Abstract
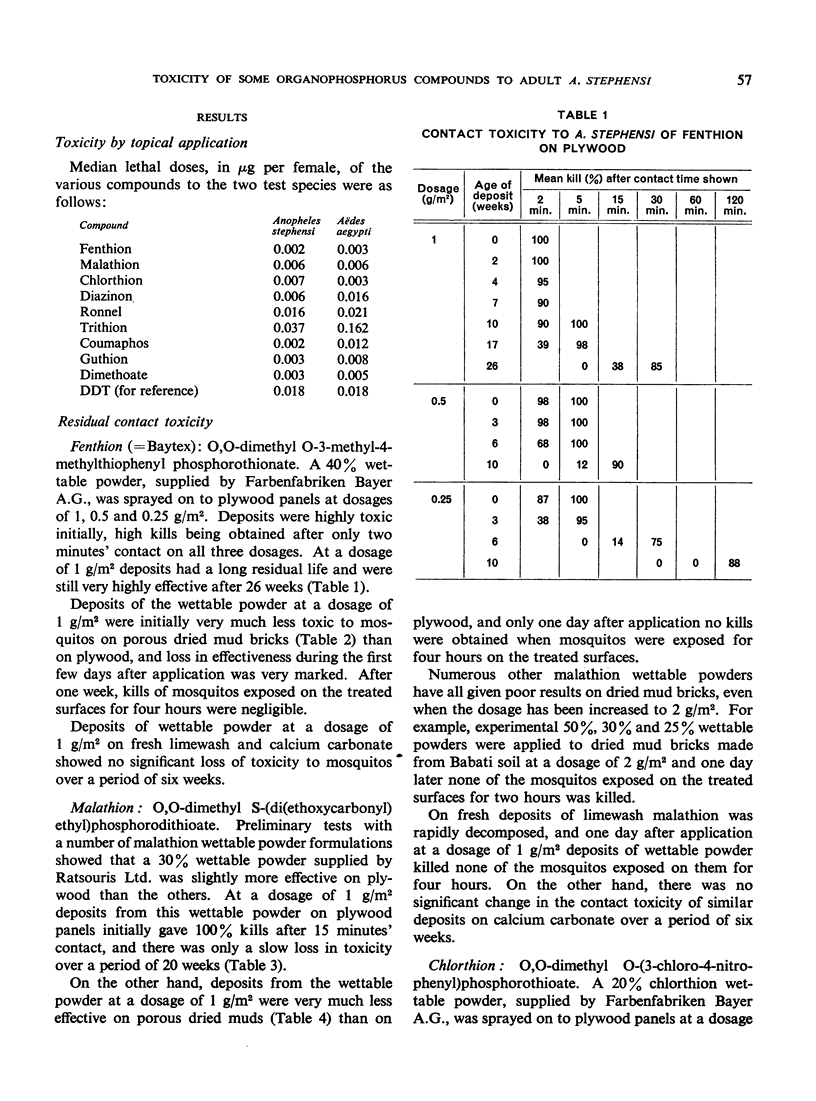
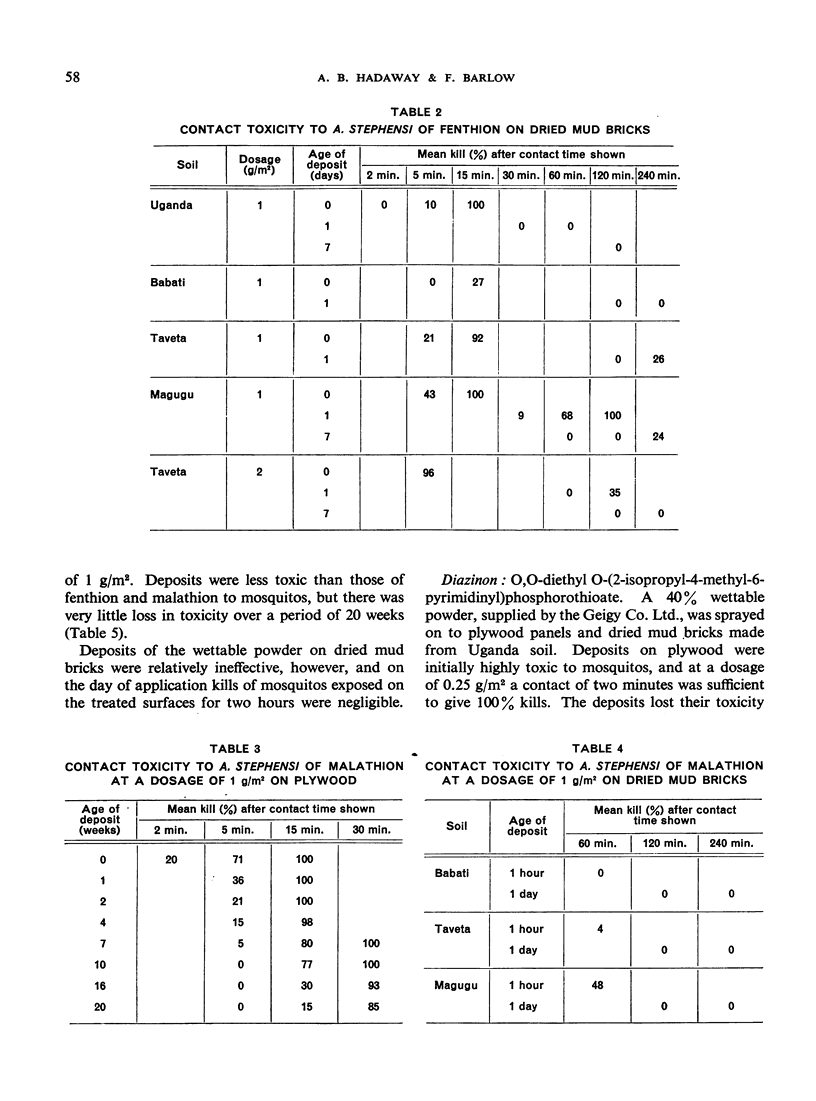
The authors have evaluated a number of organophosphorus compounds for residual contact toxicity to adult Anopheles stephensi. Fenthion and malathion were the most promising of the compounds, and wettable powder deposits at a dosage of 1 g/m2 on plywood remained effective for five months. There was, however, a rapid loss of effectiveness on dried mud bricks stored at 25°C and 50%-55% relative humidity.
