Abstract
The authors describe the entomological, chemical and toxicological findings made by the WHO Insecticide Testing Unit following the spraying of malathion, fenthion and DDT in villages in Western Nigeria.
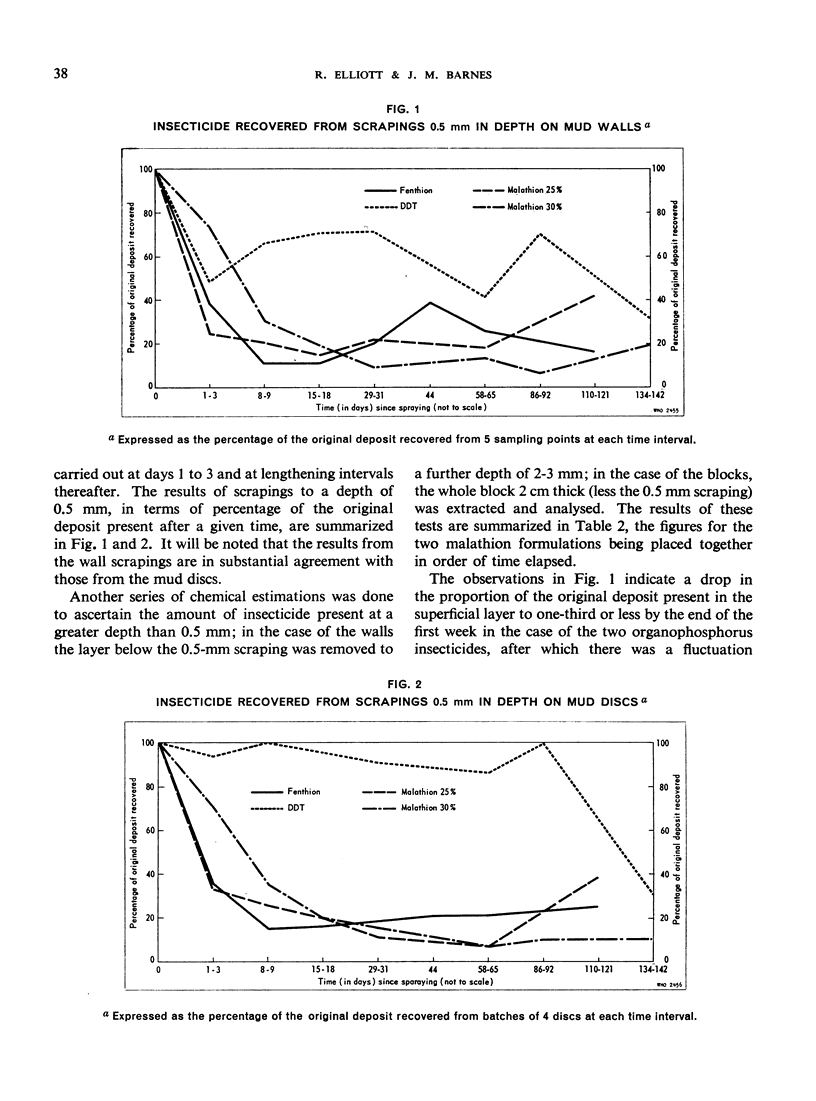
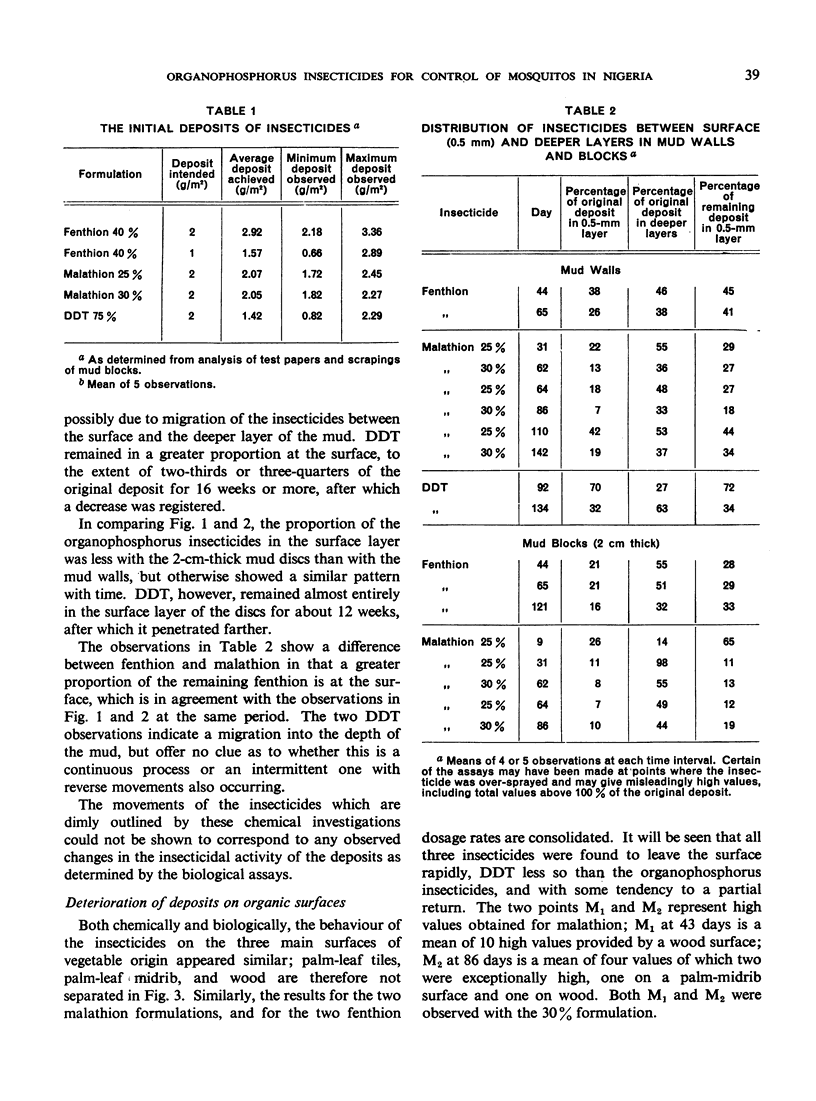
