Abstract
Adenovirus type 35 (Ad35) is a group B adenovirus that has been isolated primarily from patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and other immunodeficiency disorders. We have studied the interaction of this unique adenovirus with the immune system by analyzing Ad35 early viral proteins in infected HeLa cells. We have identified a 29,000-Mr Ad35 early glycoprotein, E29, which associates with class I antigens of the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) in the endoplasmic reticulum. Ad35 E29 is analogous to the group C Ad2 early glycoprotein E3-19K (E19), which has been shown to interfere with the expression of class I antigens on the cell surface (H. Burgert and S. Kvist, Cell 41:987-997, 1985). In contrast to the Ad2 glycoprotein, Ad35 E29 was synthesized in much smaller amounts, was more extensively glycosylated, and did not cross-react with polyclonal antibody against the Ad2 protein. As a control, a class I antigen-binding glycoprotein from another group B adenovirus, Ad7, was also characterized and was found to have properties similar to those of Ad35 E29. Therefore, the differences in the glycosylation and quantity of class I antigen-binding glycoproteins between Ad35 and Ad2 are group related. Inhibition of the expression of MHC class I antigens, which are needed for cytotoxic-T-lymphocyte recognition of virus-infected cells, appears to play a vital role in the adenovirus life cycle in vivo. Our data indicate that this function has been conserved despite significant differences in the MHC class I antigen-binding glycoprotein and in the pathogenicity between serotypes.
Full text
PDF


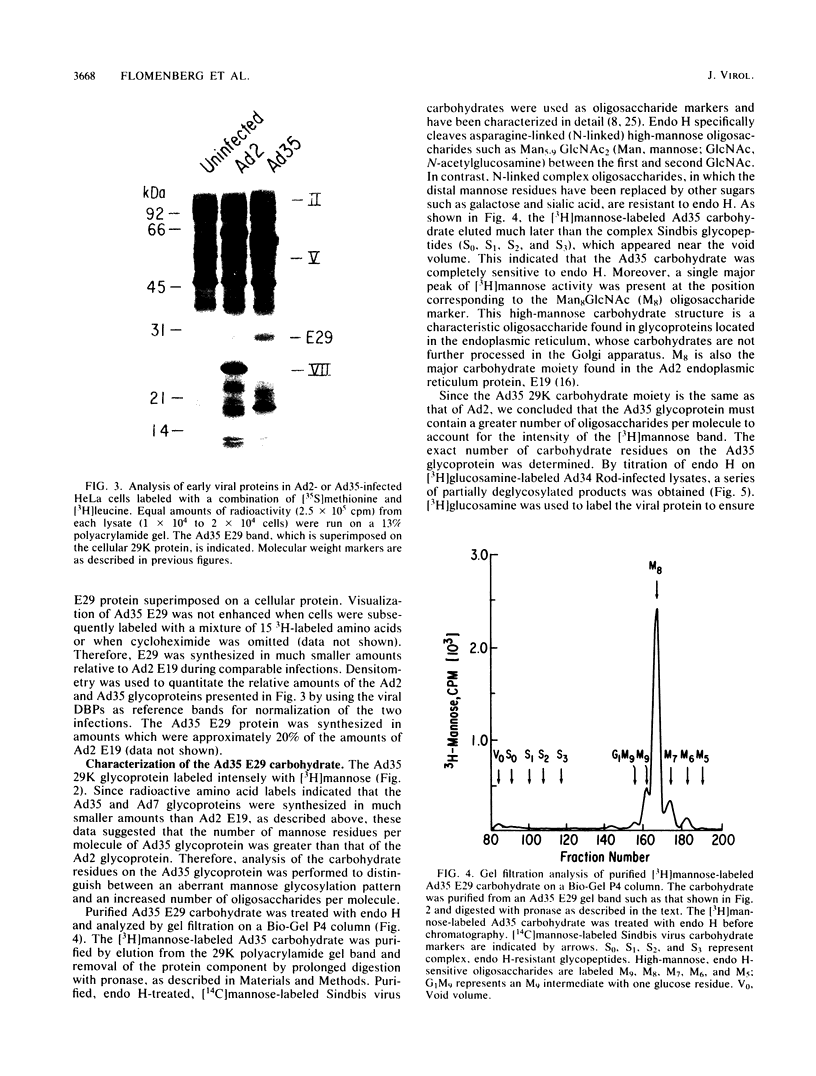


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andersson M., Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Impaired intracellular transport of class I MHC antigens as a possible means for adenoviruses to evade immune surveillance. Cell. 1985 Nov;43(1):215–222. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F., Brown G., Galfre G., Milstein C., Williams A. F., Ziegler A. Production of monoclonal antibodies to group A erythrocytes, HLA and other human cell surface antigens-new tools for genetic analysis. Cell. 1978 May;14(1):9–20. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90296-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgert H. G., Kvist S. An adenovirus type 2 glycoprotein blocks cell surface expression of human histocompatibility class I antigens. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):987–997. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80079-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doherty P. C., Zinkernagel R. M. H-2 compatibility is required for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. J Exp Med. 1975 Feb 1;141(2):502–507. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.2.502. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eggerding F., Raskas H. J. Effect of protein synthesis inhibitors on viral mRNA's synthesized early in adenovirus type 2 infection. J Virol. 1978 Jan;25(1):453–458. doi: 10.1128/jvi.25.1.453-458.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flomenberg P. R., Chen M., Munk G., Horwitz M. S. Molecular epidemiology of adenovirus type 35 infections in immunocompromised hosts. J Infect Dis. 1987 Jun;155(6):1127–1134. doi: 10.1093/infdis/155.6.1127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox J. P., Hall C. E., Cooney M. K. The Seattle Virus Watch. VII. Observations of adenovirus infections. Am J Epidemiol. 1977 Apr;105(4):362–386. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.aje.a112394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hakimi J., Carver J., Atkinson P. H. Application of high-field proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy in the structural determination of membrane-derived Sindbis virus glycopeptides. Biochemistry. 1981 Dec 8;20(25):7314–7319. doi: 10.1021/bi00528a041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hierholzer J. C., Atuk N. O., Gwaltney J. M., Jr New human adenovirus isolated from a renal transplant recipient: description and characterization of candiate adenovirus type 34. J Clin Microbiol. 1975 Apr;1(4):366–376. doi: 10.1128/jcm.1.4.366-376.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Courtois G., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI D fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 May 24;8(10):2173–2192. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.10.2173. