Abstract
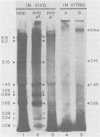
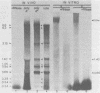
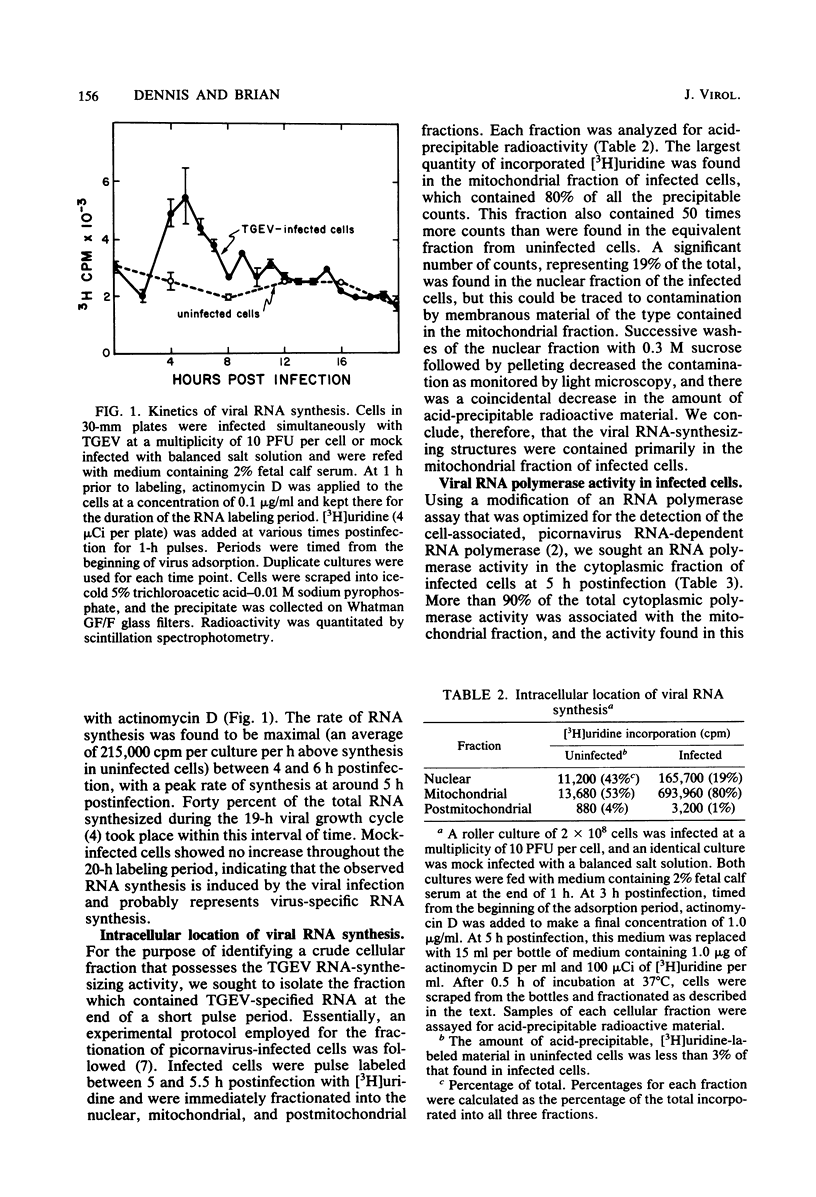
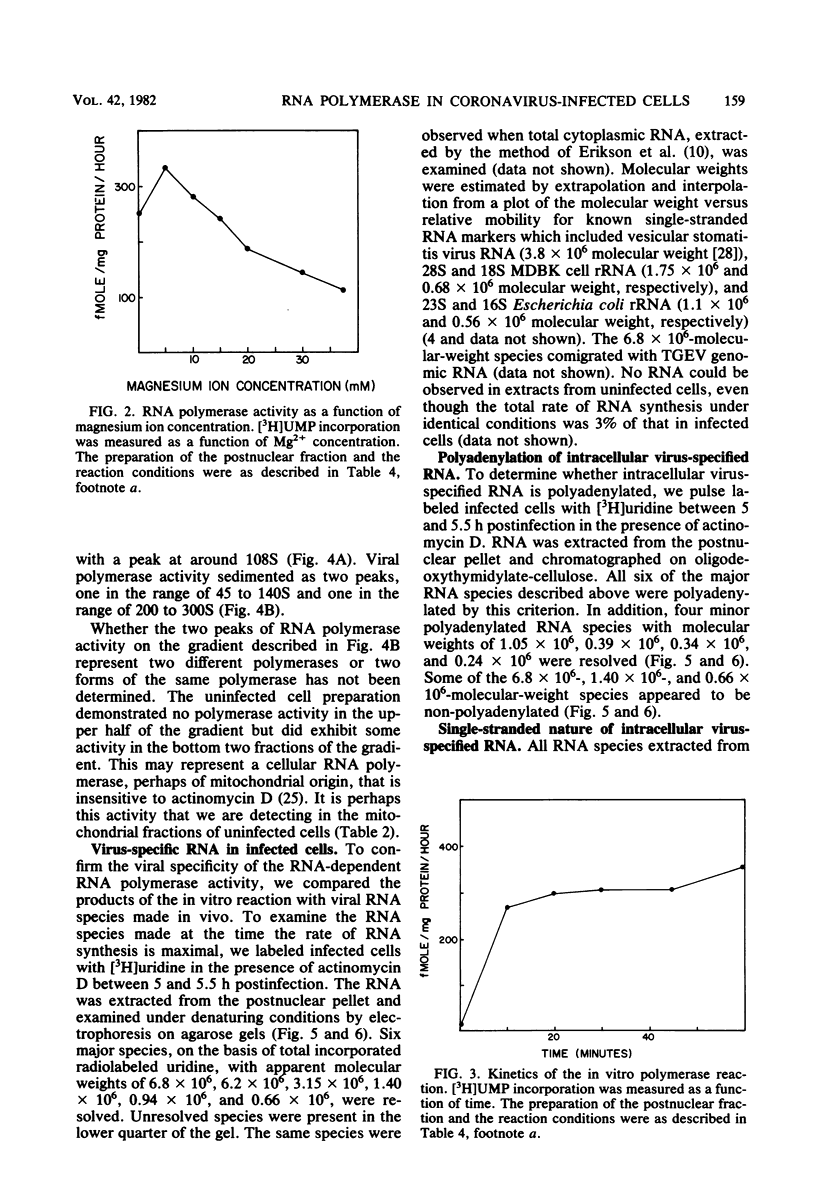
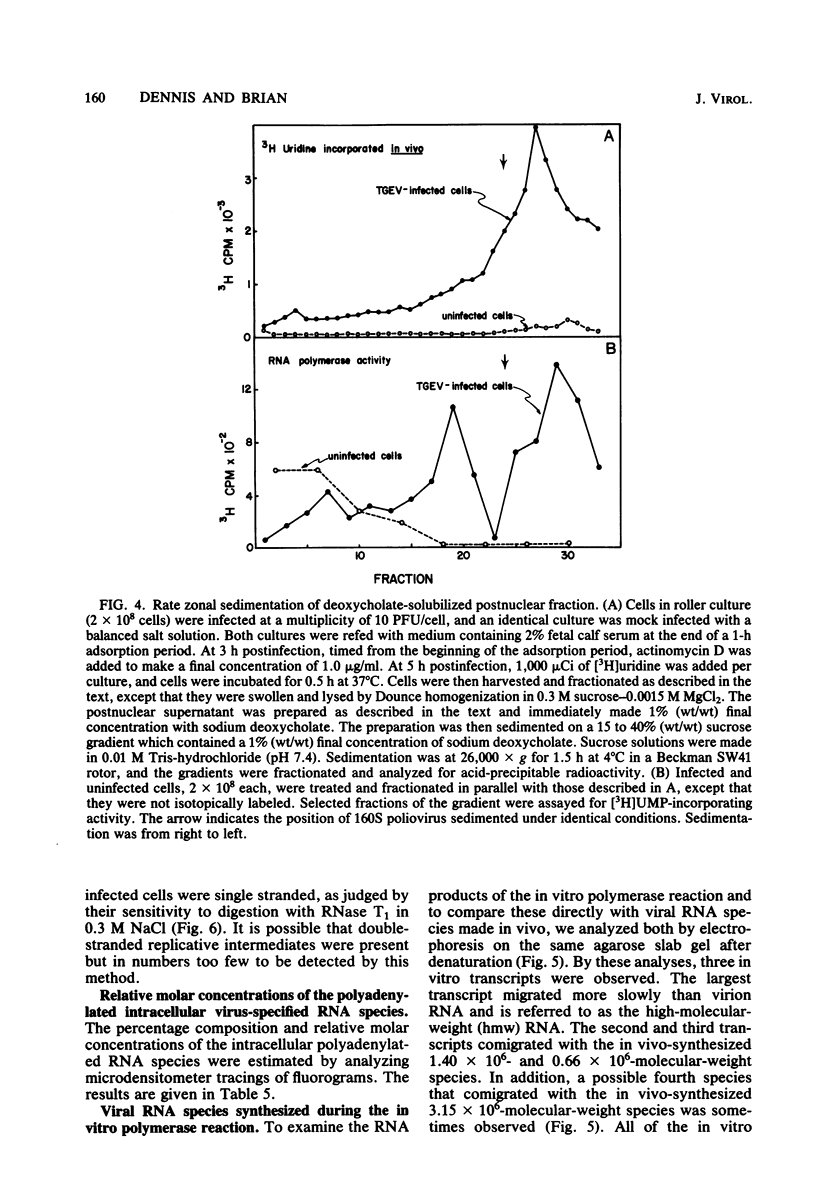
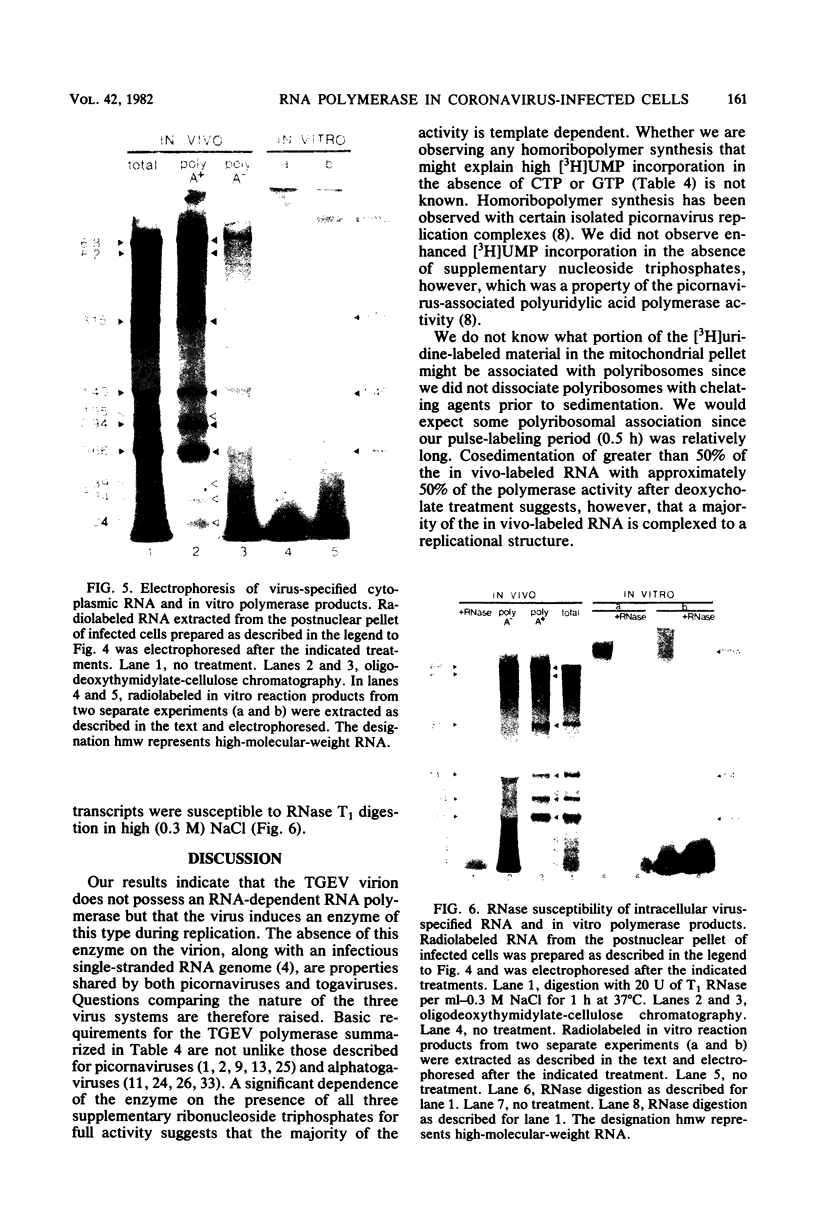
An enzymatic activity which incorporates [3H]UMP into acid-precipitable material in the presence of endogenous template was found in the cytoplasm of porcine cells infected with the transmissible gastroenteritis virus of swine. This activity was not found in uninfected control cells, nor was it found in purified virus. The activity was associated with the mitochondrial fraction of infected cells, suggesting that the enzyme is membrane bound. The activity required the presence of all three ribonucleoside triphosphates in addition to [3H]UTP, and it was not inhibited by actinomycin D. The heated product was digested by RNase but not by DNase. Mg2+ was required for enzymatic activity, and its optimal concentration was approximately 5 mM. The size of the in vitro products was compared by electrophoresis with that of in vivo-synthesized virus-specified RNA to confirm the viral specificity of the polymerase activity. Virus-specified RNA from infected cells consisted of 10 species of single-stranded, polyadenylated RNA with molecular weights of 6.8 X 10(6), 6.2 X 10(6), 3.15 X 10(6), 1.40 X 10(6), 1.05 X 10(6), 0.94 X 10(6), 0.66 X 10(6), 0.39 X 10(6), 0.34 X 10(6), and 0.24 X 10(6). In vitro synthesized RNA consisted of a high-molecular-weight species, of apparently higher molecular weight than genomic RNA, and two single-stranded species that electrophoretically comigrated with the species of 1.40 X 10(6) and 0.66 X 10(6) molecular weight made in vivo.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. Detergent-solubilized RNA polymerase from cells infected with foot-and-mouth disease virus. Science. 1967 Dec 8;158(3806):1320–1322. doi: 10.1126/science.158.3806.1320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arlinghaus R. B., Polatnick J. The isolation of two enzyme-ribonucleic acid complexes involved in the synthesis of foot-and-mouth disease virus ribonucleic acid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):821–828. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Expression of animal virus genomes. Bacteriol Rev. 1971 Sep;35(3):235–241. doi: 10.1128/br.35.3.235-241.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brian D. A., Dennis D. E., Guy J. S. Genome of porcine transmissible gastroenteritis virus. J Virol. 1980 May;34(2):410–415. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.2.410-415.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A. Analysis of RNA associated with the poliovirus RNA replication complexes. Virology. 1974 Apr;58(2):526–535. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90086-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clewley J. P., Kennedy S. I. Purification and polypeptide composition of Semliki Forest virus RNA polymerase. J Gen Virol. 1976 Sep;32(3):395–411. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-32-3-395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DALGARNO L., MARTIN E. M. STUDIES ON EMC VIRAL RNA SYNTHESIS AND ITS LOCALIZATION IN INFECTED KREBS ASCITES CELLS. Virology. 1965 Jul;26:450–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90008-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dalgarno L., Martin E. M., Liu S. L., Work T. S. Characterization of the products formed by the RNA polymerases of cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):77–91. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80210-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenfeld E., Maizel J. V., Summers D. F. Soluble RNA polymerase complex from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. Virology. 1970 Apr;40(4):840–846. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90129-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erikson E., Erikson R. L., Henry B., Pace N. R. Comparison of oligonucleotides produced by RNase T1 digestion of 7 S RNA from avian and murine oncornaviruses and from uninfected cells. Virology. 1973 May;53(1):40–46. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90463-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M., Levin J. G., Grimley P. M., Berezesky I. K. Membrane-associated replication complex in arbovirus infection. J Virol. 1972 Sep;10(3):504–515. