Abstract
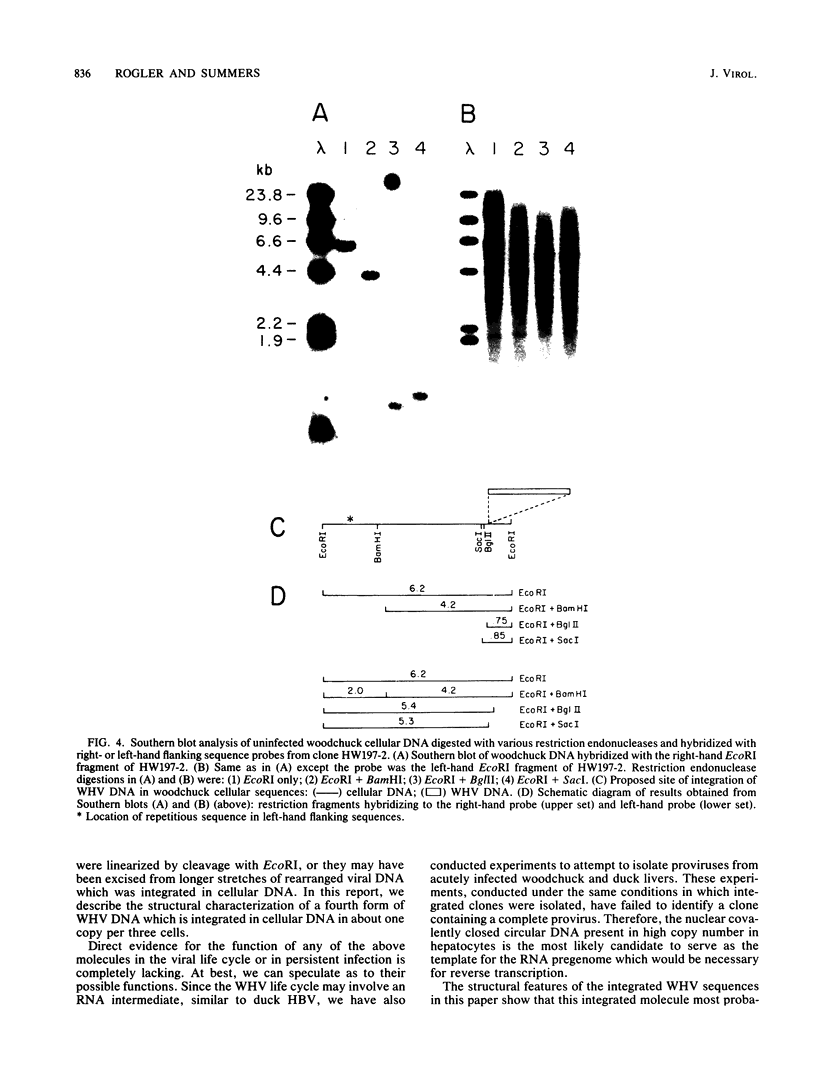
We have isolated and determined the structure of a recombinant clone in lambda phage Charon 30 which contains woodchuck hepatitis virus sequences integrated in woodchuck genomic DNA sequences. This clone, in contrast to previously reported clones (Ogston et al., Cell 29:385-394, 1982), was isolated from a chronically infected liver which never developed hepatocellular carcinoma. Southern blot analysis of viral sequences in the clone in conjunction with electron microscope heteroduplex analysis showed that the integrated viral sequences did not contain internal rearrangements, as have those from hepatomas, but were colinear with the cloned viral genome except for the deletion of approximately 500 base pairs of viral sequences (between positions 1,000 and 1,550 on the viral map). Therefore, the integration was probably a defective genome incapable of supporting viral replication. However, the complete open reading frames coding for the viral X, core, presurface , and surface antigen genes were present, indicating that the viral sequences could code for viral antigens. Southern blot analysis of the normal cellular flanking sequences, using flanking sequence probes from the clone, showed that no detectable rearrangements of cellular DNA (less than 50 base pairs) had occurred at the site of viral integration.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bréchot C., Hadchouel M., Scotto J., Fonck M., Potet F., Vyas G. N., Tiollais P. State of hepatitis B virus DNA in hepatocytes of patients with hepatitis B surface antigen-positive and -negative liver diseases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3906–3910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Brechot C., Tiollais P., Wain-Hobson S. Characterization of integrated hepatitis B viral DNA cloned from a human hepatoma and the hepatoma-derived cell line PLC/PRF/5. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(9):2505–2509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.9.2505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dejean A., Vitvitski L., Brechot C., Trepo C., Tiollais P., Charnay P. Presence and state of woodchuck hepatitis virus DNA in liver and serum of woodchucks: further analogies with human hepatitis B virus. Virology. 1982 Aug;121(1):195–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(82)90129-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L. W., Madden M. J., Schiop-Stanley P., Vande Woude G. F. Cloning of herpes simplex type 1 DNA fragments in a bacteriophage lambda vector. Science. 1979 Feb 9;203(4380):541–544. doi: 10.1126/science.216076. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enquist L., Sternberg N. In vitro packaging of lambda Dam vectors and their use in cloning DNA fragments. Methods Enzymol. 1979;68:281–298. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(79)68020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galibert F., Chen T. N., Mandart E. Nucleotide sequence of a cloned woodchuck hepatitis virus genome: comparison with the hepatitis B virus sequence. J Virol. 1982 Jan;41(1):51–65. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.1.51-65.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Mitra S. W., Goff S., Baltimore D. A detailed model of reverse transcription and tests of crucial aspects. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshy R., Koch S., von Loringhoven A. F., Kahmann R., Murray K., Hofschneider P. H. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA: evidence for integration in the single-stranded gap. Cell. 1983 Aug;34(1):215–223. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90152-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marion P. L., Oshiro L. S., Regnery D. C., Scullard G. H., Robinson W. S. A virus in Beechey ground squirrels that is related to hepatitis B virus of humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2941–2945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason W. S., Seal G., Summers J. Virus of Pekin ducks with structural and biological relatedness to human hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1980 Dec;36(3):829–836. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.3.829-836.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mims C. A. Factors in the mechanism of persistence of viral infections. Prog Med Virol. 1974;18(0):1–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molnar-Kimber K. L., Summers J., Taylor J. M., Mason W. S. Protein covalently bound to minus-strand DNA intermediates of duck hepatitis B virus. J Virol. 1983 Jan;45(1):165–172. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.1.165-172.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogston C. W., Jonak G. J., Rogler C. E., Astrin S. M., Summers J. Cloning and structural analysis of integrated woodchuck hepatitis virus sequences from hepatocellular carcinomas of woodchucks. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):385–394. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90155-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rimm D. L., Horness D., Kucera J., Blattner F. R. Construction of coliphage lambda Charon vectors with BamHI cloning sites. Gene. 1980 Dec;12(3-4):301–309. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(80)90113-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogler C. E., Summers J. Novel forms of woodchuck hepatitis virus DNA isolated from chronically infected woodchuck liver nuclei. J Virol. 1982 Dec;44(3):852–863. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.3.852-863.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafritz D. A., Shouval D., Sherman H. I., Hadziyannis S. J., Kew M. C. Integration of hepatitis B virus DNA into the genome of liver cells in chronic liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma. Studies in percutaneous liver biopsies and post-mortem tissue specimens. N Engl J Med. 1981 Oct 29;305(18):1067–1073. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198110293051807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Mason W. S. Replication of the genome of a hepatitis B--like virus by reverse transcription of an RNA intermediate. Cell. 1982 Jun;29(2):403–415. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90157-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Physical map of polyoma viral DNA fragments produced by cleavage with a restriction enzyme from Haemophilus aegyptius, endonuclease R-HaeIII. J Virol. 1975 Apr;15(4):946–953. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.4.946-953.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J., Smolec J. M., Snyder R. A virus similar to human hepatitis B virus associated with hepatitis and hepatoma in woodchucks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Sep;75(9):4533–4537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.9.4533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers J. Three recently described animal virus models for human hepatitis B virus. Hepatology. 1981 Mar-Apr;1(2):179–183. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840010215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vande Woude G. F., Oskarsson M., Enquist L. W., Nomura S., Sullivan M., Fischinger P. J. Cloning of integrated Moloney sarcoma proviral DNA sequences in bacteriophage lambda. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4464–4468. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4464. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]