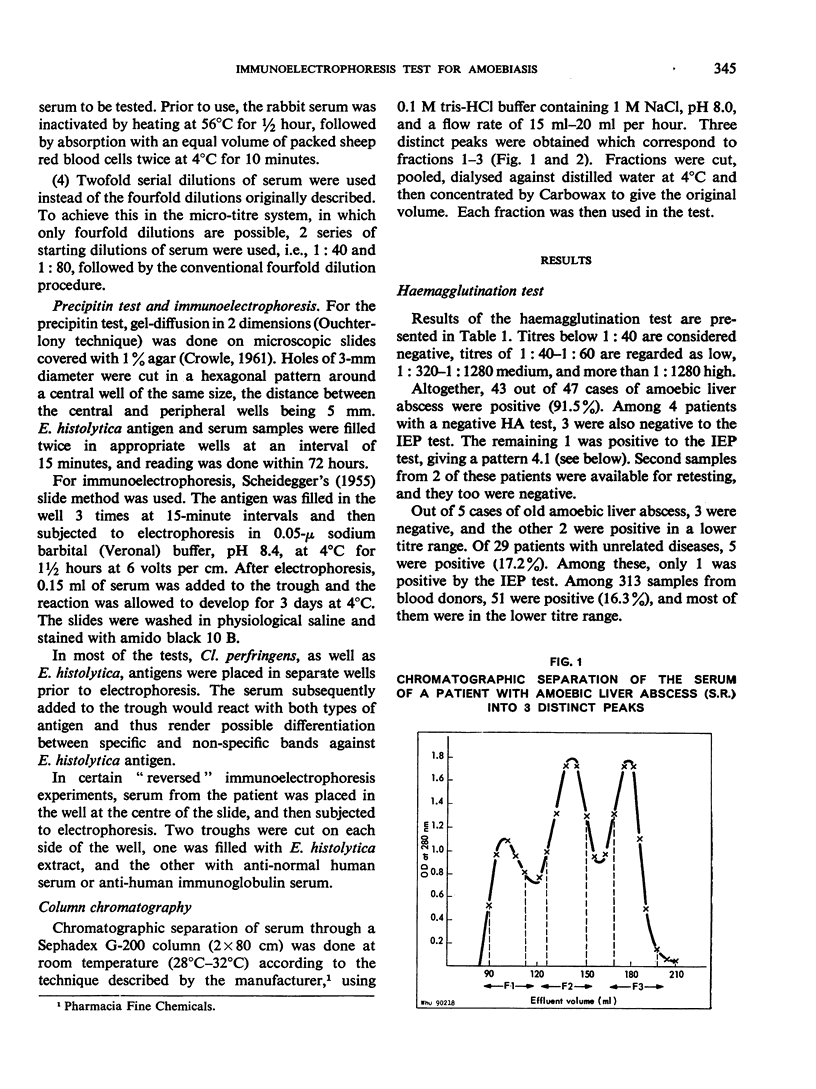
Abstract
Haemagglutination and immunoelectrophoresis tests were investigated to find which was more suitable for the immunodiagnosis of amoebiasis. Both tests were positive in more than 90% of sera from patients with amoebic liver abscess. With serum from blood donors and patients with other diseases a much lower percentage of positives was given by the immunoelectrophoresis test, showing that this test had a closer correlation with clinically important disease.