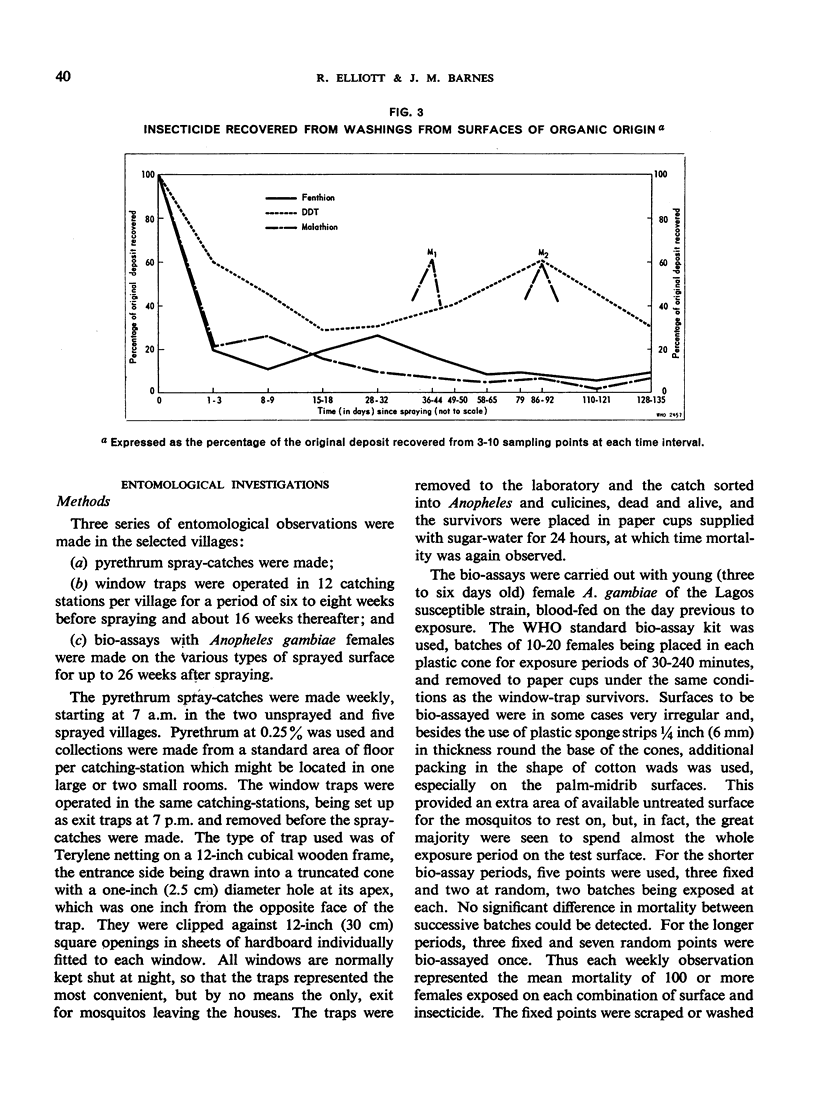
Chemical observations of the deposits indicate that on the local type of mud malathion is sorbed to a greater extent and to a deeper level than fenthion, and DDT less so. On surfaces of vegetable origin all three appeared to remain to about the same degree.
