Abstract
Polyphosphate, a linear polymer of inorganic phosphate, is present in platelet dense granules and is secreted on platelet activation. We recently reported that polyphosphate is a potent hemostatic regulator, serving to activate the contact pathway of blood clotting and accelerate factor V activation. Because polyphosphate did not alter thrombin clotting times, it appeared to exert all its procoagulant actions upstream of thrombin. We now report that polyphosphate enhances fibrin clot structure in a calcium-dependent manner. Fibrin clots formed in the presence of polyphosphate had up to 3-fold higher turbidity, had higher mass-length ratios, and exhibited thicker fibers in scanning electron micrographs. The ability of polyphosphate to enhance fibrin clot turbidity was independent of factor XIIIa activity. When plasmin or a combination of plasminogen and tissue plasminogen activators were included in clotting reactions, fibrin clots formed in the presence of polyphosphate exhibited prolonged clot lysis times. Release of polyphosphate from activated platelets or infectious microorganisms may play an important role in modulating fibrin clot structure and increasing its resistance to fibrinolysis. Polyphosphate may also be useful in enhancing the structure of surgical fibrin sealants.
Introduction
A fibrin clot is the final product of the blood clotting cascade. Thrombin catalyzes release of fibrinopeptide A from fibrinogen to create fibrin monomers, which then aggregate to protofibrils. Proteolytic release of fibrinopeptide B by thrombin permits lateral protofibril aggregation, resulting in a three-dimensional fibrin gel. Factor XIIIa, a transglutaminase activated by thrombin, covalently crosslinks these fibers to increase the strength and elasticity of the resulting clot.1 Variables known to influence fibrin clot structure include fibrinogen and thrombin concentrations,1 pH,2,3 ionic strength,3 chloride ion concentration,2 and presence of calcium ions.4 A variety of molecules are reported to affect fibrin clot structure, including homocysteine,5 decorin core protein,6 heparins,7,8 dextran,9 and hydroxyethylstarch.10 In this study, we demonstrate that inorganic polyphosphate (polyP) strongly modulates fibrin clot structure
polyP is a negatively charged, linear polymer of phosphate units linked by high-energy phosphoanhydride bonds. polyP has a wide biologic distribution,11 but its functions have been studied most extensively in prokaryotes and unicellular eukaryotes, in which high levels of polyP accumulate in organelles known as acidocalcisomes. In such organisms, polyP plays essential roles in stress responses and virulence.12 Although polyP has been studied less extensively in mammalian cells,13 it has been reported to induce apoptosis in plasma cells,14 promote calcification in osteoblasts,15 and block metastasis of melanoma cells in a mouse model.16 It has also been proposed to serve as a regulatory factor in proliferative signaling pathways.17
Dense granules of human platelets strongly resemble acidocalcisomes and contain high levels of polyP having chain lengths of approximately 75 phosphate units.18 polyP is released from platelets in response to stimulation by thrombin18 and is subsequently cleared from plasma, presumably because of degradation by plasma phosphatases.19 We recently reported that polyP is a potent hemostatic regulator, accelerating blood coagulation by activating the contact pathway of blood clotting, and also by promoting the activation of factor V.19 These combined effects result in an earlier peak of thrombin generation during plasma clotting without affecting the total amount of thrombin generated. Our previous studies demonstrated that polyP did not alter the clotting time of plasma initiated by adding thrombin, suggesting that polyP exerts its procoagulant effects upstream of thrombin.19
We now report that, although polyP has no impact on the timing of fibrin formation by thrombin, the structure of the resulting fibrin clots formed in the presence of polyP and plasma concentrations of calcium ions is altered, yielding fibrin clots with increased turbidity (because of fibers of higher mass-length ratio) and increased resistance to fibrinolysis. polyP therefore plays an additional, previously undetected role in blood clotting. Our findings also suggest that polyP may enhance the strength and stability of surgical fibrin sealants based on topical administration of fibrinogen and thrombin at wound sites.
Methods
Materials
Purified human fibrinogen in 20 mM of citrate, pH 7.4, was from Enzyme Research Laboratories (South Bend, IN), as were human α thrombin, plasmin, and factor XIII. For some experiments, citrate was removed from fibrinogen immediately before use by rapid gel filtration on Econo-Pac 10DG desalting columns (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA) equilibrated with Tris-buffered saline (TBS; 50 mM of Tris HCl, pH 7.4, 150 mM of NaCl, 0.02% NaN3). Fibrinogen concentrations were determined by measuring A280 (extinction coefficient, 1.51). Glu-plasminogen and 2-chain tissue plasminogen activator (tPA) were from Calbiochem (Gibbstown, NJ). Normal citrated plasma immunodepleted of prothrombin was from Haematologic Technologies (Essex Junction, VT). Unfractionated heparin and polyP75, a polyP preparation containing a mean polymer size of approximately 75, were from Sigma-Aldrich (St Louis, MO). Concentrations of polyP are expressed throughout in terms of phosphate monomer.
Measurements of clot turbidity
Fibrin clots were formed in 96-well, medium-binding polystyrene microplates (Corning, Corning, NY) by first preincubating a mixture of fibrinogen and polyP in TBS plus the indicated CaCl2 concentrations (for 15 minutes, unless otherwise stated). Thrombin in TBS plus the same concentration of CaCl2 was then added to trigger clot formation. Final reactant concentrations were typically 2.6 mg/mL fibrinogen, 62.5 pM to 8 nM thrombin, 0 to 8 mM polyP, and 0 to 5 mM CaCl2 in a total volume of 200 μL. In some studies, 0 to 10 U/mL unfractionated heparin, 1 mM iodoacetamide, or 100 nM factor XIII was also included. Additional studies substituted ZnCl2, MgCl2, or MnCl2 for the CaCl2 or included these metals in addition to 2.5 mM CaCl2. Clotting was evaluated by monitoring the change in turbidity (A405) for 1 hour at room temperature using a Spectramax microplate reader (Molecular Devices, Sunnyvale, CA). Clotting times were calculated from these data using SigmaPlot (Systat Software, San Jose, CA) to fit a line to the steepest segment of the absorbance curves and then determining the intersection with the initial baseline A405 (representing the lag phase before clot formation). Final turbidities (A405) of fibrin clots were typically quantified after the clots had matured for 60 minutes.
