Abstract
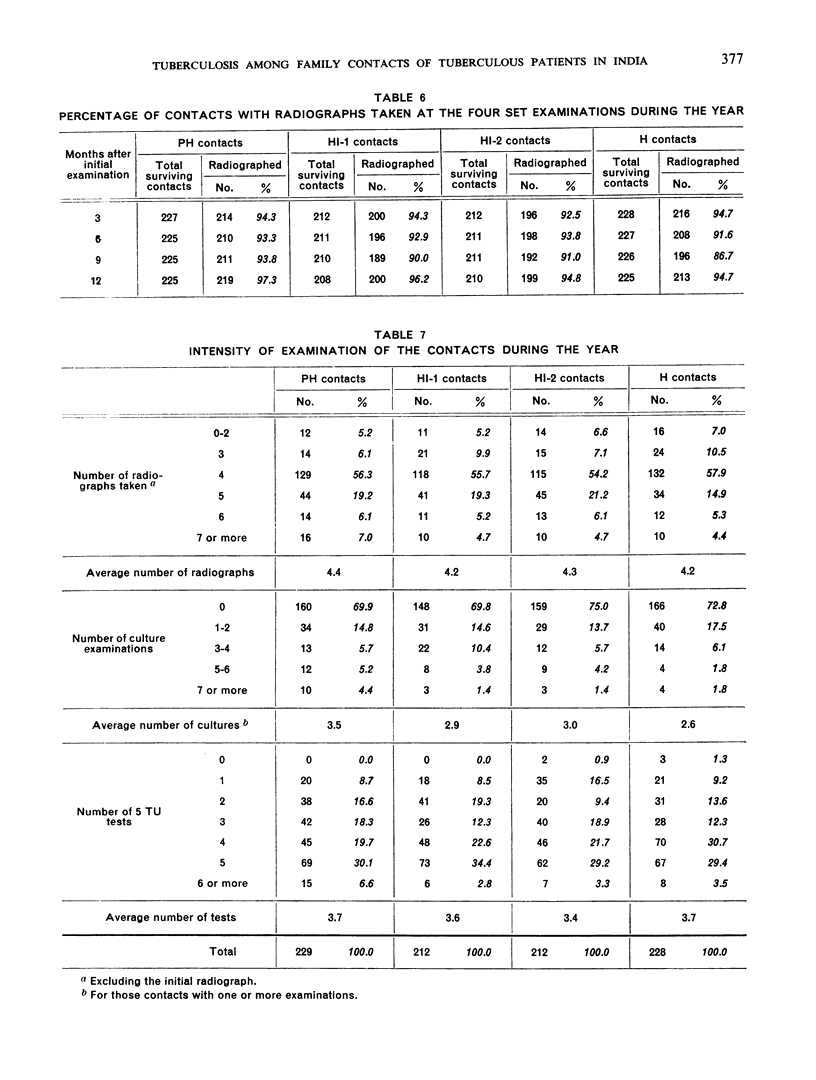
The authors present a report from the Tuberculosis Chemotherapy Centre, Madras, on the prevalence and attack rate of tuberculosis among close family contacts of tuberculous patients in South India undergoing domiciliary chemotherapy either with isoniazid plus PAS or with one of three regimens of isoniazid alone. The report gives (a) the prevalence of tuberculosis among the contacts at the time of diagnosis of the disease in the patients and (b) the incidence of tuberculosis in the contacts during the first year of treatment of the patients. The contacts were divided into four series, corresponding to the four chemotherapeutic regimens of the patients.
