Abstract
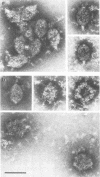
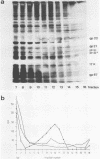
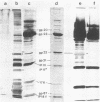
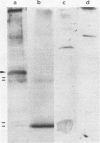
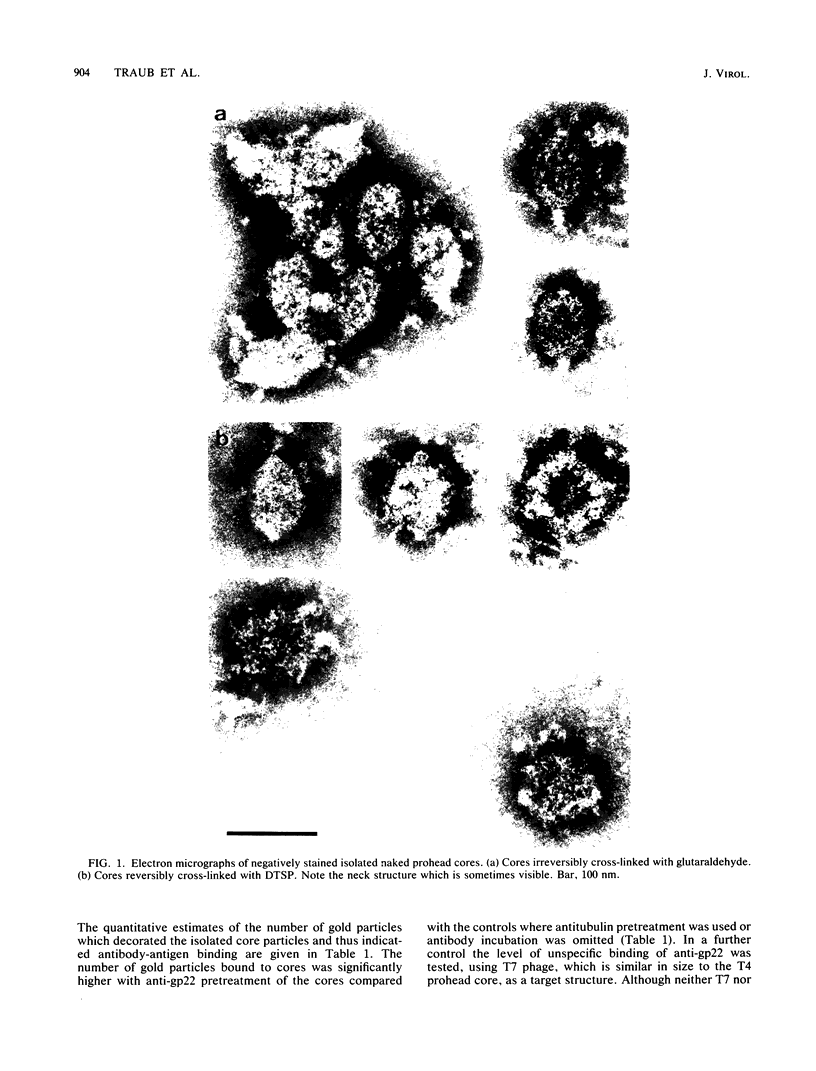
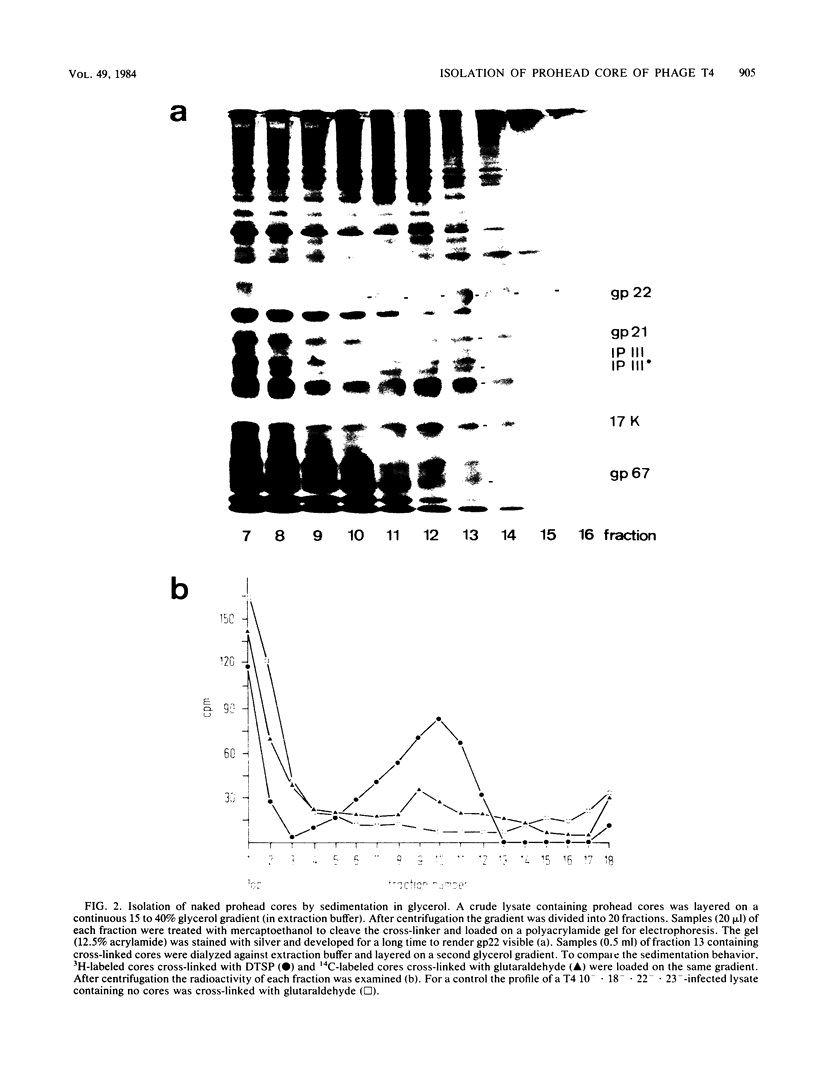
The naked core of bacteriophage T4 was isolated ex vivo after cross-linking with either glutaraldehyde or dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate). The isolated particles appeared to be morphologically identical to the cores found in thin sections, to those demonstrated in in situ lysis preparations, and to core structures assembled in vitro. Treatment with glutaraldehyde provided core particles which were morphologically well preserved, whereas dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate)-induced cross-linking was reversible and allowed analysis of the protein composition of the isolated particles. The identity of the reversibly cross-linked particles with those obtained after irreversible cross-linking was suggested by their morphology and their similar sedimentation behavior. Immunolabeling confirmed the structural presence of the main core protein in both structures. Gel electrophoresis of reversibly cross-linked cores revealed the essential head proteins gp22, gp67, and gp21, the three internal proteins IPI, IPII, and IPIII, and a 17K protein.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Carrascosa J. L., Kellenberger E. Head maturation pathway of bacteriophages T4 and T2. III. Isolation and characterization of particles produced by mutants in gene 17. J Virol. 1978 Mar;25(3):831–844. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.3.831-844.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellenberger E., Eiserling F. A., Boy de la Tour E. Studies on the morphopoiesis of the head of phage T-even. 3. The cores of head-related structures. J Ultrastruct Res. 1967 Dec 12;21(3):335–360. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(67)80099-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K., Beguin F., Gujer-Kellenberger G. A factor preventing the major head protein of bacteriophage T4 from random aggregation. J Mol Biol. 1970 Jan 14;47(1):69–85. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90402-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomant A. J., Fairbanks G. Chemical probes of extended biological structures: synthesis and properties of the cleavable protein cross-linking reagent [35S]dithiobis(succinimidyl propionate). J Mol Biol. 1976 Jun 14;104(1):243–261. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90011-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murray N. E., Gough J. A., Suri B., Bickle T. A. Structural homologies among type I restriction-modification systems. EMBO J. 1982;1(5):535–539. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01205.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller-Salamin L., Onorato L., Showe M. K. Localization of minor protein components of the head of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):121–134. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.121-134.