Abstract
Since the discovery, some ten years ago, of the pathogenic effect of polioviruses on non-nervous-tissue cells, tissue-culture methods have come to be widely used in virological research. Through these improved techniques for studying viruses, a large number of new cytopathogenic agents have been isolated from the intestinal tract of man. Many of these agents have been obtained from persons suffering from polio-like disease, but others have been isolated from apparently normal persons. The term ”orphans” is used to designate those viruses which cannot definitely be associated with any recognized disease syndrome.
The existence of these enteric pathogenic human orphan (ECHO) viruses, and their association with clinical disease in certain cases, stimulated interest in their animal counter-parts, which might constitute a serious threat to both human and animal health. In this paper, the author reviews the information at present available on the occurrence of the so-called ”orphan” enteroviruses in monkeys, cattle, swine, and other animals in various parts of the world, and discusses the possible interrelationships of these animal viruses with each other and with the human enteroviruses.
Full text
PDF










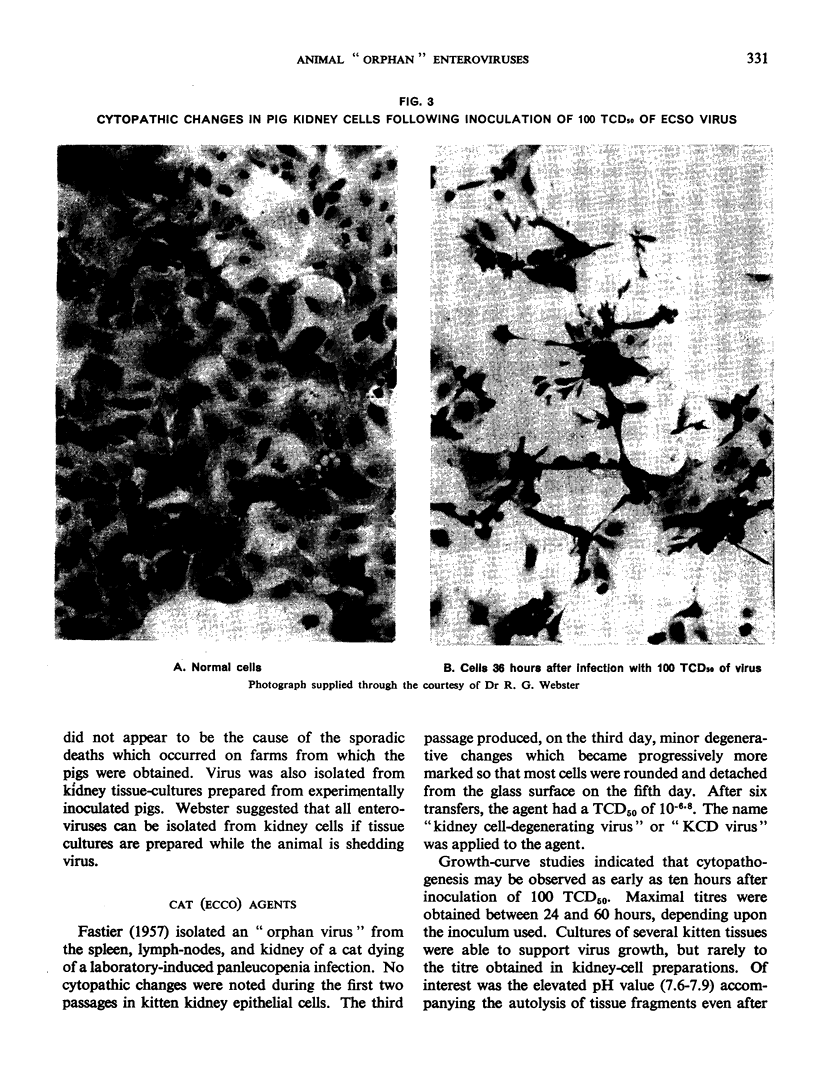






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ADAMS J. M. Comparative study of canine distemper and a respiratory disease of man. Pediatrics. 1953 Jan;11(1):15–27. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARTELL P., KLEIN M. Neutralizing antibody to viruses of poliomyelitis in sera of domestic animals. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1955 Dec;90(3):597–601. doi: 10.3181/00379727-90-22109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERAN G. W., WERDER A. A., WENNER H. A. Enteroviruses of swine. I. Their recognition, identification, and distribution in a herd of swine. Am J Vet Res. 1958 Jul;19(72):545–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BROWN L. V. Pathogenicity for rabbit kidney cell cultures of certain agents derived from normal monkey kidney tissue. I. Isolation and propagation. Am J Hyg. 1957 Mar;65(2):189–209. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119865. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CARLSTROM G. Neutralisation of canine-distemper virus by serum of patients convalescent from measles. Lancet. 1957 Aug 17;273(6990):344–344. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92241-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHANOCK R. M. Association of a new type of cytopathogenic myxovirus with infantile croup. J Exp Med. 1956 Oct 1;104(4):555–576. doi: 10.1084/jem.104.4.555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALE C. N., SONGER J. R. In vitro propagation of hog cholera virus. I. Method of cultivation and observation on color changes in the medium. Am J Vet Res. 1957 Apr;18(67):362–368. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DULBECCO R., VOGT M. Plaque formation and isolation of pure lines with poliomyelitis viruses. J Exp Med. 1954 Feb;99(2):167–182. doi: 10.1084/jem.99.2.167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dulbecco R. Production of Plaques in Monolayer Tissue Cultures by Single Particles of an Animal Virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1952 Aug;38(8):747–752. doi: 10.1073/pnas.38.8.747. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EICHENWALD H. F., ABABIO A., ARKY A. M., HARTMAN A. P. Epidemic diarrhea in premature and older infants caused by ECHO virus type 18. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Mar 29;166(13):1563–1566. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990130023005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENDERS J. F., PEEBLES T. C. Propagation in tissue cultures of cytopathogenic agents from patients with measles. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1954 Jun;86(2):277–286. doi: 10.3181/00379727-86-21073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enders J. F., Weller T. H., Robbins F. C. Cultivation of the Lansing Strain of Poliomyelitis Virus in Cultures of Various Human Embryonic Tissues. Science. 1949 Jan 28;109(2822):85–87. doi: 10.1126/science.109.2822.85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FASTIER L. B. A new feline virus isolated in tissue culture. Am J Vet Res. 1957 Apr;18(67):382–389. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GEAR J. Immunity to poliomyelitis. Ann Intern Med. 1952 Jul;37(1):1–22. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-37-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GELFAND H. M., FLYNN E. W., Jr Failure to find ECDO (enteric cytopathogenic dog orphan) viruses. Virology. 1958 Oct;6(2):568–570. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90104-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBERG H. S. The significance of the viral carrier state in tissue culture systems. Prog Med Virol. 1958;1:36–58. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GUERIN L. F., GUERIN M. M. Susceptibility of pig kidney tissue cultures to certain viruses. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1957 Nov;96(2):322–323. doi: 10.3181/00379727-96-23466. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAMMON W. M., YOHN D. S., LUDWIG E. H., PAVIA R. A., SATHER G. E., McCLOSKEY L. W. A study of certain nonpoliomyelitis and poliomyelitis enterovirus infections; clinical and serologic associations. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 Jun 7;167(6):727–735. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.72990230004011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HENLE W. Multiplication of influenza virus in the entodermal cells of the allantois of the chick embryo. Adv Virus Res. 1953;1:141–227. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60464-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOFFERT W. R., BATES M. E., CHEEVER F. S. Study of enteric viruses of simian origin. Am J Hyg. 1958 Jul;68(1):15–30. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HOTCHIN J. E., CINITS M. Lymphocytic choriomeningitis infection of mice as a model for the study of latent virus infection. Can J Microbiol. 1958 Apr;4(2):149–163. doi: 10.1139/m58-016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D., MELNICK J. L. Comparative susceptibility of kidney cells from different monkey species to enteric viruses (poliomyelitis, Coxsackie, and echo groups). J Immunol. 1957 Feb;78(2):137–146. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D., MELNICK J. L. Orphan viruses of man and animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):342–361. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35393.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D., MELNICK J. L. Plaque formation with poliomyelitis, Coxsackie, and orphan (echo) viruses in bottle cultures of monkey epithelial cells. Virology. 1955 Dec;1(5):533–535. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(55)90041-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HSIUNG G. D. Some distinctive biological characteristics of ECHO-10 virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1958 Nov;99(2):387–390. doi: 10.3181/00379727-99-24359. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULL R. N., MINNER J. R., MASCOLI C. C. New viral agents recovered from tissue cultures of monkey kidney cells. III. Recovery of additional agents both from cultures of monkey tissues and directly from tissues and excreta. Am J Hyg. 1958 Jul;68(1):31–44. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119947. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULL R. N., MINNER J. R. New viral agents recovered from tissue cultures of monkey kidney cells. II. Problems of isolation and identification. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Apr 19;67(8):413–423. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb46064.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HULL R. N., MINNER J. R., SMITH J. W. New viral agents recovered from tissue cultures of monkey kidney cells. I. Origin and properties of cytopathogenic agents S.V.1, S.V.2, S.V.4, S.V.5, S.V.6, S.V.11, S.V.12 and S.V.15. Am J Hyg. 1956 Mar;63(2):204–215. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a119804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KLEIN M. The significance of human antiviral neutralizing substances in animal sera. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):362–368. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35394.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOPROWSKI H. Counterparts of human viral disease in animals. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):369–382. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35395.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUNIN C. M., MINUSE E. The isolation in tissue culture, chick embryo and suckling mice of filtrable agents from healthy dairy cattle. J Immunol. 1958 Jan;80(1):1–11. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEE K. M., GILLESPIE J. H. Propagation of virus diarrhea virus of cattle in tissue culture. Am J Vet Res. 1957 Oct;18(69):952–953. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MADIN S. H., ANDRIESE P. C., DARBY N. B. The in vitro cultivation of tissues of domestic and laboratory animals. Am J Vet Res. 1957 Oct;18(69):932–941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MALHERBE H., HARWIN R. Seven viruses isolated from the vervet monkey. Br J Exp Pathol. 1957 Oct;38(5):539–541. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN J. D. Animal diseases: their relationship to the health of man. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1958 Jun 3;70(3):280–291. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1958.tb35387.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MELNICK J. L. Advances in the study of the enteroviruses. Prog Med Virol. 1958;1:59–105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOLL T., FINLAYSON A. V. Isolation of cytopathogenic viral agent from feces of cattle. Science. 1957 Aug 30;126(3270):401–402. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3270.401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOSCOVICI C., MAISEL J. Hemagglutination with bovine viruses. Virology. 1958 Dec;6(3):769–770. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90122-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OUDIN J. L'allotypie de certains antigènes protéidiques du sérum. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1956 May 23;242(21):2606–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRIER J. E., LEBEAU R. W. Cellular lesions in monkey kidney epithelium induced by adenoviruses and viruses of simian origin. Am J Pathol. 1958 Jul-Aug;34(4):789–801. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMOS-ALVAREZ M. Cytopathogenic enteric viruses associated with undifferentiated diarrheal syndromes in early childhood. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1957 Apr 19;67(8):326–331. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1957.tb46056.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMOS-ALVAREZ M., SABIN A. B. Enteropathogenic viruses and bacteria; role in summer diarrheal diseases of infancy and early childhood. J Am Med Assoc. 1958 May 10;167(2):147–156. doi: 10.1001/jama.1958.02990190001001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMOS-ALVAREZ M., SABIN A. B. Intestinal viral flora of healthy children demonstrable by monkey kidney tissue culture. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1956 Mar;46(3):295–299. doi: 10.2105/ajph.46.3.295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HARTLEY J. W., WATERMAN S., TURNER H. C., HUEBNER R. J. Cytopathogenic agent resembling human salivary gland virus recovered from tissue cultures of human adenoids. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1956 Jun;92(2):418–424. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ROWE W. P., HUEBNER R. J., GILMORE L. K., PARROTT R. H., WARD T. G. Isolation of a cytopathogenic agent from human adenoids undergoing spontaneous degeneration in tissue culture. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1953 Dec;84(3):570–573. doi: 10.3181/00379727-84-20714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMORI N., NOMURA S., MORIOKA Y., NAKANO M., KITAOKA M. Minute plaque mutant of type 2 poliovirus. Science. 1957 Nov 1;126(3279):924–925. doi: 10.1126/science.126.3279.924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMORI N., NOMURA S., NAKANO M., HENMI M., KITAOKA M. New mutation in polioviruses. Science. 1957 Jun 14;125(3259):1196–1198. doi: 10.1126/science.125.3259.1196. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEMORI N., NOMURA S., NAKANO M., MORIOKA Y., HENMI M., KITAOKA M. Mutation of polioviruses to resistance to neutralizing substances in normal bovine sera. Virology. 1958 Feb;5(1):30–55. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(58)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Theiler M. SPONTANEOUS ENCEPHALOMYELITIS OF MICE, A NEW VIRUS DISEASE. J Exp Med. 1937 Apr 30;65(5):705–719. doi: 10.1084/jem.65.5.705. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub E. A FILTERABLE VIRUS RECOVERED FROM WHITE MICE. Science. 1935 Mar 22;81(2099):298–299. doi: 10.1126/science.81.2099.298. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- YORK C. J., BAKER J. A. A new member of the psittacosis-lymphogranuloma group of viruses that causes infection in calves. J Exp Med. 1951 Jun;93(6):587–604. doi: 10.1084/jem.93.6.587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]