Fibrin clots were also formed with minimally diluted prothrombin-deficient plasma. Solutions of CaCl2 and polyP in TBS were added to plasma 15 minutes before initiation of clotting with thrombin, during which no clotting (ie, no observable change in A405) occurred. Thrombin was then added to initiate fibrin formation and the increase in A405 was monitored for 1 hour at room temperature. Final concentrations were 80% (vol/vol) plasma, 8.7 mM citrate (contributed by the plasma), 13.7 mM CaCl2, 0 to 50 μM polyP, and 10 nM thrombin in a total volume of 100 μL.
Fibrin cross-link formation
Rates of α and γ cross-link formation were studied in clotting reactions carried out as described for turbidity measurements, using purified fibrinogen containing only a small amount of contaminating factor XIII, except that fibrin clots were formed in polypropylene tubes at 37°C and reactions were stopped at various times by adding an equal volume of 2× sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) sample buffer with immediate boiling at 95°C for 5 minutes; 10-μL samples were then subjected to SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) using 7.5% polyacrylamide gels, and stained with Coomassie (Gelcode Blue; Pierce Chemical, Rockford, IL) according to the manufacturer's directions.
Determination of fibril thickness
Relative fibril mass-to-length ratios were determined using a modification20 of the method of Carr and Gabriel9 for clots with high turbidity. Briefly, fibrin clots were allowed to mature for 2 hours after thrombin addition, after which absorbance was scanned from 400 to 800 nm on a Spectramax microplate reader. A plot of 1/τ*λ3 (y-axis) versus 1/λ2 (x-axis) was used to determine the y intercept, the inverse of which is proportional to the mass-length ratio of the fibers.9 Data were normalized in comparison to clots formed under identical conditions but in the absence of polyP, whose relative mass-length ratio was defined as 1.0.21
Scanning electron microscopy
Fibrin clots formed in triplicate as described in “Measurements of clot turbidity” for turbidity measurements were allowed to mature for 2 hours after thrombin addition. Clots were washed 4 times in 0.1 M cacodylate, fixed in Karnovsky's glutaraldehyde solution overnight, then processed by stepwise ethanol gradient, critical point drying, and sputter coating with gold palladium. Clots were observed and photographed using an XL30 ESEM-FEG environmental scanning electron microscope with field emission electron gun (FEI, Hillsboro, OR) at 5.0 kV, with a spot size of 2.1 nm with images captured using the instrument-supplied microscope control software. The thickness of 10 different fibers in images of each of 4 different representative areas (photographed at 65 000× magnification) was measured using ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health) for a total of 40 fibers per clot (3 clots per polyP concentration). Additional images were obtained at 35 000× magnification. Final image processing was with Adobe Photoshop 6.0.
Detection of polyP incorporated into fibrin clots
Fibrin clots were formed as described for turbidity experiments, in which the fibrinogen, calcium, and polyP (when included) were preincubated for 15 minutes before adding thrombin. Clotting reactions were prepared in polypropylene tubes (total volume, 400 μL) containing 1 mg/mL fibrinogen, 2.5 mM CaCl2, 1 mM iodoacetamide, 3 nM thrombin, and either polyP (0, 100 μM, 500 mM, or 1 mM) or NaH2PO4 (1 mM). Clots were allowed to mature for 1 hour. Some clots made without polyP were subsequently soaked for 15 minutes in 1 mM polyP. All clots were then washed 3 times (30 minutes each) in 1 mL TBS with 2.5 mM CaCl2 and then stained for 30 minutes with 30 mg/L toluidine blue, destained for 15 hours (overnight) in water, dried under vacuum, and then digested in 1 mL of 40 mM acetic acid for 2 hours. The toluidine blue concentration of digested clots was then quantified in a 96-well microplate by measuring A630.
Thromboelastography
Thromboelastography was performed using the ROTEM 4 channel system (Pentapharm, Munich, Germany), using the supplied software package and a manual pipette, with reaction components as described in “Measurements of clot turbidity” in the microplate assay for clot turbidity. Reactant concentrations were 2.6 mg/mL fibrinogen, 3 nM thrombin, 0 or 1 mM polyP, and 2.5 mM CaCl2 in a total volume of 300 μL. Clot firmness for each clot was recorded 30 minutes after thrombin addition.
Fibrinolysis
Fibrin clots were formed in microplates using purified fibrinogen (as for the turbidity experiments), except that the fibrinogen concentration was 1 mg/mL and A405 was monitored for up to 6 hours. In some experiments, 8 nM plasmin was added immediately before thrombin addition. In other experiments, 200 nM plasminogen was added to the fibrinogen, and clotting was initiated by a mixture of thrombin (1 nM final) and tPA (375 pM final). Because of markedly higher turbidities in the presence of polyP, turbidity data were normalized to maximal turbidity. The 50% lysis time was defined as the time elapsed, during the lysis phase, from the maximal to the half-maximal A405 value.
