Abstract
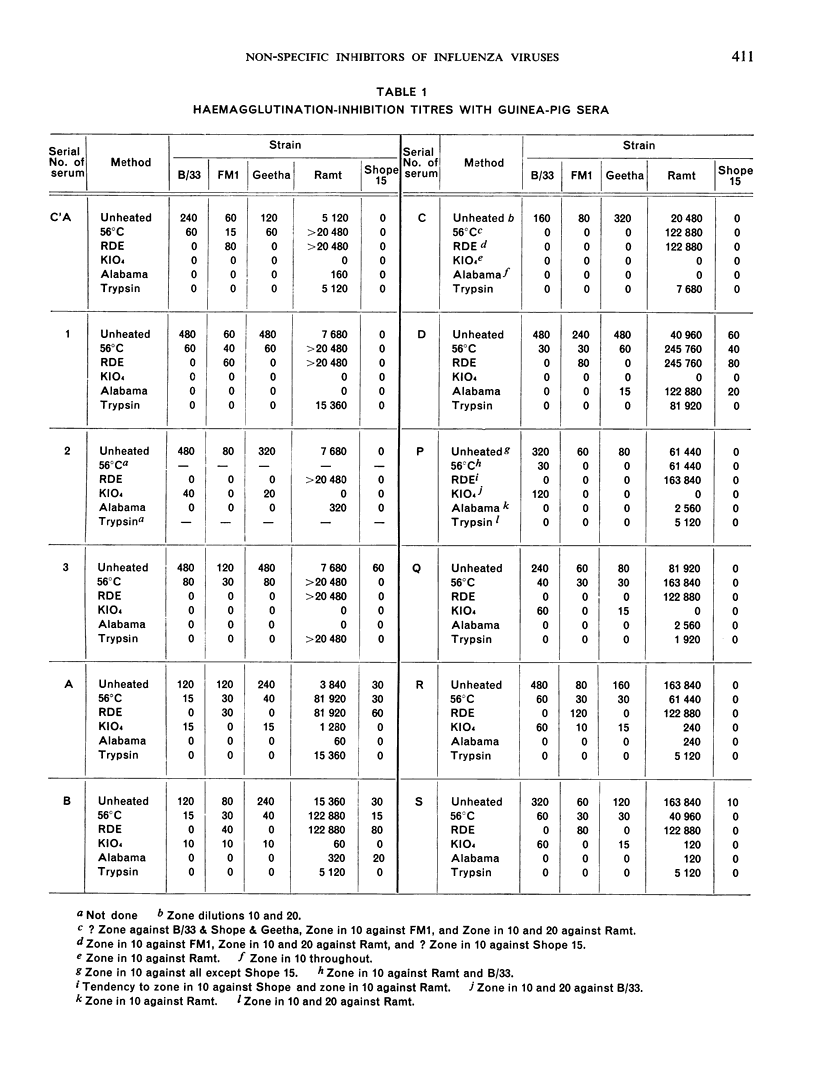
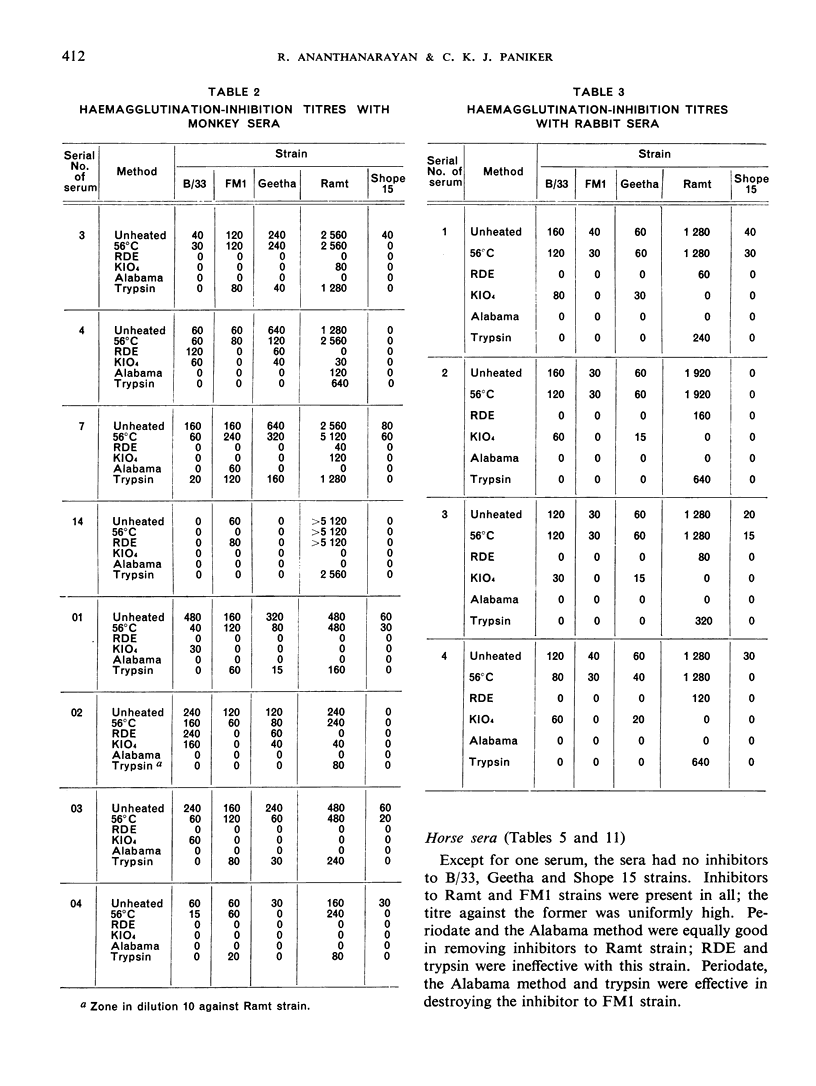
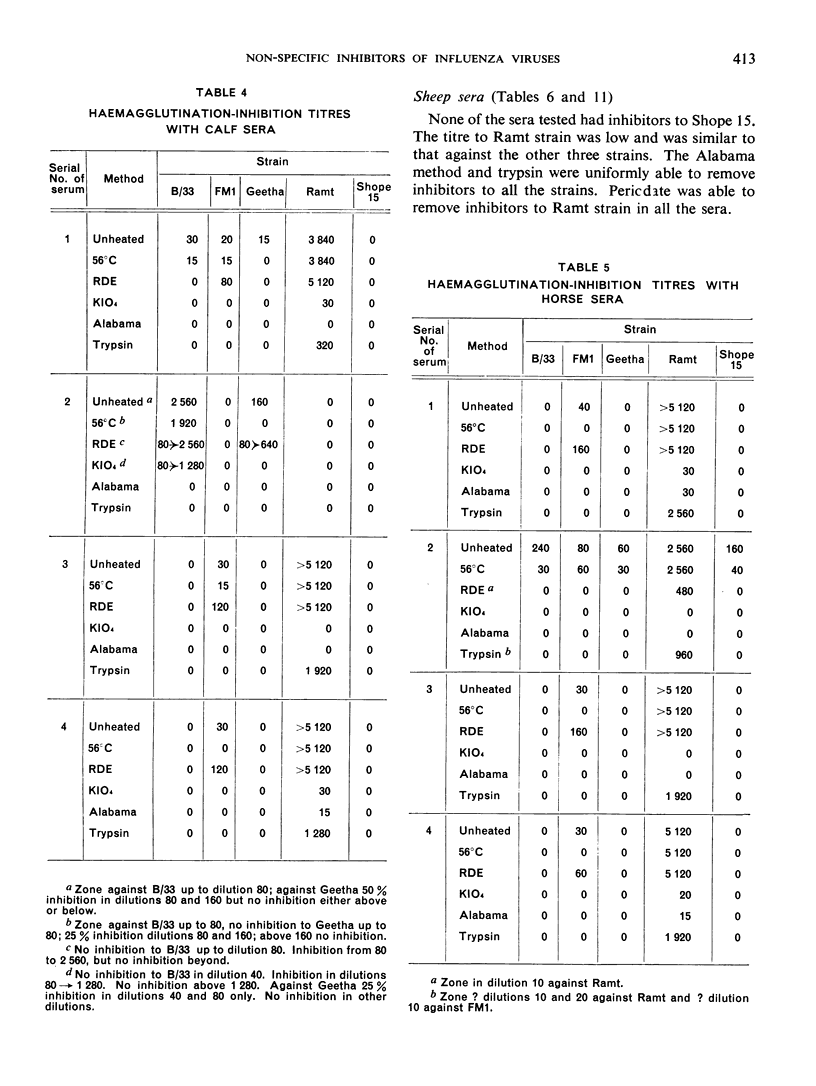
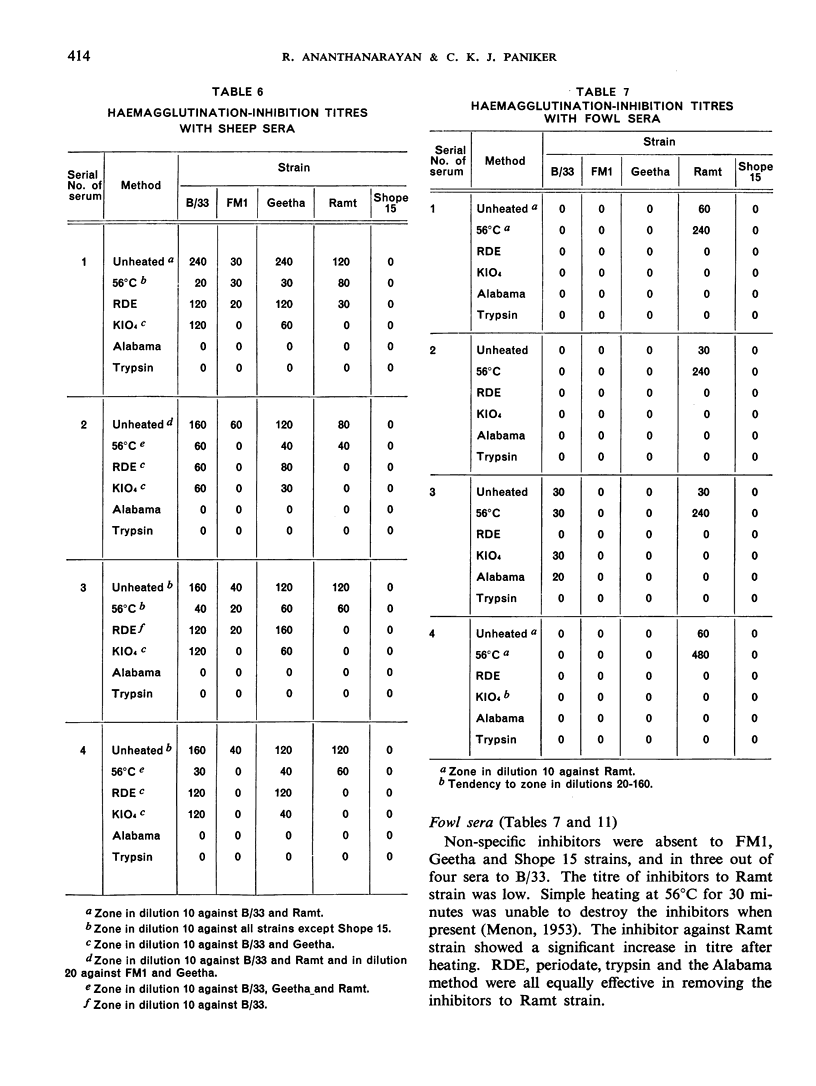
The presence of non-specific inhibitors in immune influenza sera may falsify the antibody pattern as shown by the haemagglutination-inhibition test, and it is consequently often necessary to pre-treat sera in order to inactivate these inhibitors. A number of different methods are in use for this purpose. It was therefore thought useful to compare the efficacy of the various methods with different representative influenza strains and normal sera from eight animal species and acute-phase human sera. Tests were carried out with simple heating at 56°C, the use of receptor-destroying enzyme, the use of potassium periodate, and two methods involving the use of trypsin. No one technique was found to be universally applicable for all types of serum against all strains, and further testing with larger numbers of sera is advocated. It is felt that a combination of potassium periodate and trypsin with a change in concentration and times of action may be found advantageous.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BURNET F. M. Mucoproteins in relation to virus action. Physiol Rev. 1951 Apr;31(2):131–150. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1951.31.2.131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHU C. M. The action of normal mouse serum on influenza virus. J Gen Microbiol. 1951 Oct;5(4):739–757. doi: 10.1099/00221287-5-4-739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE SAMPAIO A. A. C., ISAACS A. The action of trypsin on normal serum inhibitors of influenza virus agglutination. Br J Exp Pathol. 1953 Apr;34(2):152–158. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francis T. DISSOCIATION OF HEMAGGLUTINATING AND ANTIBODY-MEASURING CAPACITIES OF INFLUENZA VIRUS. J Exp Med. 1947 Jan 1;85(1):1–7. doi: 10.1084/jem.85.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRST G. K. The nature of the virus receptors of red cells; evidence on the chemical nature of the virus receptors of red cells and of the existence of a closely analogous substance in normal serum. J Exp Med. 1948 Apr 1;87(4):301–314. doi: 10.1084/jem.87.4.301. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst G. K. THE QUANTITATIVE DETERMINATION OF INFLUENZA VIRUS AND ANTIBODIES BY MEANS OF RED CELL AGGLUTINATION. J Exp Med. 1942 Jan 1;75(1):49–64. doi: 10.1084/jem.75.1.49. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ISAACS A., BOZZO A. The use of V. cholerae filtrates in the destruction of non-specific inhibitor in ferret sera. Br J Exp Pathol. 1951 Aug;32(4):325–335. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KAPLAN M. M., PAYNE A. M. Serological survey in animals for type A influenza in relation to the 1957 pandemic. Bull World Health Organ. 1959;20(2-3):465–488. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LUNDBACK H. Serological diagnosis in mumps. Br J Exp Pathol. 1949 Jun;30(3):221–231. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MAGILL T. P., JOTZ A. C. A pattern of influenza virus variation. J Bacteriol. 1952 Nov;64(5):619–628. doi: 10.1128/jb.64.5.619-628.1952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SMITH W., WESTWOOD J. C. N., BELYAVIN G. Influenza; a study of four virus strains isolated in 1951. Lancet. 1951 Dec 29;2(6696):1189–1193. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(51)93200-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SVEDMYR A. Studies on a factor in normal allantoic fluid inhibiting influenza virus haemagglutination; precipitation reaction in mixtures of inactive virus and inhibitor. Br J Exp Pathol. 1949 Aug;30(4):248–254. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TYRRELL D. A. Separation of inhibitors of hemagglutination and specific antibodies for influenza viruses by starch zone electrophoresis. J Immunol. 1954 Jun;72(6):494–502. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