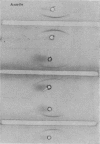
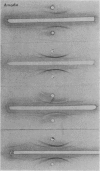
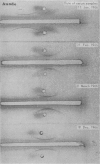
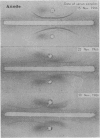
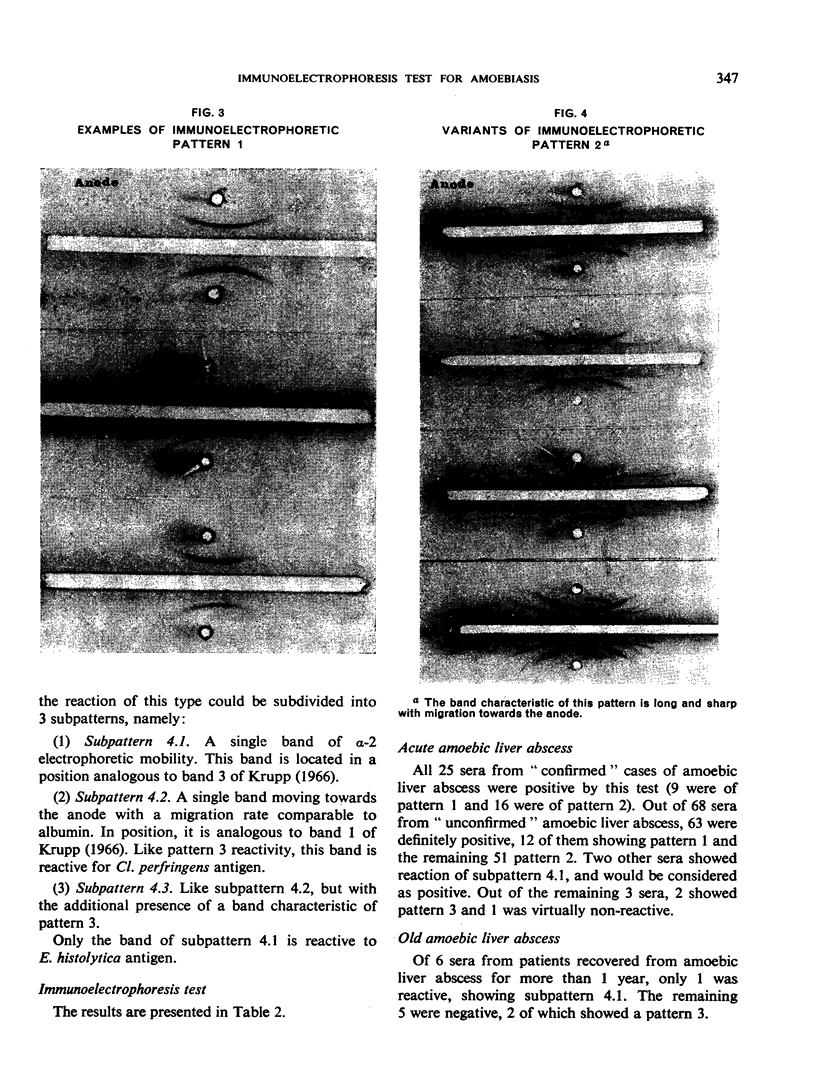
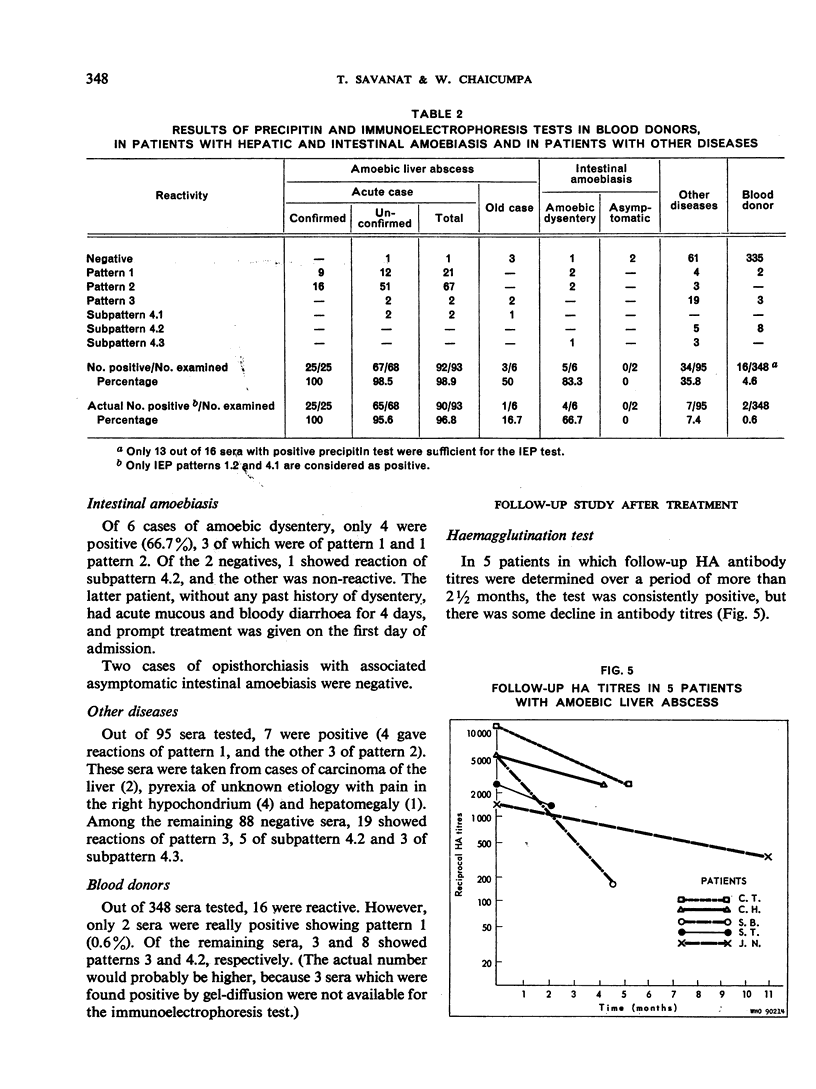
The immunoelectrophoretic patterns were of several varieties, but a single prominent band located near the well was considered as characteristic of amoebiasis.
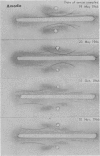
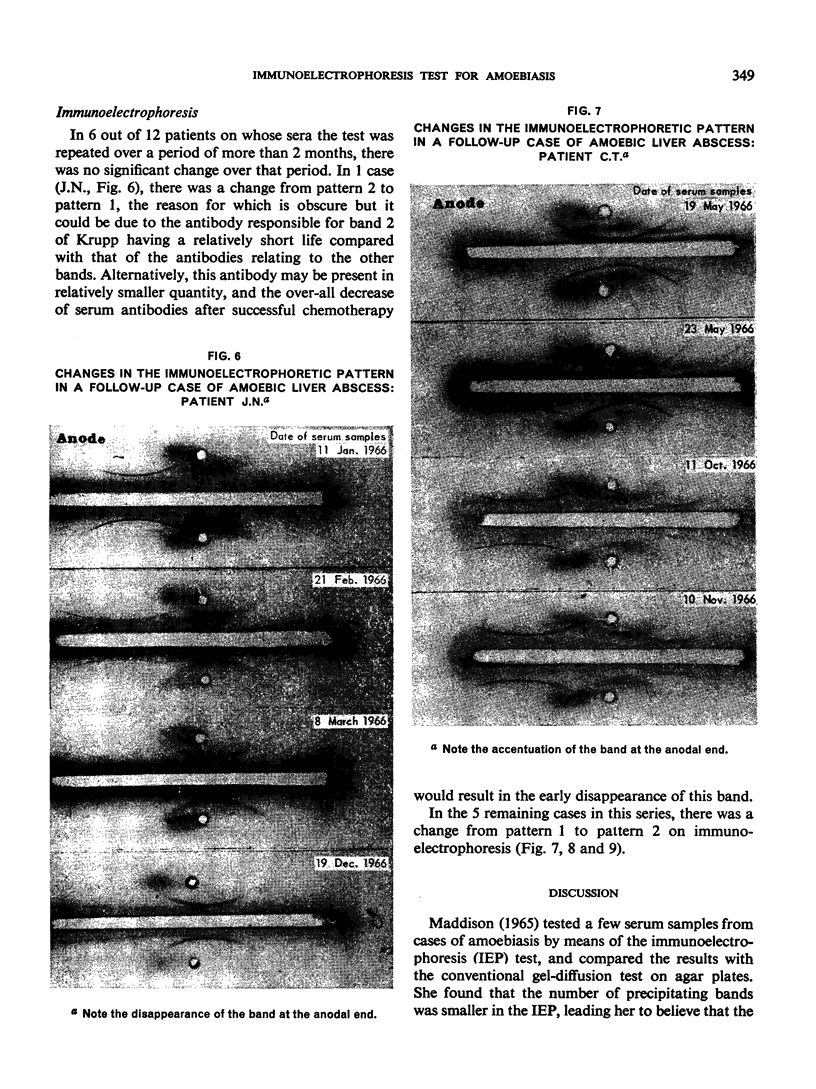
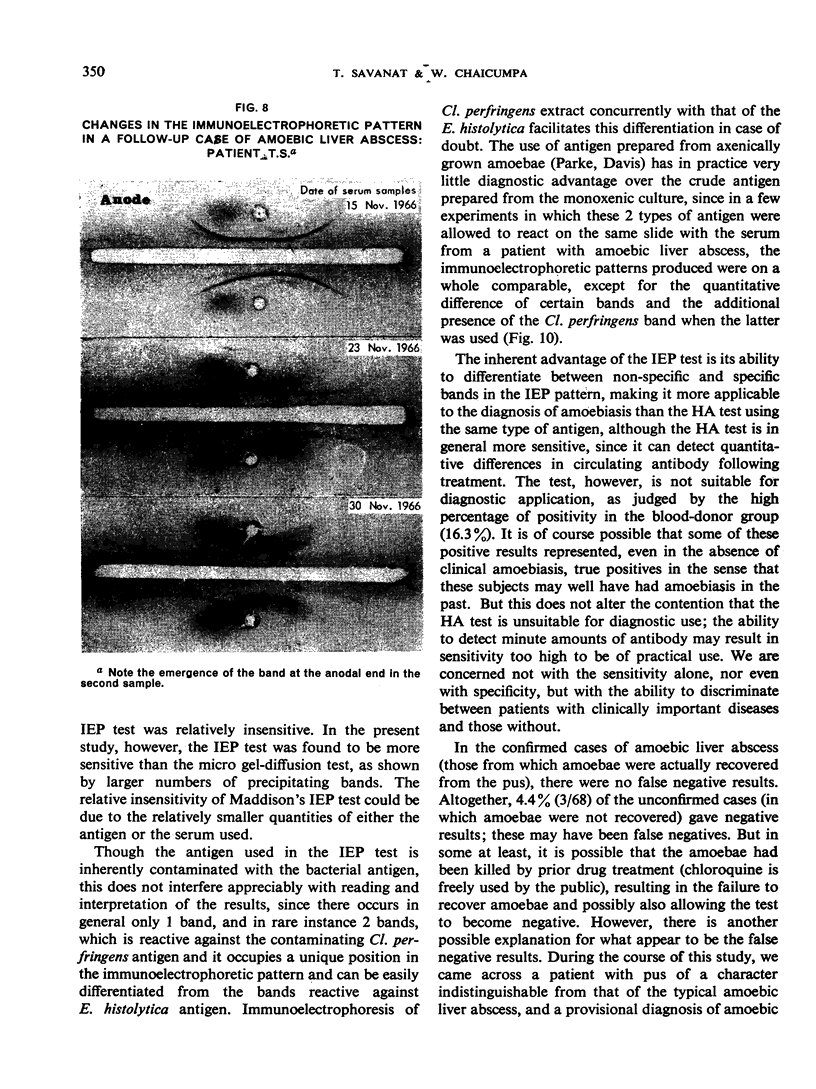
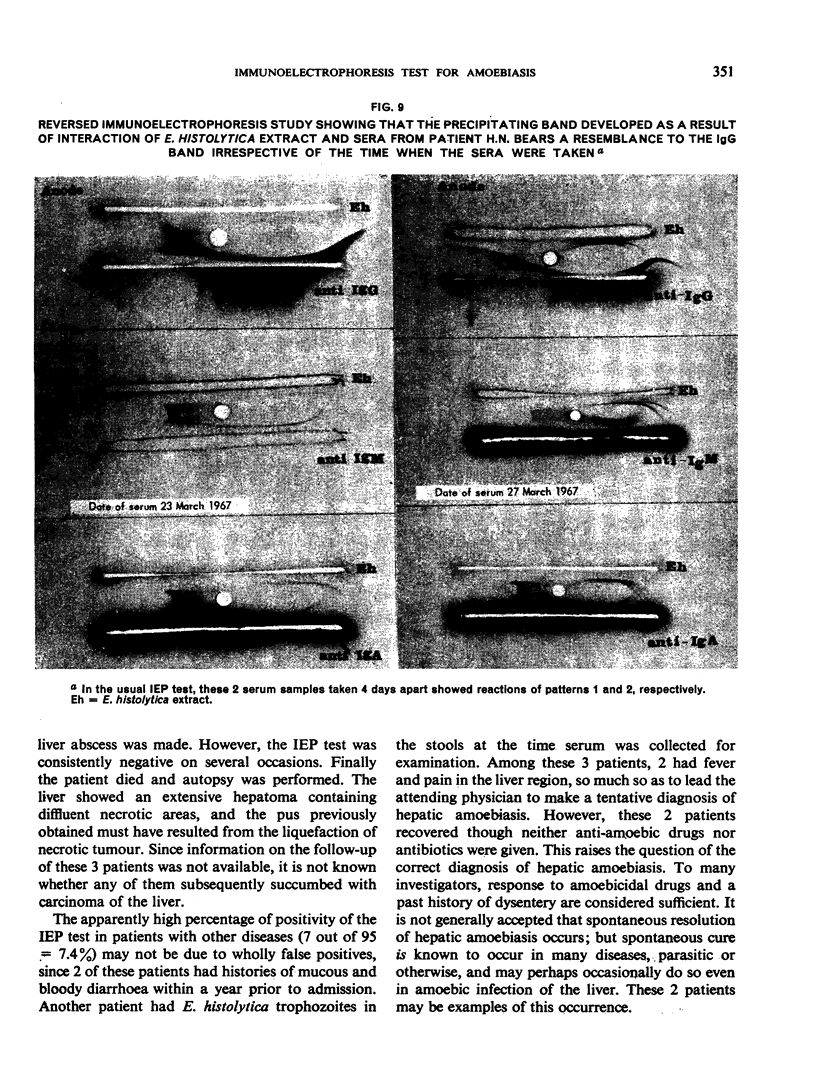
Follow-up studies showed that both haemagglutinating and precipitating antibodies persisted for several months, accompanied in certain patients by changes in the immunoelectrophoretic