Results
Turbidity measurements
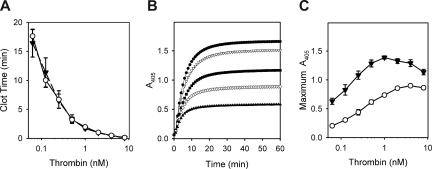
We previously showed that adding polyP to plasma did not influence the time to clot formation initiated by thrombin,19 suggesting that all relevant effects of polyP on plasma coagulation occur upstream of thrombin. To further characterize any potential impact of polyP on the terminal portion of the coagulation cascade, we evaluated fibrin clots made from purified proteins by measuring the change in turbidity (A405) during clotting induced by thrombin. As we previously observed with plasma, polyP did not alter the clotting time of purified fibrinogen in response to thrombin, a finding that was consistent through a wide range of thrombin concentrations (Figure 1A). In contrast to the lack of effect on clotting time, polyP markedly increased the final turbidity of fibrin clots (Figure 1B) regardless of the amount of thrombin added (Figure 1C). Interestingly, the ability of polyP to modulate the turbidity of the resulting fibrin gel was dependent on the Ca2+ concentration. In the absence of Ca2+, polyP did not affect clot turbidity, but at low mM Ca2+ concentrations, adding polyP increased final clot turbidity in a concentration-dependent manner (Figure 2). The polyP concentration exerting maximal effect on clot turbidity depended on the Ca2+ concentration: 1 mM polyP at 2 mM Ca2+; 1 to 2 mM polyP at 2.5 mM Ca2+; 2 to 4 mM polyP at 3 mM Ca2+; and 3 to 8 mM polyP at 5 mM Ca2+.
Figure 1.
Polyphosphate increases final clot turbidity but does not alter clotting time over a wide range of thrombin concentrations. Clotting reactions contained 2.6 mg/mL of citrate-free fibrinogen, which was preincubated for 15 minutes in the presence of 2.5 mM CaCl2, with or without polyphosphate (polyP), before clot initiation by thrombin. (A) Clotting times of reactions containing 1 mM polyP (▼) or no polyP (○) as a function of various thrombin concentrations. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 3). (B) Time courses of fibrin formation (turbidity increase) in reactions containing 0 (▲), 188 μM (◇), 375 μM (■), 750 μM (▼), or 1.5 mM (●) polyP, with clotting initiated by 3 nM thrombin. Data are from a representative experiment. (C) Maximum fibrin clot turbidities in reactions containing 1 mM polyP (▼) or no polyP (○) as a function of various thrombin concentrations. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 3).
Figure 2.
The concentrations of both polyP and Ca2+ influence fibrin clot turbidity. The final turbidities of clots formed from fibrinogen/thrombin mixtures were quantified as described in “Measurements of clot turbidity.” Reactions contained 2.6 mg/mL citrate-free fibrinogen, which was preincubated for 15 minutes with CaCl2 and the indicated concentrations of polyP (x-axis), after which clotting was initiated with 1 nM thrombin. Ca2+ concentrations were 0 (●), 2 mM (▼), 2.5 mM (□), 3 mM (▼), and 5 mM (◇). Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 3).
Because Ca2+ was required for polyP to affect clot turbidity, we explored the ability of other divalent cations to support enhancement of clot turbidity by polyP, including ZnCl2, MgCl2, and MnCl2, either alone or in addition to 2.5 mM of CaCl2. None of these metals could substitute for Ca2+ in promoting the ability of polyP to increase clot turbidity, although Zn2+ and Mn2+ enhanced clot turbidity in a polyP-independent manner (Figure S1, available on the Blood website; see the Supplemental Materials link at the top of the online article).
We next compared the effect of polyP versus heparin, another anionic polymer, in enhancing clot turbidity. Fibrinogen contains a heparin binding site,22 and heparin is known to increase the turbidity of clots formed from purified fibrinogen and thrombin.23 We found that heparin modestly increased fibrin turbidity in a dose-dependent fashion (examined from 0 to 10 units/mL heparin), but the magnitude of the turbidity increase was markedly lower than that observed with polyP (Figure 3). Furthermore, adding unfractionated heparin to fibrinogen clotting reactions did not reduce the effect of polyP on clot turbidity. Rather, the mild increase in clot turbidity because of inclusion of heparin appeared to be additive to the much larger polyP effect (Figure 3). These results suggest that the polyP effect on fibrin clot turbidity is distinct from that of heparin.
Figure 3.
polyP influences clot turbidity to a much greater extent than does heparin. The final turbidities of clots formed with fibrinogen mixed with thrombin were quantified as described in “Measurements of clot turbidity.” Reactions contained 2.6 mg/mL fibrinogen preincubated for 15 minutes in the presence of: various heparin concentrations without CaCl2 (□); various heparin concentrations with 2.5 mM CaCl2 (○); various polyP concentrations with 2.5 mM CaCl2 (▼); or various polyP concentrations with 2.5 mM CaCl2 and 5 U/mL heparin (♦). Clotting was then initiated with 1 nM thrombin. Heparin and polyP concentrations are indicated on the x-axes. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 4).
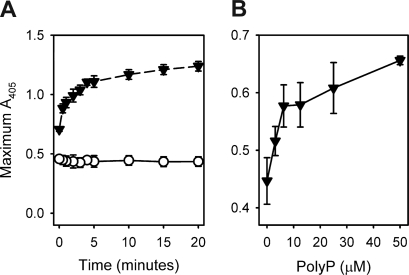
We found that the ability of polyP to increase fibrin clot turbidity required the preincubation of fibrinogen, Ca2+, and polyP before clotting, an effect that was maximal when the three were preincubated together for 10 to 15 minutes before adding thrombin (Figure 4A). Varying the order of addition of these components demonstrated that all three had to be present during the preincubation period to achieve maximal increases in clot turbidity (Figure S2).
Figure 4.
