Abstract
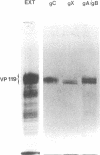
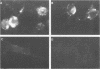
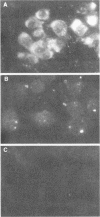
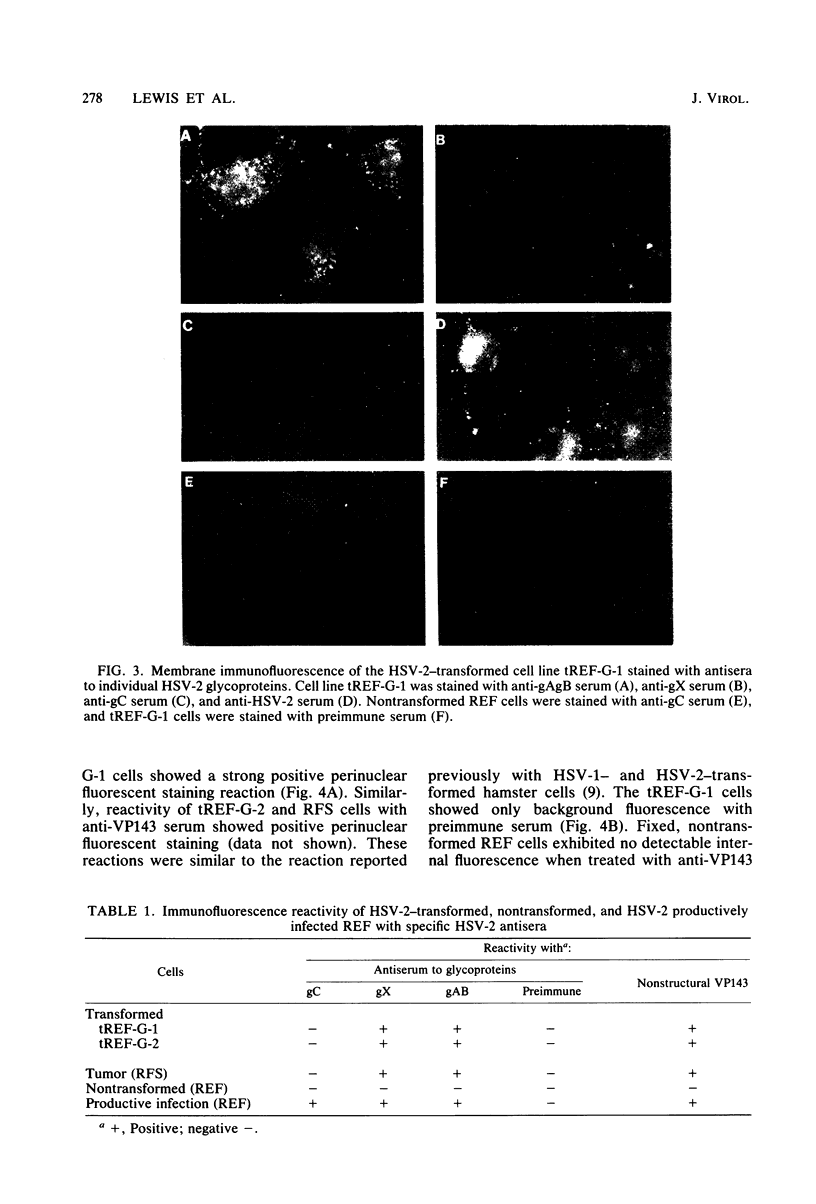
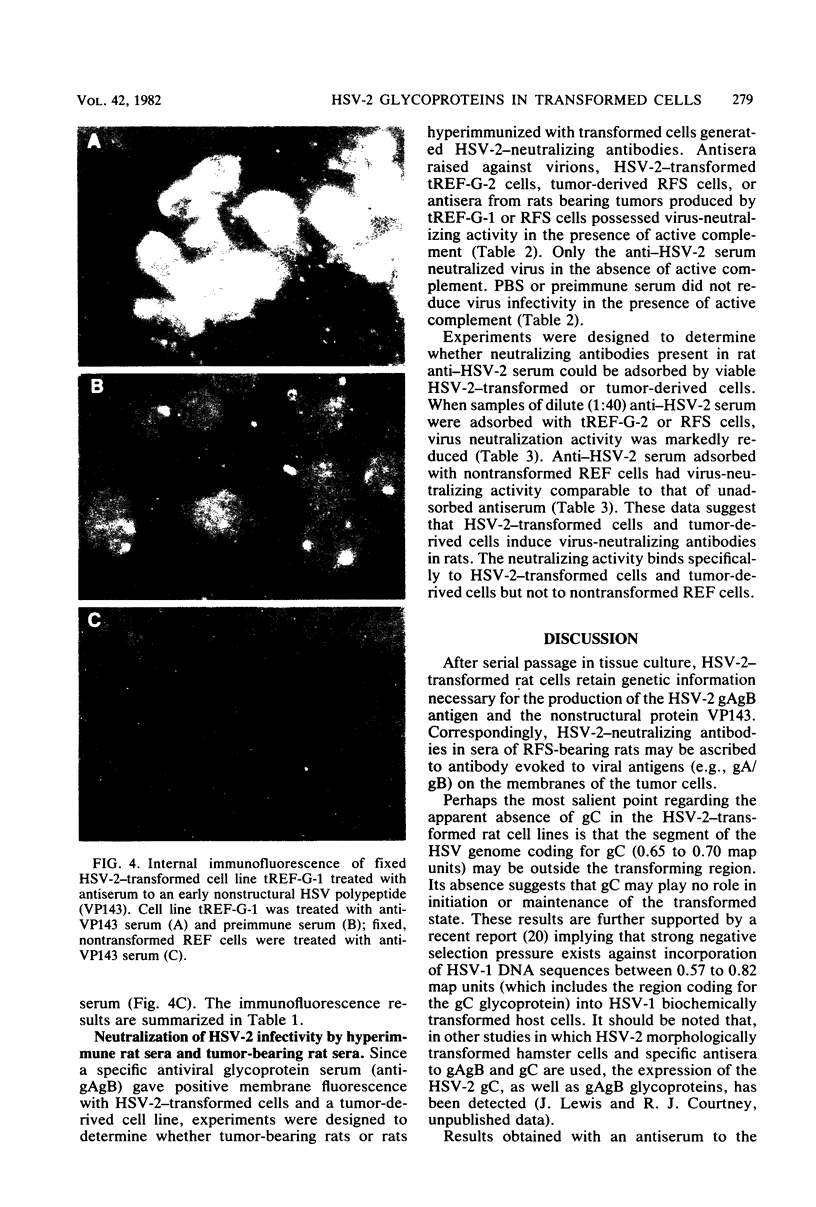
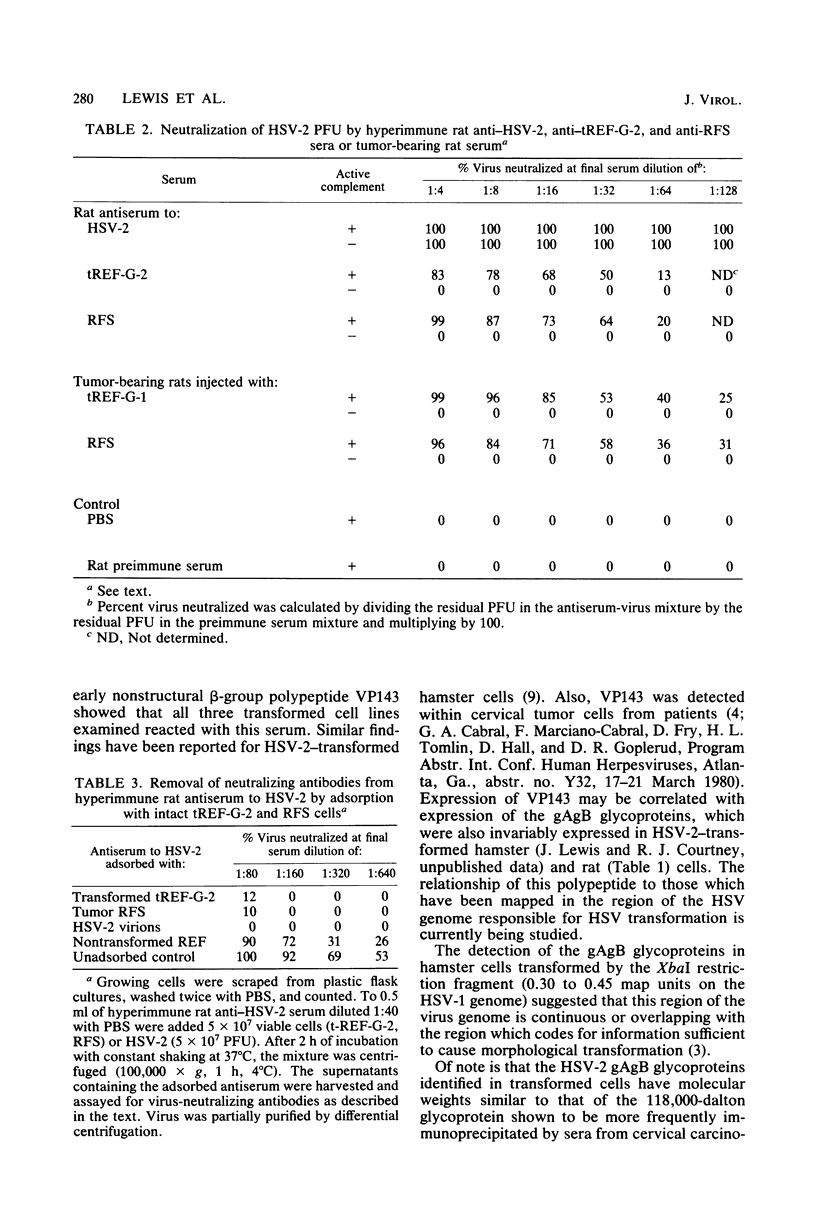
Rat embryo fibroblasts transformed by herpes simplex virus type 2 (HSV-2) were assayed for the expression of certain virus-specific glycoproteins on the surface membranes. Monospecific antisera to HSV-2-specific glycoproteins, designated gAgB, gC, and gX, were used in membrane immunofluorescence studies with HSV-2-transformed cell lines tREF-G-1, tREF-G-2, and a tumor-derived rat fibrosarcoma cells line produced in syngeneic rats inoculated with tREF-G-1 cells. Analysis of the three HSV-2-transformed cell lines showed that antisera to the gAgB and gX glycoproteins were reactive with these cells. In contrast, no significant reactivity was observed when anti-gC serum was reacted with the HSV-2-transformed