Abstract
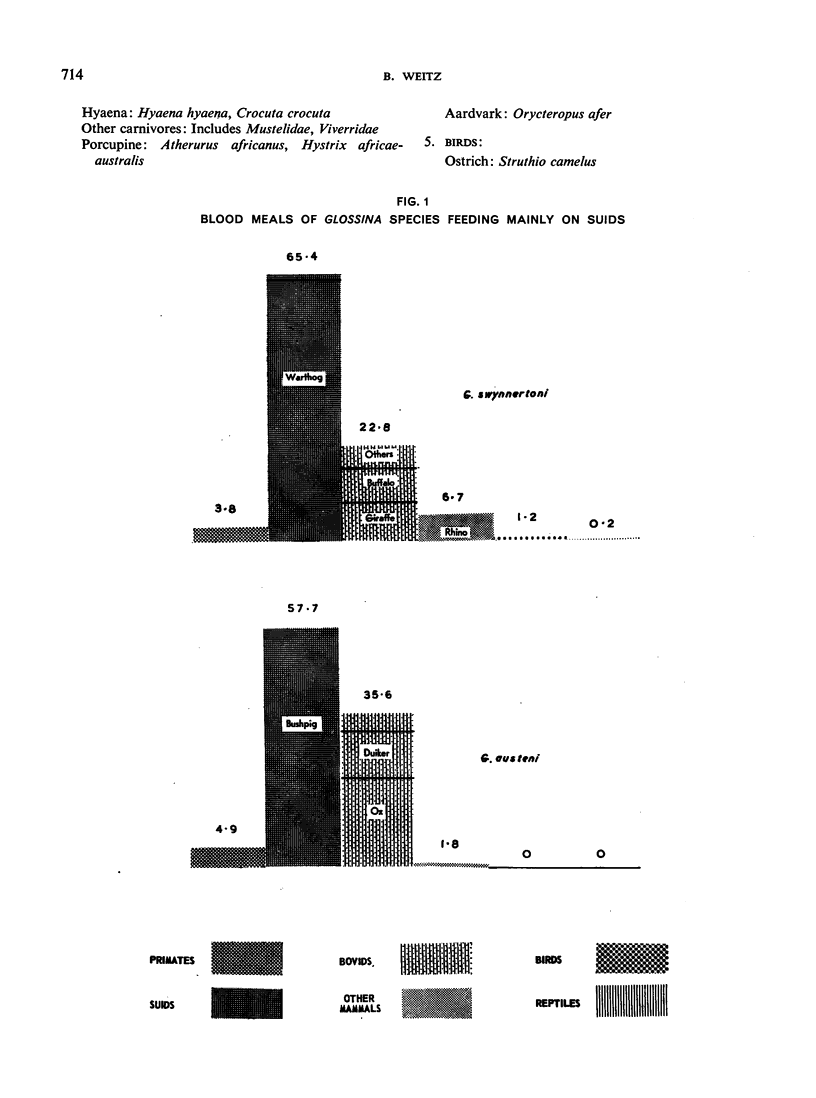
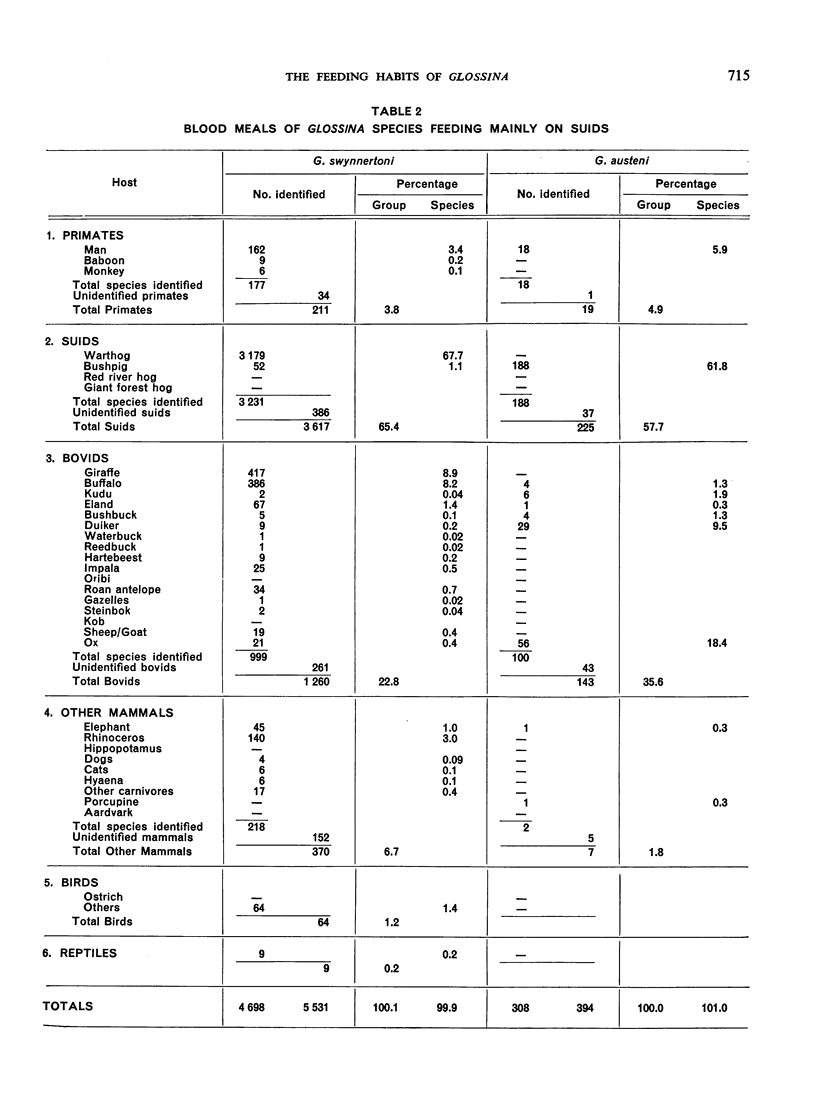
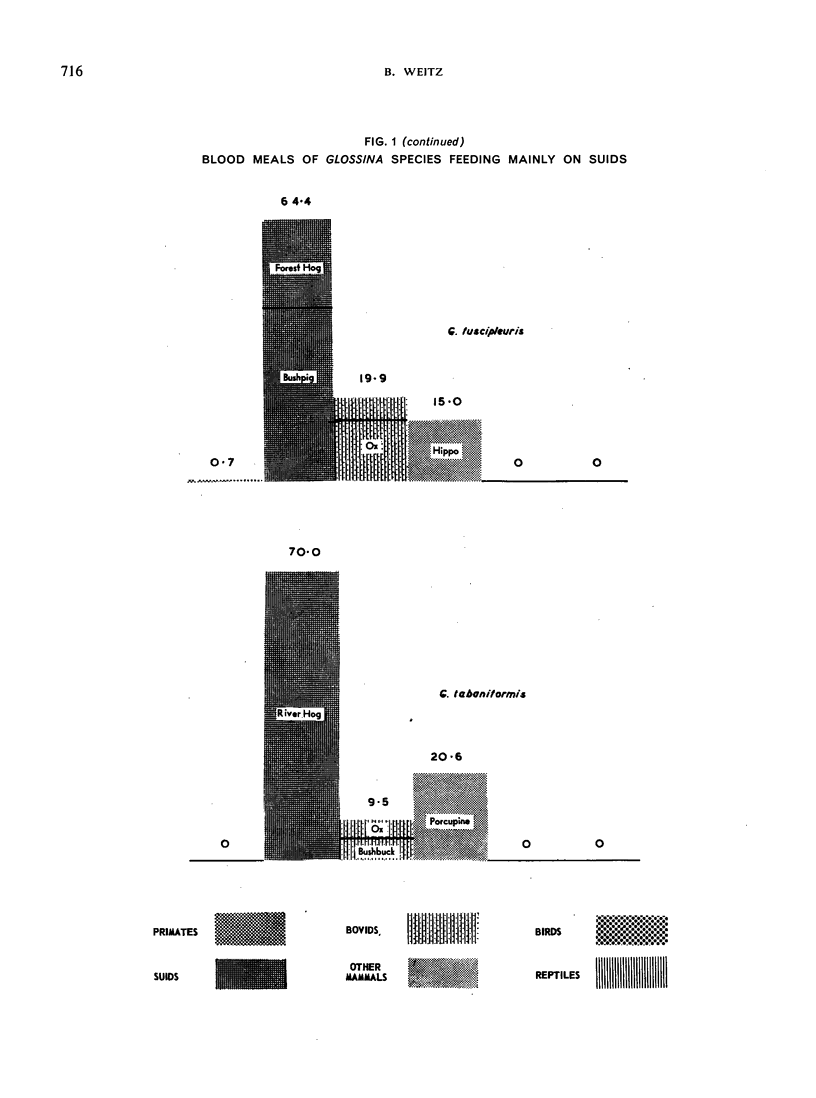
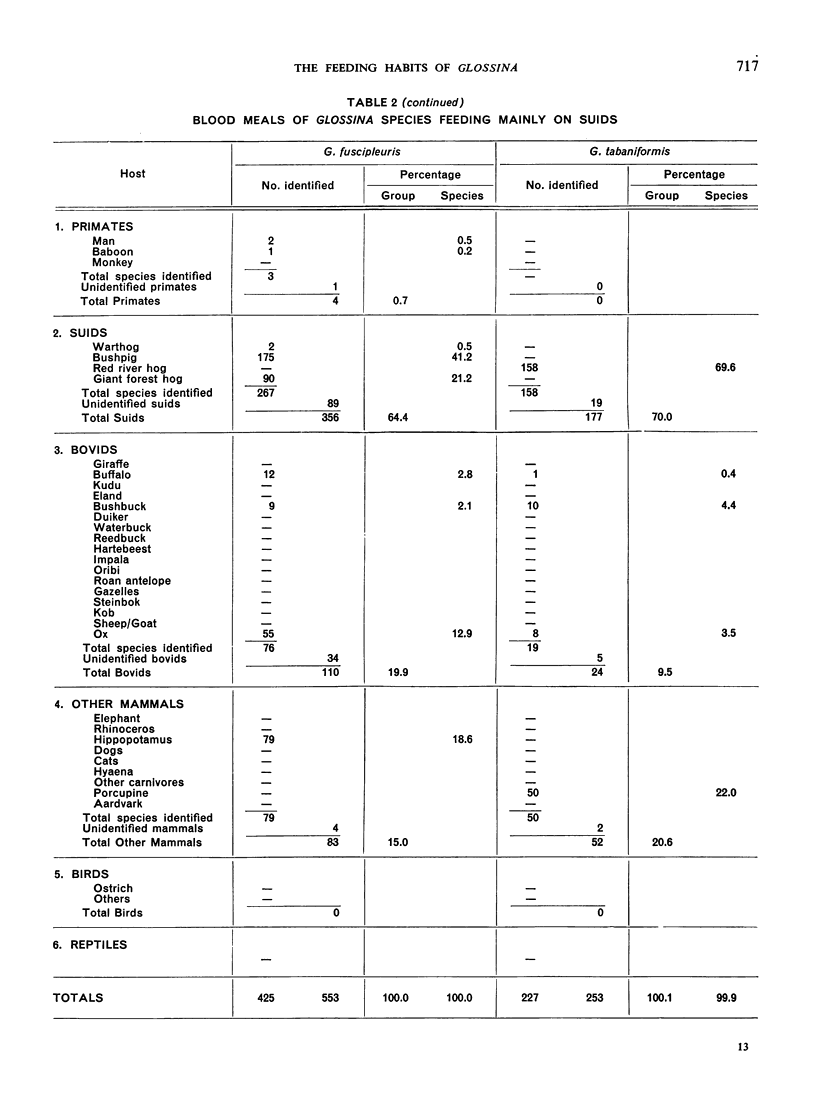
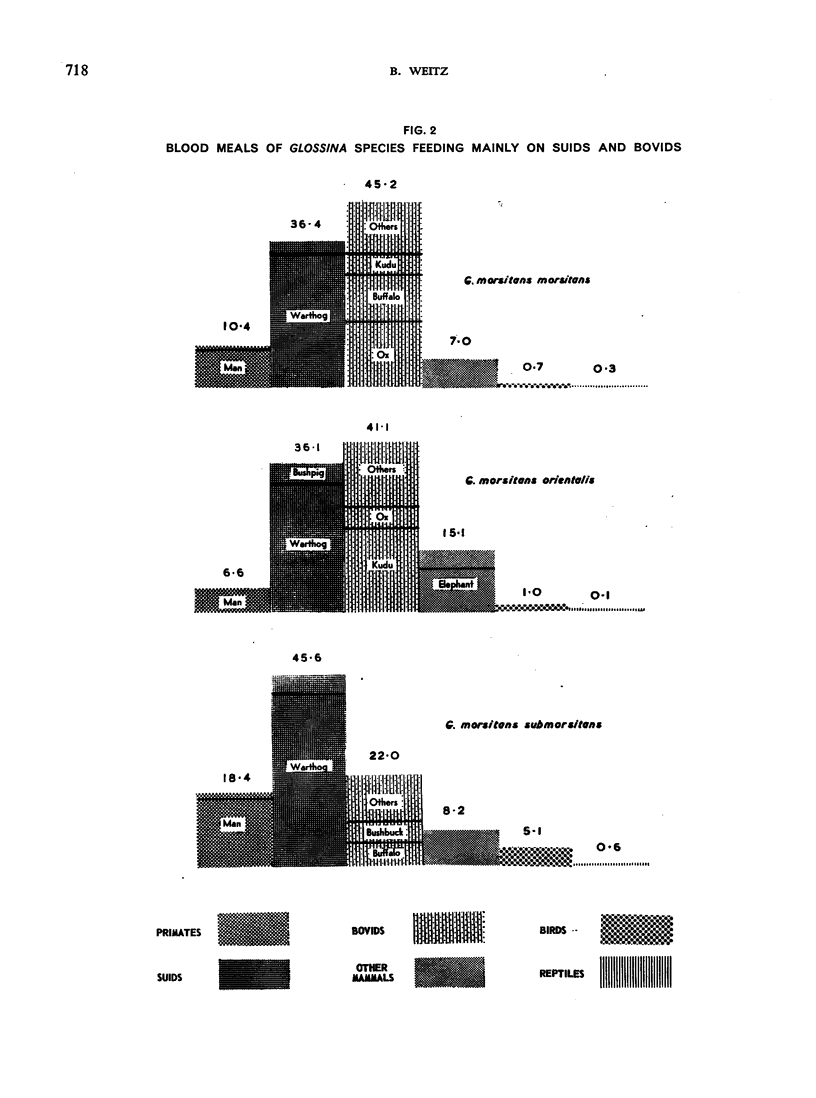
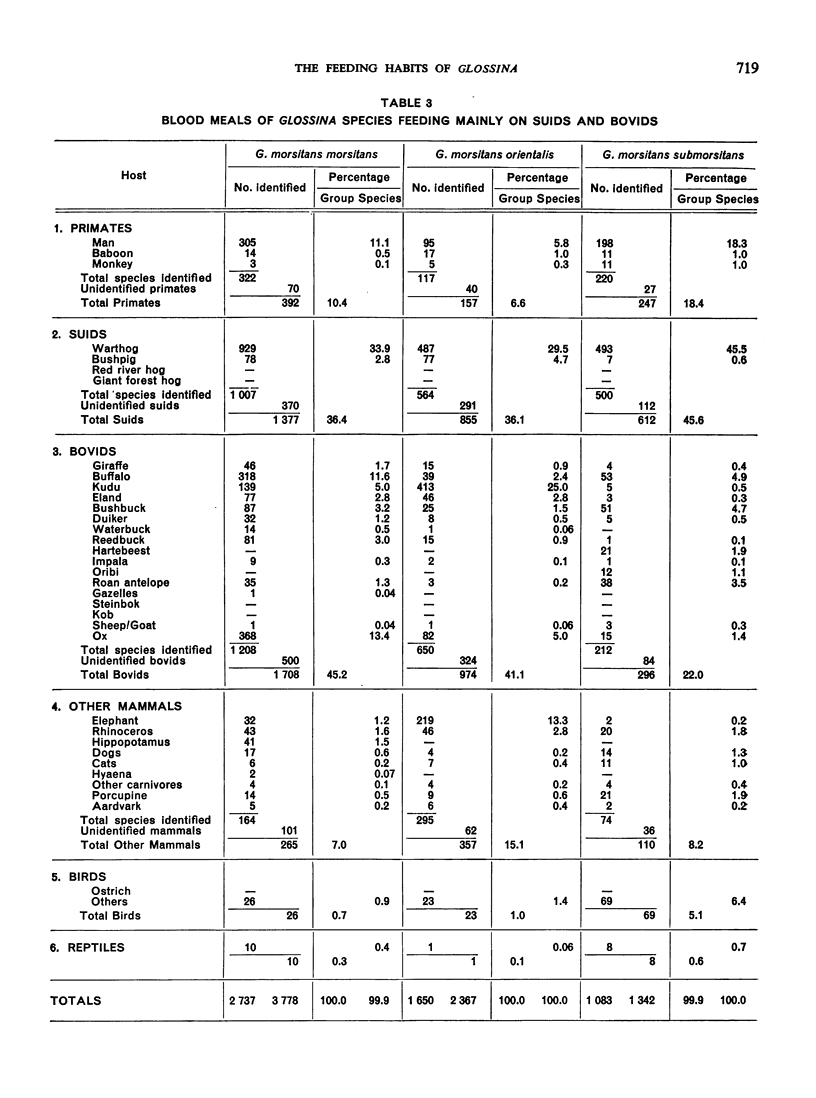
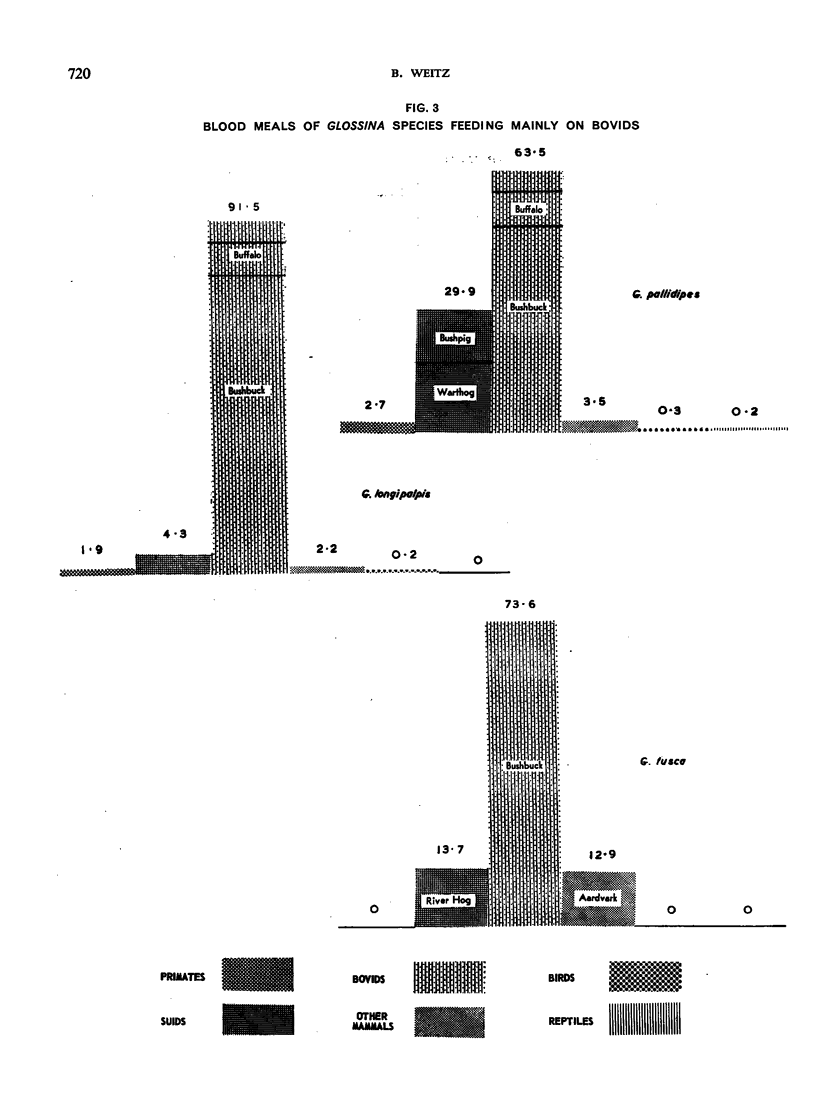