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hérissé J., Galibert F. Nucleotide sequence of the EcoRI E fragment of adenovirus 2 genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Mar 11;9(5):1229–1240. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.5.1229. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapoor Q. S., Wold W. S., Chinnadurai G. A nonessential glycoprotein is coded by early region E3 of adenovirus type 7. Virology. 1981 Jul 30;112(2):780–784. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90326-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly T. J., Jr, Lewis A. M., Jr Use of nondefective adenovirus-simian virus 40 hybrids for mapping the simian virus 40 genome. J Virol. 1973 Sep;12(3):643–652. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.3.643-652.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Wold W. S. Structures of the oligosaccharides of the glycoprotein coded by early region E3 of adenovirus 2. J Virol. 1981 Nov;40(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.40.2.440-449.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichy J. H., Horwitz M. S., Hurwitz J. Formation of a covalent complex between the 80,000-dalton adenovirus terminal protein and 5'-dCMP in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 May;78(5):2678–2682. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.5.2678. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maizel J. V., Jr, White D. O., Scharff M. D. The polypeptides of adenovirus. I. Evidence for multiple protein components in the virion and a comparison of types 2, 7A, and 12. Virology. 1968 Sep;36(1):115–125. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90121-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Katze M. G., Philipson L. Purification of a native membrane-associated adenovirus tumor antigen. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):905–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.905-917.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Signäs C., Philipson L. Purification and characterization of an early glycoprotein from adenovirus type 2-infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):938–948. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.938-948.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Päbo S., Nilsson T., Peterson P. A. Adenoviruses of subgenera B, C, D, and E modulate cell-surface expression of major histocompatibility complex class I antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9665–9669. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9665. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shields A. F., Hackman R. C., Fife K. H., Corey L., Meyers J. D. Adenovirus infections in patients undergoing bone-marrow transplantation. N Engl J Med. 1985 Feb 28;312(9):529–533. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198502283120901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Signäs C., Akusjärvi G., Pettersson U. Region E3 of human adenoviruses; differences between the oncogenic adenovirus-3 and the non-oncogenic adenovirus-2. Gene. 1986;50(1-3):173–184. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90322-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stalder H., Hierholzer J. C., Oxman M. N. New human adenovirus (candidate adenovirus type 35) causing fatal disseminated infection in a renal transplant recipient. J Clin Microbiol. 1977 Sep;6(3):257–265. doi: 10.1128/jcm.6.3.257-265.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanley P., Chaney W. Control of carbohydrate processing: the lec1A CHO mutation results in partial loss of N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase I activity. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1204–1211. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaessen R. T., Houweling A., van der Eb A. J. Post-transcriptional control of class I MHC mRNA expression in adenovirus 12-transformed cells. Science. 1987 Mar 20;235(4795):1486–1488. doi: 10.1126/science.3823900. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wadell G. Molecular epidemiology of human adenoviruses. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;110:191–220. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-46494-2_7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zahradnik J. M., Spencer M. J., Porter D. D. Adenovirus infection in the immunocompromised patient. Am J Med. 1980 May;68(5):725–732. doi: 10.1016/0002-9343(80)90262-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]