Abstract
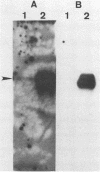
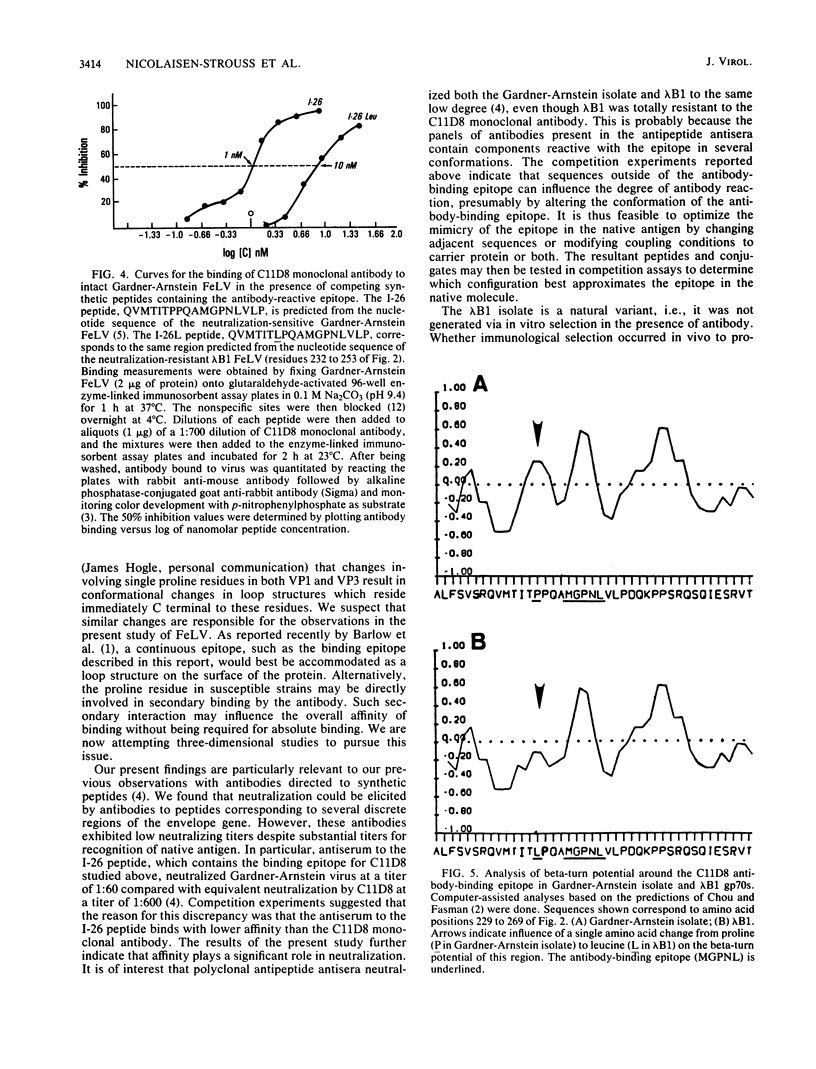
We have molecularly cloned a natural variant of feline leukemia virus subtype B. This isolate is unique in that it is not neutralized by a monoclonal antibody which neutralized all other feline leukemia virus isolates tested, including members of the A, B, and C subtypes. Western immunoblotting indicated that the monoclonal antibody was less able to bind to the gp70 of the resistant isolate (designated lambda B1) than to the gp70s of susceptible viruses. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the envelope gene of lambda B1 revealed a high degree of homology with the susceptible Snyder-Theilen, Gardner-Arnstein, and Rickard subtype B isolates, including the presence of a 5-amino-acid minimal binding epitope required for binding by the neutralizing monoclonal antibody. The only change within the vicinity of this epitope was in a single nucleotide, and this difference changed a proline residue to leucine three amino acids from the N terminus of the binding epitope. Competitive binding studies with synthetic peptides indicated that substitution of leucine for proline resulted in a 10-fold decrease in the ability of the peptide to compete for antibody binding to native antigen. The results are consistent with the interpretation that this amino acid change lowers the affinity of antibody binding, resulting in failure of the antibody to neutralize the variant virus.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow D. J., Edwards M. S., Thornton J. M. Continuous and discontinuous protein antigenic determinants. Nature. 1986 Aug 21;322(6081):747–748. doi: 10.1038/322747a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chou P. Y., Fasman G. D. Prediction of protein conformation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 15;13(2):222–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00699a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Douillard J. Y., Hoffman T. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay for screening monoclonal antibody production using enzyme-labeled second antibody. Methods Enzymol. 1983;92:168–174. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)92016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., McGee J. S., Munson M., Houghten R. A., Kloetzer W., Bittle J. L., Grant C. K. Localization of neutralizing regions of the envelope gene of feline leukemia virus by using anti-synthetic peptide antibodies. J Virol. 1987 Jan;61(1):8–15. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.1.8-15.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Mullins J. I. Nucleotide sequence of the envelope gene of Gardner-Arnstein feline leukemia virus B reveals unique sequence homologies with a murine mink cell focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):871–880. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.871-880.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grant C. K., Ernisse B. J., Jarrett O., Jones F. R. Feline leukemia virus envelope gp70 of subgroups B and C defined by monoclonal antibodies with cytotoxic and neutralizing functions. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):3042–3048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hawkes R., Niday E., Gordon J. A dot-immunobinding assay for monoclonal and other antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1982 Jan 1;119(1):142–147. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90677-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogle J. M., Chow M., Filman D. J. Three-dimensional structure of poliovirus at 2.9 A resolution. Science. 1985 Sep 27;229(4720):1358–1365. doi: 10.1126/science.2994218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghten R. A. General method for the rapid solid-phase synthesis of large numbers of peptides: specificity of antigen-antibody interaction at the level of individual amino acids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5131–5135. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lerner R. A. Tapping the immunological repertoire to produce antibodies of predetermined specificity. Nature. 1982 Oct 14;299(5884):593–596. doi: 10.1038/299592a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mullins J. I., Chen C. S., Hoover E. A. Disease-specific and tissue-specific production of unintegrated feline leukaemia virus variant DNA in feline AIDS. Nature. 1986 Jan 23;319(6051):333–336. doi: 10.1038/319333a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Rodgers G., Gilbert J. H., Snead R. M. Method to map antigenic determinants recognized by monoclonal antibodies: localization of a determinant of virus neutralization on the feline leukemia virus envelope protein gp70. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3675–3679. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3675. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunberg J. H., Williams M. E., Innis M. A. Nucleotide sequences of the envelope genes of two isolates of feline leukemia virus subgroup B. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):629–632. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.629-632.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarma P. S., Log T. Subgroup classification of feline leukemia and sarcoma viruses by viral interference and neutralization tests. Virology. 1973 Jul;54(1):160–169. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90125-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaffhausen B. S., Silver J. E., Benjamin T. L. Tumor antigen(s) in cell productively infected by wild-type polyoma virus and mutant NG-18. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jan;75(1):79–83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.1.79. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart M. A., Warnock M., Wheeler A., Wilkie N., Mullins J. I., Onions D. E., Neil J. C. Nucleotide sequences of a feline leukemia virus subgroup A envelope gene and long terminal repeat and evidence for the recombinational origin of subgroup B viruses. J Virol. 1986 Jun;58(3):825–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.58.3.825-834.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]