Abstract
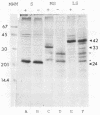
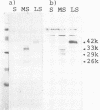
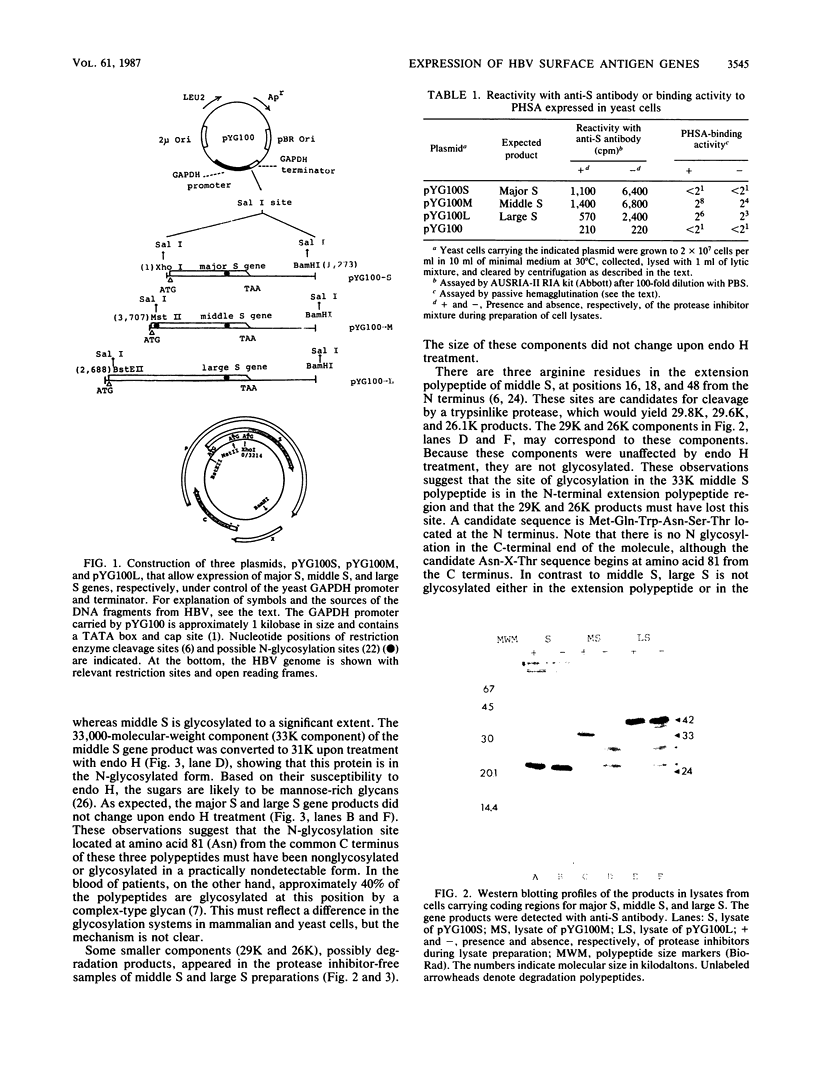
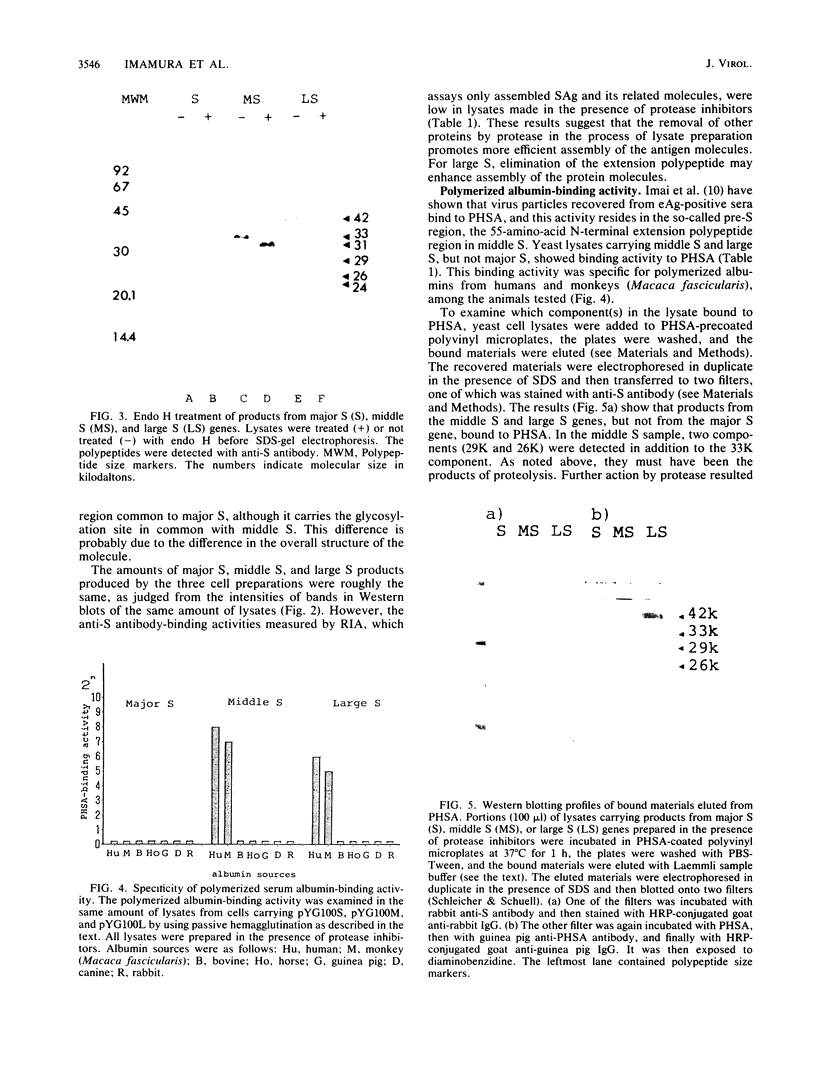
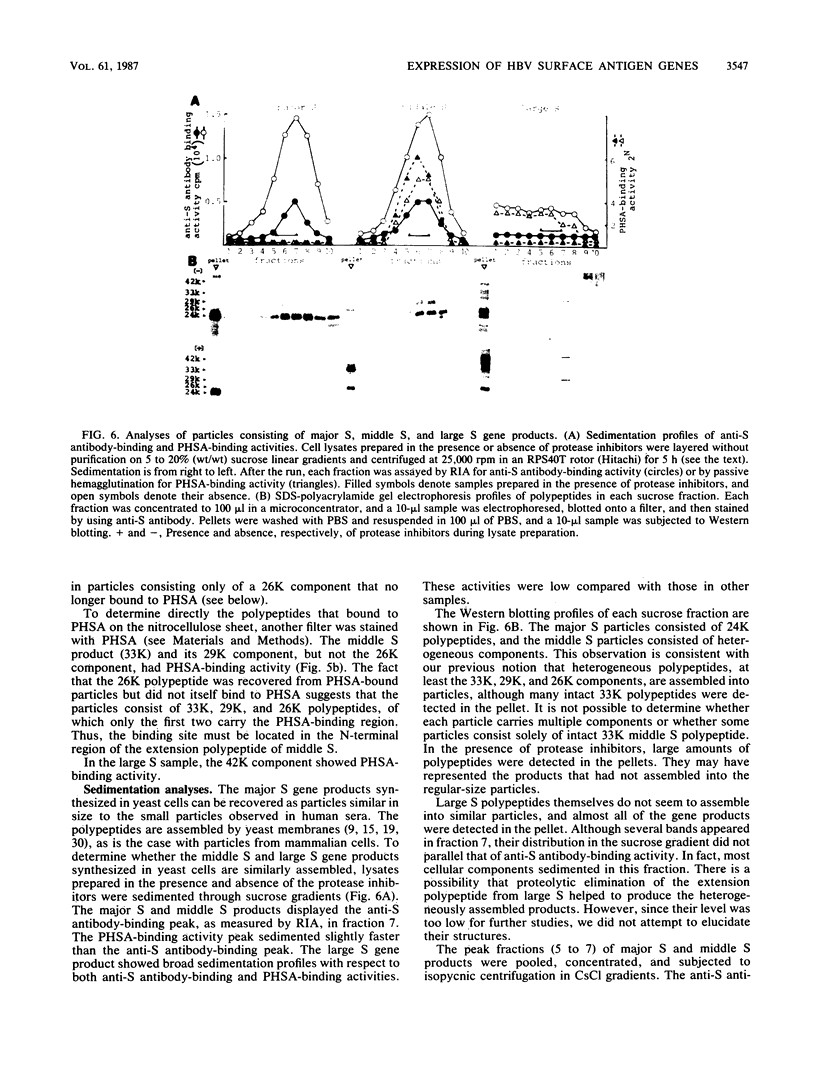
The hepatitis B virus genome carries the surface antigen (SAg) gene and an open reading frame that encodes two SAg-related polypeptides: SAg with a 55-amino-acid N-terminal extension polypeptide and SAg with a 174-amino-acid N-terminal extension polypeptide. These are termed middle S and large S, respectively. These polypeptides or their glycosylated derivatives have been detected in Dane particles, but their chemical and biological properties have remained largely unknown because of their limited availability. We attempted to produce these proteins in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by placing the coding regions under the control of the promoter of the yeast glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) gene. Yeast cells carrying middle S and large S coding sequences produced 33,000- and 42,000-dalton products, respectively, each of which reacted with anti-S antibody and bound to polymerized human serum albumin, in accordance with the known properties of pre-S proteins from particles in human sera (K. H. Heermann, U. Goldmann, W. Schwartz, T. Seyffarth, H. Baumgarten, and W. H. Gerlich, J. Virol. 52:396-402, 1984; A. Machida, S. Kishimoto, H. Ohnuma, K. Baba, Y. Ito, H. Miyamoto, G. Funatsu, K. Oda, S. Usuda, S. Togami, T. Nakamura, Y. Miyakawa, and M. Mayumi, Gastroenterology 86:910-918, 1984). The middle S polypeptide is glycosylated and can be assembled into particles whose size and density are similar to those of SAg. However, this polypeptide was highly susceptible to proteolytic degradation into 29,000- and 26,000-dalton polypeptides, of which only the former retained the binding activity to polymerized albumin. The large S polypeptides are nonglycosylated, relatively stable, and do not seem to assemble into particles by themselves.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bitter G. A., Egan K. M. Expression of heterologous genes in Saccharomyces cerevisiae from vectors utilizing the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(3):263–274. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90002-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bostian K. A., Lemire J. M., Cannon L. E., Halvorson H. O. In vitro synthesis of repressible yeast acid phosphatase: identification of multiple mRNAs and products. