Abstract
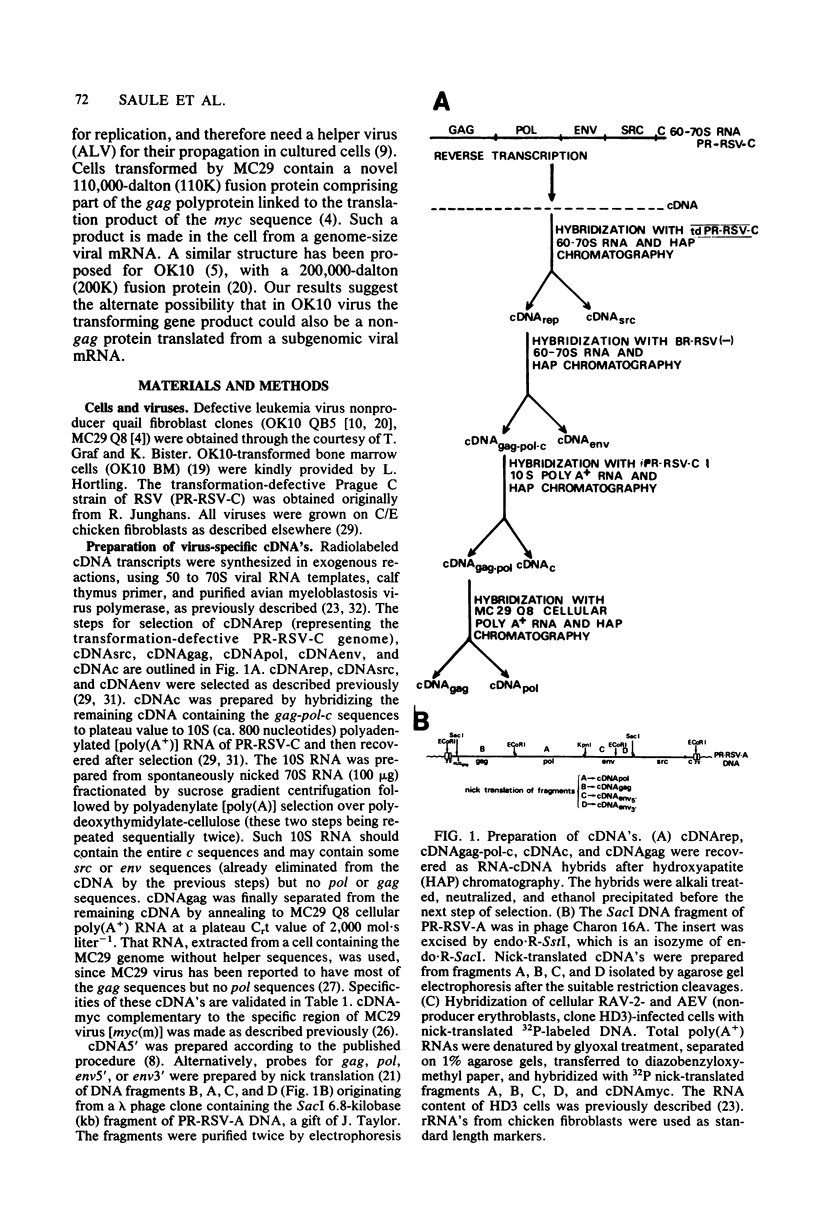
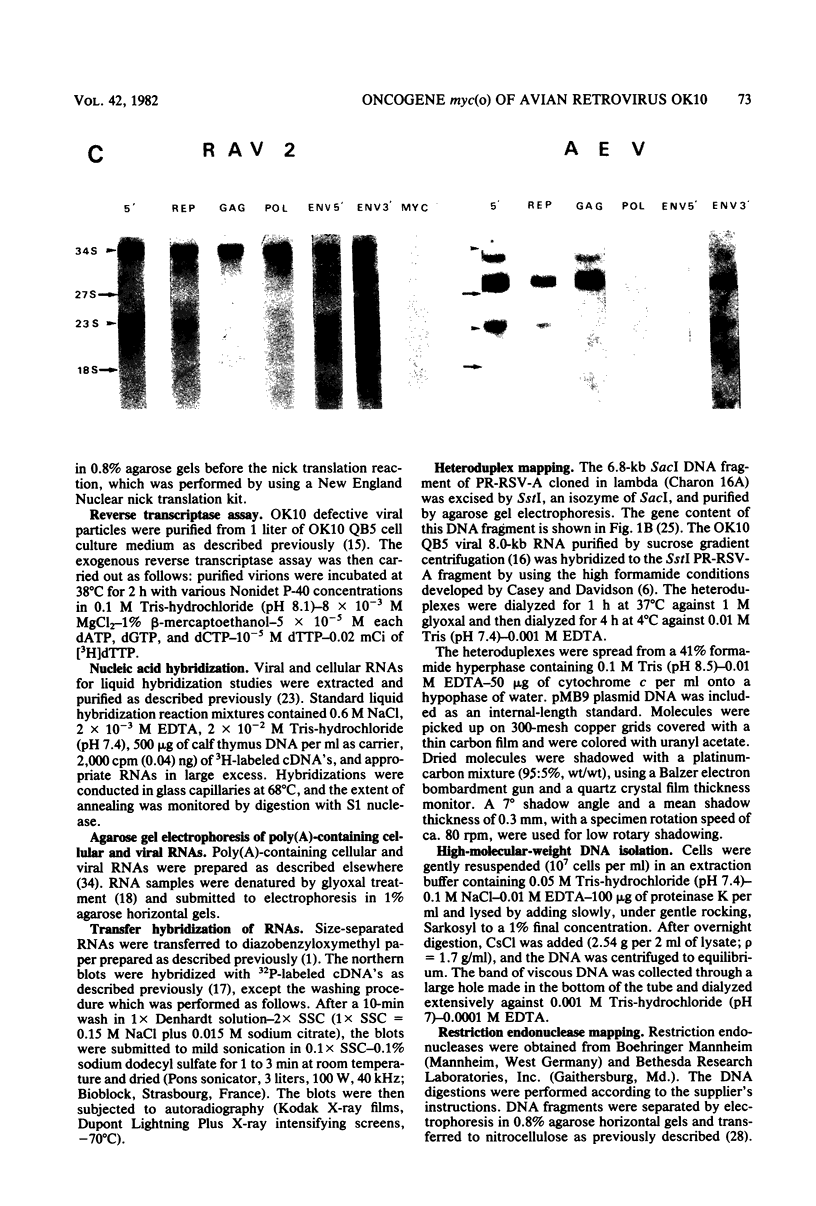
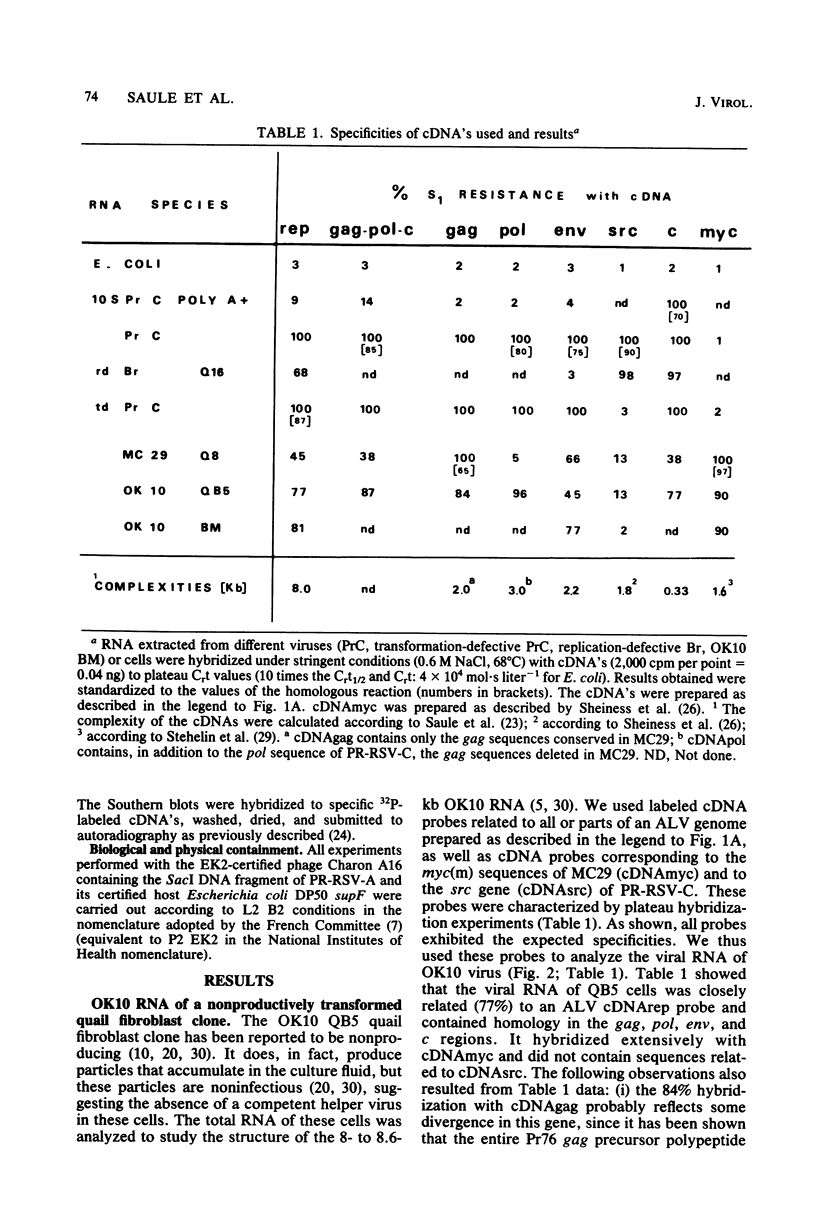
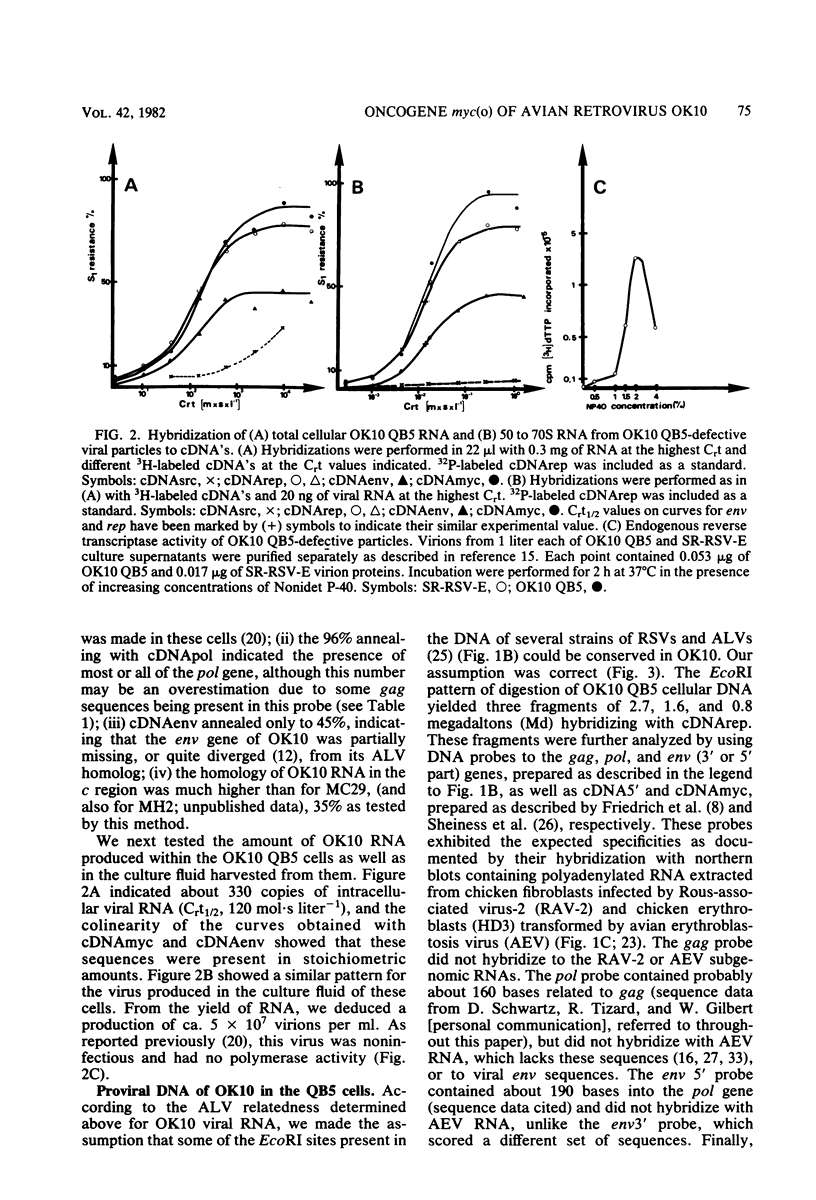
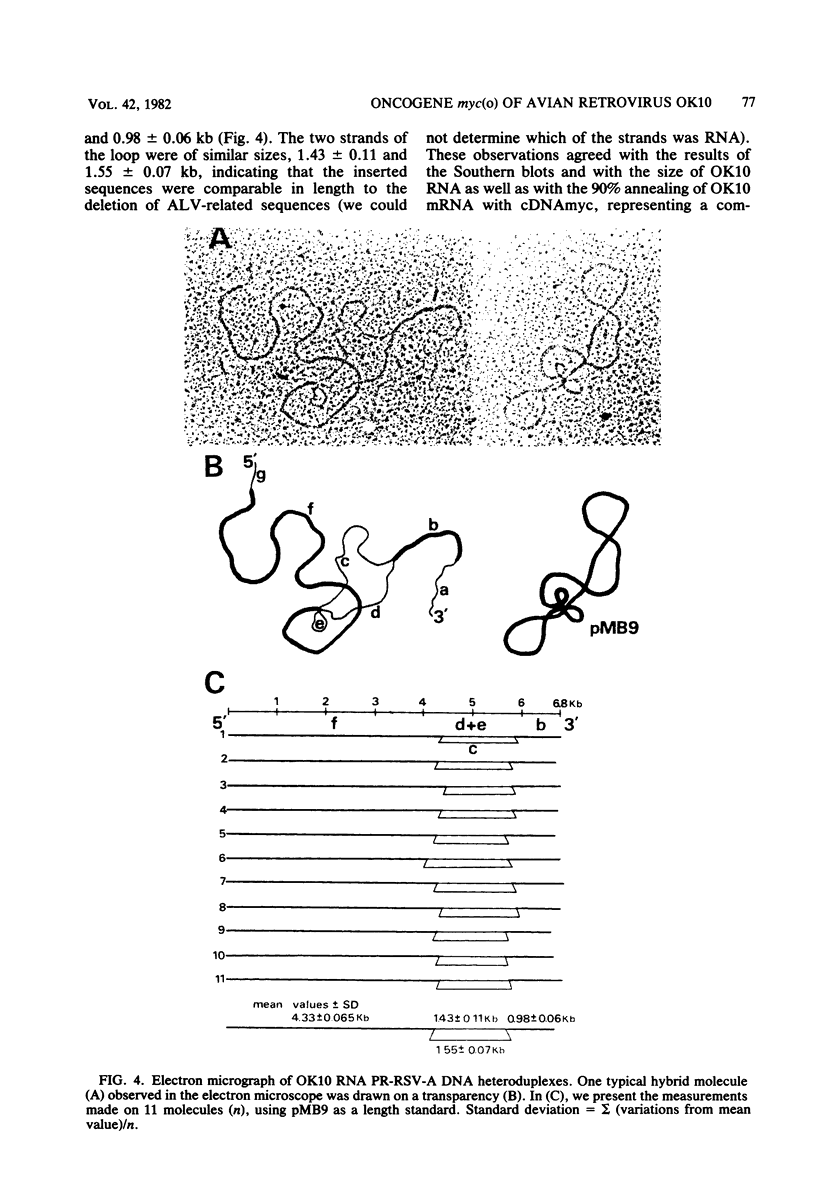
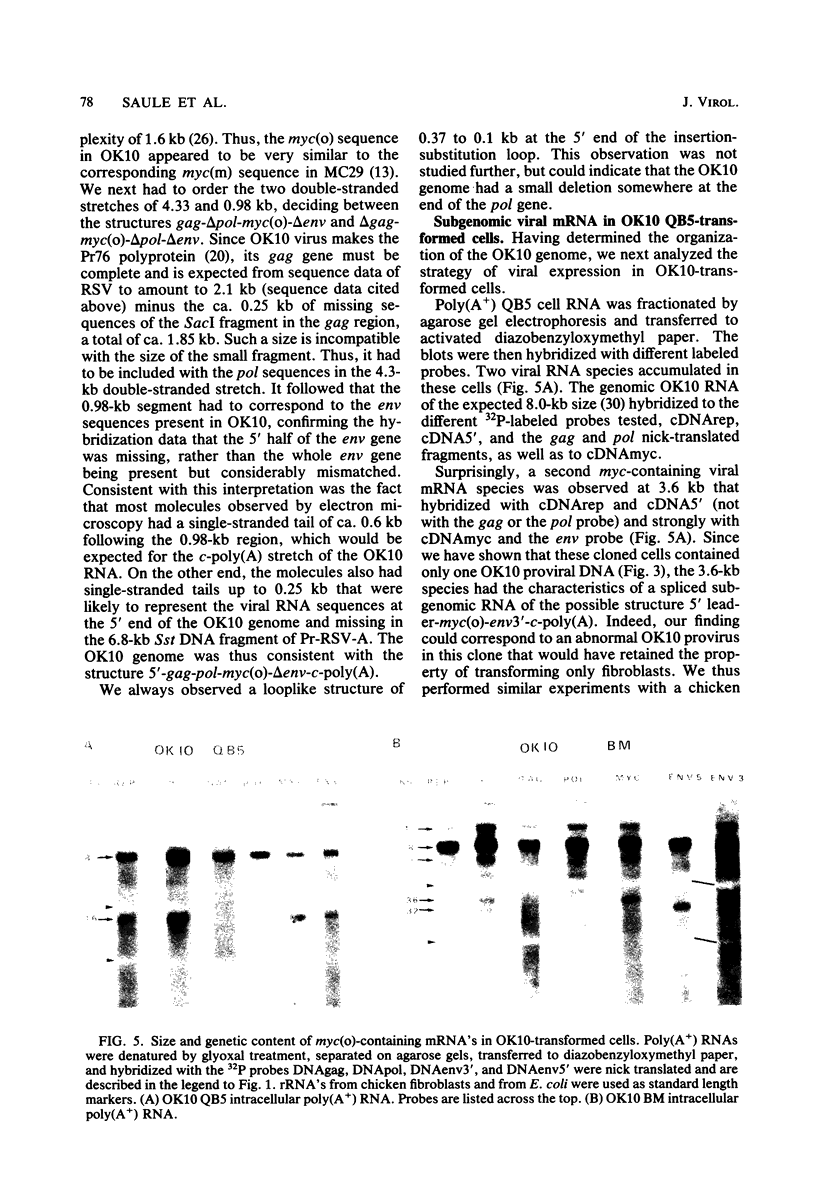
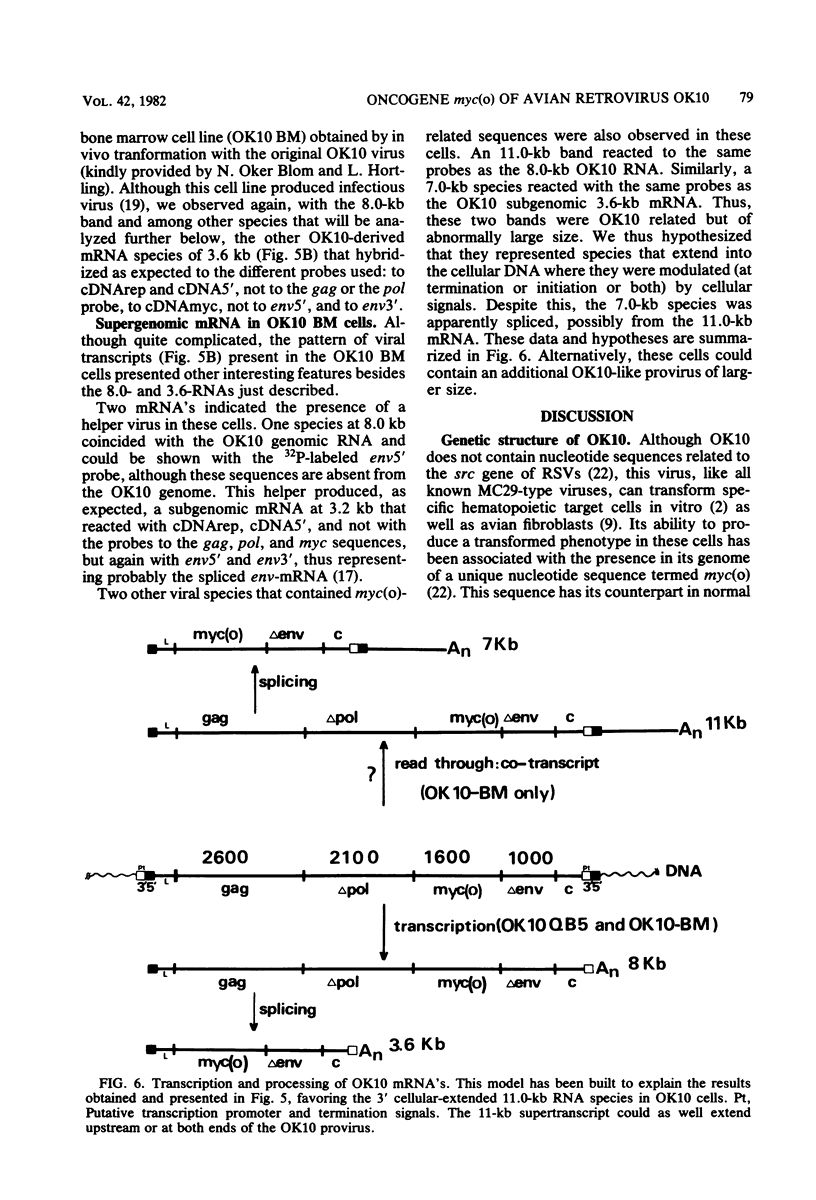
OK10, a defective leukemia virus, is produced as a defective particle by so-called nonproducer transformed quail fibroblasts. OK10 defective viral particles contain an 8-kilobases (kb)-long genomic RNA, lack any detectable reverse transcriptase activity, and are not infectious. We studied the genetic content of OK10 RNA extracted from both virions and infected cells. As shown by RNA-cDNA hybridizations in stringent conditions, about 77% (6.4 kb) of the OK10 8.0kb RNA was related to avian leukosis viruses in the three structural genes gag, pol, and env, as well as in the c region. The remainder of the OK10 genome-encoding capacity (≤1.6 kb) was homologous to the MC29-specific transforming sequence myc(m) and therefore has been named myc(o). EcoRI restriction analysis of the OK10 integrated proviral DNA with different probes indicated the presence of only one provirus in the OK10 QB5 clone, which agreed with the gene order: 5′-gag-Δpol-myc(o)-Δenv-c- 3′. Heteroduplex molecules formed between the viral OK10 8.0-kb RNA and the 6.8-kb SacI DNA fragment of the Prague A strain of Rous sarcoma virus confirmed that structure and indicated that the myc(o) sequence formed a continuous