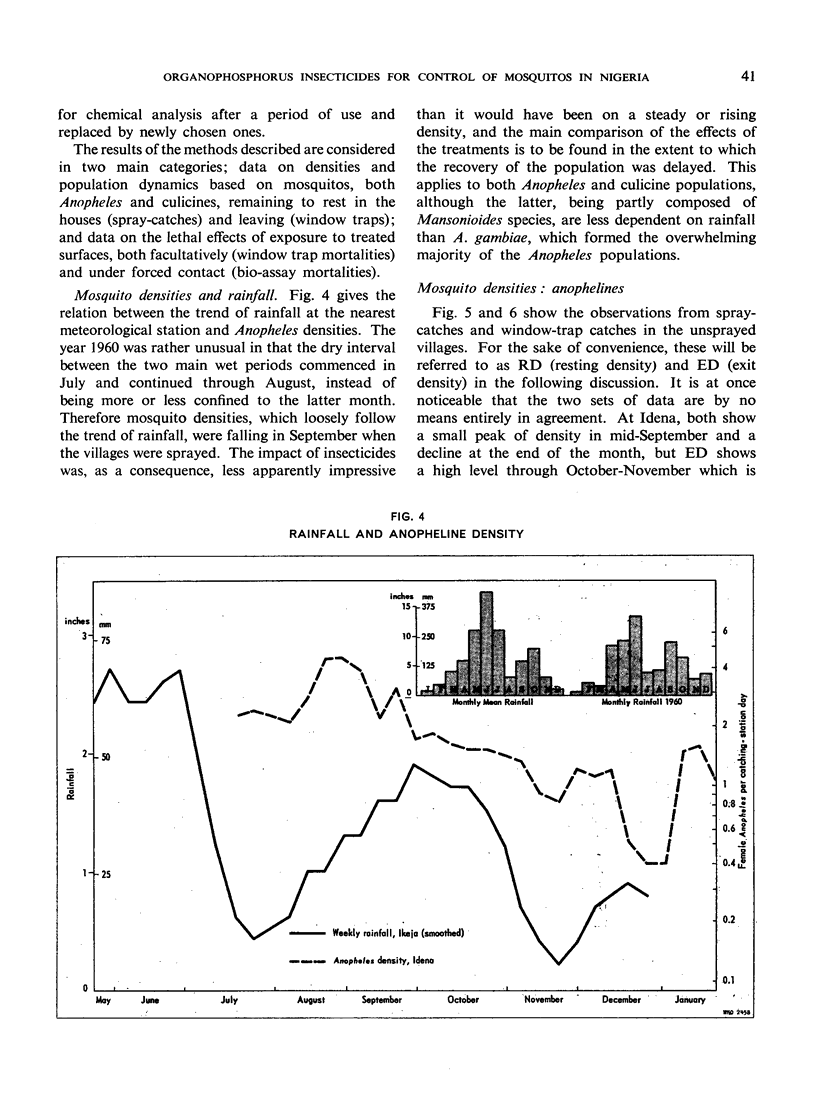
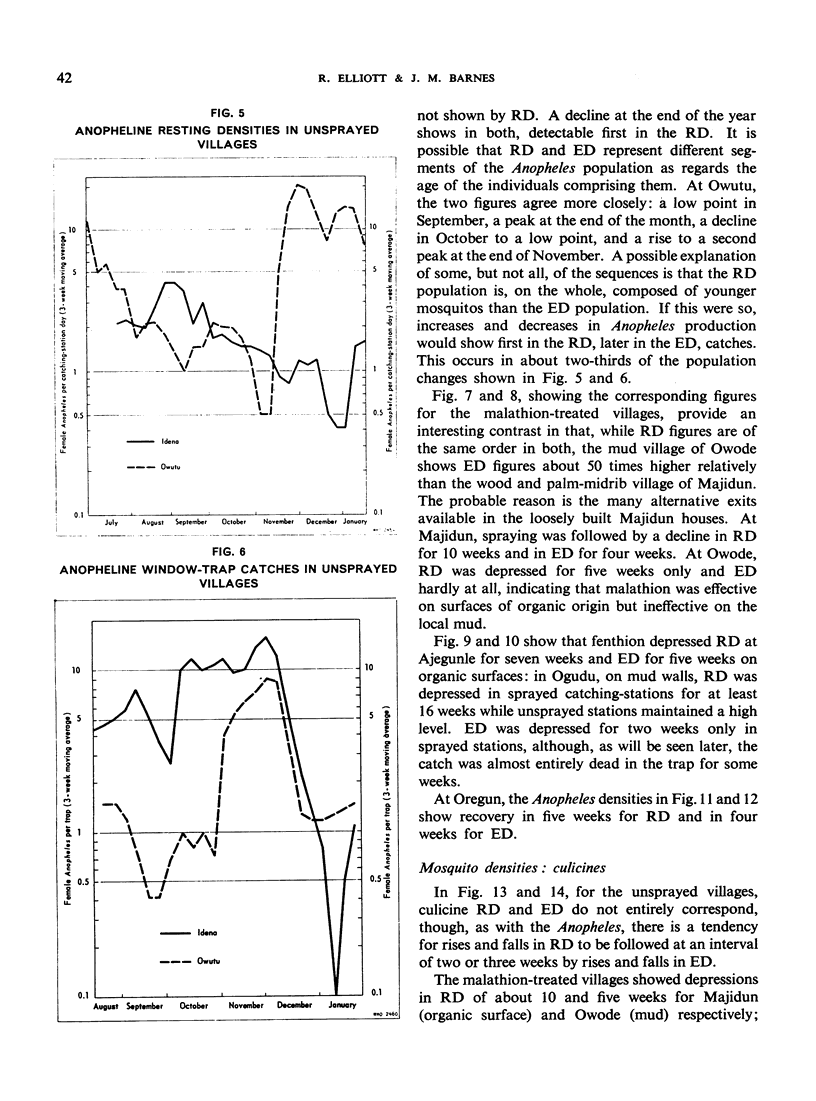
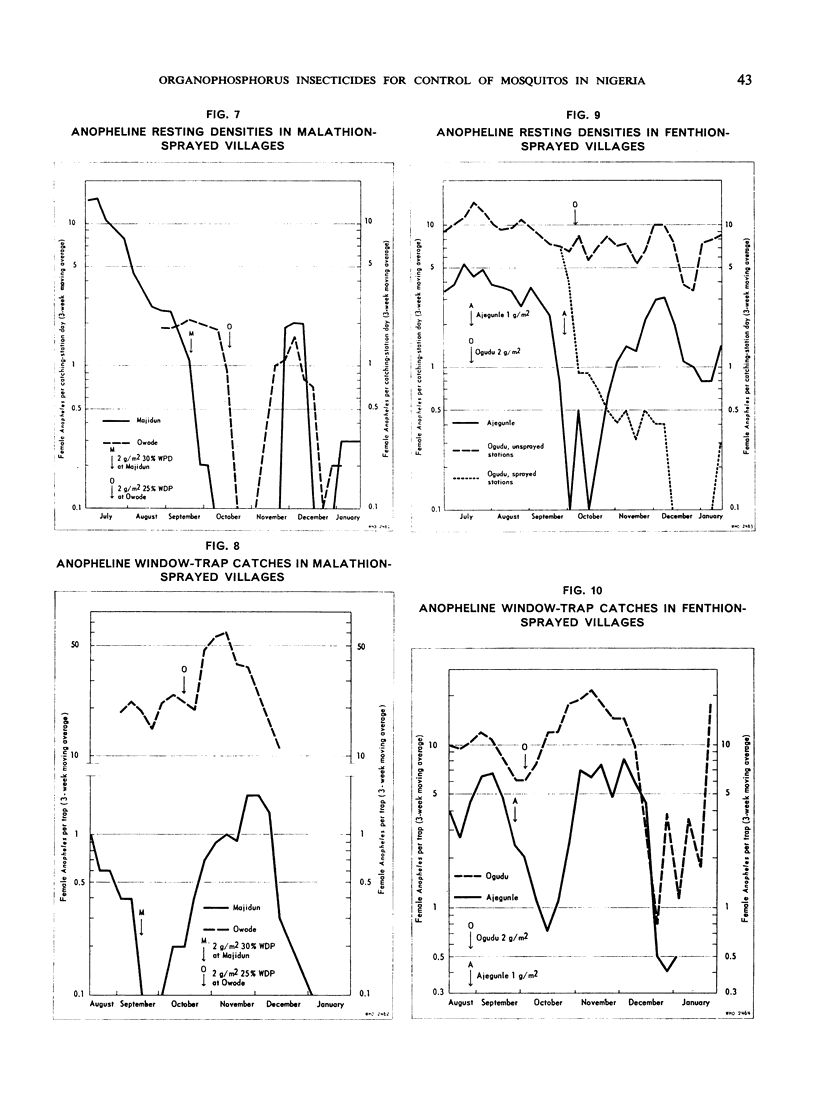
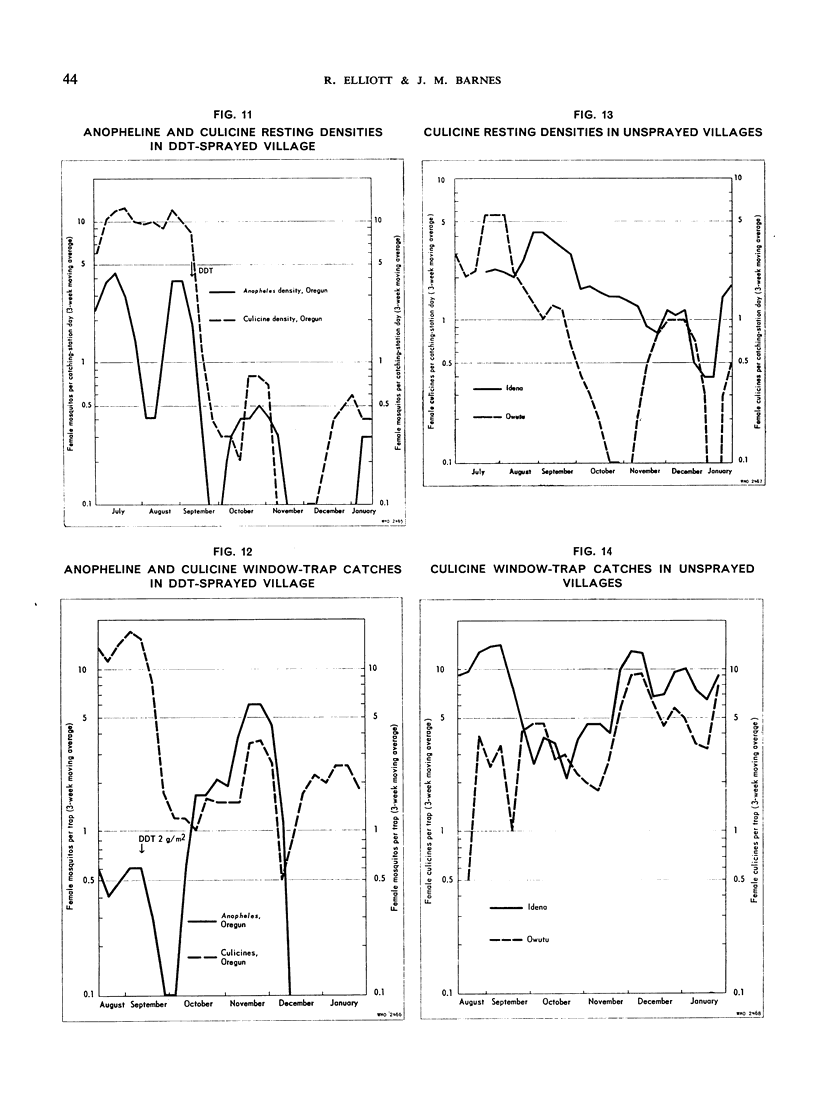
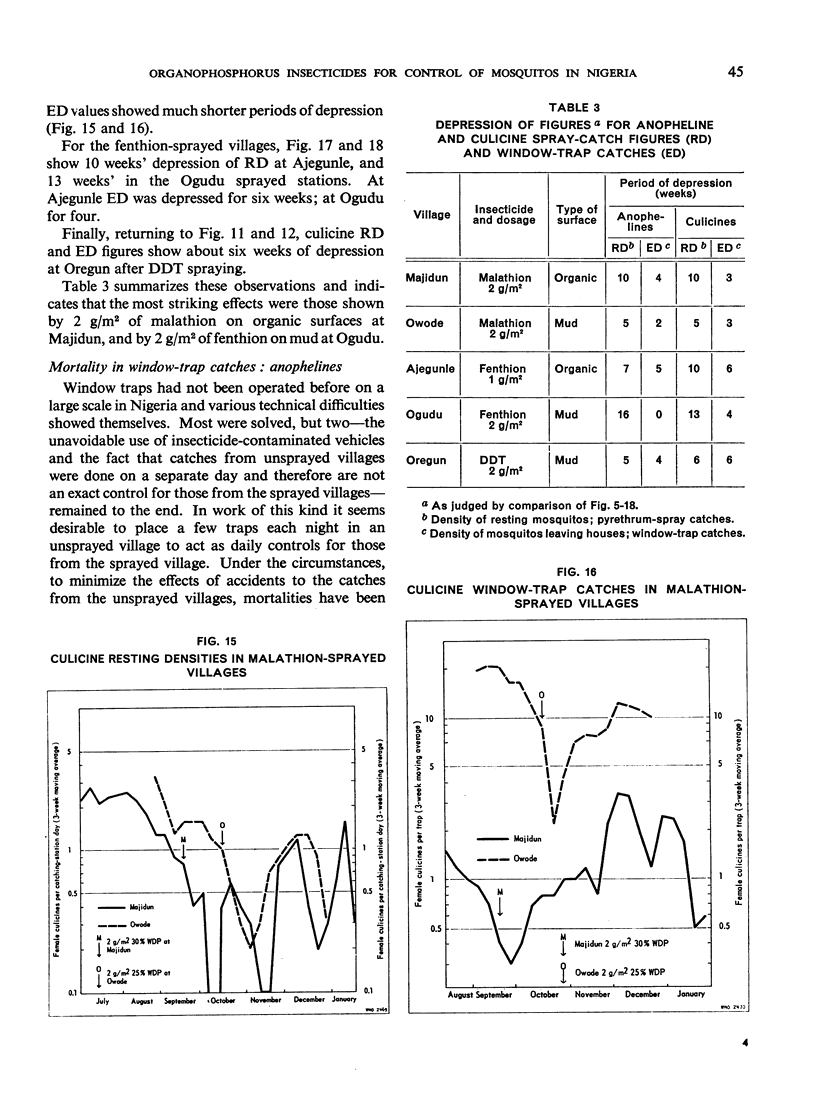
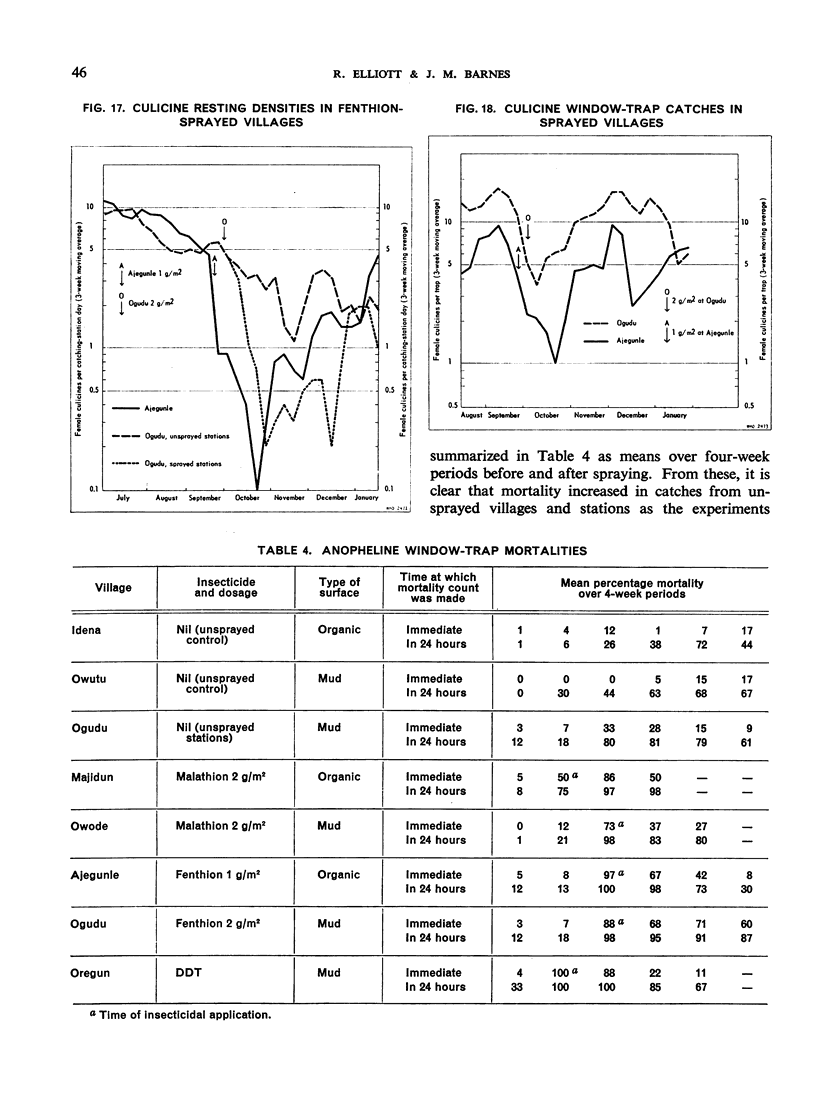