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onorato L., Showe M. K. Gene 21 protein-dependent proteolysis in vitro of purified gene 22 product of bacteriophage T4. J Mol Biol. 1975 Mar 5;92(3):395–412. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(75)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Onorato L., Stirmer B., Showe M. K. Isolation and characterization of bacteriophage T4 mutant preheads. J Virol. 1978 Aug;27(2):409–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.2.409-426.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richards F. M., Knowles J. R. Glutaraldehyde as a protein cross-linkage reagent. J Mol Biol. 1968 Oct 14;37(1):231–233. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90086-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roth J., Bendayan M., Orci L. Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem. 1978 Dec;26(12):1074–1081. doi: 10.1177/26.12.366014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showe M. K., Black L. W. Assembly core of bacteriophage T4: an intermediate in head formation. Nat New Biol. 1973 Mar 21;242(116):70–75. doi: 10.1038/newbio242070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Showe M. K., Isobe E., Onorato L. Bacteriophage T4 prehead proteinase. I. Purification and properties of a bacteriophage enzyme which cleaves the capsid precursor proteins. J Mol Biol. 1976 Oct 15;107(1):35–54. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(76)80016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Traub F., Maeder M. Formation of the prohead core of bacteriophage T4 in vivo. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):892–901. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.892-901.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsugita A., van den Broek R., Gregor I. Protein chemical approaches for the investigation of T4-head morphogenesis. Biosystems. 1980;12(3-4):225–238. doi: 10.1016/0303-2647(80)90019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Völker T. A., Kuhn A., Showe M. K., Bickle T. A. Gene 67, a new, essential bacteriophage T4 head gene codes for a prehead core component, PIP. II. The construction in vitro of unconditionally lethal mutants and their maintenance. J Mol Biol. 1982 Nov 15;161(4):491–504. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90403-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray W., Boulikas T., Wray V. P., Hancock R. Silver staining of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. Anal Biochem. 1981 Nov 15;118(1):197–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90179-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Driel R., Couture E. Assembly of the scaffolding core of bacteriophage T4 preheads. J Mol Biol. 1978 Aug 25;123(4):713–719. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90217-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Driel R., Traub F., Showe M. K. Probable localization of the bacteriophage T4 prehead proteinase zymogen in the center of the prehead core. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):220–223. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.220-223.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]