RNA stretch of 1.4 to 1.6 kb long between Δpol and Δenv. We also examined the myc(o)-containing mRNA's transcribed in OK10-transformed cells. OK10-transformed quail fibroblasts (OK10 QB5) transcribed two mRNA species of 8.0 and 3.6 kb containing the myc(o) sequence. The genetic content of the 3.6-kb species made it a possible maturation product of the genome size 8-kb species by splicing out the gag and pol sequences. In OK10-transformed bone marrow cells (OK10 BM), a stable bone marrow-derived cell line producing OK10, the myc(o) sequence was found in four RNA species of 11.0, 8.0, 7.0, and 3.6 kb. Again, the genetic content of these mRNA's indicated that (i) the 3.6-kb species could be spliced out of the 8.0-kb-genome size mRNA and (ii) the 11.0-kb-long mRNA could represent a read-through of the OK10 provirus, the corresponding maturation product being, then, a 7.0-kb mRNA. The 7.0- and 3.6- kb mRNA's both contained the myc(o) sequence, but no sequences related to the gag or pol gene. In conclusion, whereas the myc sequences have been generally thought to be expressed through a gag-onc fusion protein, as for MC29 and CMII viruses, our experiments indicate that they could also be expressed as a non-gag-related product made from a subgenomic mRNA in the OK10-transformed cells.