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.3.504-515.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horton E., Liu S. L., Martin E. M., Work T. S. Properties of a virus-induced RNA polymerase in ascites cells infected with encephalomyocarditis virus. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jan;15(1):62–76. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80209-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Baltimore D., Bratt M. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase in virions of Newcastle disease virus: comparison with the vesicular stomatitis virus polymerase. J Virol. 1971 Mar;7(3):389–394. doi: 10.1128/jvi.7.3.389-394.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koliais S. I., Dimmock N. J. Rhinovirus RNA polymerase: products and kinetics of appearance in human diploid cells. J Virol. 1974 Nov;14(5):1035–1039. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.5.1035-1039.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai M. M., Stohlman S. A. RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Virol. 1978 May;26(2):236–242. doi: 10.1128/jvi.26.2.236-242.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskey R. A., Mills A. D. Quantitative film detection of 3H and 14C in polyacrylamide gels by fluorography. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Aug 15;56(2):335–341. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02238.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehrach H., Diamond D., Wozney J. M., Boedtker H. RNA molecular weight determinations by gel electrophoresis under denaturing conditions, a critical reexamination. Biochemistry. 1977 Oct 18;16(21):4743–4751. doi: 10.1021/bi00640a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B. Biological properties of avian coronavirus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1977 Sep;36(3):531–533. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-36-3-531. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomniczi B., Kennedy I. Genome of infectious bronchitis virus. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):99–107. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.99-107.