Preincubation of fibrinogen with polyP and Ca2+ influences final clot turbidity. (A) Final turbidities of clots formed with fibrinogen mixed with thrombin were quantified as described in “Measurements of clot turbidity.” Reactions contained 2.6 mg/mL fibrinogen preincubated for the indicated times in the presence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 with 1 mM polyP (▼) or without polyP (○), after which clotting was initiated with 8 nM thrombin. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 3). (B) Final turbidities of clots formed with prothrombin-deficient plasma mixed with thrombin were quantified as described in “Measurements of clot turbidity.” Reactions contained citrated plasma (80%) with added CaCl2 (13.7 mM) and were preincubated for 15 minutes with polyP concentrations as indicated on the x-axis. Clotting was then initiated with 10 nM thrombin. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 4).
We next investigated the ability of polyP to enhance clot turbidity in plasma. These studies were complicated by the fact that polyP must be preincubated for several minutes with fibrinogen and calcium ions to enhance clot turbidity. Because preincubating plasma with polyP and Ca2+ will trigger clotting via the contact pathway, it is technically difficult to recapitulate the effect of polyP on clot turbidity using conventional clotting assays with normal plasma. Instead, we used prothrombin-deficient plasma to prevent thrombin generation during the preincubation phase of plasma with polyP and Ca2+. The highest concentrations of polyP caused precipitation when added to the minimally diluted citrated plasma, probably because of an interaction between polyP, citrate, and possibly the excess calcium included in the reaction. Lower polyP concentrations than were evaluated in the purified protein system were therefore used in this plasma-based system. Adding Ca2+ and polyP to minimally diluted, prothrombin-deficient plasma showed that polyP elicited a concentration-dependent increase in final clot turbidity after thrombin addition (Figure 4B).
Fibrin cross-linking
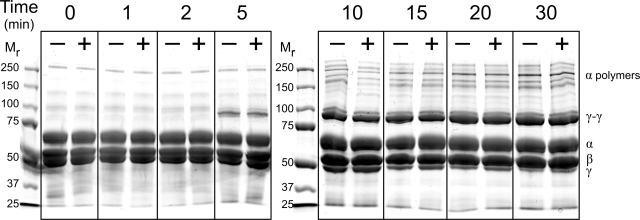
The fact that polyP enhanced clot turbidity only in the presence of Ca2+ suggested that this enhancement might be associated with factor XIIIa cross-linking activity, which is also calcium dependent. Because purified fibrinogen contains small amounts of contaminating factor XIII, some degree of covalent cross-linking occurs during the formation of fibrin gels. However, when we added additional preactivated factor XIIIa to the clotting mixtures, polyP still increased fibrin clot turbidity (Figure S3). Furthermore, iodoacetamide, a transglutaminase inhibitor, failed to antagonize the polyP enhancement of final clot turbidity (Figure S3). Finally, SDS-PAGE analyses revealed no impact of polyP on the time-dependent disappearance of the fibrinogen γ chains or the appearance of γ-γ dimers or α polymers (Figure 5), indicating that the increase in fibrin gel turbidity associated with polyP was not mediated by changes in the rate or extent of cross-linking by factor XIIIa.
Figure 5.
The rate and extent of fibrin cross-linking are not influenced by polyP. Fibrin cross-linking was examined using SDS-PAGE for reactions containing 2.6 mg/mL citrate-free fibrinogen (containing a small amount of contaminating factor XIII), which was preincubated for 15 minutes in the presence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 with 1 mM polyP (+) or without polyP (−). Thrombin (1 nM) was then added, and reactions were stopped at the indicated times. (Left) Mr markers. (Right) Locations of fibrin chains (α, β, γ, cross-linked γ-γ dimers and cross-linked α chain polymers).
Fibrin fiber thickness
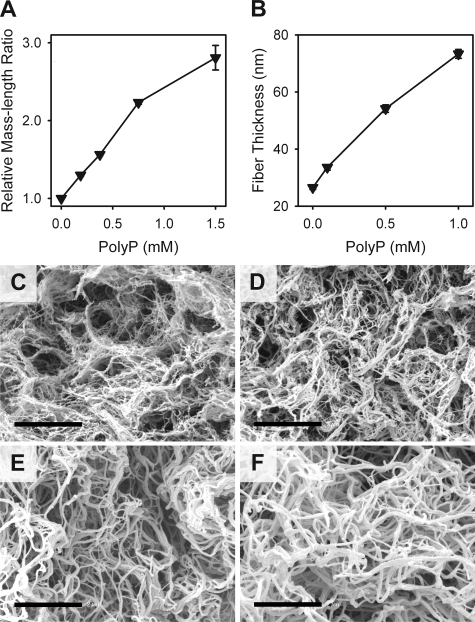
Previous reports have indicated that the turbidity of fibrin gels formed from purified fibrinogen and thrombin is primarily a function of fiber diameter.24 The increased turbidity of clots formed in the presence of polyP might therefore be caused by altered fibrin assembly, resulting in thicker fibrils. We measured normalized mass-length ratios for fibrin gels, prepared with and without polyP, and found that polyP resulted in higher mass-length ratios for fibrin fibrils (Figure 6A): 100 μM polyP increased the mass-length ratio by approximately 15%, whereas 1.5 mM polyP increased the mass-length ratio almost 3-fold.
Figure 6.
polyP increases the thickness of fibrin fibrils. Clots were formed by preincubating 2.6 mg/mL of fibrinogen for 15 minutes in the presence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 plus the indicated polyP concentrations, after which clotting was initiated with 3 nM thrombin. (A) Mass-length ratios of the resulting fibrin preparations (relative to the condition without polyP), calculated from scans of optical densities from 400 to 800 nm as described in “Determination of fibril thickness.” Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 4). (B) Fiber thickness is measured from scanning electron micrographs, as described in “Scanning electron microscopy.” Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 120). (C-F) Representative scanning electron micrographs of fibrin clots formed in the presence of (C) no polyP, (D) 100 μM polyP, (E) 500 μM polyP, and (F) 1 mM polyP. Bar represents 2 μm.