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alwine J. C., Kemp D. J., Stark G. R. Method for detection of specific RNAs in agarose gels by transfer to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and hybridization with DNA probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5350–5354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beug H., von Kirchbach A., Döderlein G., Conscience J. F., Graf T. Chicken hematopoietic cells transformed by seven strains of defective avian leukemia viruses display three distinct phenotypes of differentiation. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):375–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90057-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bishop J. M., Courtneidge S. A., Levinson A. D., Oppermann H., Quintrell N., Sheiness D. K., Weiss S. R., Varmus H. E. Origin and function of avian retrovirus transforming genes. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 2):919–930. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Hayman M. J., Vogt P. K. Defectiveness of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: isolation of long-term nonproducer cultures and analysis of virus-specific polypeptide synthesis. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):431–448. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bister K., Ramsay G., Hayman M. J., Duesberg P. H. OK10, an avian acute leukemia virus of the MC 29 subgroup with a unique genetic structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Dec;77(12):7142–7146. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.12.7142. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casey J., Davidson N. Rates of formation and thermal stabilities of RNA:DNA and DNA:DNA duplexes at high concentrations of formamide. Nucleic Acids Res. 1977;4(5):1539–1552. doi: 10.1093/nar/4.5.1539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich R., Kung H. J., Baker B., Varmus H. E., Goodman H. M., Bishop J. M. Characterization of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences at the 5'-terminus of the avian sarcoma virus genome. Virology. 1977 Jun 1;79(1):198–215. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90345-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Beug H. Avian leukemia viruses: interaction with their target cells in vivo and in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 17;516(3):269–299. doi: 10.1016/0304-419x(78)90011-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graf T., Oker-Blom N., Todorov T. G., Beug H. Transforming capacities and defectiveness of avian leukemia viruses OK10 and E 26. Virology. 1979 Dec;99(2):431–436. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90024-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayman M. J., Kitchener G., Graf T. Cells transformed by avian myelocytomatosis virus strain CMII contain a 90K gag-related protein. Virology. 1979 Oct 15;98(1):191–199. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90537-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. F., Lai M. M., Vogt P. K. Characterization of the env gene in avian oncoviruses by heteroduplex mapping. J Virol. 