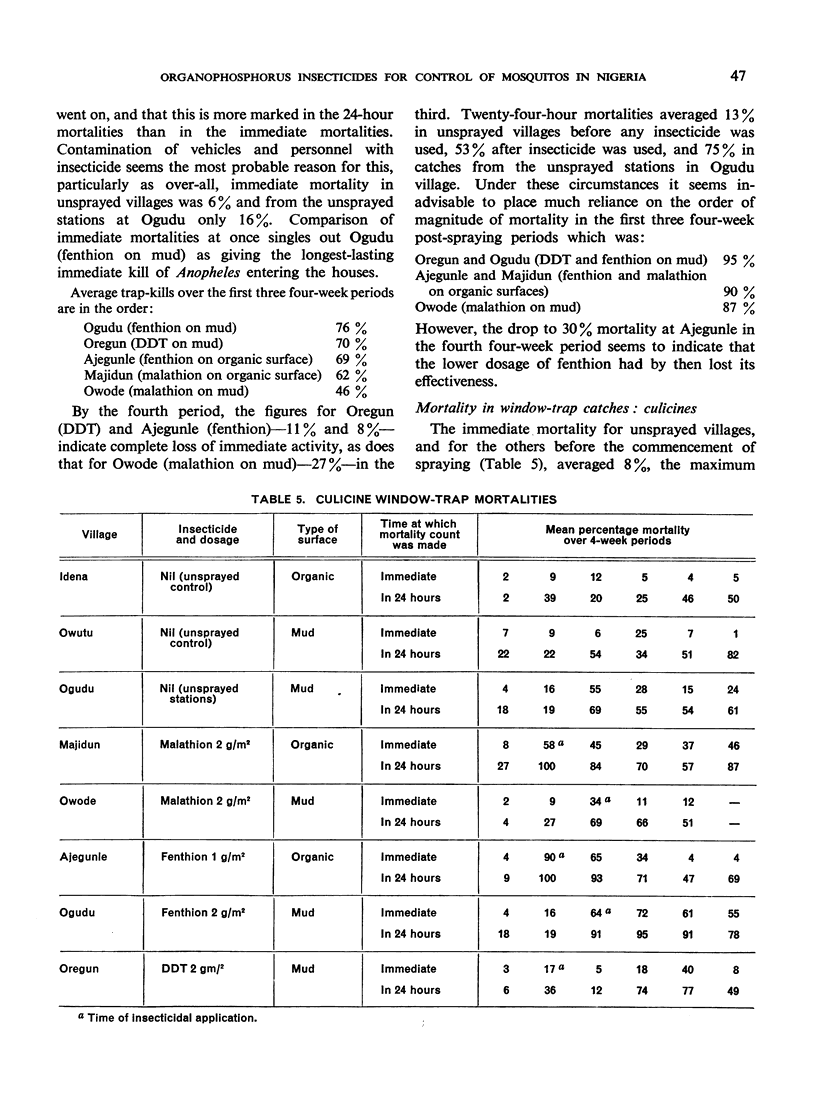
The greatest effect on both anophelines and culicines as determined by the pyrethrumspray technique was shown by fenthion on mud, followed by malathion and then fenthion on organic substrates, with malathion and DDT