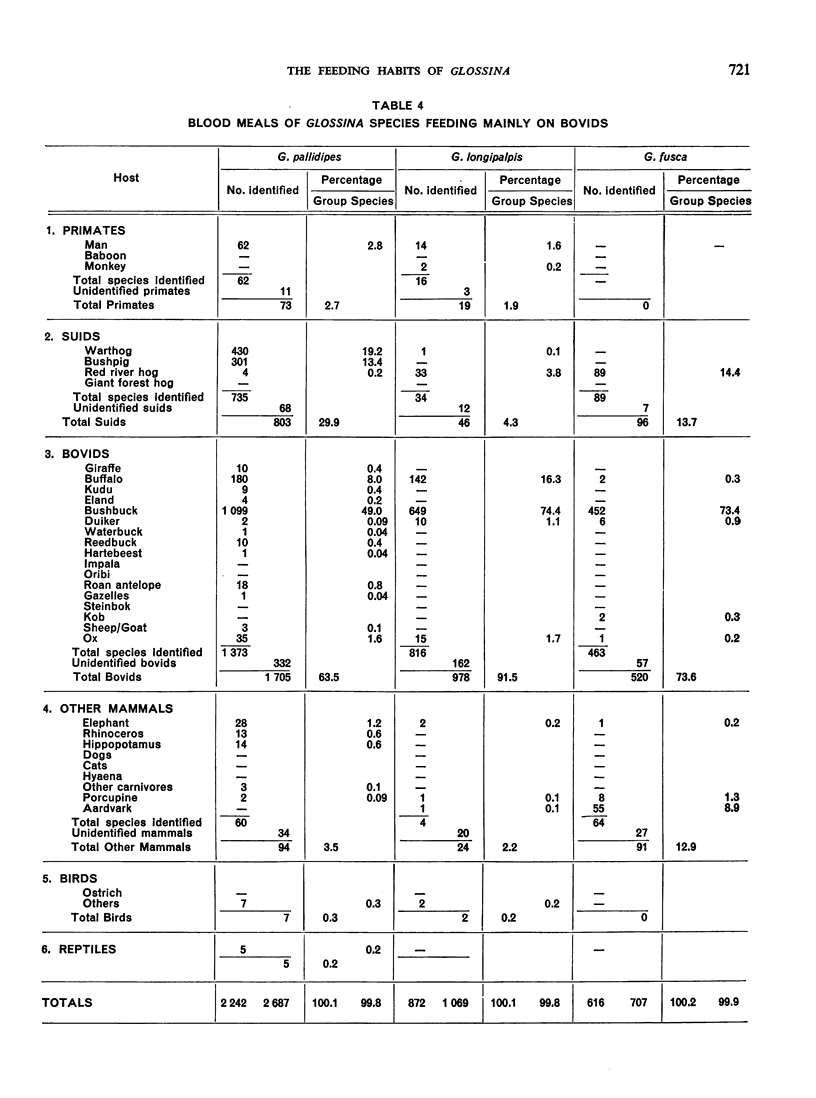
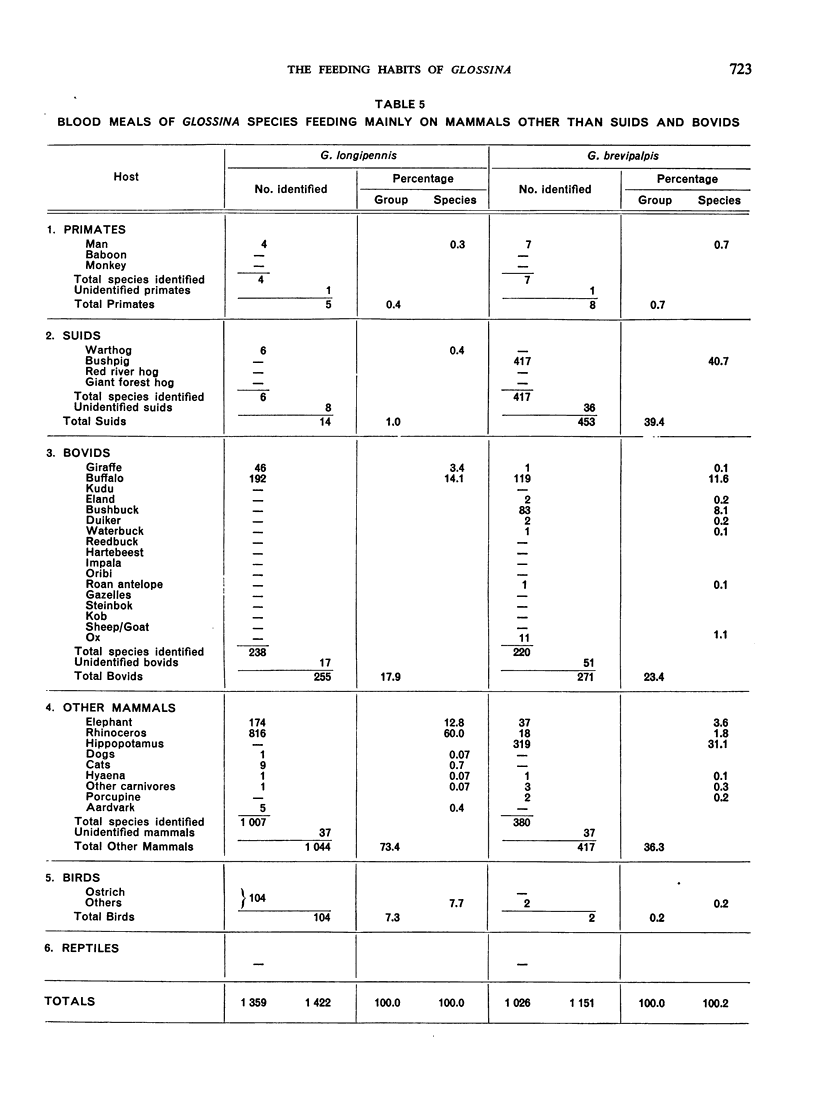
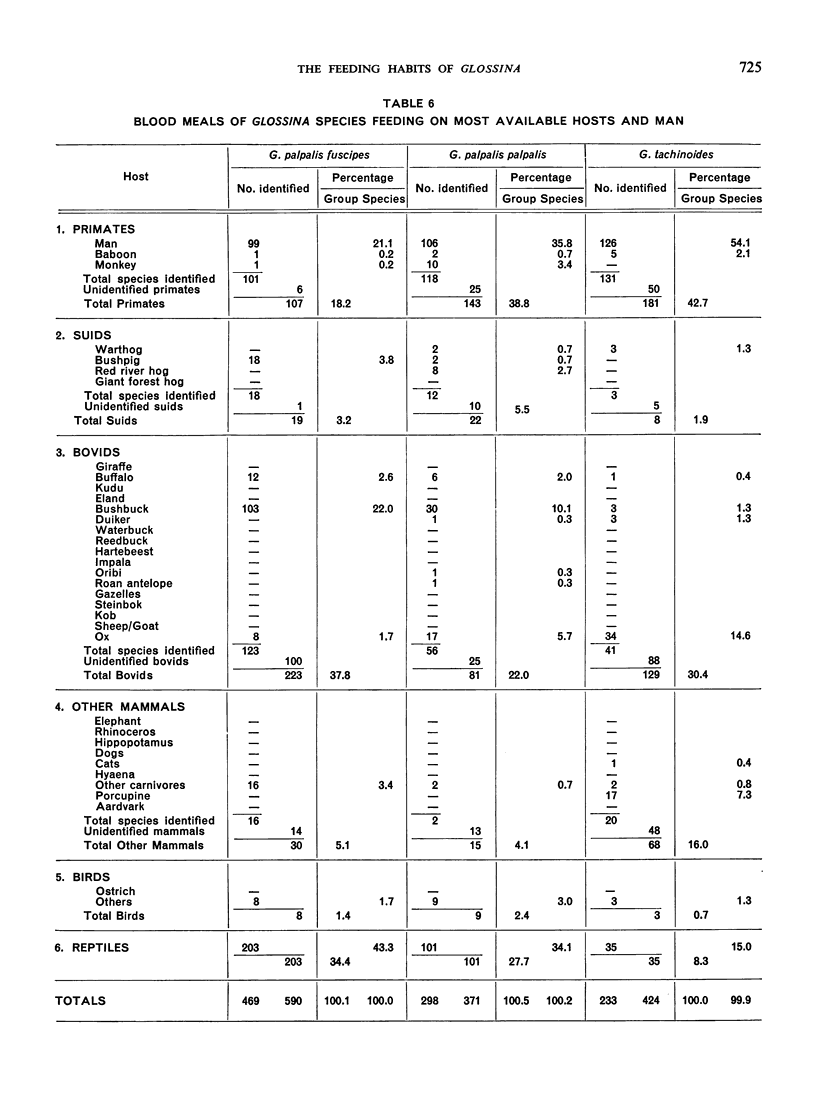
The feeding habits of 15 species of Glossina have been studied by the identification of their blood meals. Representative samples of the blood meals from each of these species of tsetse fly and from different