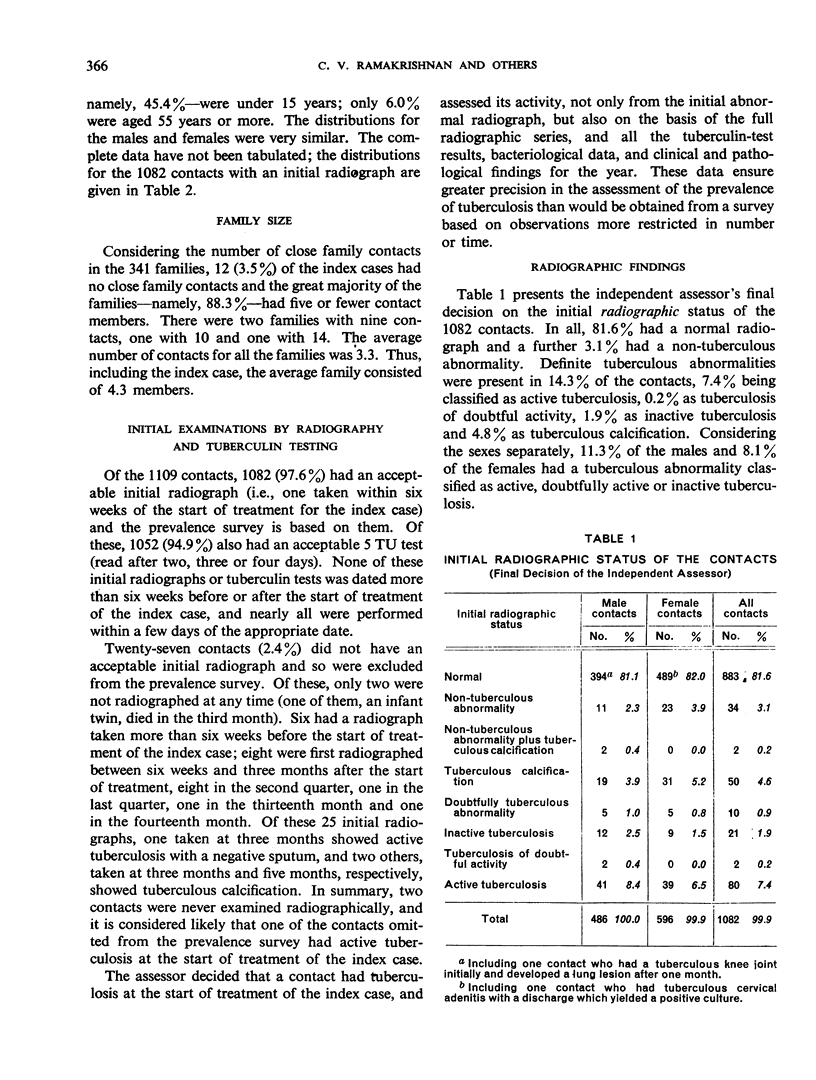
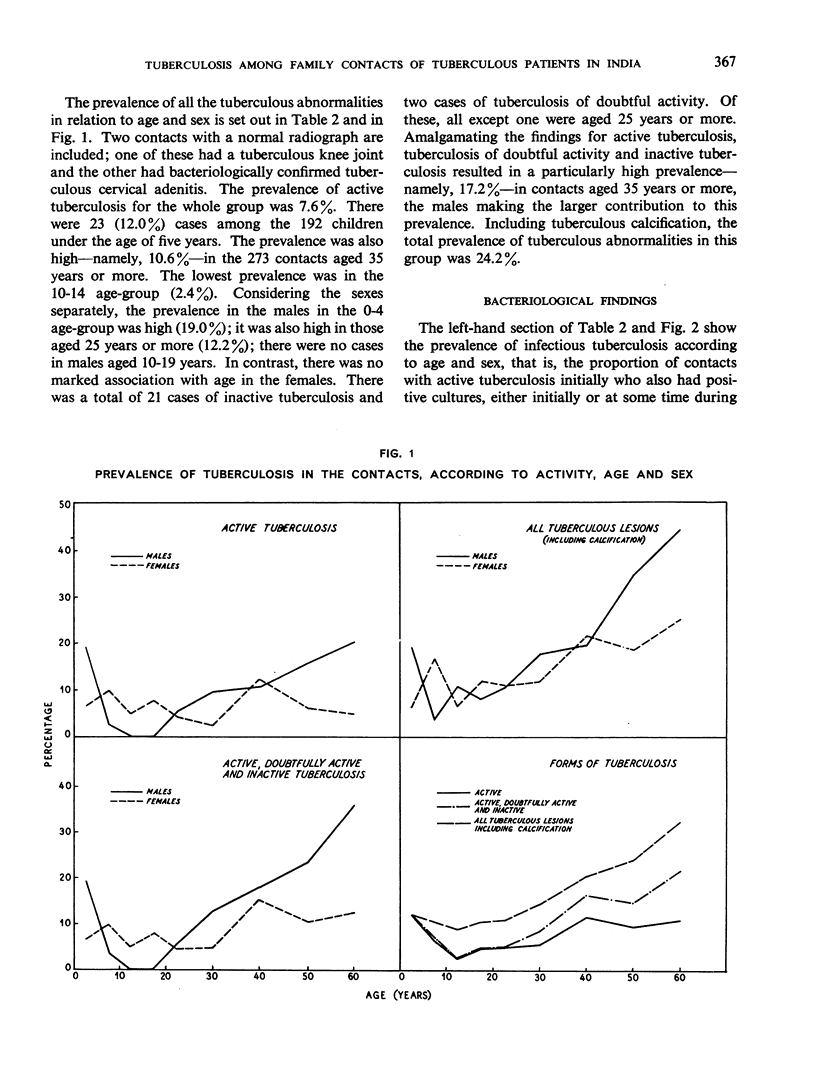
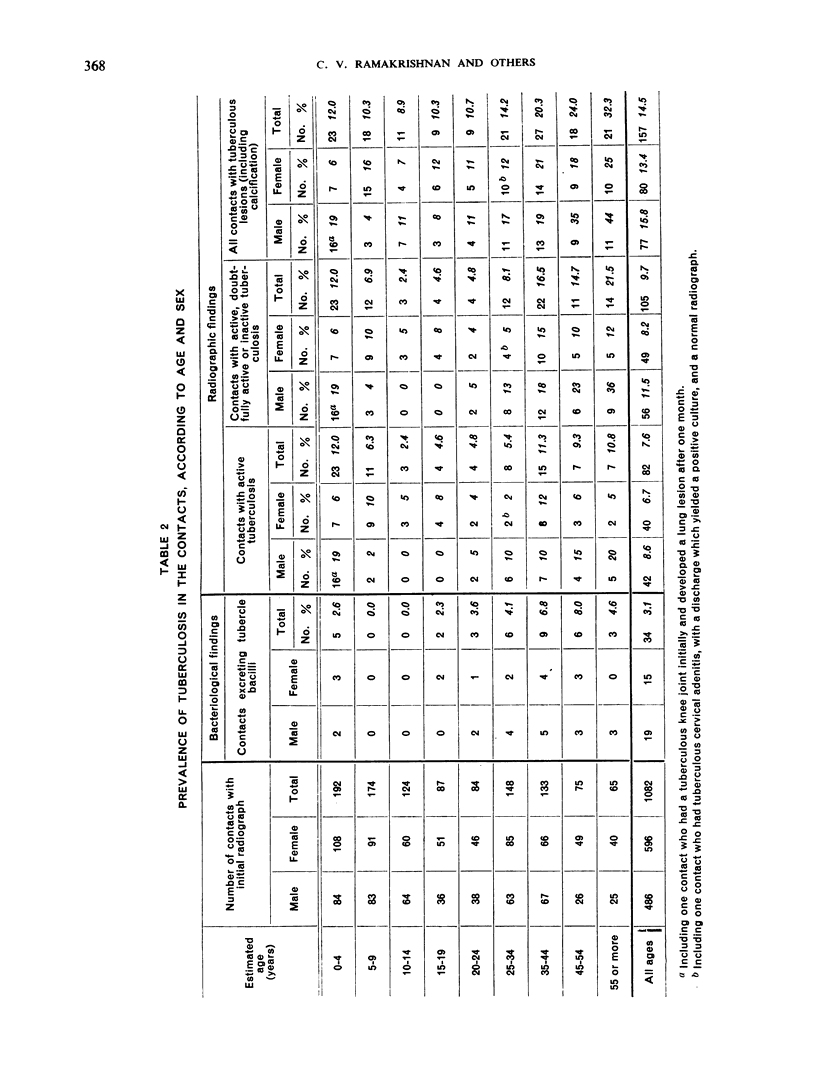
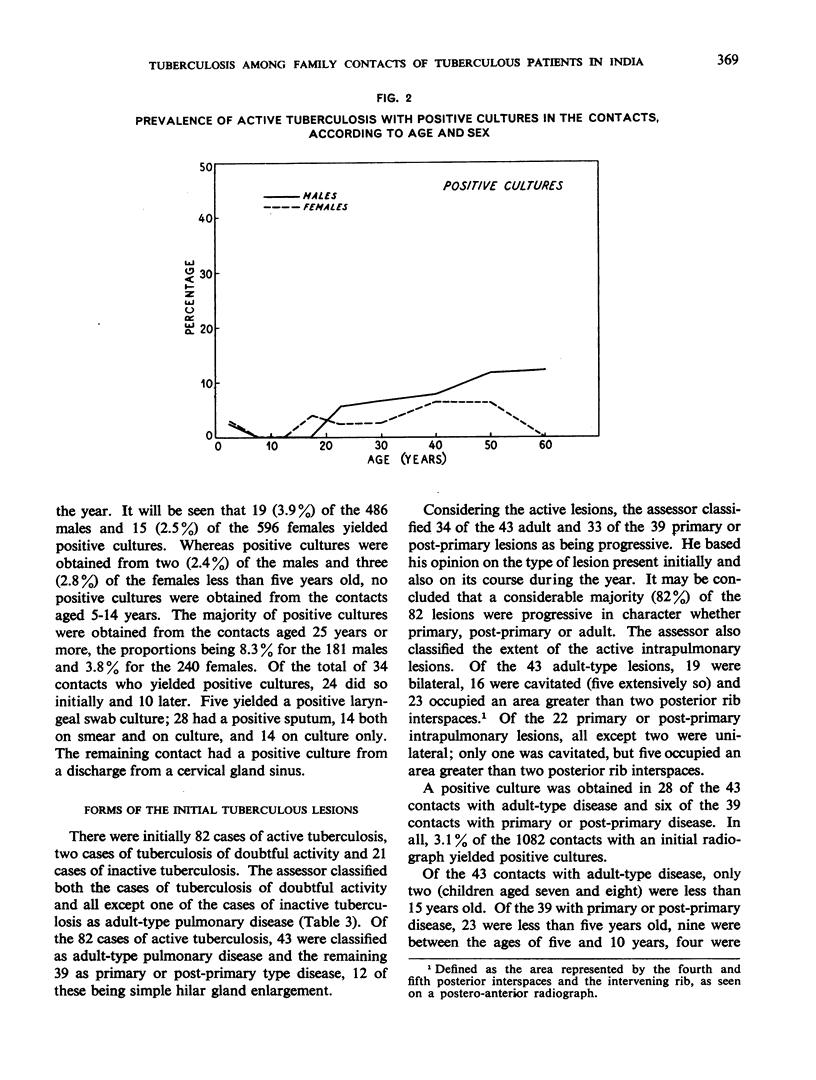
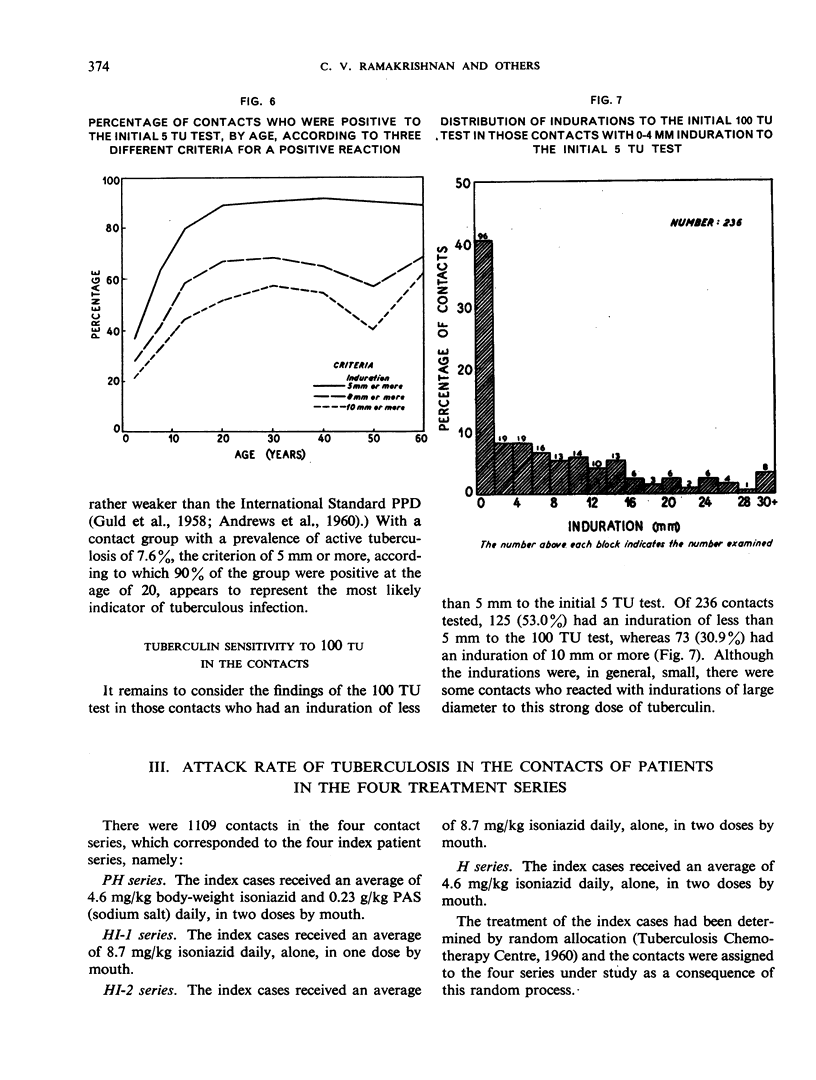
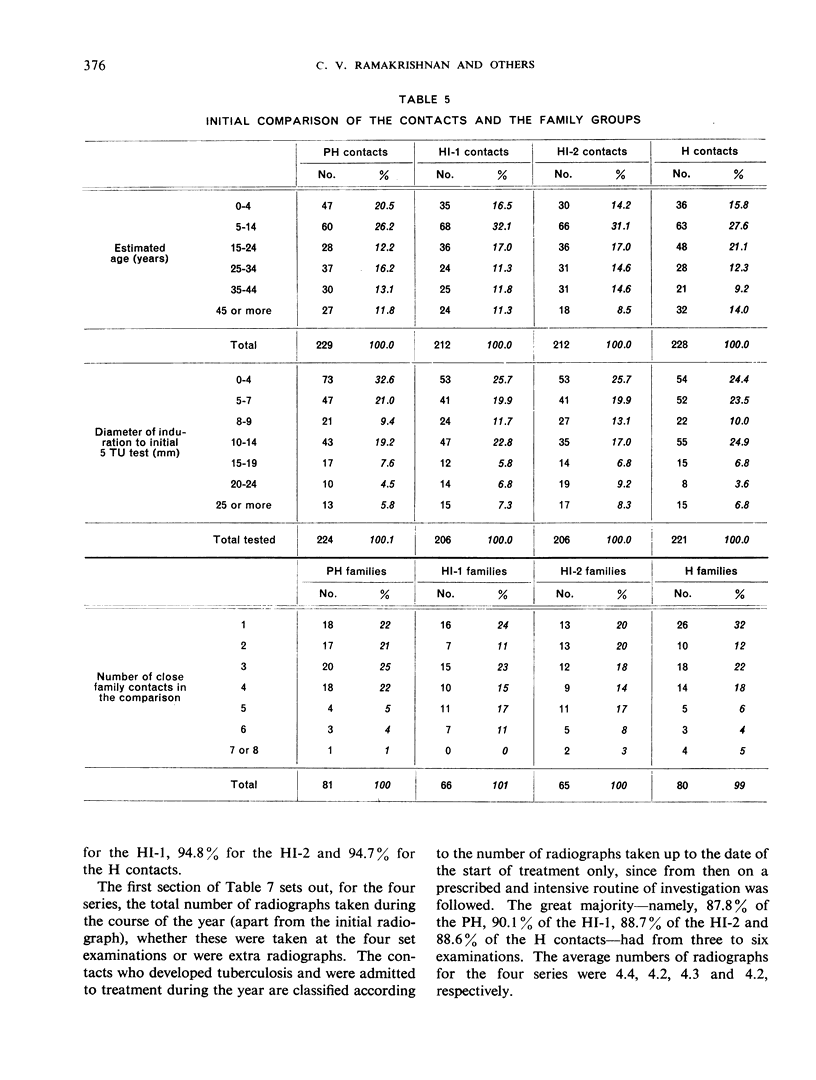
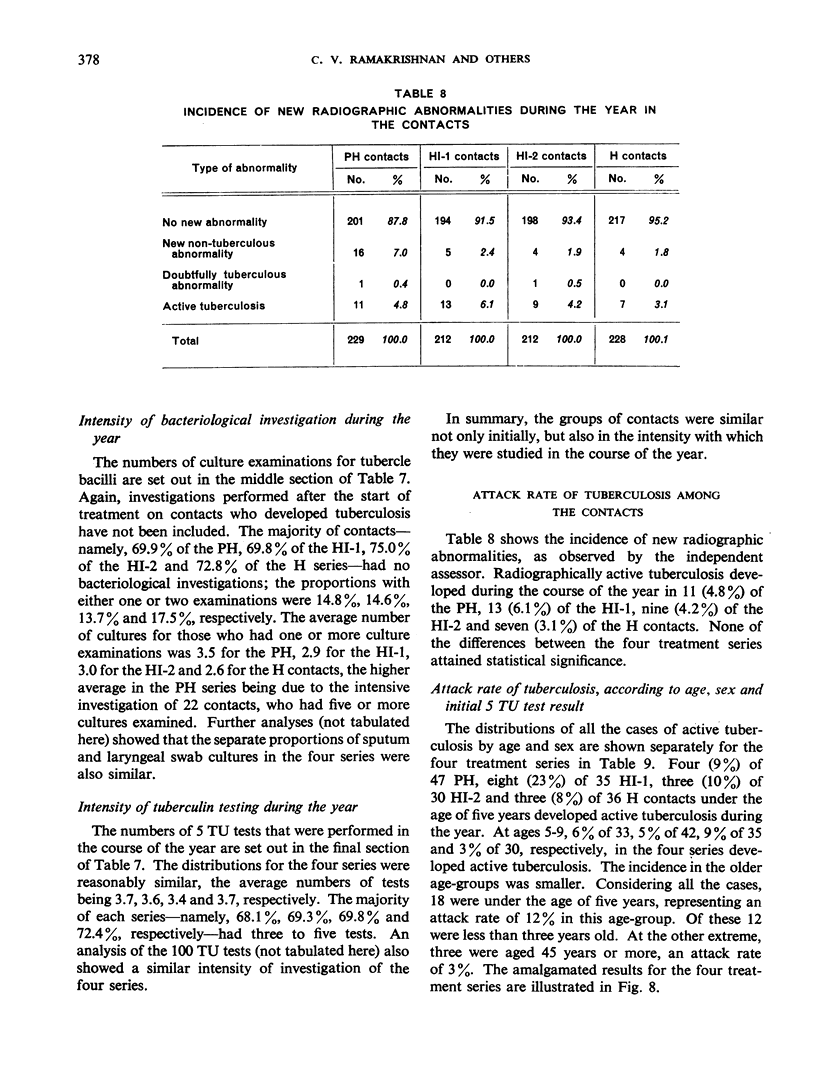
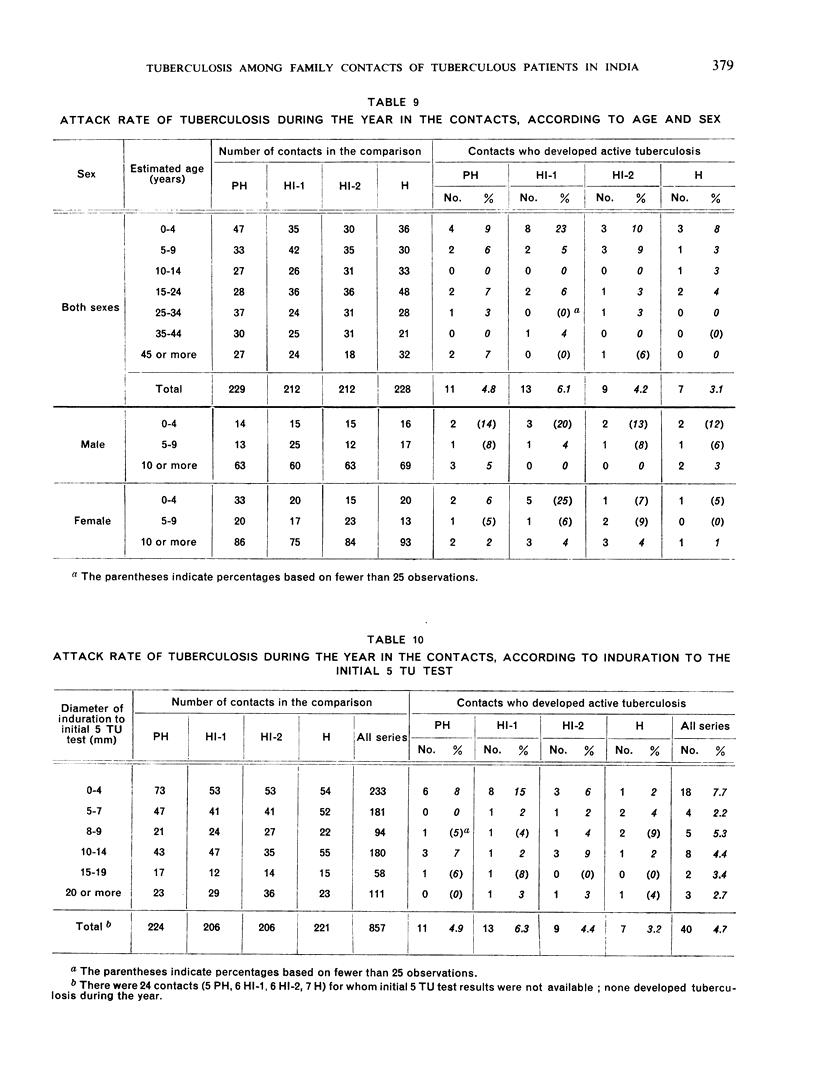
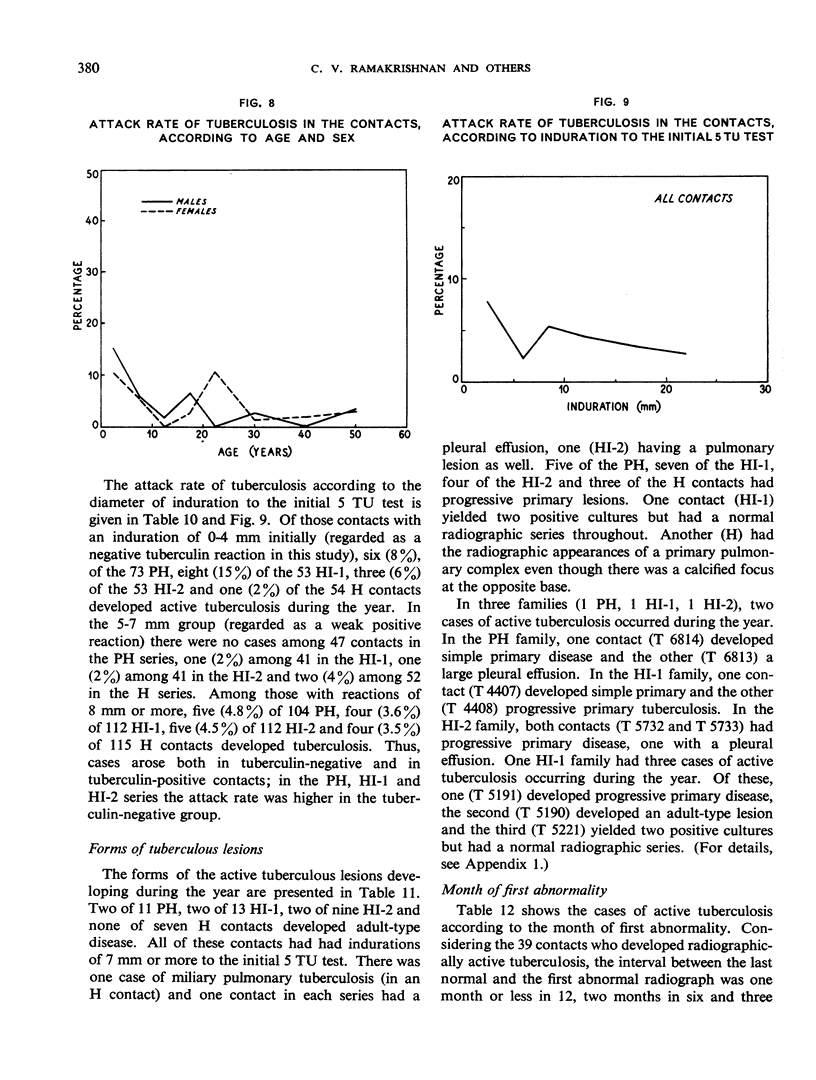
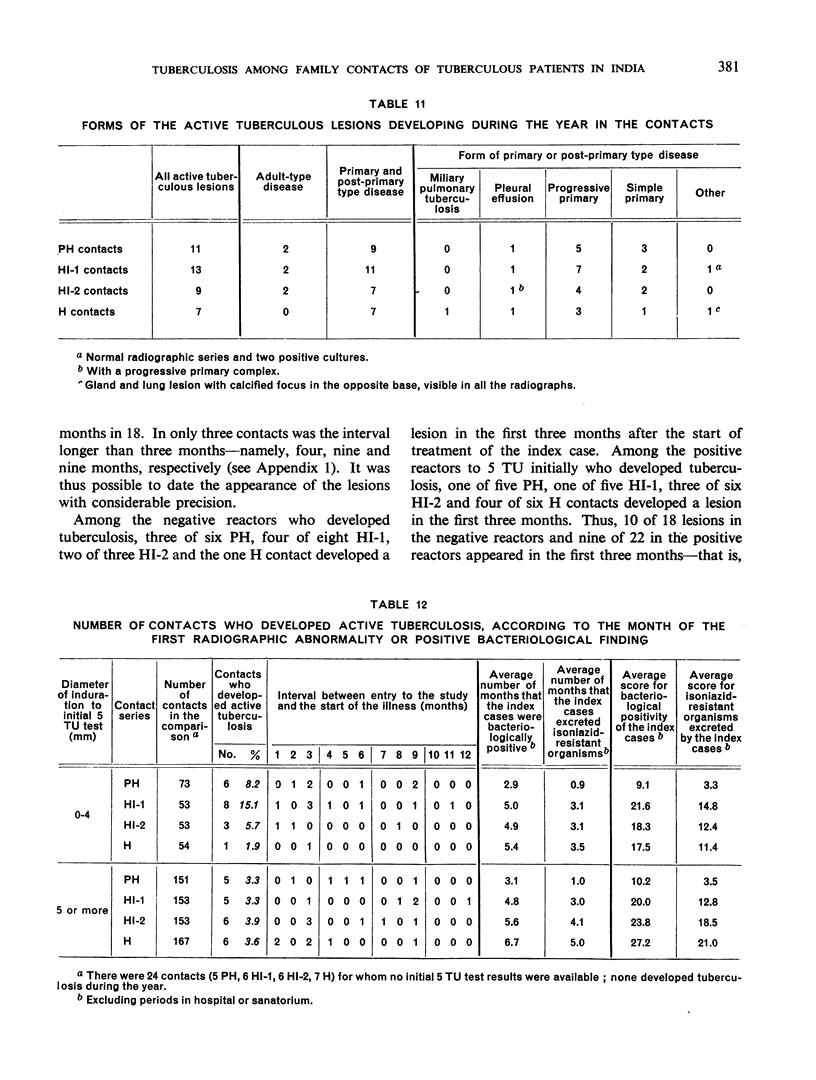
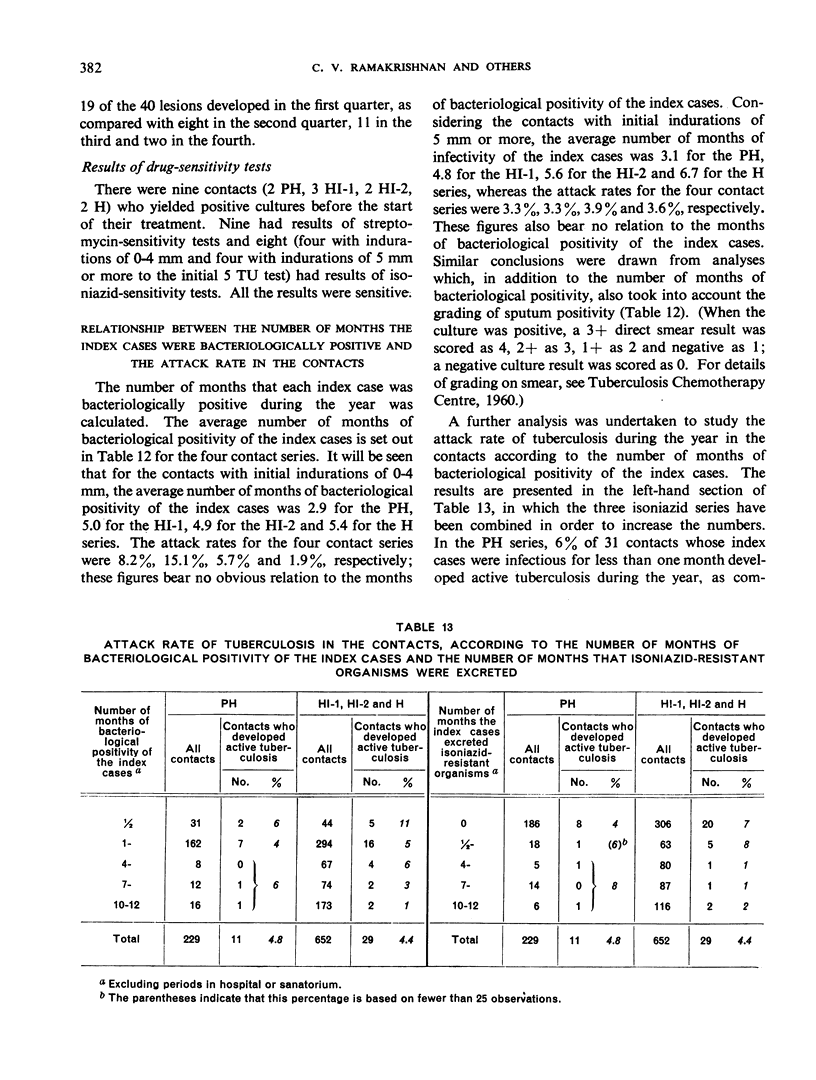
The prevalence of active tuberculosis was found to be particularly high among children under five years of age, being 