pattern. Antibody activities were shown by means of column chromatography and “reversed” immunoelectrophoresis to be associated with serum IgG.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boonpucknavig S., Lynraven G. S., Nairn R. C., Ward H. A. Subcellular localization of Entamoeba histolytica antigen. Nature. 1967 Dec 23;216(5121):1232–1233. doi: 10.1038/2161232a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boonpucknavig S., Nairn R. C. Serological diagnosis of amoebiasis by immunofluorescence. J Clin Pathol. 1967 Nov;20(6):875–878. doi: 10.1136/jcp.20.6.875. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M. Evaluation of a fluorescent antibody test for amebiasis using two widely differing ameba strains as antigen. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Sep;15(5):694–700. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldman M., Siddiqui W. A. Antigenic comparison of two substrains of Entamoeba histolytica by gel diffusion and immunoelectrophoresis. Exp Parasitol. 1965 Dec;17(3):326–331. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(65)90077-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanes A. L. Indirect fluorescent antibody test in diagnosis of hepatic amoebiasis. Br Med J. 1966 Jun 11;1(5501):1464–1464. doi: 10.1136/bmj.1.5501.1464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp I. M. Immunoelectrophoretic analysis of several strains of Entamoeba histolytica. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1966 Nov;15(6):849–854. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1966.15.849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADDISON S. E. CHARACTERIZATION OF ENTAMOEBA HISTOLYTICA ANTIGEN ANTIBODY REACTION BY GEL DIFFUSION. Exp Parasitol. 1965 Apr;16:224–235. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(65)90047-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milgram E. A., Healty G. R., Kagan I. G. Studies on the use of the indirect hemagglutination test in the diagnosis of amebiasis. Gastroenterology. 1966 May;50(5):645–649. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHEIDEGGER J. J. Une micro-méthode de l'immuno-electrophorèse. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1955;7(2):103–110. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]