Abstract
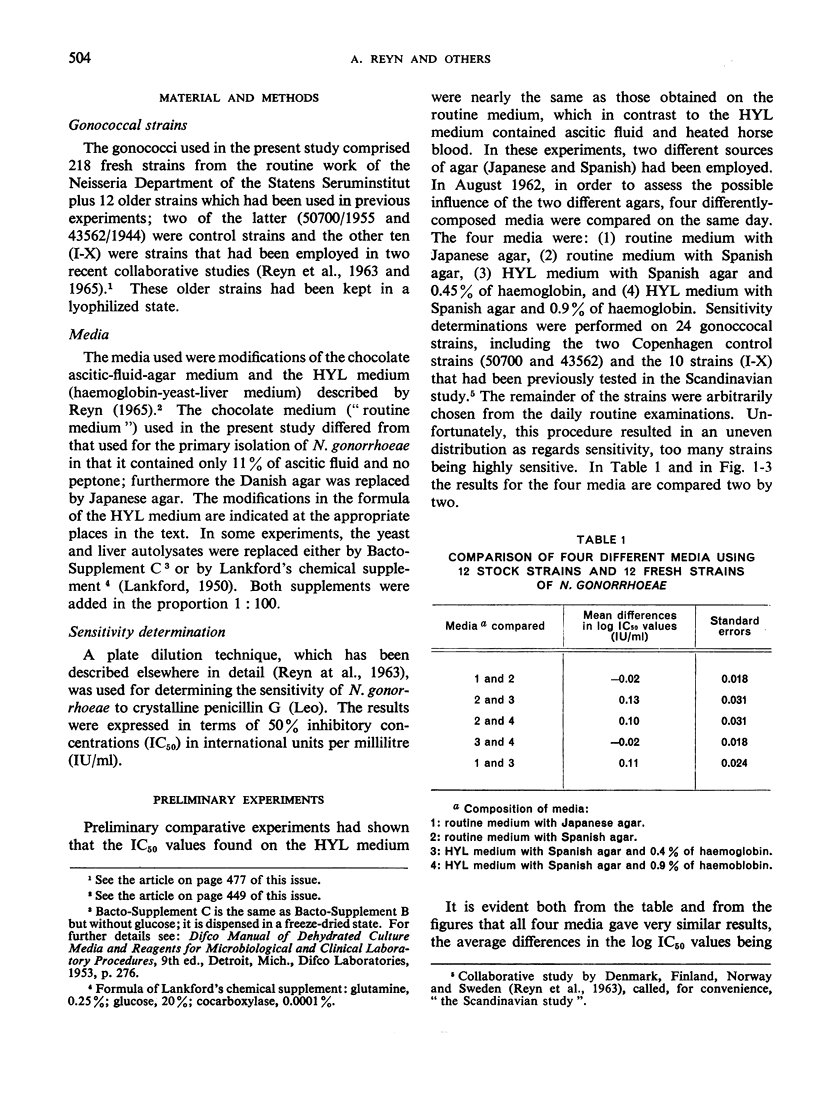
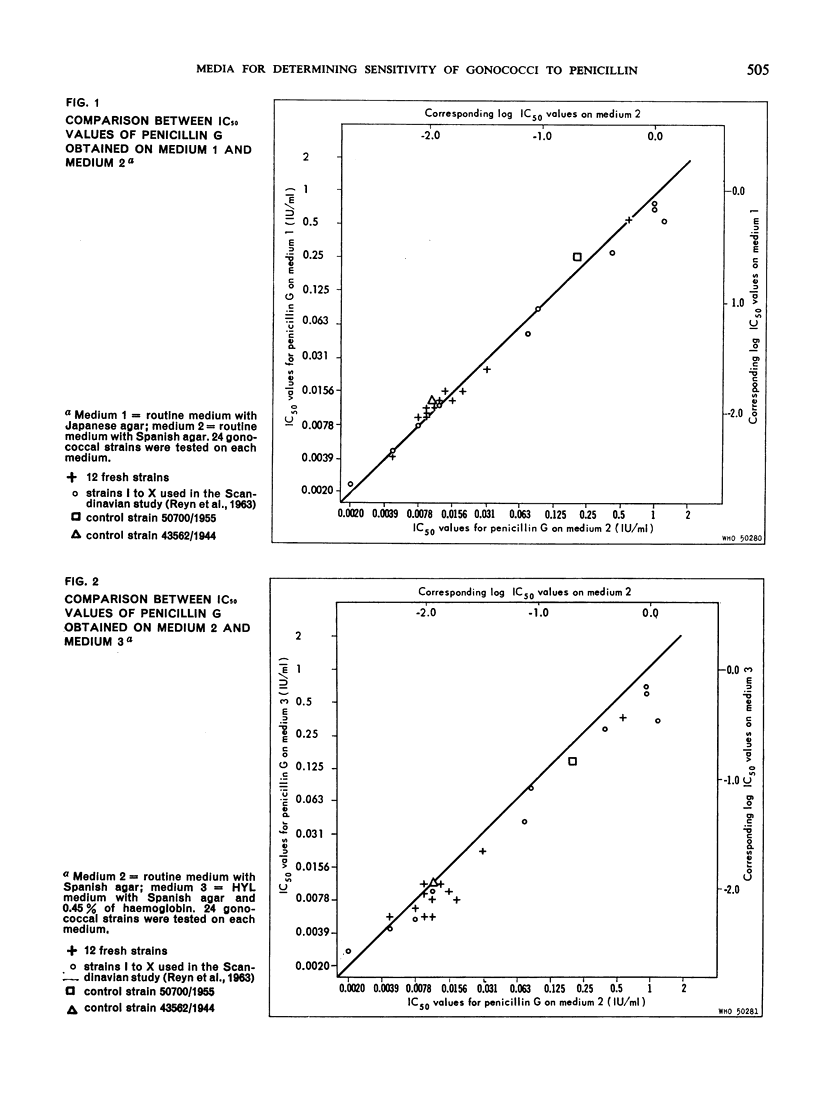
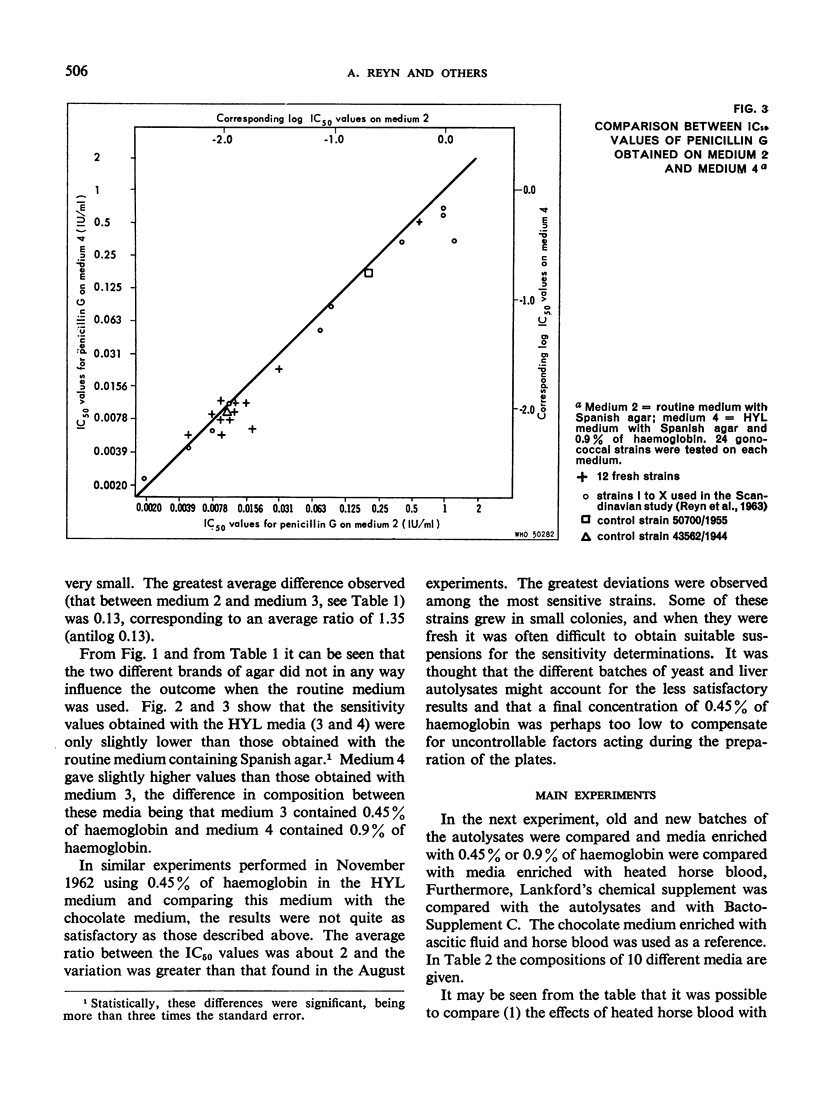
The increasing frequency of strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae with reduced sensitivity to penicillin is making it more and more important to determine the sensitivity of individual strains before and after treatment with this antibiotic. It was recently demonstrated that the concentrations of penicillin inhibitory to Neisseria gonorrhoea depend upon the medium employed. This important observation made it desirable to have available for interlaboratory comparisons a non-commercial reproducible medium which would support the growth of the vast majority of the gonococcal strains in circulation. Using a plate dilution procedure, various modifications of the HYL medium described elsewhere were compared with the routine medium for carrying out sensitivity determinations. Both stock and fresh strains of Neisseria gonorrhoeae were used in the experiments. The 50% inhibitory concentrations observed on the two media did not differ to any great extent, being only about 40% higher on the routine medium than on the HYL medium. The difference between the HYL medium and the routine medium was somewhat greater for the less sensitive strains than for the more sensitive strains. The variations in the difference from strain to strain were larger for the more sensitive fresh strains than for the less sensitive strains and the stock strains. This observation limits the value of a correction method employing, for example, three reference strains as a means of ensuring comparability between the results of different laboratories.