on mud as the least effective. As estimated by window-trap catches, the densities were most affected by fenthion on organic surfaces, least by fenthion on mud, and intermediately by DDT on mud and malathion on organic surfaces.
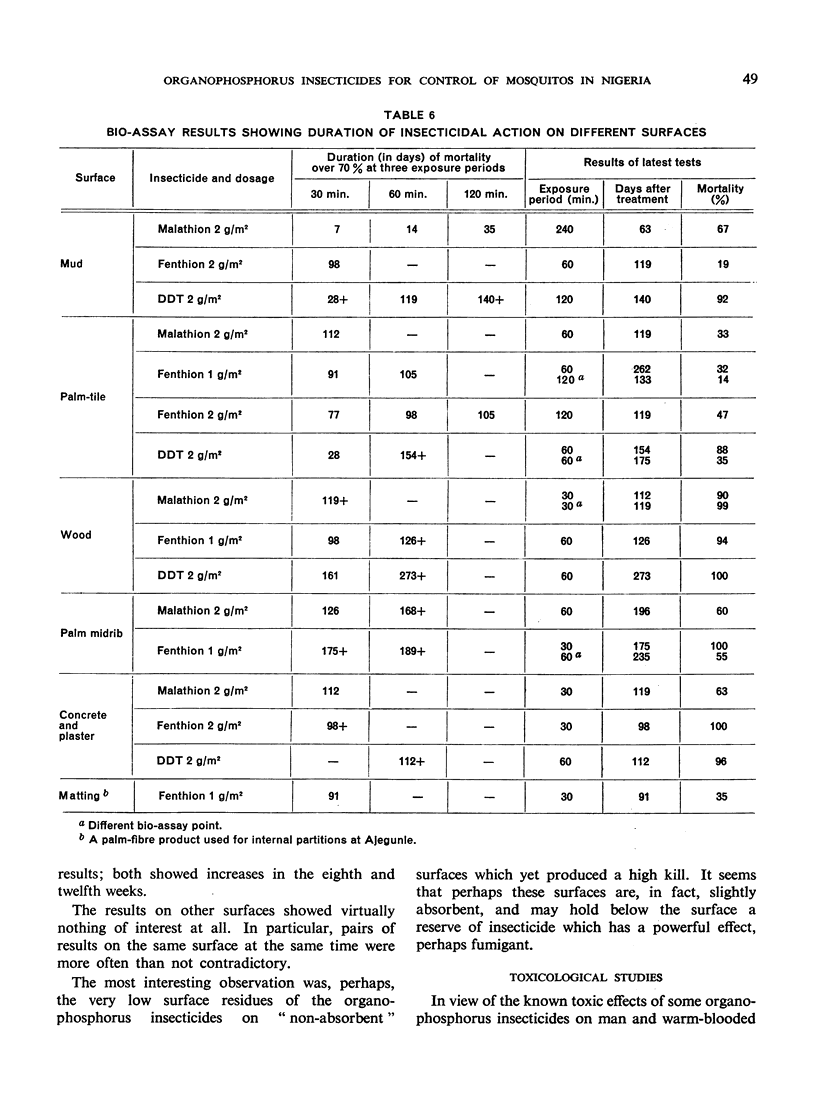
Anopheline mortality was greatest with fenthion on mud, followed by DDT on mud and malathion on organic surfaces, and least with malathion with mud. With culicines, fenthion was most active, and DDT least so, on both types of surface.