Scanning electron microscopy
We examined the impact of polyP on fibrin clot structure using scanning electron microscopy (representative micrographs in Figure 6C-F). Clots made in the presence of polyP exhibited strikingly thicker fibers than clots made without polyP, with mean fiber diameters increasing as the polyP concentration increased (Figure 6B). These findings agree with the effects of polyP on fibril mass-length ratios reported in “Fibrin fiber thickness.” In these micrographs, although fiber diameter was markedly increased by the inclusion of polyP, pore size appeared not to be affected. One possible explanation is that increased fiber diameter results from incorporation of polyP into the fibers.
Incorporation of polyP into fibrin clots
To evaluate whether or not polyP was incorporated into the polymerizing fibrin clots, we detected clot-associated polyP using toluidine blue staining. Clots were allowed to polymerize in the presence or absence of polyP, whereas negative control clots were formed in the presence of an equivalent concentration of monophosphate. In addition, some clots that had been polymerized without polyP were soaked in polyP afterward, to determine whether polyP could associate with previously polymerized fibrin. All clots were washed to remove unbound polyP, then stained with toluidine blue, a metachromatic dye that stains polyP a characteristic pink color. All clots that had been formed with polyP present during polymerization stained strongly pink, whereas clots that had been formed without polyP (or treated with polyP after polymerization) stained lightly blue (not shown). When the amount of clot-bound toluidine blue was quantified, we found that clots made without polyP contained very little dye (0.3 ± 0.1 mg toluidine blue/L), as did clots made with 1 mM of monophosphate (0.3 ± 0.1 mg/L). Clots treated with polyphosphate after fibrin polymerization contained only slightly more dye (0.7 ± 0.1 mg/L). In contrast, clots that had been polymerized in the presence of polyP contained considerably more dye, with the amount of clot-associated toluidine blue increasing as the polyP concentration increased (data are mean toluidine blue concentrations in mg/L ± standard error; n = 6): 1.9 plus or minus 0.2 at 100 μM polyP, 3.8 plus or minus 0.3 at 500 μM polyP, and 5.1 plus or minus 0.4 mg/L at 1 mM polyP. These findings indicate that polyP becomes incorporated into polymerizing fibrin clots but that it binds less well to fibrin that has already been polymerized.
Thromboelastography
We examined the effect of polyP on the elastic properties of fibrin using thromboelastography, in experiments in which fibrinogen was preincubated for 15 minutes with 1 mM polyP and 2.5 mM Ca2+, after which clotting was initiated with thrombin. Thirty minutes after clot formation, we analyzed clot properties and found that clots formed with polyP exhibited greater firmness (29.8 ± 0.9 mm) than did clots formed without polyP (24.5 ± 0.6 mm; data are mean plus or minus SE; n = 4).
Fibrinolysis
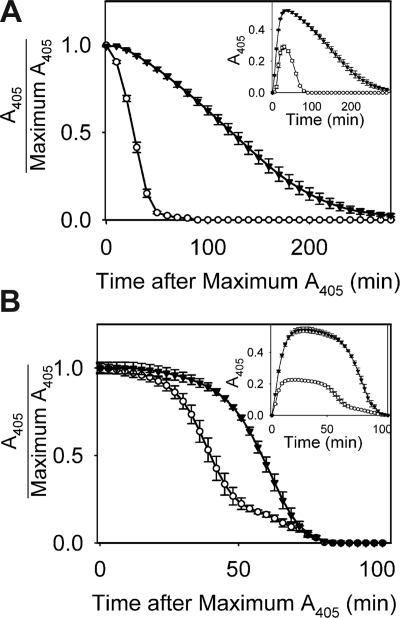
The impact of polyP on the rate of fibrinolysis was assessed in 2 ways. In one approach, plasmin was added to clotting mixtures immediately before adding thrombin (Figure 7A). The mean time to 50% lysis for fibrin clots formed without polyP was 28.5 plus or minus 0.8 minutes (n = 8) but was 120.4 plus or minus 5.6 minutes for clots formed in the presence of polyP. In another approach, a mixture of plasminogen and tPA was added to clotting reactions (Figure 7B). The mean time to 50% lysis for fibrin clots formed without polyP was 40.8 plus or minus 2.5 minutes (n = 4) but was 62.6 plus or minus 1.8 minutes when clots were formed in the presence of polyP. Fibrin clots containing polyP therefore lysed more slowly than clots not containing polyP.
Figure 7.
polyP slows the rate of fibrinolysis. (A) Lysis of clots formed by preincubating 1.0 mg/mL fibrinogen for 15 minutes in the presence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 with 1 mM polyP (▼) or without polyP (○), after which 8 nM plasmin was added followed immediately by 1 nM thrombin. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 8). (B) Lysis of clots formed by preincubating 1.0 mg/mL fibrinogen and 200 nM plasminogen for 15 minutes in the presence of 2.5 mM CaCl2 with 1 mM polyP (▽) or without polyP (○), after which 375 pM tPA and 1 nM thrombin were added to initiate clotting. In both panels, absorbance data were normalized to the maximal A405 value for each curve, plotted versus time after reaching maximal A405. The insets show the entire turbidity profiles from the point of thrombin addition, without normalization. Data are mean plus or minus SE (n = 4).