12.0% as compared with 7.6% for all age-groups combined. The incidence of active tuberculosis during the year of treatment of the patients was also found to be highest in the under five years' age-group—a further indication that child contacts are especially vulnerable to infection. The incidence was considerably higher in the first quarter of the year than in the other quarters, and it was lowest in the last quarter. This finding, together with the fact that the attack rates in the four contact series were not related either to the duration of bacteriological positivity in the patients or to the period of excretion of isoniazid-resistant organisms by the patients, suggests that the major risk to contacts in the first year results from exposure to the patient before treatment rather than from exposure during treatment. These results thus confirm the findings in an earlier study by the Centre of the contacts of patients in a controlled comparison of chemotherapy with isoniazid plus PAS at home and in sanatorium.
Full text
PDF














Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDREWS R. H., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., RADHAKRISHNA S., RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., VELU S. Prevalence of tuberculosis among close family contacts of tuberculous patients in South India, and influence of segregation of the patient on early attack rate. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;23:463–510. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CHAUDHURI S. An Indian village. Lancet. 1959 Jan 17;1(7064):144–145. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(59)90021-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FRIMODT-MOLLER J. A community-wide tuberculosis study in a South Indian rural population, 1950-1955. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;22:61–170. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GULD J., BENTZON M. W., BLEIKER M. A., GRIEP W. A., MAGNUSSON M., WAALER H. Standardization of a new batch of purified tuberculin (PPD) intended for international use. Bull World Health Organ. 1958;19(5):845–951. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., ANDREWS R. H., DEVADATTA S., FOX W., RADHAKRISHNA S., SOMASUNDARAM P. R., VELU S. Influence of segregation to tuberculous patients for one year on the attack rate of tuberculosis in a 2-year period in close family contacts in South India. Bull World Health Organ. 1961;24:129–148. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RAMAKRISHNAN C. V., RAJENDRAN K., JACOB P. G., FOX W., RADHAKRISHNA S. The role of diet in the treatment of pulmonary tuberculosis. An evaluation in a controlled chemotherapy study in home and sanatorium patients in South India. Bull World Health Organ. 1961;25:339–359. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SELKON J. B., SUBBAIAH T. V., BHATIA A. L., RADHAKRISHNA S., MITCHISON D. A. A comparison of the sensitivity to p-aminosalicylic acid of tubercle bacilli from South Indian and British patients. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;23:599–611. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WARAWDEKAR M. S., SHAH J. R. Pulmonary tuberculosis in the contacts: a mass miniature roentgenographic study. Indian J Med Sci. 1958 Oct;12(10):797–801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


