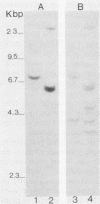
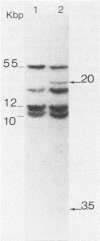
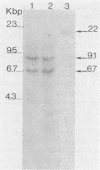
Abstract
AKV and AKR mink cell focus-forming virus-specific probes from the envelope and long terminal repeat (LTR) regions were prepared for study of the structure of recombinant proviruses in tumor tissues of AKR mice. The results showed that (i) all somatically acquired proviruses possessed, besides a recombinant gp70 gene, an altered U3 LTR; (ii) in a substantial portion of the somatically acquired AKR mink cell focus-forming proviruses, the LTR comprised sequences derived from the same xenotropic-like provirus; (iii) this U3 LTR donating parental provirus (Xeno-dL) was present only once per genome equivalent in several mouse strains; (iv) in the strains containing the Xeno-dL provirus, the provirus was present in the same chromosomal site; (v) restriction analysis of the Xeno-dL revealed that the mink cell focus-forming gp70 sequences were derived from a parental provirus, different from Xeno-dL. Therefore, at least two non-ecotropic parents participate in the generation of leukemogenic AKR mink cell focus-forming viruses: a xenotropic-like virus, Xeno-dL, donating U3 LTR sequences, and another xenotropic-like virus or viruses providing gp70 sequences.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berns A. J., Lai M. H., Bosselman R. A., McKennett M. A., Bacheler L. T., Fan H., Maandag E. C., van der Putten H. V., Verma I. M. Molecular cloning of unintegrated and a portion of integrated moloney murine leukemia viral DNA in bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.254-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berns A., Jaenisch R. Increase of AKR-specific sequences in tumor tissues of leukemic AKR mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Jul;73(7):2448–2452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.7.2448. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buckler C. E., Staal S. P., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Variation in the number of copies and in the genomic organization of ecotropic murine leukemia virus proviral sequences in sublines of AKR mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):629–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.629-640.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan R., Lieber M. M., Todaro G. J. Nucleic acid homology of murine xenotropic type C viruses. J Virol. 1975 Jun;15(6):1378–1384. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.6.1378-1384.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Cloyd M. W., Linemeyer D. L., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Cellular origin and role of mink cell focus-forming viruses in murine thymic lymphomas. Nature. 1982 Jan 7;295(5844):25–31. doi: 10.1038/295025a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Gupta S., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Origin of mink cytopathic focus-forming (MCF) viruses:comparison with ecotropic and xenotropic murine leukemia virus genomes. Virology. 1981 Sep;113(2):465–483. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90175-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lander M. R., Rands E., Lowy D. R. Structure of endogenous murine leukemia virus DNA in mouse genomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):5774–5778. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.5774. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Teich N. M., Levine A. S., Rowe W. P. Qualitative and quantitative studies of AKR-type murine leukemia virus sequences in mouse DNA. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1975;39(Pt 2):1085–1101. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1974.039.01.124. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cloyd M. W., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P. Lymphomagenicity of recombinant mink cell focus-inducing murine leukemia viruses. J Exp Med. 1980 Mar 1;151(3):542–552. doi: 10.1084/jem.151.3.542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta S. K., Thomas C. Y., Nicklas J. A., Coffin J. M. Thymic epithelial genotype influences the production of recombinant leukemogenic retroviruses in mice. J Virol. 1983 Jul;47(1):33–45. doi: 10.1128/jvi.47.1.33-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DesGroseillers L., Rassart E., Jolicoeur P. Thymotropism of murine leukemia virus is conferred by its long terminal repeat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4203–4207. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartley J. W., Wolford N. K., Old L. J., Rowe W. P. A new class of murine leukemia virus associated with development of spontaneous lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):789–792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Corbin V., Gilbert W. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' half of AKV. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6931–6944. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herr W., Gilbert W. Somatically acquired recombinant murine leukemia proviruses in thymic leukemias of AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1983 Apr;46(1):70–82. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.1.70-82.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoggan M. D., Buckler C. E., Sears J. F., Chan H. W., Rowe W. P., Martin M. A. Internal organization of endogenous proviral DNAs of xenotropic murine leukemia viruses. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):8–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.8-17.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G., Taylor B. A., Lee B. K. Organization, distribution, and stability of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia virus DNA sequences in chromosomes of Mus musculus. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):26–36. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.26-36.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawashima K., Ikeda H., Hartley J. W., Stockert E., Rowe W. P., Old L. J. Changes in expression of murine leukemia virus antigens and production of xenotropic virus in the late preleukemic period in AKR mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Dec;73(12):4680–4684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.12.4680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly M., Holland C. A., Lung M. L., Chattopadhyay S. K., Lowy D. R., Hopkins N. H. Nucleotide sequence of the 3' end of MCF 247 murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):291–298. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.291-298.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy J. A. Xenotropic viruses: murine leukemia viruses associated with NIH Swiss, NZB, and other mouse strains. Science. 1973 Dec 14;182(4117):1151–1153. doi: 10.1126/science.182.4117.1151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Chattopadhyay S. K., Teich N. M., Rowe W. P., Levine A. S. AKR murine leukemia virus genome: frequency of sequences in DNA of high-, low-, and non-virus-yielding mouse strains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3555–3559. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3555. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowy D. R., Rands E., Chattopadhyay S. K., Garon C. F., Hager G. L. Molecular cloning of infectious integrated murine leukemia virus DNA from infected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jan;77(1):614–618. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.1.614. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. H. Large RNase T1-resistant oligonucleotides encoding p15E and the U3 region of the long terminal repeat distinguish two biological classes of mink cell focus-forming type C viruses of inbred mice. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):275–290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.275-290.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lung M. L., Hering C., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Analysis of the genomes of mink cell focus-inducing murine type-C viruses: a progress report. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):1269–1274. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Donnell P. V., Stockert E., Obata Y., Old L. J. Leukemogenic properties of AKR dualtropic (MCF) viruses: amplification of murine leukemia virus-related antigens on thymocytes and acceleration of leukemia development in AKR mice. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):548–563. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90301-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poncz M., Solowiejczyk D., Ballantine M., Schwartz E., Surrey S. "Nonrandom" DNA sequence analysis in bacteriophage M13 by the dideoxy chain-termination method. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(14):4298–4302. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.14.4298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., Quax W., van der Putten H., Berns A. Characterization of AKR murine leukemia virus sequences in AKR mouse substrains and structure of integrated recombinant genomes in tumor tissues. J Virol. 1981 Jul;39(1):1–10. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.1.1-10.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quint W., van der Putten H., Janssen F., Berns A. Mobility of endogenous ecotropic murine leukemia viral genomes within mouse chromosomal DNA and integration of a mink cell focus-forming virus-type recombinant provirus in the germ line. J Virol. 1982 Mar;41(3):901–908. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.3.901-908.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowe W. P., Pincus T. Quantitative studies of naturally occurring murine leukemia virus infection of AKR mice. J Exp Med. 1972 Feb 1;135(2):429–436. doi: 10.1084/jem.135.2.429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Bird S., Weinberg R. A. Evidence for the Asiatic origin of endogenous AKR-type murine leukemia proviruses. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):824–835. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.824-835.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steffen D. L., Taylor B. A., Weinberg R. A. Continuing germ line integration of AKV proviruses during the breeding of AKR mice and derivative recombinant inbred strains. J Virol. 1982 Apr;42(1):165–175. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.1.165-175.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas C. Y., Coffin J. M. Genetic alterations of RNA leukemia viruses associated with the development of spontaneous thymic leukemia in AKR/J mice. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):416–426. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.416-426.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Quint W., van Raaij J., Maandag E. R., Verma I. M., Berns A. M-MuLV-induced leukemogenesis: integration and structure of recombinant proviruses in tumors. Cell. 1981 Jun;24(3):729–739. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90099-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Putten H., Terwindt E., Berns A., Jaenisch R. The integration sites of endogenous and exogenous Moloney murine leukemia virus. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):109–116. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90359-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]