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Aug;77(8):4504–4508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.8.4504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burrell C. J., Mackay P., Greenaway P. J., Hofschneider P. H., Murray K. Expression in Escherichia coli of hepatitis B virus DNA sequences cloned in plasmid pBR322. Nature. 1979 May 3;279(5708):43–47. doi: 10.1038/279043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Pourcel C., Louise A., Fritsch A., Tiollais P. Cloning in Escherichia coli and physical structure of hepatitis B virion DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 May;76(5):2222–2226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.5.2222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng K. C., Moss B. Selective synthesis and secretion of particles composed of the hepatitis B virus middle surface protein directed by a recombinant vaccinia virus: induction of antibodies to pre-S and S epitopes. J Virol. 1987 Apr;61(4):1286–1290. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.4.1286-1290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujiyama A., Miyanohara A., Nozaki C., Yoneyama T., Ohtomo N., Matsubara K. Cloning and structural analyses of hepatitis B virus DNAs, subtype adr. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jul 11;11(13):4601–4610. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.13.4601. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heermann K. H., Goldmann U., Schwartz W., Seyffarth T., Baumgarten H., Gerlich W. H. Large surface proteins of hepatitis B virus containing the pre-s sequence. J Virol. 1984 Nov;52(2):396–402. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.2.396-402.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinnen A., Hicks J. B., Fink G. R. Transformation of yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Apr;75(4):1929–1933. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.4.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hitzeman R. A., Chen C. Y., Hagie F. E., Patzer E. J., Liu C. C., Estell D. A., Miller J. V., Yaffe A., Kleid D. G., Levinson A. D. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen in yeast. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 May 11;11(9):2745–2763. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.9.2745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imai M., Yanase Y., Nojiri T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A receptor for polymerized human and chimpanzee albumins on hepatitis B virus particles co-occurring with HBeAg. Gastroenterology. 1979 Feb;76(2):242–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Hayakawa T., Fujisawa Y. Expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen P31 gene in yeast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Jul 16;138(1):268–274. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90275-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoh Y., Takai E., Ohnuma H., Kitajima K., Tsuda F., Machida A., Mishiro S., Nakamura T., Miyakawa Y., Mayumi M. A synthetic peptide vaccine involving the product of the pre-S(2) region of hepatitis B virus DNA: protective efficacy in chimpanzees. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(23):9174–9178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.23.9174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Machida A., Kishimoto S., Ohnuma H., Baba K., Ito Y., Miyamoto H., Funatsu G., Oda K., Usuda S., Togami S. A polypeptide containing 55 amino acid residues coded by the pre-S region of hepatitis B virus deoxyribonucleic acid bears the receptor for polymerized human as well as chimpanzee albumins. Gastroenterology. 1984 May;86(5 Pt 1):910–918. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McAleer W. J., Buynak E. B., Maigetter R. Z., Wampler D. E., Miller W. J., Hilleman M. R. Human hepatitis B vaccine from recombinant yeast. Nature. 1984 Jan 12;307(5947):178–180. doi: 10.1038/307178a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. L., Pontisso P., Sobczak E., Malpièce Y., Streeck R. E., Tiollais P. Synthesis in animal cells of hepatitis B surface antigen particles carrying a receptor for polymerized human serum albumin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7708–7712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., McNamara M. K., McLachlan A., Thornton G. B., Chisari F. V. Distinct H-2-linked regulation of T-cell responses to the pre-S and S regions of the same hepatitis B surface antigen polypeptide allows circumvention of nonresponsiveness to the S region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8168–8172. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milich D. R., Thornton G. B., Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Michel M. L., Tiollais P., Chisari F. V. Enhanced immunogenicity of the pre-S region of hepatitis B surface antigen. Science. 