Abstract
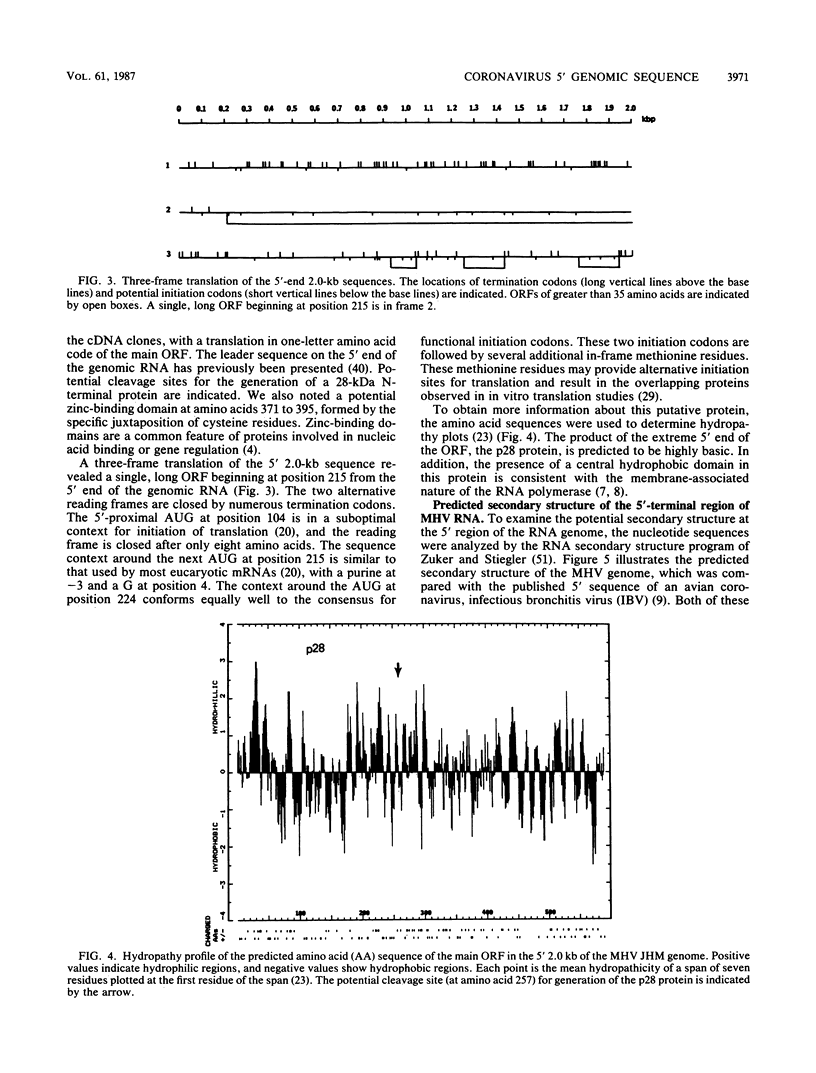
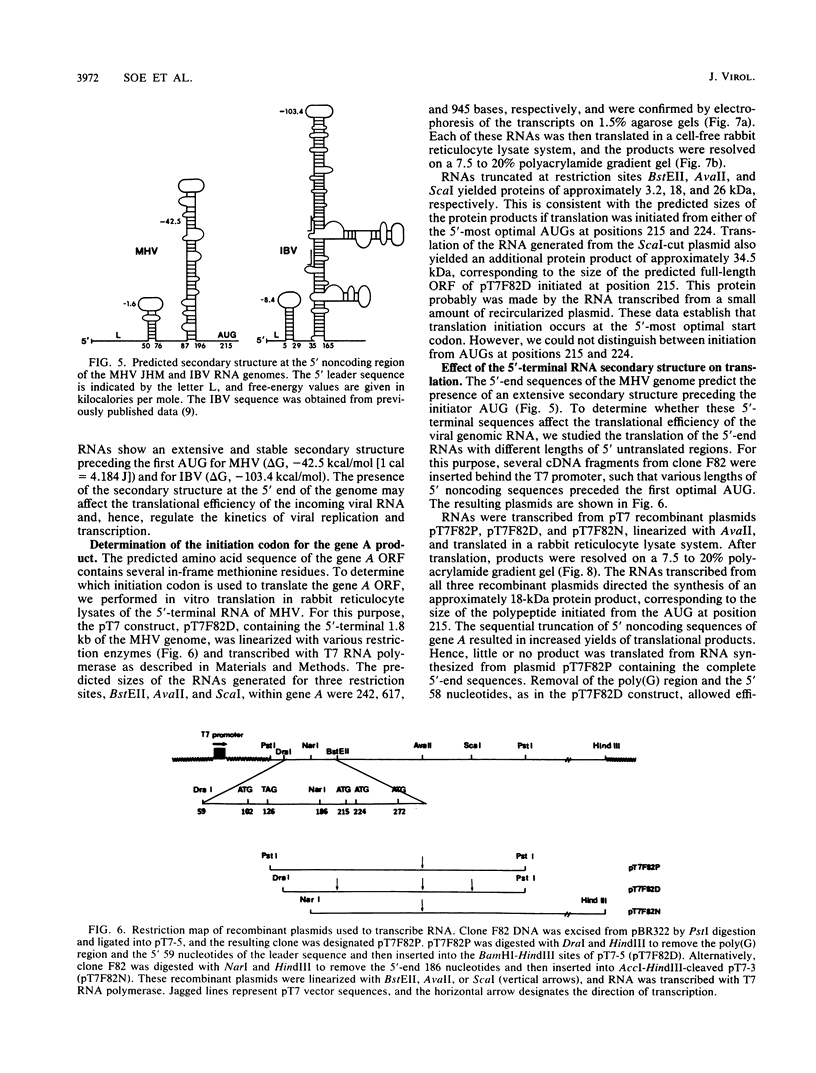
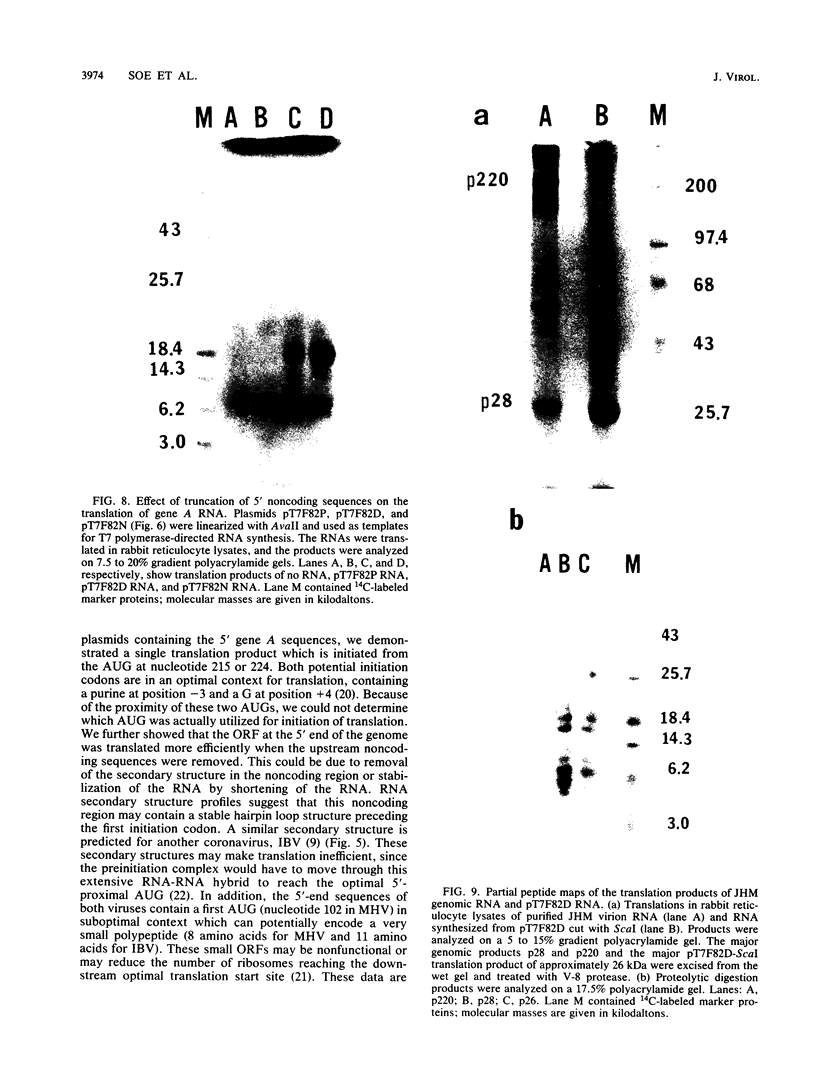
A 28-kilodalton protein has been suggested to be the amino-terminal protein cleavage product of the putative coronavirus RNA polymerase (gene A) (M.R. Denison and S. Perlman, Virology 157:565-568, 1987). To elucidate the structure and mechanism of synthesis of this protein, the nucleotide sequence of the 5' 2.0 kilobases of the coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain JHM genome was determined. This sequence contains a single, long open reading frame and predicts a highly basic amino-terminal region. Cell-free translation of RNAs transcribed in vitro from DNAs containing gene A sequences in pT7 vectors yielded proteins initiated from the 5'-most optimal initiation codon at position 215 from the 5' end of the genome. The sequence preceding this initiation codon predicts the presence of a stable hairpin loop structure. The presence of an RNA secondary structure at the 5' end of the RNA genome is supported by the observation that gene A sequences were more efficiently translated in vitro when upstream noncoding sequences were removed. By comparing the translation products of virion genomic RNA and in vitro transcribed RNAs, we established that our clones encompassing the 5'-end mouse hepatitis virus genomic RNA encode the 28-kilodalton N-terminal cleavage product of the gene A protein. Possible cleavage sites for this protein are proposed.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Characterization of replicative intermediate RNA of mouse hepatitis virus: presence of leader RNA sequences on nascent chains. J Virol. 1983 Dec;48(3):633–640. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.3.633-640.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A., Razavi M. K., Lai M. M. Characterization of leader-related small RNAs in coronavirus-infected cells: further evidence for leader-primed mechanism of transcription. Virus Res. 1985 Jul;3(1):19–33. doi: 10.1016/0168-1702(85)90038-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berg J. M. Potential metal-binding domains in nucleic acid binding proteins. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):485–487. doi: 10.1126/science.2421409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biggin M. D., Gibson T. J., Hong G. F. Buffer gradient gels and 35S label as an aid to rapid DNA sequence determination. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3963–3965. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Ganges R. G., Stohlman S. A. Host cell nuclear function and murine hepatitis virus replication. J Gen Virol. 1981 Oct;56(Pt 2):457–460. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-56-2-457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of two RNA polymerase activities induced by mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):847–853. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.847-853.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brayton P. R., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Further characterization of mouse hepatitis virus RNA-dependent RNA polymerases. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):197–201. