Abstract
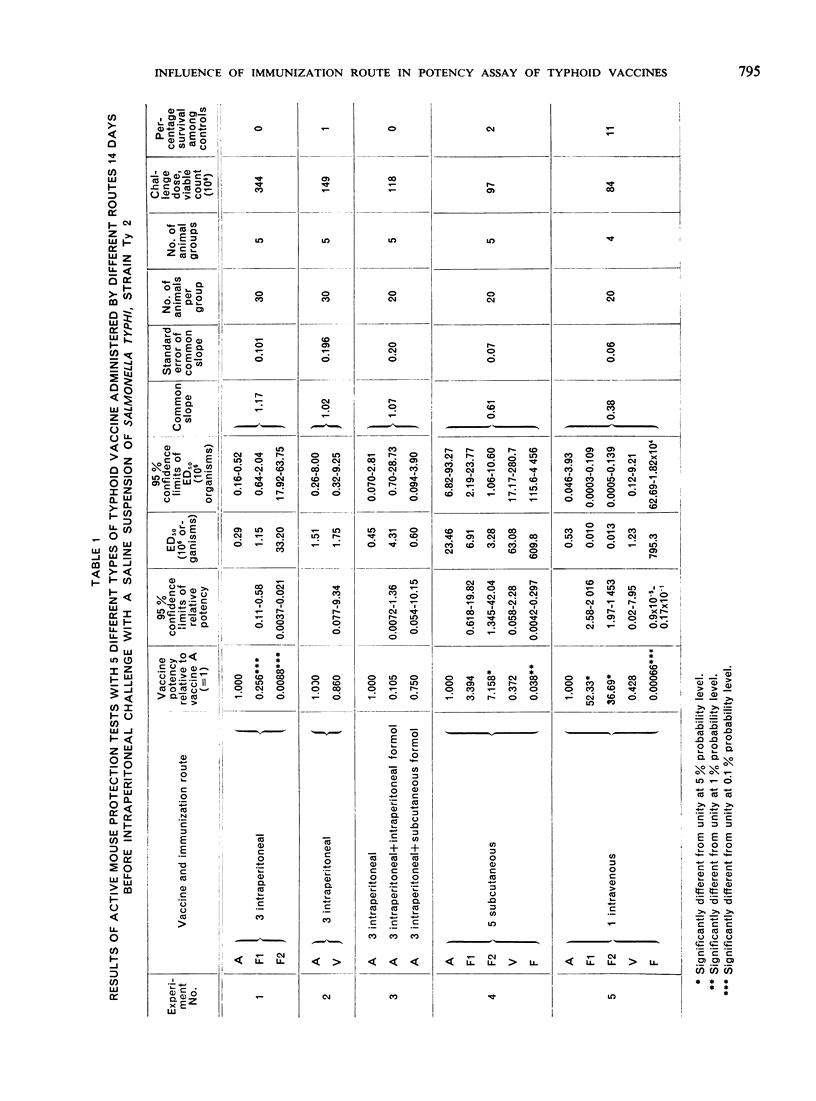
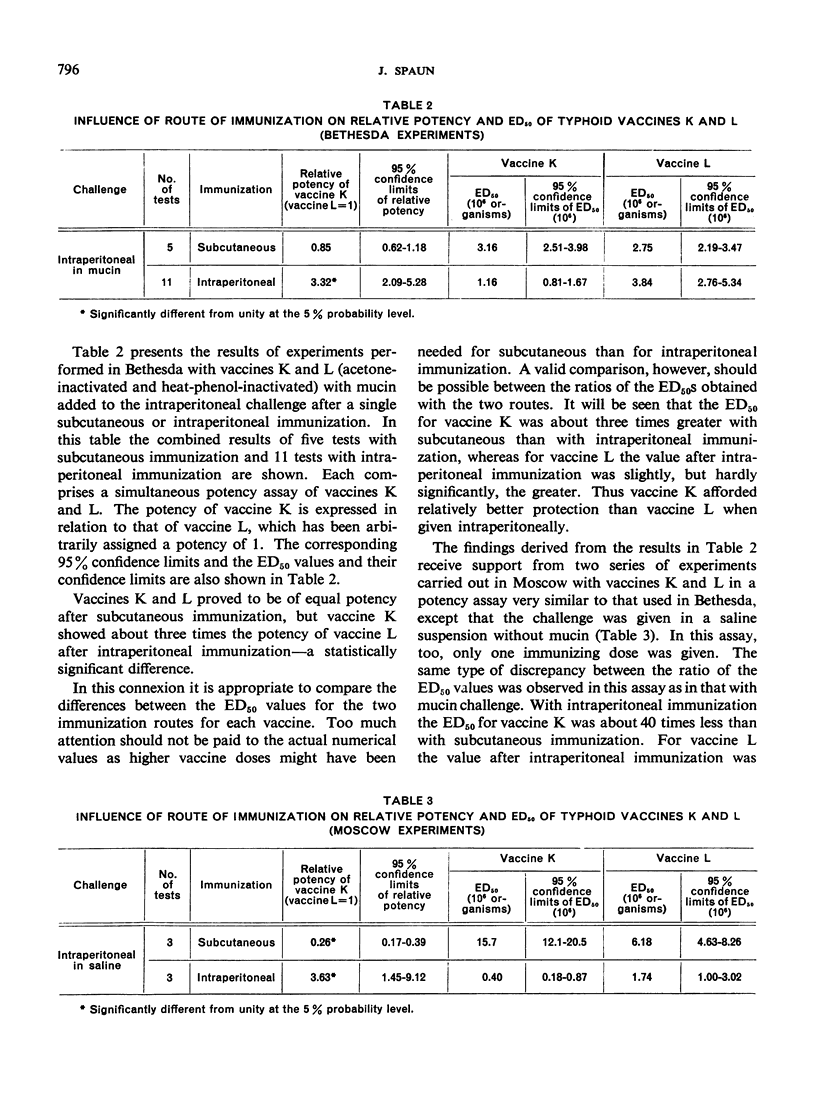
In order to determine the reasons for the differences found in the potencies of typhoid vaccines in the course of active mouse protection tests when immunization was done subcutaneously or intraperitoneally and followed by intraperitoneal challenge, a series of experiments were conducted which have suggested that intraperitoneal immunization and challenge may be adversely or favourably influenced by the presence of undetermined substances in certain types of vaccine.
Vaccines that prove least effective when administered intraperitoneally may affect the experimental animals in such a way that they do not respond optimally to the antigenic components of the vaccine, or some components of those vaccines may damage the peritoneum so that the animals are rendered more susceptible to the subsequent intraperitoneal challenge. On the other hand, it is possible that, where other vaccines show their greatest efficacy when administered intraperitoneally, this may be due to the presence of substances that enhance the vaccine's activity by inducing a non-specific local resistance in the peritoneum.
The author suggests lines along which these questions may be investigated.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- SPAUN J. Biological standardization of typhoid vaccines by antibody measurements. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1956;39(6):469–480. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1956.tb05074.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