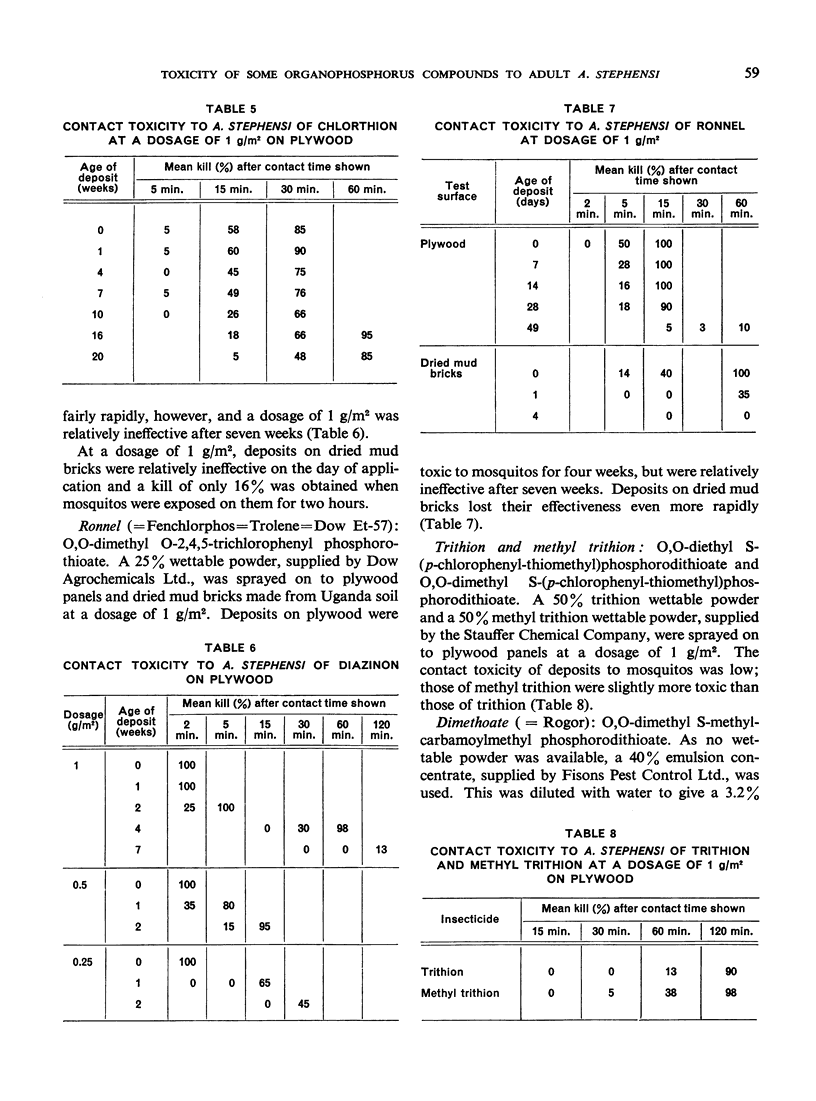
Diazinon and ronnel were less persistent on plywood. Guthion and coumaphos, although highly toxic by topical application, were both ineffective as contact insecticides when applied as solids in suspension. Trithion and methyl trithion were relatively low in toxicity both by topical application and as contact insecticides.
Full text
PDF