1978 Sep;27(3):667–676. doi: 10.1128/jvi.27.3.667-676.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Lai M. M., Vogt P. K. Genome of avian myelocytomatosis virus MC29: analysis by heteroduplex mapping. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1265–1268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu S. S., Moscovici C., Vogt P. K. The defectiveness of Mill Hill 2, a carcinoma-inducing avian oncovirus. Virology. 1978 Aug;89(1):162–178. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90049-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Hu S. S., Vogt P. K. Avian erythroblastosis virus: transformation-specific sequences form a contiguous segment of 3.25 kb located in the middle of the 6-kb genome. Virology. 1979 Sep;97(2):366–377. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90347-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M. Phosphoproteins of Rous sarcoma viruses. Virology. 1976 Oct 15;74(2):287–301. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(76)90336-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee J. S., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific messenger RNAs in permissive cells infected by avian sarcoma virus. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):8015–8022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMaster G. K., Carmichael G. G. Analysis of single- and double-stranded nucleic acids on polyacrylamide and agarose gels by using glyoxal and acridine orange. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Nov;74(11):4835–4838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.11.4835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfeifer S., Kallio A., Vaheri A., Pettersson R., Oker-Blom N. Stable bone-marrow-derived cell line producing transforming avian acute leukemia virus OK 10. Int J Cancer. 1980 Feb 15;25(2):235–242. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910250211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsay G., Hayman M. J. Analysis of cells transformed by defective leukemia virus OK10: production of noninfectious particles and synthesis of Pr76gag and an additional 200,000-dalton protein. Virology. 1980 Oct 15;106(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(80)90222-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roussel M., Saule S., Lagrou C., Rommens C., Beug H., Graf T., Stehelin D. Three new types of viral oncogene of cellular origin specific for haematopoietic cell transformation. Nature. 1979 Oct 11;281(5731):452–455. doi: 10.1038/281452a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saule S., Roussel M., Lagrou C., Stehelin D. Characterization of the oncogene (erb) of avian erythroblastosis virus and its cellular progenitor. J Virol. 1981 May;38(2):409–419. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.2.409-419.