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARTIN R. G., AMES B. N. A method for determining the sedimentation behavior of enzymes: application to protein mixtures. J Biol Chem. 1961 May;236:1372–1379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin E. M., Sonnabend J. A. Ribonucleic acid polymerase catalyzing synthesis of double-stranded arbovirus ribonucleic acid. J Virol. 1967 Feb;1(1):97–109. doi: 10.1128/jvi.1.1.97-109.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClurkin A. W., Norman J. O. Studies on transmissible gastroenteritis of swine. II. Selected characteristics of a cytopathogenic virus common to five isolates from transmissible gastroenteritis. Can J Comp Med Vet Sci. 1966 Jul;30(7):190–198. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michel M. R., Gomatos P. J. Semliki forest virus-specific RNAs synthesized in vitro by enzyme from infected BHK cells. J Virol. 1973 Jun;11(6):900–914. doi: 10.1128/jvi.11.6.900-914.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plagemann P. G., Swim H. E. Symposium on replication of viral nucleic acids. 3. Replication of mengovirus ribonucleic acid. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Jun;30(2):288–308. doi: 10.1128/br.30.2.288-308.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qureshi A. A., Trent D. W. Saint Louis encephalitis viral ribonucleic acid replication complex. J Virol. 1972 Apr;9(4):565–573. doi: 10.1128/jvi.9.4.565-573.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Repik P., Bishop D. H. Determination of the molecular weight of animal RNA viral genomes by nuclease digestions. I. Vesicular stomatitis virus and its defective T particle. J Virol. 1973 Nov;12(5):969–983. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.5.969-983.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottier P. J., Spaan W. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Translation of three mouse hepatitis virus strain A59 subgenomic RNAs in Xenopus laevis oocytes. J Virol. 1981 Apr;38(1):20–26. doi: 10.1128/jvi.38.1.20-26.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schochetman G., Stevens R. H., Simpson R. W. Presence of infectious polyadenylated RNA in coronavirus avian bronchitis virus. Virology. 1977 Apr;77(2):772–782. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90498-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siddell S. G., Wege H., Barthel A., ter Meulen V. Coronavirus JHM: cell-free synthesis of structural protein p60. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):10–17. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.10-17.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spaan W. J., Rottier P. J., Horzinek M. C., van der Zeijst B. A. Isolation and identification of virus-specific mRNAs in cells infected with mouse hepatitis virus (MHV-A59). Virology. 1981 Jan 30;108(2):424–434. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(81)90449-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreevalsan T., Yin F. H. Sindbis virus-induced viral ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Virol. 1969 Jun;3(6):599–604. doi: 10.1128/jvi.3.6.599-604.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kennedy S. I. Coronavirus multiplication strategy. I. Identification and characterization of virus-specified RNA. J Virol. 1980 Jun;34(3):665–674. doi: 10.1128/jvi.34.3.665-674.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern D. F., Kennedy S. I. Coronavirus multiplication strategy. II. Mapping the avian infectious bronchitis virus intracellular RNA species to the genome. J Virol. 1980 Nov;36(2):440–449. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.2.440-449.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tyrrell D. A., Almeida J. D., Cunningham C. H., Dowdle W. R., Hofstad M. S., McIntosh K., Tajima M., Zakstelskaya L. Y., Easterday B. C., Kapikian A. Coronaviridae. Intervirology. 1975;5(1-2):76–82. doi: 10.1159/000149883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wege H., Müller A., ter Meulen V. Genomic RNA of the murine coronavirus JHM. J Gen Virol. 1978 Nov;41(2):217–227. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-41-2-217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yogo Y., Hirano N., Hino S., Shibuta H., Matumoto M. Polyadenylate in the virion RNA of mouse hepatitis virus. J Biochem. 1977 Oct;82(4):1103–1108. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131782. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]