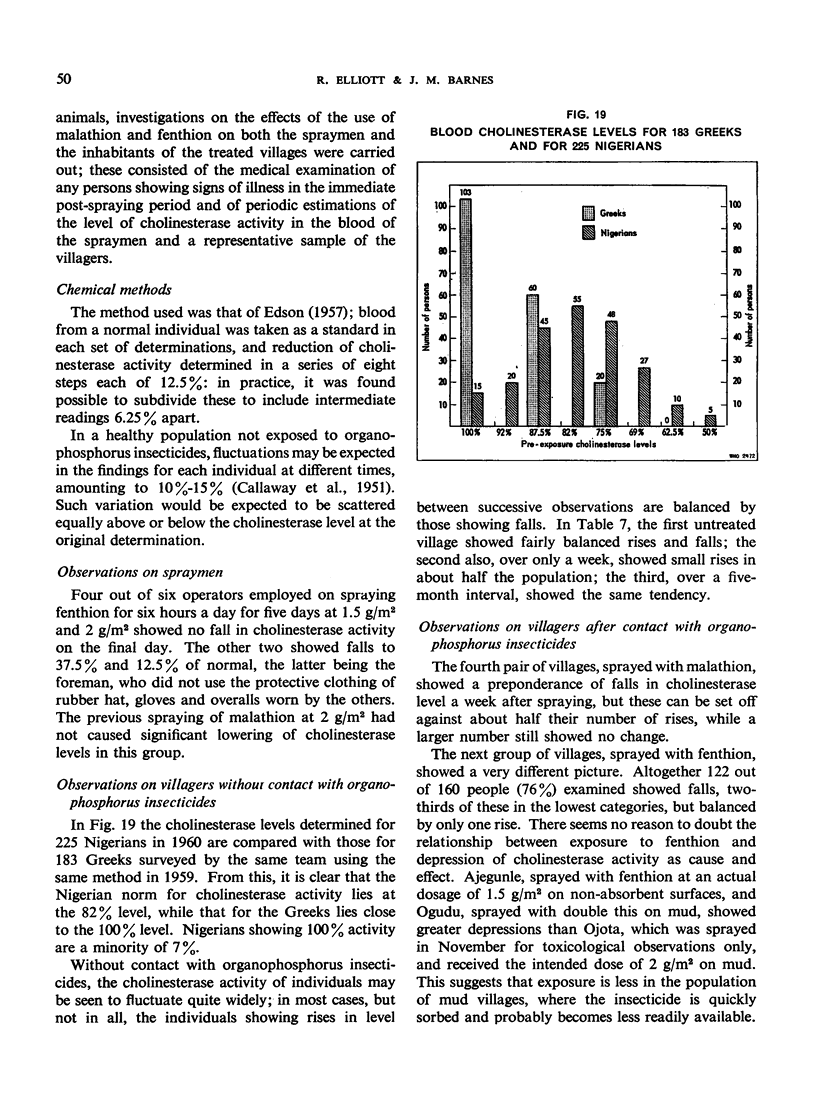
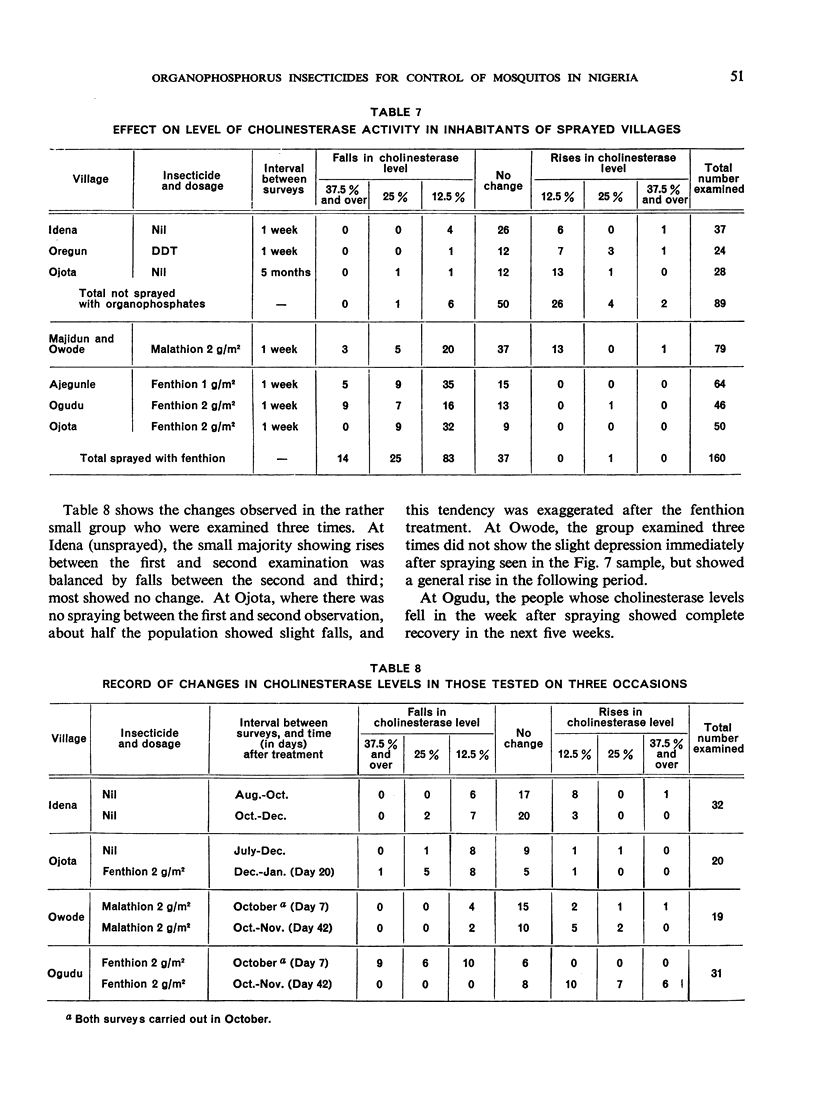
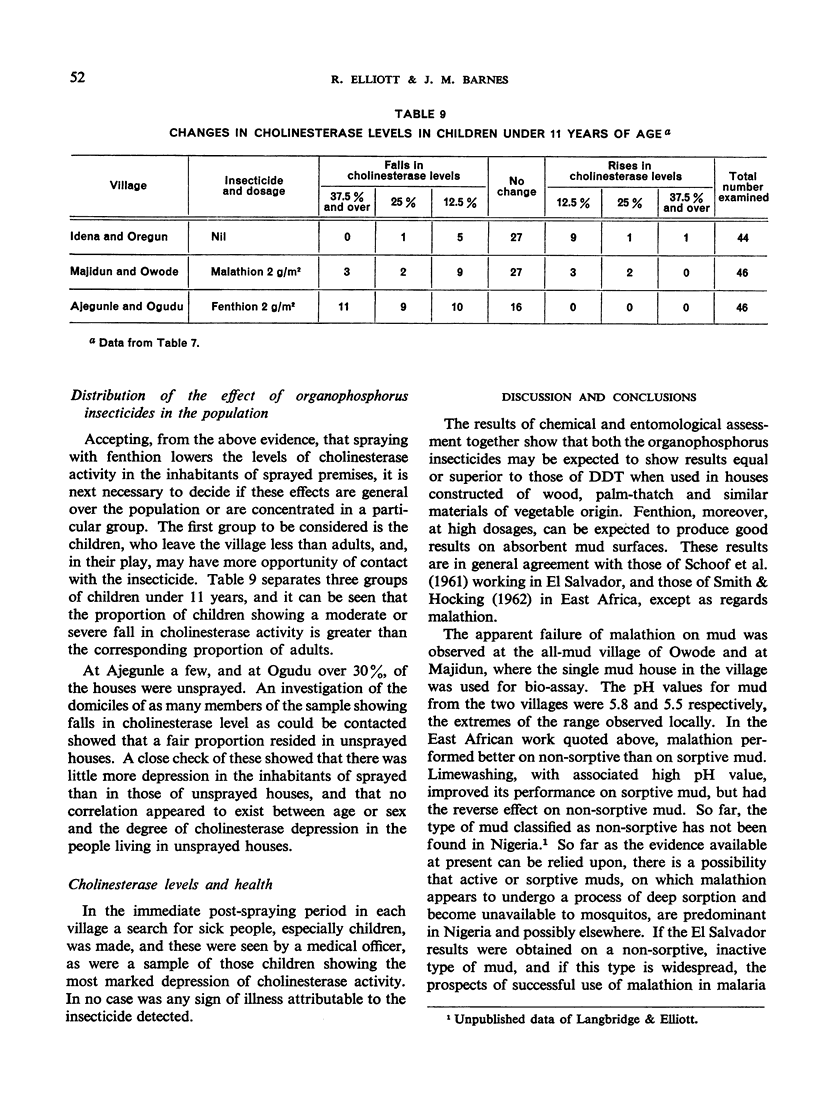
After spraying, the blood cholinesterase levels in the inhabitants of the sprayed villages fell quite markedly with fenthion and less so with malathion. The falls were temporary, being reversed within six weeks, were not confined to any ascertainable population group and were not associated with detectable illness. The authors stress that until more is known of the significance of these changes and of possible effects on health, the introduction of organophosphorus insecticides, especially fenthion, for malaria eradication should be carried out with caution.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- CALLAWAY S., DAVIES D. R., RUTLAND J. P. Blood cholinesterase levels and range of personal variation in a healthy adult population. Br Med J. 1951 Oct 6;2(4735):812–816. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.4735.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCHOOF H. F., MATHIS W., AUSTIN J. R. Field tests on the residual effectiveness of deposits of malathion and Bayer 29493 against resistant Anopheles albimaus in El Salvador. Bull World Health Organ. 1961;24:475–487. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH A., HOCKING K. S. Assessment of the residual toxicity to Anopheles gambiae of the organophosphorus insecticides Malathion and Baytex. Bull World Health Organ. 1962;27:231–238. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