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Kung H. J., Majors J. E., Quintrell N., Guntaka R. V., Bishop J. M., Varmus H. E. Mapping unintegrated avian sarcoma virus DNA: termini of linear DNA bear 300 nucleotides present once or twice in two species of circular DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1383–1395. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank P. R., Hughes S. H., Varmus H. E. Restriction endonuclease mapping of the DNA of Rous-associated virus O reveals extensive homology in structure and sequence with avian sarcoma virus DNA. Virology. 1981 Jan 15;108(1):177–188. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90537-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Fanshier L., Bishop J. M. Identification of nucleotide sequences which may encode the oncogenic capacity of avian retrovirus MC29. J Virol. 1978 Nov;28(2):600–610. doi: 10.1128/jvi.28.2.600-610.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheiness D., Vennstrom B., Bishop J. M. Virus-specific RNAs in cells infected by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus: modes of oncogene expression. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):291–300. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90293-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stehelin D., Guntaka R. V., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Purification of DNA complementary to nucleotide sequences required for neoplastic transformation of fibroblasts by avian sarcoma viruses. J Mol Biol. 1976 Mar 5;101(3):349–365. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90152-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tal J., Fujita D. J., Kawai S., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Purification of DNA complementary to the env gene of avian sarcoma virus and analysis of relationships among the env genes of avian leukosis-sarcoma viruses. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):497–505. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.497-505.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor J. M., Illmensee R., Summers J. Efficeint transcription of RNA into DNA by avian sarcoma virus polymerase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1976 Sep 6;442(3):324–330. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(76)90307-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Fanshier L., Moscovici C., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning of the avian erythroblastosis virus genome and recovery of oncogenic virus by transfection of chicken cells. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):575–585. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.575-585.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verma I. M. Genome organization of RNA tumor viruses. I. In vitro synthesis of full-genome-length single-stranded and double-stranded viral DNA transcripts. J Virol. 1978 Jun;26(3):615–629. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.3.615-629.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]