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BOND J. M., BARBER M., LIGHTBOWN J. W., WATERWORTH P. M. A COMPARISON OF FOUR PHENOXYPENICILLINS. Br Med J. 1963 Oct 19;2(5363):956–961. doi: 10.1136/bmj.2.5363.956. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BUNN P., KNIGHT R. Problems in determining concentrations of newer penicillins in human serum. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1961 Mar;11:190–195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARPENTER C. M., BUCCA M. A. Evaluation of 12 media for the isolation of the gonococcus. Am J Syph Gonorrhea Vener Dis. 1949 Mar;33(2):164–176. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chow B. F., McKee C. M. INTERACTION BETWEEN CRYSTALLINE PENICILLIN AND HUMAN PLASMA PROTEINS. Science. 1945 Jan 19;101(2612):67–68. doi: 10.1126/science.101.2612.67. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GOUREVITCH A., HUNT G. A., LEIN J. Structure-activity relationships in a series of synthetic penicillins. Antibiot Chemother (Northfield) 1960 Feb;10:121–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LIGHTBOWN J. W., SULITZEANU D. The assay of penicillin in blood-serum using Sarcina lutea. Bull World Health Organ. 1957;17(4-5):553–567. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARNER I. L., LUND E. Examination of the penicillin concentration in electrophoretically seperated groups of serum protein. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1957;40(3):267–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLLER V., REYN A. A NEW SOLID MEDIUM FOR THE ISOLATION OF NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:471–476. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OEFF K., RUST S., SCHWARZ E., WEISE H. J. Zur Frage der Bindung von Penicillin an Serumeiweisskörper. Klin Wochenschr. 1955 May 1;33(17-18):419–421. doi: 10.1007/BF01467981. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A., BENTZON M. W., ERICSSON H. Comparative investigations of the sensitivity of N. gonorrhoeae to penicillin. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1963;57:235–255. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1963.tb03447.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A., BENTZON M. W., THAYER J. D., WILKINSON A. E. RESULTS OF COMPARATIVE EXPERIMENTS USING DIFFERENT METHODS FOR DETERMINING THE SENSITIVITY OF NEISSERIA GONORRHOEAE TO PENICILLIN G. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:477–502. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REYN A. LABORATORY DIAGNOSIS OF GONOCOCCAL INFECTIONS. Bull World Health Organ. 1965;32:449–469. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tompsett R., Shultz S., McDermott W. The Relation of Protein Binding to the Pharmacology and Antibacterial Activity of Penicillins X, G, Dihydro F, and K. J Bacteriol. 1947 May;53(5):581–595. doi: 10.1128/jb.53.5.581-595.1947. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


