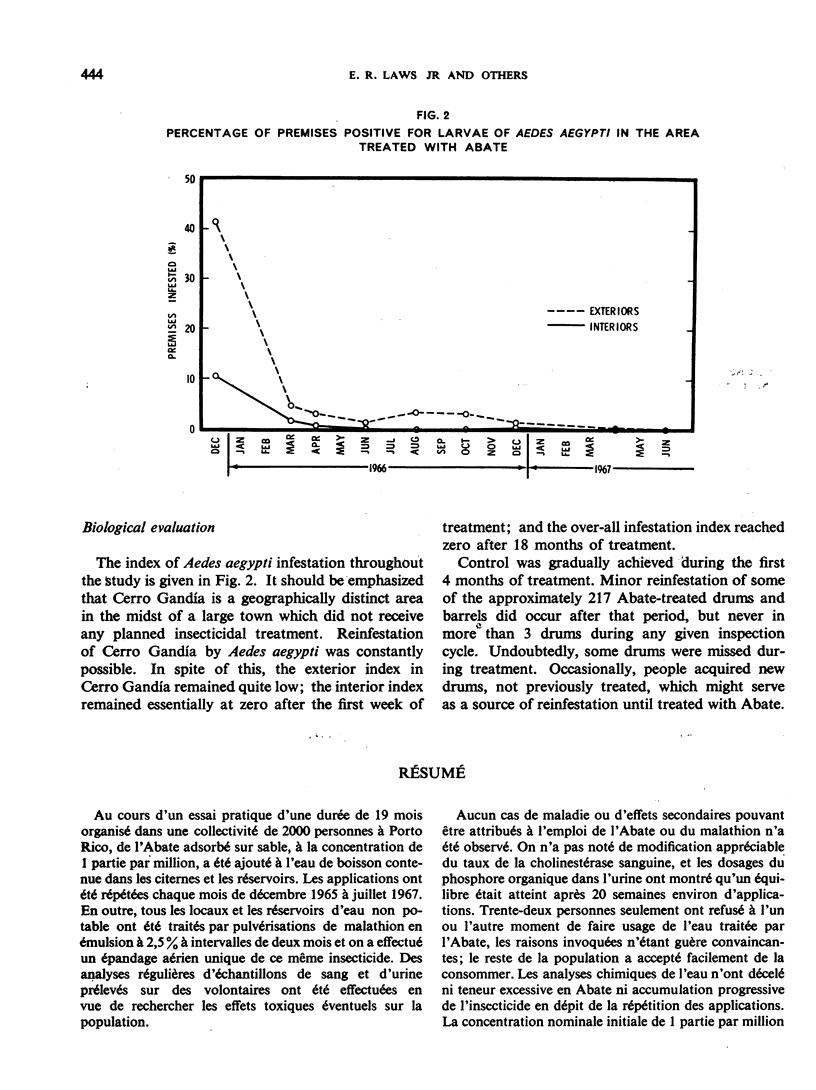
In a 19-month test in Puerto Rico, Abate was added to the drums and cisterns in which a community of about 2000 persons stored their drinking-water. This use of Abate and other insecticidal measures (malathion spraying) gradually achieved control of A. aegypti during the first 4 months of treatment and control was maintained thereafter although the test area was surrounded by active breeding-sites. There was no accumulation of Abate in the water in spite of monthly additions of the compound. With minor exceptions, residents readily accepted this use of Abate. Careful surveillance failed to reveal any illness or significant side-effects attributable to measures adopted in the control programme. Abate is considered safe for full-scale field use according to directions.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Gaines T. B., Kimbrough R., Laws E. R., Jr Toxicology of Abate in laboratory animals. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Feb;14(2):283–288. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JENSEN-HOLM J., LAUSEN H. H., MILTHERS K., MOLLER K. O. Determination of the cholinesterase activity in blood and organs by automatic titration; with some observations on seious errors of the method and remarks of the photometric determination. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1959;15:384–394. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1959.tb00307.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laws E. R., Jr, Morales F. R., Hayes J., Jr, Joseph C. R. Toxicology of Abate in volunteers. Arch Environ Health. 1967 Feb;14(2):289–291. doi: 10.1080/00039896.1967.10664733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