Discussion
Our initial report on the ability of polyP to modulate blood coagulation revealed that polyP activates the contact pathway and, perhaps more importantly, accelerates the proteolytic conversion of factor V to Va.19 This latter effect causes the prothrombinase complex to assemble more quickly, which in turn accelerates the burst of thrombin generation, resulting in more rapid clot formation. We now report that polyP also modulated fibrin clot structure in a calcium-dependent fashion. polyP was incorporated into clots during polymerization, and the resulting clots exhibited increased turbidity, contained thicker fibrils, were firmer, and were more resistant to fibrinolysis.
A number of studies have evaluated the effects of charged polymers on fibrin assembly. Cationic polymers, such as poly(L-arginine) or poly(L-lysine), resulted in a concentration-dependent increase of fiber mass/length ratio, whereas anionic polymers, such as poly(L-aspartate) or poly(L-glutamate), generally had no effect.25 This indicates that not all anionic polymers increase fibril thickness. Some polymers, such as dextran, increased clot turbidity through enhancement of lateral association of protofibrils.9 Heparin has previously been reported to increase fibrin clot turbidity,23,26 which was confirmed in this study (although the magnitude of the turbidity increase induced by heparin was small). Fibrinogen contains a heparin-binding domain.22,27 Interestingly, clots formed in the presence of heparin are reportedly more sensitive to lysis,26 whereas we found that clots formed in the presence of polyP were more resistant to lysis.
Of interest is the calcium dependence of the ability of polyP to increase fibril thickness. None of the steps in the generation of polymerized fibrin after thrombin cleavage of fibrinogen absolutely requires calcium ions, although Ca2+ has previously been shown to affect fibril thickness.4 We should point out that polyP could not be causing the observed effect simply by sequestering calcium ions because the Ca2+ concentrations typically used in our experiments were in substantial molar excess over the concentration of phosphate groups. For example, 1.5 mM phosphate could, at maximum, bind 0.75 mM Ca2+. Our experiments using 2.5 mM total Ca2+ would therefore still have 1.75 mM free Ca2+, which is a large molar excess over the fibrinogen concentration. Furthermore, lowering the Ca2+ concentration (in the absence of polyP) resulted in thinner fibers, rather than the thicker fibers that were observed in the presence of polyP.
Fibrinogen contains several high- and low-affinity Ca2+ binding sites, although their precise number and location are targets of active research.28,29 We found that the effect of polyP on clot turbidity was most profound when Ca2+, polyp, and fibrinogen were preincubated together before adding thrombin. Preloading of fibrinogen with Ca2+ would typically not occur in clotting reactions performed with citrated plasma, in which most of the free Ca2+ is chelated by citrate until clotting is triggered by adding excess Ca2+ and an activator of the clotting cascade. However, fibrinogen circulating in vivo is already equilibrated with Ca2+. Release of polyP (and additional Ca2+) from platelet dense granules in response to thrombin would then allow for the ready combination of fibrinogen, Ca2+, and polyP at the site of clotting.
The mechanism of polyP enhancement of fibrin clot structure is not yet clear. Elegant kinetic modeling of the fibril formation by Weisel and Nagaswami30 suggests that fibrin fibril thickness is dependent on multiple parameters, including the rates of fibrinopeptide A (FpA) cleavage, protofibril initiation, fiber initiation, fiber growth, and fiber aggregation. It is unlikely that polyP significantly alters the rate of FpA removal because polyP has no discernable effect on the lag period before initial rise in clot turbidity (defined here as “clot time”). Rather, the effect of polyP on the observed turbidity profiles is most consistent with polyP changing either the rate of fiber growth or the rate of fiber aggregation as defined in the model.30 On the other hand, this kinetic model did not include contributions from fibrinopeptide B (FpB) release, which is not strictly required for fibrin polymerization. Comparative studies of fibrin clot formation by reptilase (which does not cause FpB release) and thrombin have shown that thrombin cleavage of fibrinogen results in thicker fibers than does reptilase cleavage.4 Furthermore, slower FpB release from the γ′ fibrinogen variant favors delayed lateral aggregation of protofibrils, leading to clots with smaller diameter fibers.31 Thus, these studies indicate that faster removal of FpB promotes thicker fibers. Binding of Ca2+ appears to be connected to the release of FpB.29 Synthetic peptides (based on the B knob sequence) that bind in the b hole enhance the turbidity of fibrin clots, resulting in clots that are more resistant to fibrinolysis.32 One might speculate, therefore, that the impact of polyP on fibril thickness could be related to FpB release or interactions between the B knob and the b hole.
With the exception of synthetic peptides that bind to the b hole (causing more turbid clots with increased resistance to fibrinolysis),32 it is notable that in most reports to date, circumstances resulting in thicker fibrin fibers are generally associated with increased susceptibility to fibrinolysis.33–37 In contrast, we found that polyP promoted the formation of fibers with higher mass-length ratios that were more resistant to fibrinolysis than clots formed without polyP. One possibility is that polyP affects B-b interactions as discussed in this section. Another is that polyP affects binding of thrombin or plasmin to the developing clot, or the activity of clot-bound enzymes within the clot. It was previously shown that clots with thicker fibers tend to have more thrombin binding sites and lower Kd for thrombin binding than clots with thinner fibers.38 We have found that polyP binds thrombin (N.J. Mutch and J.H. Morrissey, unpublished observations, 2007) and that polyP accelerates the rate at which thrombin cleaves factor V.19 It is possible that the presence of polyP enhances the activity of clot-bound thrombin, which in turn affects the relative susceptibility of fibrin to plasmin. The potential impact, if any, of polyP on plasminogen binding and activation awaits further study.
