Abstract
Mass vaccination of the juvenile population with live poliovirus vaccine was carried out in Poland in 1959 and 1960. In all, some 7 239 000 children 6 months to 14 years old were given type 1 (CHAT) virus, and nearly 6 818 500 children of the same age-group received type 3 (W-Fox) virus.
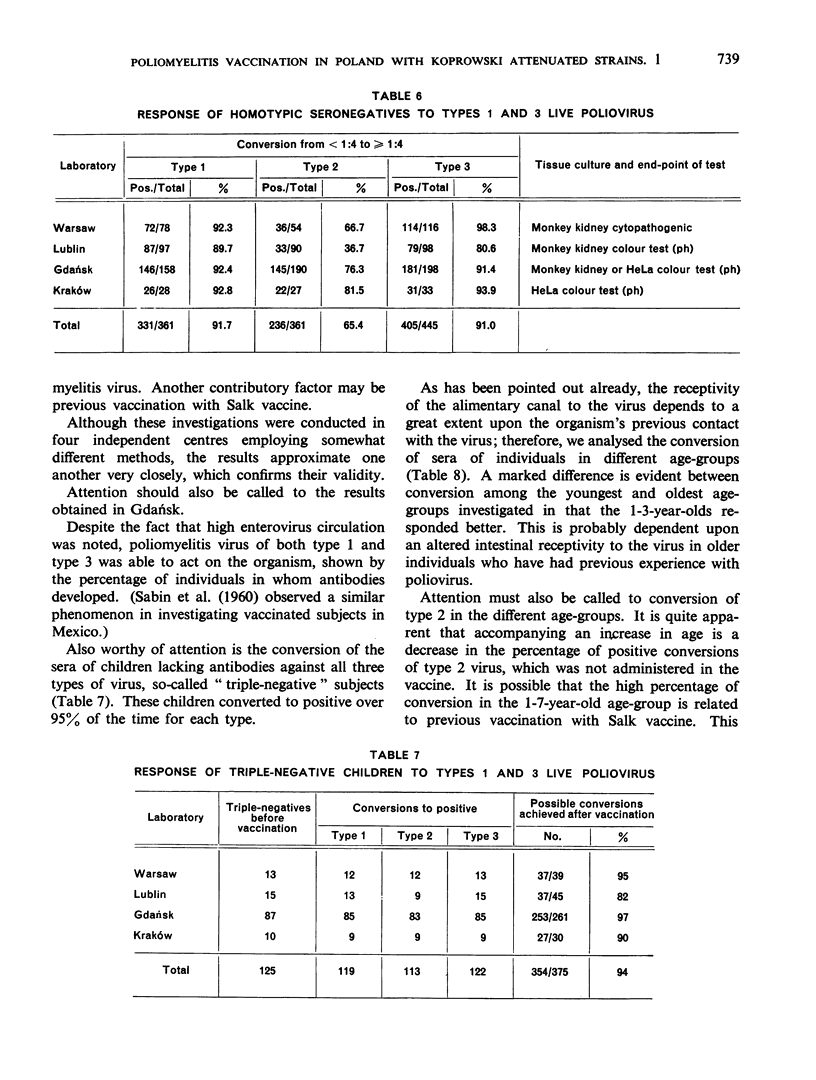
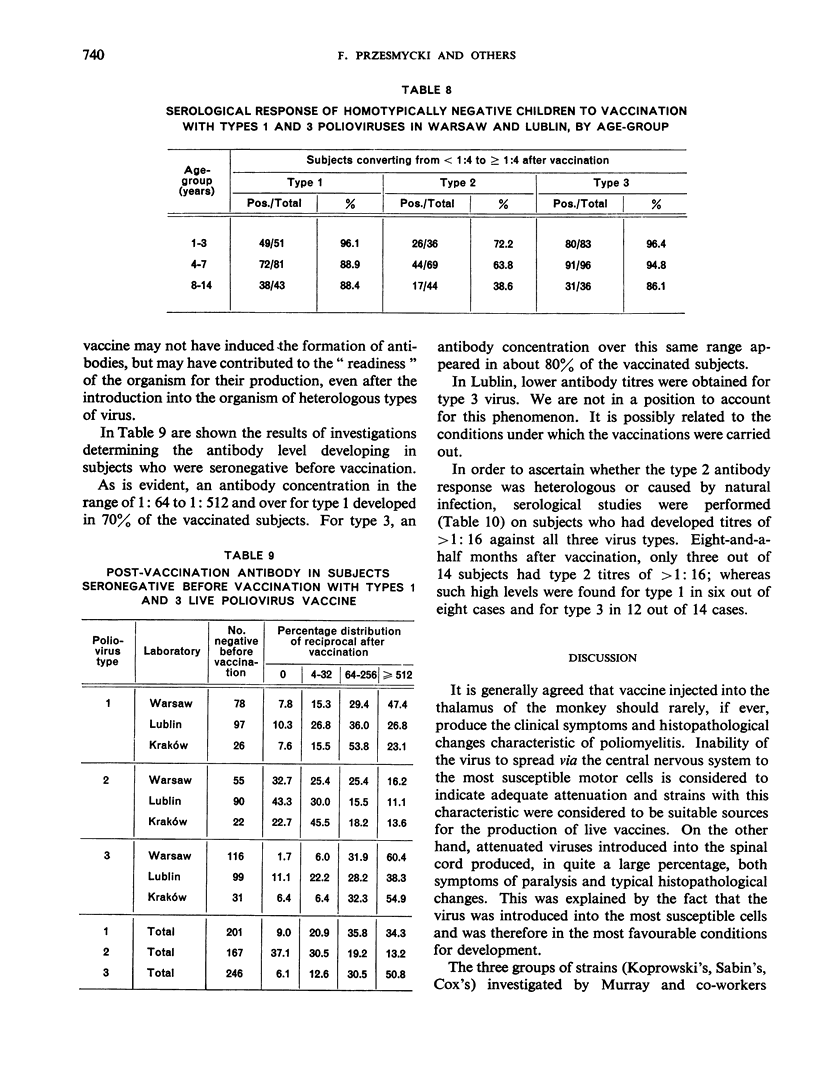
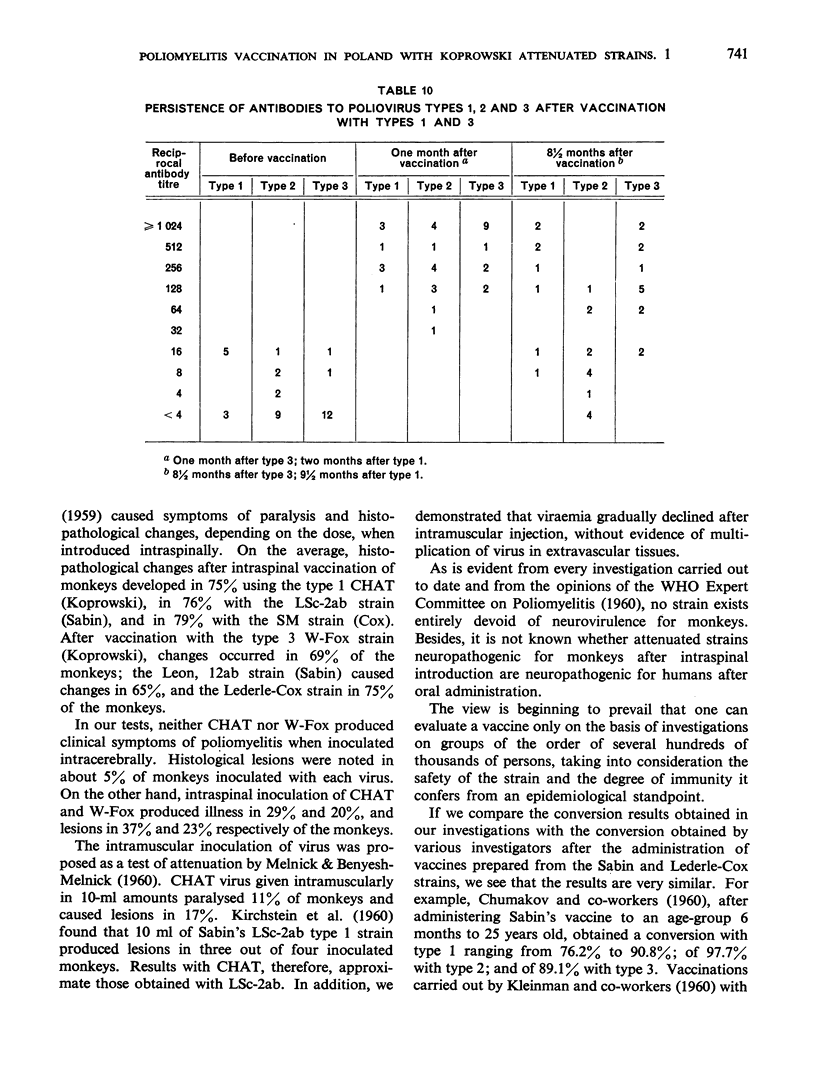
A serological conversion rate (from <1:4 to ≥1:4) of 91.7% was achieved with type 1 and of 91.0% with type 3—a satisfactory demonstration of the immunogenicity of the strains used. Although type 2 virus was not administered, seroconversion with this type occurred in 65.4%. This may have been caused by antigenic elements common to the three poliovirus types, and previous vaccination with Salk vaccine may also have been a contributory factor.
The authors conclude that the mass vaccination described in this paper has created a highly immune population in Poland.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- PLOTKIN S. A., LEBRUN A., KOPROWSKI H. Vaccination with the CHAT strain of type 1 attenuated poliomyelitis virus in Leopoldville. Belgian Congo. 2. Studies of the safety and efficacy of vaccination. Bull World Health Organ. 1960;22:215–234. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRZESMYCKI F., DOBROWOLSKA H., GEORGIADES J., OLAKOWSKI T., STANCZYK R., NARUSZEWICZ D. Report on field trials with live attenuated poliomyelitis vaccine of Koprowski in Poland. Am J Hyg. 1960 May;71:275–284. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a120111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PRZESMYCKI F., DOBROWOLSKA H., OLAKOWSKI T., STANCZYK R., NARUSZEWICZ D. [Vaccination in Poland with a live attenuated vaccine against poliomyelitis]. Med Dosw Mikrobiol. 1960;12:1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


