Abstract
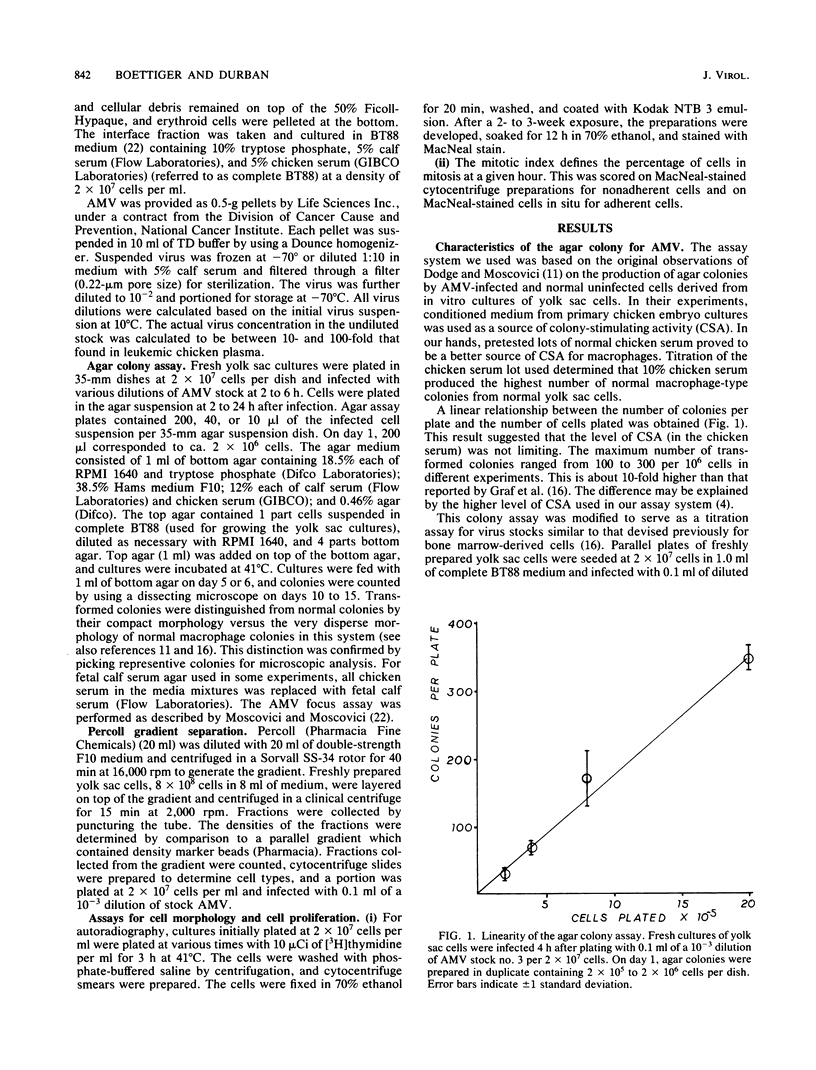
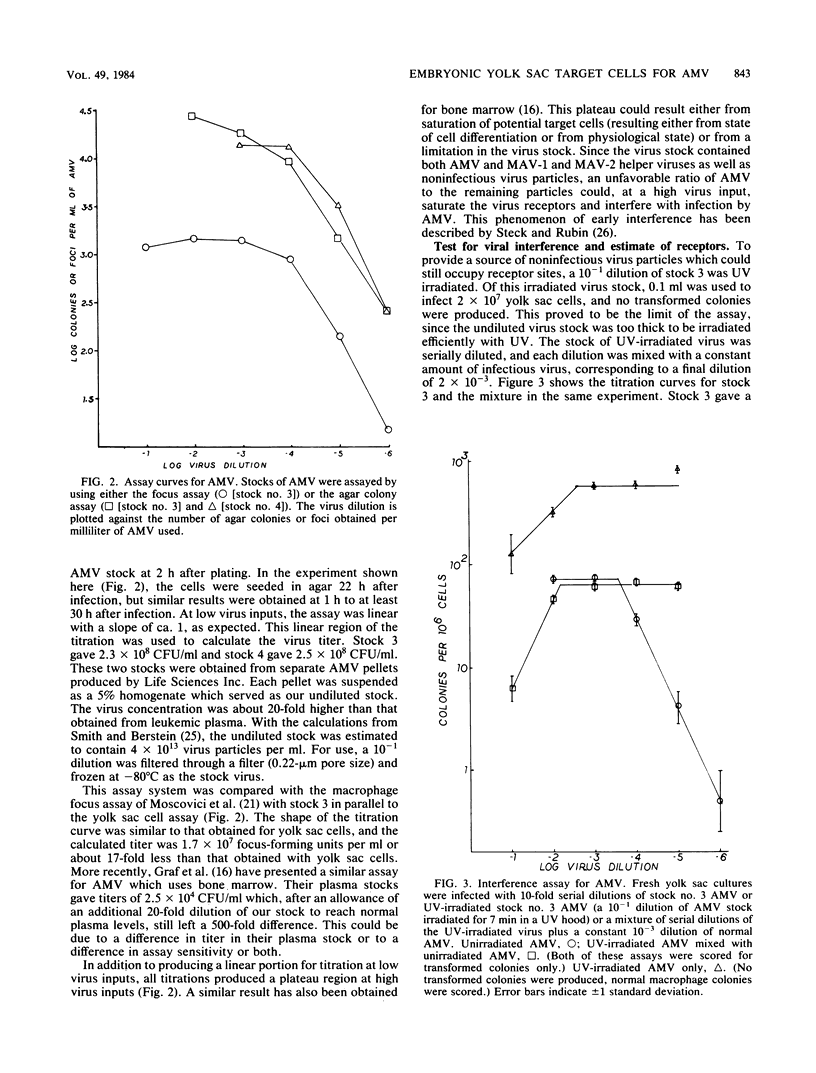
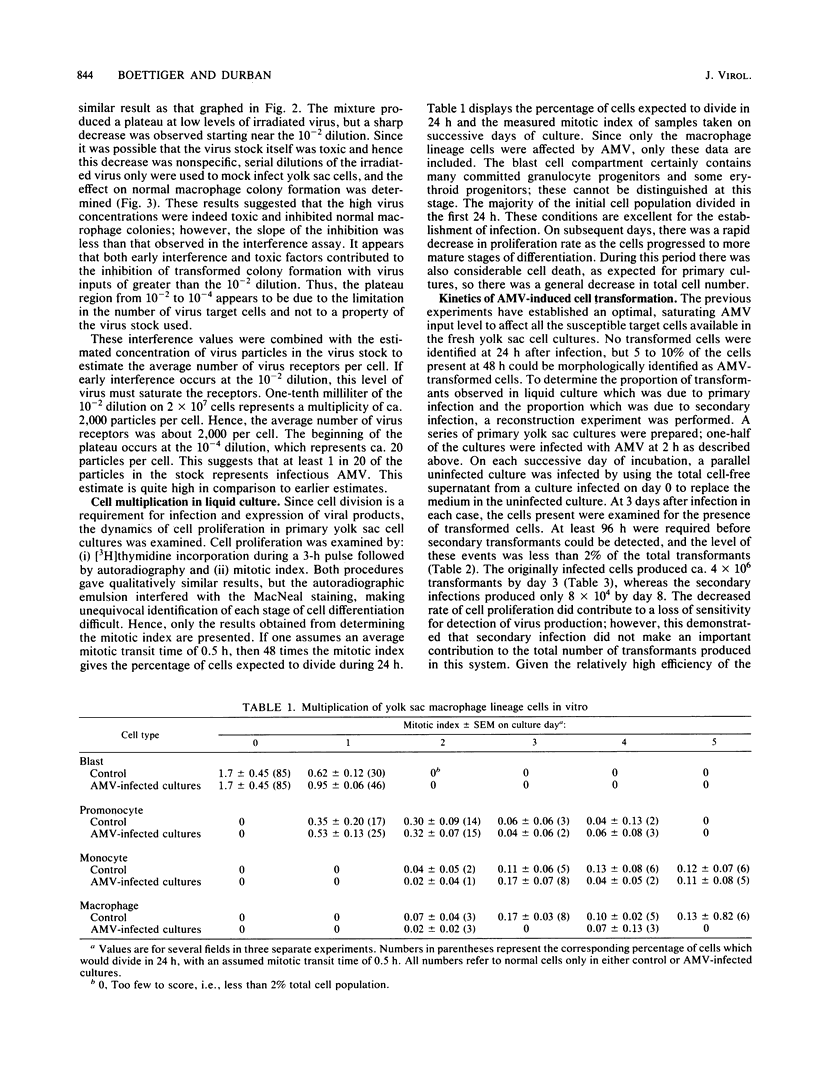
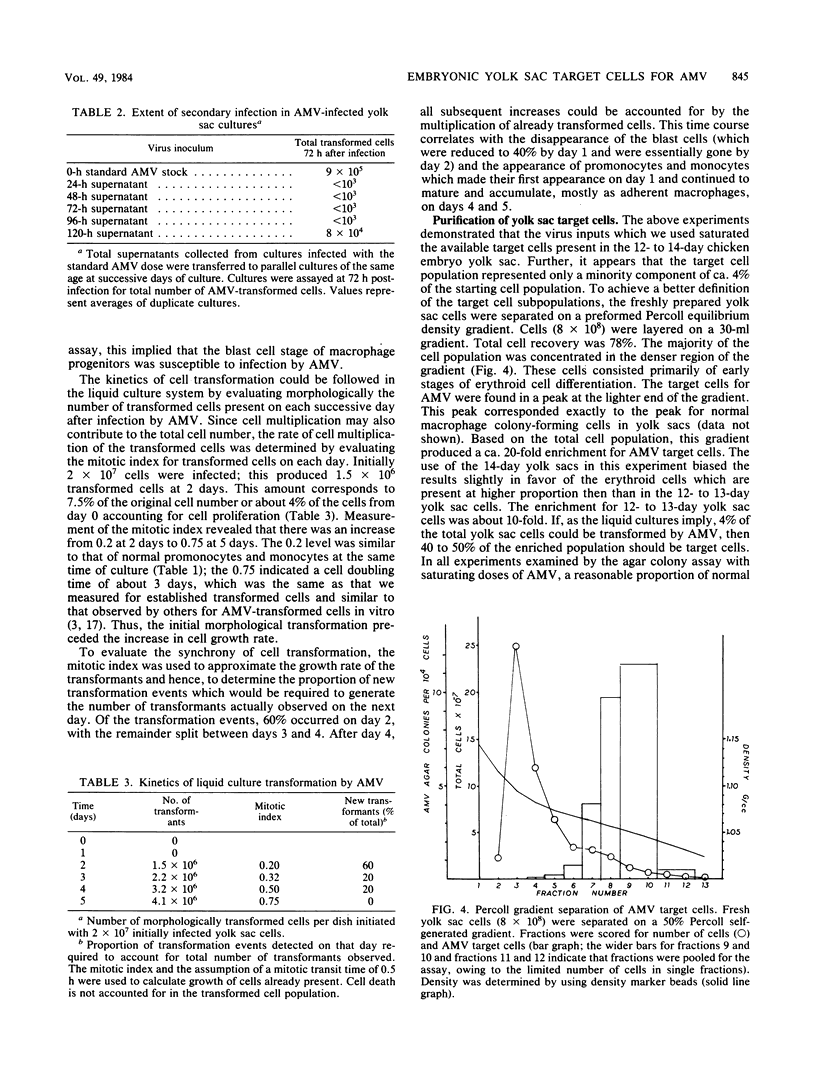
The yolk sac of the 12-day chicken embryo retains the blast stage progenitors to cells of the myeloid lineages with a very low level of contamination by more mature myeloid cells which have begun to express the characteristic myeloid cell markers. Both in vivo and in vitro experiments have supported the hypothesis that target cells for the BAI-A strain of avian myeloblastosis virus are contained within the myeloid lineages. An assay system for avian myeloblastosis virus was developed which utilizes this yolk sac cell system and which appears to be more sensitive than previous published assays. In addition, the kinetics of a liquid culture transformation system is presented in which at least 4% of the yolk sac cell population was transformed in a relatively synchronous fashion at 2 days after infection. The morphological transformation preceded an increased rate of cell proliferation. Cell separation procedures provided a 10- to 20-fold enrichment of target cells and demonstrated that the target cell population copurifies with macrophage colony-forming cells which are the committed progenitors to the macrophage lineage. In combination with earlier work, this work demonstrated that cells committed to the macrophage lineage at all stages of differentiation may serve as target cells for infection by avian myeloblastosis virus.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BALUDA M. A. Properties of cells infected with avian myeloblastosis virus. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1962;27:415–425. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1962.027.001.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEARD J. W. AVIAN VIRUS GROWTHS AND THEIR ETIOLOGIC AGENTS. Adv Cancer Res. 1963;7:1–127. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60982-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BEAUDREAU G. S., BECKER C., BONAR R. A., WALLBANK A. M., BEARD D., BEARD J. W. Virus of avian myeloblastosis. XIV. Neoplastic response of normal chicken bone marrow treated with the virus in tissue culture. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1960 Feb;24:395–415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BURMESTER B. R., WALTER W. G., GROSS M. A., FONTES A. K. The oncogenic spectrum of two pure strains of avian leukosis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1959 Aug;23:277–291. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettiger D., Durban E. M. Progenitor-cell populations can be infected by RNA tumor viruses, but transformation is dependent on the expression of specific differentiated functions. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1249–1254. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.135. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettiger D., Soltesz R., Holtzer H., Pacifici M. Infection of chick limb bud presumptive chondroblasts by a temperature-sensitive mutant of Rous sarcoma virus and the reversible inhibition of their terminal differentiation in culture. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Aug;3(8):1518–1526. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.8.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boettiger D., Temin H. M. Light inactivation of focus formation by chicken embryo fibroblasts infected with avian sarcoma virus in the presence of 5-bromodeoxyuridine. Nature. 1970 Nov 14;228(5272):622–624. doi: 10.1038/228622a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dexter T. M., Allen T. D., Testa N. G., Scolnick E. Friend disease in vitro. J Exp Med. 1981 Sep 1;154(3):594–608. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.3.594. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterlen-Lievre F. On the origin of haemopoietic stem cells in the avian embryo: an experimental approach. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1975 Jun;33(3):607–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodge W. H., Moscovici C. Colony formation by chicken hematopoietic cells and virus-induced myeloblasts. J Cell Physiol. 1973 Jun;81(3):371–386. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040810310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durban E. M., Boettiger D. Replicating, differentiated macrophages can serve as in vitro targets for transformation by avian myeloblastosis virus. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):488–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.488-492.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gazzolo L., Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G., Samarut J. Response of hemopoietic cells to avian acute leukemia viruses: effects on the differentiation of the target cells. Cell. 1979 Mar;16(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90036-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Kirchbach A., Beug H. Characterization of the hematopoietic target cells of AEV, MC29 and AMV avian leukemia viruses. Exp Cell Res. 1981 Feb;131(2):331–343. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(81)90236-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., von Kirchbach A., Beug H. Mechanism of leukemogenesis and of target cell specificity by defective avian leukemia viruses: a hypothesis. Haematol Blood Transfus. 1979;23:429–438. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67057-2_57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanafusa H. Rapid transformation of cells by Rous sarcoma virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Jun;63(2):318–325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.63.2.318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalf D. Hemopoietic colonies: in vitro cloning of normal and leukemic cells. Recent Results Cancer Res. 1977;(61):Title page, 1-227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C. A quantitative assay for avian myeloblastosis virus. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Aug-Sep;125(4):1213–1215. doi: 10.3181/00379727-125-32316. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Gazzolo L., Moscovici M. G. Focus assay and defectiveness of avian myeloblastosis virus. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):173–181. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90159-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Moscovici M. G. Tissue culture of avian hematopoietic cells. Methods Cell Biol. 1973;7:313–328. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61784-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moscovici C., Samarut J., Gazzolo L., Moscovici M. G. Myeloid and erythroid neoplastic responses to avian defective leukemia viruses in chickens and in quail. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):765–768. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90205-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarut J., Gazzolo L. Target cells infected by avian erythroblastosis virus differentiate and become transformed. Cell. 1982 Apr;28(4):921–929. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90071-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. E., Bernstein E. H. Production and purification of large amounts of Rous sarcoma virus. Appl Microbiol. 1973 Mar;25(3):346–353. doi: 10.1128/am.25.3.346-353.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steck F. T., Rubin H. The mechanism of interference between an avian leukosis virus and Rous sarcoma virus. I. Establishment of interference. Virology. 1966 Aug;29(4):628–641. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(66)90287-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tushinski R. J., Oliver I. T., Guilbert L. J., Tynan P. W., Warner J. R., Stanley E. R. Survival of mononuclear phagocytes depends on a lineage-specific growth factor that the differentiated cells selectively destroy. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90376-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