We evaluated the impact of polyP on clot structure in a purified system, using polyP concentrations ranging from 100 μM to 8 mM. Previous work has demonstrated that polyP is released from human platelets in response to thrombin stimulation, readily reaching 3 μM in whole blood, with orders of magnitude higher concentrations possible within platelet-rich thrombi.18 At the expected physiologic concentrations of polyP released from platelets during in vivo clot formation (at least in whole blood), the effect of polyP on fibrin may be smaller than the 3-fold increase in fibril thickness seen with millimolar concentrations of polyP. However, even minor changes in fibril thickness and susceptibility to lysis could have a significant impact on thrombotic risk. Many studies have identified associations between conditions that result in abnormal clot structure and increased risk of thrombosis, including elevated plasma prothrombin concentration,21 elevated levels of γ′ fibrinogen,31 and dysfibrinogenemias, such as fibrinogens Caracass II39 and Dusart.40 The role of polyP in clot structure could therefore represent a possible target for modification of risk for thrombosis in a variety of prothrombotic disorders.
We found that low concentrations of polyP (50-100 μM) had a detectable impact on fibrin structure, whereas higher (mM) concentrations of polyP had a profound impact. Potentially, the large increases in fibril thickness associated with what may be supraphysiologic polyP concentrations could be exploited by adding polyP to the purified fibrinogen used in surgical fibrin sealants. Fibrin tissue sealants consist of purified thrombin and fibrinogen (typically formulated at supraphysiologic concentrations), which are mixed together and applied topically at bleeding sites intraoperatively.41 polyP may therefore have utility as an adjuvant for the fibrinogen component to enhance the structure, properties, and stability of the clot formed.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Jee Hong Lee and David Rodriguez for assistance, Diagnostica Stago-US for generously lending the ROTEM system, Lou Ann Miller of the University of the Illinois Center for Microscopic Imaging for skilled processing of samples for electron microscopy, and Scott Robinson and Cate Wallace of the University of Illinois Imaging Technology Center for expert assistance with scanning electron microscopy.
This work was supported by the National Heart, Lung and Blood Institute of the National Institutes of Health (grant R01 HL47014) and the Roy J. Carver Charitable Trust (grant 06-2328).
Footnotes
An Inside Blood analysis of this article appears at the front of this issue.
The online version of this article contains a data supplement.
The publication costs of this article were defrayed in part by page charge payment. Therefore, and solely to indicate this fact, this article is hereby marked “advertisement” in accordance with 18 USC section 1734.
Authorship
Contribution: S.A.S. performed research and wrote the manuscript; J.H.M. analyzed research and wrote the manuscript.
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: The authors are coinventors on patent applications pertaining to this work.
Correspondence: James H. Morrissey, Department of Biochemistry, College of Medicine, University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign, 417 Medical Science Bldg MC-714, 506 S Mathews, Urbana, IL 61801; e-mail: jhmorris@uiuc.edu.
References
- 1.Wolberg AS. Thrombin generation and fibrin clot structure. Blood Rev. 2007;21:131–142. doi: 10.1016/j.blre.2006.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Di Stasio E, Nagaswami C, Weisel JW, Di Cera E. Cl regulates the structure of the fibrin clot. Biophys J. 1998;75:1973–1979. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(98)77638-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Nair CH, Shah GA, Dhall DP. Effect of temperature, pH and ionic strength and composition on fibrin network structure and its development. Thromb Res. 1986;42:809–816. doi: 10.1016/0049-3848(86)90117-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Carr ME, Jr, Gabriel DA, McDonagh J. Influence of Ca2+ on the structure of reptilase-derived and thrombin-derived fibrin gels. Biochem J. 1986;239:513–516. doi: 10.1042/bj2390513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lauricella AM, Quintana I, Castanon M, Sassetti B, Kordich L. Influence of homocysteine on fibrin network lysis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006;17:181–186. doi: 10.1097/01.mbc.0000220238.99843.45. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dugan TA, Yang VW, McQuillan DJ, Hook M. Decorin modulates fibrin assembly and structure. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:38208–38216. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M607244200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Carr ME, Jr, Powers PL. Effect of glycosaminoglycans on thrombin- and atroxin-induced fibrin assembly and structure. Thromb Haemost. 1989;62:1057–1061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Parise P, Morini M, Agnelli G, Ascani A, Nenci GG. Effects of low molecular weight heparins on fibrin polymerization and clot sensitivity to t-PA-induced lysis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1993;4:721–727. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Carr ME, Jr, Gabriel DA. Dextran-induced changes in fibrin fiber size and density based on wavelength dependence of gel turbidity. Macromolecules. 1980;13:1473–1477. [Google Scholar]
- 10.Carr ME., Jr Effect of hydroxyethyl starch on the structure of thrombin- and reptilase-induced fibrin gels. J Lab Clin Med. 1986;108:556–561. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Kornberg A, Rao NN, Ault-Riche D. Inorganic polyphosphate: a molecule of many functions. Annu Rev Biochem. 1999;68:89–125. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biochem.68.1.89. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Kulaev IS, Kulakovskaya TV, Andreeva NA, Lichko LP. Metabolism and function of polyphosphates in bacteria and yeast. Prog Mol Subcell Biol. 1999;23:27–43. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-58444-2_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kumble KD, Kornberg A. Inorganic polyphosphate in mammalian cells and tissues. J Biol Chem. 1995;270:5818–5822. doi: 10.1074/jbc.270.11.5818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Hernandez-Ruiz L, Gonzalez-Garcia I, Castro C, Brieva JA, Ruiz FA. Inorganic polyphosphate and specific induction of apoptosis in human plasma cells. Haematologica. 2006;91:1180–1186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Kawazoe Y, Shiba T, Nakamura R, et al. Induction of calcification in MC3T3-E1 cells by inorganic polyphosphate. J Dent Res. 2004;83:613–618. doi: 10.1177/154405910408300806. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Han KY, Hong BS, Yoon YJ, et al. Polyphosphate blocks tumour metastasis via anti-angiogenic activity. Biochem J. 2007;406:49–55. doi: 10.1042/BJ20061542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Wang L, Fraley CD, Faridi J, Kornberg A, Roth RA. Inorganic polyphosphate stimulates mammalian TOR, a kinase involved in the proliferation of mammary cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100:11249–11254. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1534805100. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ruiz FA, Lea CR, Oldfield E, Docampo R. Human platelet dense granules contain polyphosphate and are similar to acidocalcisomes of bacteria and unicellular eukaryotes. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:44250–44257. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M406261200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Smith SA, Mutch NJ, Baskar D, et al. Polyphosphate modulates blood coagulation and fibrinolysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103:903–908. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0507195103. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Wolberg AS, Gabriel DA, Hoffman M. Analyzing fibrin clot structure using a microplate reader. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2002;13:533–539. doi: 10.1097/00001721-200209000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Wolberg AS, Monroe DM, Roberts HR, Hoffman M. Elevated prothrombin results in clots with an altered fiber structure: a possible mechanism of the increased thrombotic risk. Blood. 2003;101:3008–3013. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-08-2527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yakovlev S, Gorlatov S, Ingham K, Medved L. Interaction of fibrin(ogen) with heparin: further characterization and localization of the heparin-binding site. Biochemistry. 2003;42:7709–7716. doi: 10.1021/bi0344073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Collen A, Smorenburg SM, Peters E, et al. Unfractionated and low molecular weight heparin affect fibrin structure and angiogenesis in vitro. Cancer Res. 2000;60:6196–6200. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Carr ME, Jr, Hermans J. Size and density of fibrin fibers from turbidity. Macromolecules. 1978;11:46–50. doi: 10.1021/ma60061a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Carr ME, Jr, Cromartie R, Gabriel DA. Effect of homo poly(L-amino acids) on fibrin assembly: role of charge and molecular weight. Biochemistry. 1989;28:1384–1388. doi: 10.1021/bi00429a066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Nenci GG, Parise P, Morini M, Rossini A, Agnelli G. Fibrin clots obtained from plasma containing heparin show a higher sensitivity to t-PA-induced lysis. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1992;3:279–285. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199206000-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Odrljin TM, Shainoff JR, Lawrence SO, Simpson-Haidaris PJ. Thrombin cleavage enhances exposure of a heparin binding domain in the N-terminus of the fibrin beta chain. Blood. 1996;88:2050–2061. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Profumo A, Turci M, Damonte G, et al. Kinetics of fibrinopeptide release by thrombin as a function of CaCl2 concentration: different susceptibility of FPA and FPB and evidence for a fibrinogen isoform-specific effect at physiological Ca2+ concentration. Biochemistry. 2003;42:12335–12348. doi: 10.1021/bi034411e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Mihalyi E. Review of some unusual effects of calcium binding to fibrinogen. Biophys Chem. 2004;112:131–140. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2004.07.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Weisel JW, Nagaswami C. Computer modeling of fibrin polymerization kinetics correlated with electron microscope and turbidity observations: clot structure and assembly are kinetically controlled. Biophys J. 1992;63:111–128. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(92)81594-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Cooper AV, Standeven KF, Ariens RA. Fibrinogen gamma-chain splice variant gamma' alters fibrin formation and structure. Blood. 2003;102:535–540. doi: 10.1182/blood-2002-10-3150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Doolittle RF, Pandi L. Binding of synthetic B knobs to fibrinogen changes the character of fibrin and inhibits its ability to activate tissue plasminogen activator and its destruction by plasmin. Biochemistry. 2006;45:2657–2667. doi: 10.1021/bi0524767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Gabriel DA, Muga K, Boothroyd EM. The effect of fibrin structure on fibrinolysis. J Biol Chem. 1992;267:24259–24263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sauls DL, Wolberg AS, Hoffman M. Elevated plasma homocysteine leads to alterations in fibrin clot structure and stability: implications for the mechanism of thrombosis in hyperhomocysteinemia. J Thromb Haemost. 2003;1:300–306. doi: 10.1046/j.1538-7836.2003.00053.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Gruber A, Mori E, del Zoppo GJ, Waxman L, Griffin JH. Alteration of fibrin network by activated protein C. Blood. 1994;83:2541–2548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Collet JP, Nagaswami C, Farrell DH, Montalescot G, Weisel JW. Influence of gamma' fibrinogen splice variant on fibrin physical properties and fibrinolysis rate. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2004;24:382–386. doi: 10.1161/01.ATV.0000109748.77727.3e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Carr ME, Jr, Alving BM. Effect of fibrin structure on plasmin-mediated dissolution of plasma clots. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 1995;6:567–573. doi: 10.1097/00001721-199509000-00011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Banninger H, Lammle B, Furlan M. Binding of alpha-thrombin to fibrin depends on the quality of the fibrin network. Biochem J. 1994;298:157–163. doi: 10.1042/bj2980157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Woodhead JL, Nagaswami C, Matsuda M, et al. The ultrastructure of fibrinogen Caracas II molecules, fibers, and clots. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:4946–4953. doi: 10.1074/jbc.271.9.4946. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Collet JP, Woodhead JL, Soria J, et al. Fibrinogen Dusart: electron microscopy of molecules, fibers and clots, and viscoelastic properties of clots. Biophys J. 1996;70:500–510. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(96)79596-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Lee MG, Jones D. Applications of fibrin sealant in surgery. Surg Innov. 2005;12:203–213. doi: 10.1177/155335060501200304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.