1985 Jun 7;228(4704):1195–1199. doi: 10.1126/science.2408336. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N. Location and chemical synthesis of a pre-S gene coded immunodominant epitope of hepatitis B virus. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):392–395. doi: 10.1126/science.6200931. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath A. R., Kent S. B., Strick N., Taylor P., Stevens C. E. Hepatitis B virus contains pre-S gene-encoded domains. Nature. 1985 May 9;315(6015):154–156. doi: 10.1038/315154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson D. L., Nath N., Gavilanes F. Structure of hepatitis B surface antigen. Correlation of subtype with amino acid sequence and location of the carbohydrate moiety. J Biol Chem. 1982 Sep 10;257(17):10414–10420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sninsky J. J., Siddiqui A., Robinson W. S., Cohen S. N. Cloning and endonuclease mapping of the hepatitis B viral genome. Nature. 1979 May 24;279(5711):346–348. doi: 10.1038/279346a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stibbe W., Gerlich W. H. Structural relationships between minor and major proteins of hepatitis B surface antigen. J Virol. 1983 May;46(2):626–628. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.2.626-628.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi K., Kishimoto S., Ohnuma H., Machida A., Takai E., Tsuda F., Miyamoto H., Tanaka T., Matsushita K., Oda K. Polypeptides coded for by the region pre-S and gene S of hepatitis B virus DNA with the receptor for polymerized human serum albumin: expression on hepatitis B particles produced in the HBeAg or anti-HBe phase of hepatitis B virus infection. J Immunol. 1986 May 1;136(9):3467–3472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Gray P., Quiroga M., Zaldivar J., Goodman H. M., Rutter W. J. Nucleotide sequence of the gene coding for the major protein of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nature. 1979 Aug 30;280(5725):815–819. doi: 10.1038/280815a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Valenzuela P., Medina A., Rutter W. J., Ammerer G., Hall B. D. Synthesis and assembly of hepatitis B virus surface antigen particles in yeast. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):347–350. doi: 10.1038/298347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]