Abstract
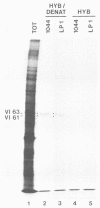
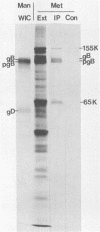
The possible identity of the herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) 65K (65,000-Mr) virion protein which stimulates transcription from immediate-early genes with the HSV-1 65K DNA-binding protein was investigated. The two proteins were found to be distinct by the three separate criteria of immunological reactivity, tryptic peptide fingerprinting, and mobility in two-dimensional gels. Using HSV-1/HSV-2 intertypic recombinants and a serotype-specific antiserum, we located the gene encoding the 65K DNA-binding protein between coordinates 0.574 and 0.682 on the HSV-1 genome. The protein is posttranslationally modified by phosphorylation. In crude extracts of HSV-1-infected cells the 65K trans-inducing protein did not detectably bind to double-stranded calf thymus DNA under the conditions of our assay.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. W., Baum P. R., Gesteland R. F. Processing of adenovirus 2-induced proteins. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):241–252. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.241-252.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson K. P., Frink R. J., Devi G. B., Gaylord B. H., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Detailed characterization of the mRNA mapping in the HindIII fragment K region of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome. J Virol. 1981 Mar;37(3):1011–1027. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.3.1011-1027.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bacchetti S., Evelegh M. J., Muirhead B. Identification and separation of the two subunits of the herpes simplex virus ribonucleotide reductase. J Virol. 1986 Mar;57(3):1177–1181. doi: 10.1128/jvi.57.3.1177-1181.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterson W., Roizman B. Characterization of the herpes simplex virion-associated factor responsible for the induction of alpha genes. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):371–377. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.371-377.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bayliss G. J., Marsden H. S., Hay J. Herpes simplex virus proteins: DNA-binding proteins in infected cells and in the virus structure. Virology. 1975 Nov;68(1):124–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90154-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berk A. J., Lee F., Harrison T., Williams J., Sharp P. A. Pre-early adenovirus 5 gene product regulates synthesis of early viral messenger RNAs. Cell. 1979 Aug;17(4):935–944. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90333-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown S. M., Ritchie D. A., Subak-Sharpe J. H. Genetic studies with herpes simplex virus type 1. The isolation of temperature-sensitive mutants, their arrangement into complementation groups and recombination analysis leading to a linkage map. J Gen Virol. 1973 Mar;18(3):329–346. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-18-3-329. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bzik D. J., Preston C. M. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of herpes simplex virus immediate early gene 3: DNA sequences required for enhancer-like activity and response to trans-activation by a virion polypeptide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Jan 24;14(2):929–943. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.2.929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campbell M. E., Palfreyman J. W., Preston C. M. Identification of herpes simplex virus DNA sequences which encode a trans-acting polypeptide responsible for stimulation of immediate early transcription. J Mol Biol. 1984 Nov 25;180(1):1–19. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90427-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chartrand P., Wilkie N. M., Timbury M. C. Physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutations of herpes simplex virus type 2 by marker rescue. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):121–133. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clements J. B., Watson R. J., Wilkie N. M. Temporal regulation of herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription: location of transcripts on the viral genome. Cell. 1977 Sep;12(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90205-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalziel R. G., Marsden H. S. Identification of two herpes simplex virus type 1-induced proteins (21K and 22K) which interact specifically with the a sequence of herpes simplex virus DNA. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1467–1475. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Wilkie N. M. One functional copy of the long terminal repeat gene specifying the immediate-early polypeptide IE 110 suffices for a productive infection of human foetal lung cells by herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jul;55(Pt 1):179–191. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-55-1-179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferguson B., Krippl B., Andrisani O., Jones N., Westphal H., Rosenberg M. E1A 13S and 12S mRNA products made in Escherichia coli both function as nucleus-localized transcription activators but do not directly bind DNA. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2653–2661. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2653. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., Marsden H. S., Dutia B. M. The ribonucleotide reductase induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 involves minimally a complex of two polypeptides (136K and 38K). J Gen Virol. 1985 Jul;66(Pt 7):1581–1587. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-7-1581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frame M. C., McGeoch D. J., Rixon F. J., Orr A. C., Marsden H. S. The 10K virion phosphoprotein encoded by gene US9 from herpes simplex virus type 1. Virology. 1986 Apr 30;150(2):321–332. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(86)90297-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freeman M. J., Powell K. L. DNA-binding properties of a herpes simplex virus immediate early protein. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):1084–1087. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.1084-1087.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Anderson K. P., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus type 1 HindIII fragment L encodes spliced and complementary mRNA species. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):559–572. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.559-572.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frink R. J., Eisenberg R., Cohen G., Wagner E. K. Detailed analysis of the portion of the herpes simplex virus type 1 genome encoding glycoprotein C. J Virol. 1983 Feb;45(2):634–647. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.2.634-647.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S., Preston C. M., Smiley J. R., Summers W. C., Summers W. P. Utilization of internal AUG codons for initiation of protein synthesis directed by mRNAs from normal and mutant genes encoding herpes simplex virus-specified thymidine kinase. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):512–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.512-519.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S. Two-dimensional gel analysis of HSV type 1-induced polypeptides and glycoprotein processing. J Gen Virol. 1981 Jan;52(Pt 1):77–92. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-52-1-77. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall L. M., Draper K. G., Frink R. J., Costa R. H., Wagner E. K. Herpes simplex virus mRNA species mapping in EcoRI fragment I. J Virol. 1982 Aug;43(2):594–607. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.2.594-607.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Oroszlan S., Konigsberg W. A micromethod for complete removal of dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Anal Biochem. 1979 Feb;93(1):153–157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. I. Cascade regulation of the synthesis of three groups of viral proteins. J Virol. 1974 Jul;14(1):8–19. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.1.8-19.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honess R. W., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis: sequential transition of polypeptide synthesis requires functional viral polypeptides. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Apr;72(4):1276–1280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.4.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones N., Shenk T. An adenovirus type 5 early gene function regulates expression of other early viral genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3665–3669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones P. C., Roizman B. Regulation of herpesvirus macromolecular synthesis. VIII. The transcription program consists of three phases during which both extent of transcription and accumulation of RNA in the cytoplasm are regulated. J Virol. 1979 Aug;31(2):299–314. doi: 10.1128/jvi.31.2.299-314.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ko J. L., Dalie B. L., Goldman E., Harter M. L. Adenovirus-2 early region IA protein synthesized in Escherichia coli extracts indirectly associates with DNA. EMBO J. 1986 Jul;5(7):1645–1651. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04407.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACPHERSON I., STOKER M. Polyoma transformation of hamster cell clones--an investigation of genetic factors affecting cell competence. Virology. 1962 Feb;16:147–151. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(62)90290-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mackem S., Roizman B. Structural features of the herpes simplex virus alpha gene 4, 0, and 27 promoter-regulatory sequences which confer alpha regulation on chimeric thymidine kinase genes. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):939–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.939-949.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Haarr L., Preston C. M. Processing of herpes simplex virus proteins and evidence that translation of thymidine kinase mRNA is initiated at three separate AUG codons. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):434–445. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.434-445.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marsden H. S., Stow N. D., Preston V. G., Timbury M. C., Wilkie N. M. Physical mapping of herpes simplex virus-induced polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):624–642. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.624-642.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLauchlan J., Clements J. B. Organization of the herpes simplex virus type 1 transcription unit encoding two early proteins with molecular weights of 140000 and 40000. J Gen Virol. 1983 May;64(Pt 5):997–1006. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-5-997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLean C., Buckmaster A., Hancock D., Buchan A., Fuller A., Minson A. Monoclonal antibodies to three non-glycosylated antigens of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1982 Dec;63(2):297–305. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-63-2-297. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. Z., Goodman H. M., O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of basic as well as acidic proteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):1133–1141. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90176-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Post L. E., Mackem S., Roizman B. Regulation of alpha genes of herpes simplex virus: expression of chimeric genes produced by fusion of thymidine kinase with alpha gene promoters. Cell. 1981 May;24(2):555–565. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90346-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M. Control of herpes simplex virus type 1 mRNA synthesis in cells infected with wild-type virus or the temperature-sensitive mutant tsK. J Virol. 1979 Jan;29(1):275–284. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.1.275-284.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., Cordingley M. G., Stow N. D. Analysis of DNA sequences which regulate the transcription of a herpes simplex virus immediate early gene. J Virol. 1984 Jun;50(3):708–716. doi: 10.1128/jvi.50.3.708-716.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston C. M., McGeoch D. J. Identification and mapping of two polypeptides encoded within the herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase gene sequences. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):593–605. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.593-605.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Davison A. J., Marsden H. S., Timbury M. C., Subak-Sharpe J. H., Wilkie N. M. Recombinants between herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2: analyses of genome structures and expression of immediate early polypeptides. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):499–517. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.499-517.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Fisher F. B. Identification of the herpes simplex virus type 1 gene encoding the dUTPase. Virology. 1984 Oct 15;138(1):58–68. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90147-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Preston V. G., Palfreyman J. W., Dutia B. M. Identification of a herpes simplex virus type 1 polypeptide which is a component of the virus-induced ribonucleotide reductase. J Gen Virol. 1984 Sep;65(Pt 9):1457–1466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-65-9-1457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevely W. S., Katan M., Stirling V., Smith G., Leader D. P. Protein kinase activities associated with the virions of pseudorabies and herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):661–673. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanstrom R. I., Pivo K., Wagner E. K. Restricted transcription of the herpes simplex virus genome occurring early after infection and in the presence of metabolic inhibitors. Virology. 1975 Jul;66(1):140–150. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(75)90185-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timbury M. C. Temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. J Gen Virol. 1971 Nov;13(2):373–376. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-13-2-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitton J. L., Rixon F. J., Easton A. J., Clements J. B. Immediate-early mRNA-2 of herpes simplex viruses types 1 and 2 is unspliced: conserved sequences around the 5' and 3' termini correspond to transcription regulatory signals. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Sep 24;11(18):6271–6287. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.18.6271. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]