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90439-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown T. D., Boursnell M. E., Binns M. M., Tomley F. M. Cloning and sequencing of 5' terminal sequences from avian infectious bronchitis virus genomic RNA. J Gen Virol. 1986 Feb;67(Pt 2):221–228. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-67-2-221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budzilowicz C. J., Wilczynski S. P., Weiss S. R. Three intergenic regions of coronavirus mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 genome RNA contain a common nucleotide sequence that is homologous to the 3' end of the viral mRNA leader sequence. J Virol. 1985 Mar;53(3):834–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.3.834-840.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M. R., Perlman S. Translation and processing of mouse hepatitis virus virion RNA in a cell-free system. J Virol. 1986 Oct;60(1):12–18. doi: 10.1128/jvi.60.1.12-18.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denison M., Perlman S. Identification of putative polymerase gene product in cells infected with murine coronavirus A59. Virology. 1987 Apr;157(2):565–568. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90303-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. N., Pheiffer B. H., Boehnert J. A. Chemical and electrophoretic properties of solubilizable disulfide gels. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jun;105(1):192–201. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90445-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. N. Use of solubilizable acrylamide disulfide gels for isolation of DNA fragments suitable for sequence analysis. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):146–151. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90337-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano N., Fujiwara K., Hino S., Matumoto M. Replication and plaque formation of mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-2) in mouse cell line DBT culture. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1974;44(3):298–302. doi: 10.1007/BF01240618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs L., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Synthesis of subgenomic mRNA's of mouse hepatitis virus is initiated independently: evidence from UV transcription mapping. J Virol. 1981 Aug;39(2):401–406. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.2.401-406.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck J. G., Stohlman S. A., Soe L. H., Makino S., Lai M. M. Multiple recombination sites at the 5'-end of murine coronavirus RNA. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):331–341. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90413-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Semler B. L., Rothberg P. G., Larsen G. R., Adler C. J., Dorner A. J., Emini E. A., Hanecak R., Lee J. J., van der Werf S. Primary structure, gene organization and polypeptide expression of poliovirus RNA. Nature. 1981 Jun 18;291(5816):547–553. doi: 10.1038/291547a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Bifunctional messenger RNAs in eukaryotes. Cell. 1986 Nov 21;47(4):481–483. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90609-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Compilation and analysis of sequences upstream from the translational start site in eukaryotic mRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 25;12(2):857–872. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.2.857. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influences of mRNA secondary structure on initiation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2850–2854. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2850. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Baric R. S., Brayton P. R., Stohlman S. A. Characterization of leader RNA sequences on the virion and mRNAs of mouse hepatitis virus, a cytoplasmic RNA virus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(12):3626–3630. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.12.3626. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Brayton P. R., Armen R. C., Patton C. D., Pugh C., Stohlman S. A. Mouse hepatitis virus A59: mRNA structure and genetic localization of the sequence divergence from hepatotropic strain MHV-3. J Virol. 1981 Sep;39(3):823–834. doi: 10.1128/jvi.39.3.823-834.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Baric R. S., Stohlman S. A. Presence of leader sequences in the mRNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1983 Jun;46(3):1027–1033. doi: 10.1128/jvi.46.3.1027-1033.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Patton C. D., Stohlman S. A. Replication of mouse hepatitis virus: negative-stranded RNA and replicative form RNA are of genome length. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):487–492. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.487-492.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leibowitz J. L., Weiss S. R., Paavola E., Bond C. W. Cell-free translation of murine coronavirus RNA. J Virol. 1982 Sep;43(3):905–913. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.3.905-913.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Fujioka N., Fujiwara K. Structure of the intracellular defective viral RNAs of defective interfering particles of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1985 May;54(2):329–336. doi: 10.1128/jvi.54.2.329-336.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Leader sequences of murine coronavirus mRNAs can be freely reassorted: evidence for the role of free leader RNA in transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jun;83(12):4204–4208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.12.4204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Makino S., Taguchi F., Fujiwara K. Defective interfering particles of mouse hepatitis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90420-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. A new method for sequencing DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):560–564. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.560. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Vieira J. A new pair of M13 vectors for selecting either DNA strand of double-digest restriction fragments. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):269–276. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90016-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Translation of three mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 subgenomic RNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.20-26.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schubert M., Harmison G. G., Richardson C. D., Meier E. Expression of a cDNA encoding a functional 241-kilodalton vesicular stomatitis virus RNA polymerase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):7984–7988. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.7984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shieh C. K., Soe L. H., Makino S., Chang M. F., Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. The 5'-end sequence of the murine coronavirus genome: implications for multiple fusion sites in leader-primed transcription. Virology. 1987 Feb;156(2):321–330. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(87)90412-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. Coronavirus JHM: coding assignments of subgenomic mRNAs. J Gen Virol. 1983 Jan;64(Pt 1):113–125. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-64-1-113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: intracellular protein synthesis. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):145–155. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W., Delius H., Skinner M., Armstrong J., Rottier P., Smeekens S., van der Zeijst B. A., Siddell S. G. Coronavirus mRNA synthesis involves fusion of non-contiguous sequences. EMBO J. 1983;2(10):1839–1844. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01667.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stohlman S. A., Lai M. M. Phosphoproteins of murine hepatitis viruses. J Virol. 1979 Nov;32(2):672–675. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.2.672-675.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Rice C. M., Strauss J. H. Complete nucleotide sequence of the genomic RNA of Sindbis virus. Virology. 1984 Feb;133(1):92–110. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(84)90428-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss E. G., Strauss J. H. Replication strategies of the single stranded RNA viruses of eukaryotes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1983;105:1–98. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69159-1_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sturman L. S. I. Structural proteins: effects of preparative conditions on the migration of protein in polyacrylamide gels. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):637–649. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90488-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabor S., Richardson C. C. A bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase/promoter system for controlled exclusive expression of specific genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1074–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1074. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Müller A., ter Meulen V. Genomic RNA of the murine coronavirus JHM. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):217–227. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Leibowitz J. L., Bond C. W., Robb J. A. The replication of murine coronaviruses in enucleated cells. Virology. 1981 Apr 15;110(1):225–230. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90027-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuker M., Stiegler P. Optimal computer folding of large RNA sequences using thermodynamics and auxiliary information. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 10;9(1):133–148. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.1.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]