habitats were collected and 22 640 blood meals were identified. The feeding patterns are characteristic for each species of tsetse fly and do not appear to depend entirely on the availability of different hosts, suggesting that the feeding habits of Glossina are genetically determined. However, a broad grouping can be made into five categories: species feeding mainly on suids, those feeding on suids and bovids, those feeding mainly on bovids, those feeding mainly on mammals other than suids and bovids, and those feeding on most available hosts and on man.
The possibility of control by selective elimination of the main hosts of these groups is discussed.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- GLASGOW J. P., WEITZ B. The natural hosts of some species of Glossina in East Africa. Trans R Soc Trop Med Hyg. 1956 Nov;50(6):593–612. doi: 10.1016/0035-9203(56)90065-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HEISCH R. B., McMAHON J. P., MANSONBAHR P. E. The isolation of Trypanosoma rhodesiense from a bushbuck. Br Med J. 1958 Nov 15;2(5106):1203–1204. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5106.1203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- JORDAN A. M., LEE-JONES F., WEITZ B. The natural hosts of tsetse flies in the forest belt of Nigeria and the Southern Cameroons. Ann Trop Med Parasitol. 1961 Jul;55:167–179. doi: 10.1080/00034983.1961.11686033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEITZ B. Identification of blood meals of blood-sucking arthropods. Bull World Health Organ. 1956;15(3-5):473–490. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEITZ B. The antigenicity of sera of man and animals in relation to the preparation of specific precipitating antisera. J Hyg (Lond) 1952 Sep;50(3):275–294. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400019616. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


