Abstract
Controlled field trials of two dried inactivated typhoid vaccines have been carried out in British Guiana and Yugoslavia under the sponsorship of the World Health Organization. This paper gives details of the methods of preparation of these vaccines in such a manner as to permit of replication by others.
Both vaccines were derived from the Ty 2 strain of Salmonella typhosa. For production of the acetone-inactivated vaccine, a portion of the surface agar growth of the Ty 2 strain was treated with acetone by the Landy method modified so that inactivation and handling were done in liquid suspensions rather than on a filter, and the vaccine was dried in the final containers. For the heat-phenol product, another portion of the same growth was processed by heating, the addition of 0.5% phenol and holding at room temperature for 72 hours followed by freeze-drying in the final containers. These vaccines are designed for use within a few hours of the addition of the reconstituting fluid.
Full text
PDF

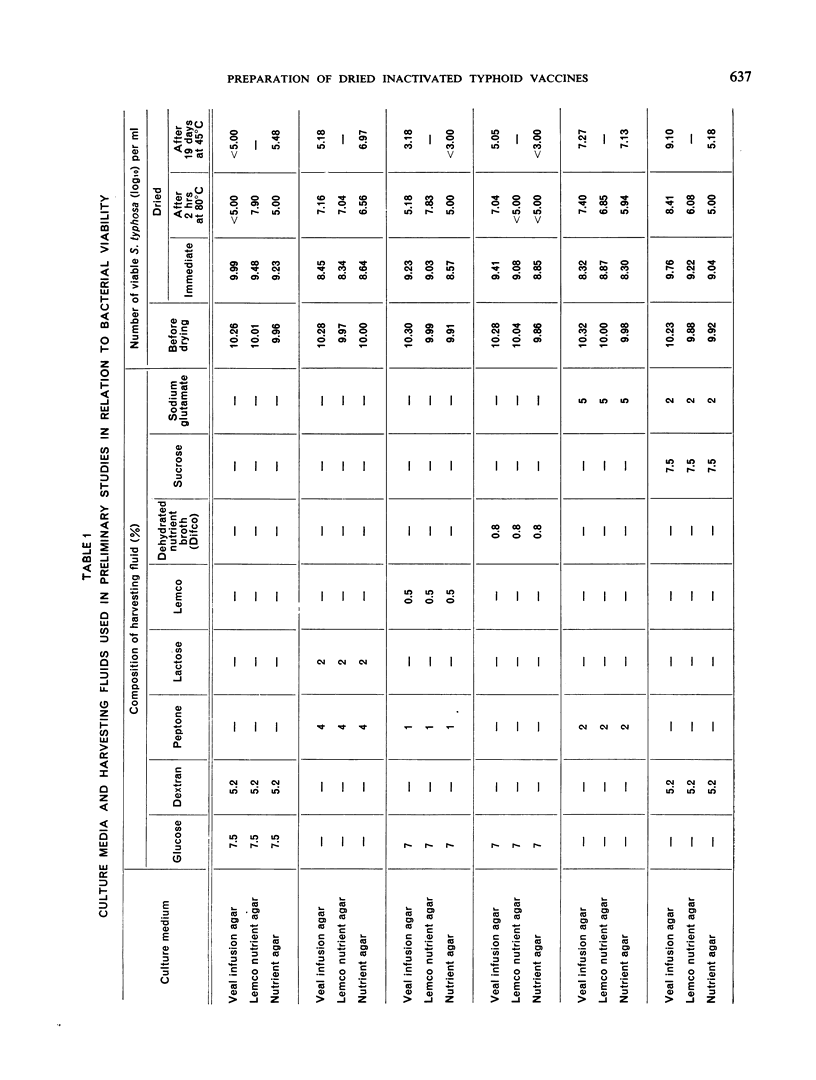









Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- LANDY M. Enhancement of the immunogenicity of typhoid vaccine by retention of the V1 antigen. Am J Hyg. 1953 Sep;58(2):148–164. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPAUN J. On the Vi antigen of Salmonella typhi. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1954;34(6):609–624. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1954.tb00308.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