cell lines. All three antiglycoprotein sera reacted positively with rat cells productively infected with HSV-2. Additionally, the HSV-2-transformed and tumor-derived cell lines showed positive internal immunofluorescence after reaction with antiserum to an early, nonstructural viral protein designated VP143 (molecular weight, 143,000). Infectivity of HSV-2 in standard plaque assays was neutralized by hyperimmune rat antisera to tREF-G-2 or rat fibrosarcoma cells and to HSV-2 virions and by sera from rats bearing the fibrosarcoma. Adsorption of rat-anti-HSV-2 serum with tREF-G-2 or rat fibrosarcoma cells reduced neutralizing activity to 10 and 12%, respectively, compared with 90% neutralization by antiserum adsorbed with nontransformed rat embryo fibroblast cells and 100% neutralization with unadsorbed antiserum. In summary, HSV-2-transformed rat cells retained and expressed genetic information necessary for the production of HSV-2 glycoproteins and a nonstructural protein after high passage in tissue culture or in the syngeneic host.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baucke R. B., Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. V. Identification of an Fc-binding glycoprotein. J Virol. 1979 Dec;32(3):779–789. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.3.779-789.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boyd A. L., Orme T. W. Transformation of mouse cells after infection with ultraviolet irradiation-inactivated herpes simplex virus type 2. Int J Cancer. 1975 Oct 15;16(4):526–538. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910160403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Camacho A., Spear G. Transformation of hamster embryo fibroblasts by a specific fragment of the herpes simplex virus genome. Cell. 1978 Nov;15(3):993–1002. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90283-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dreesman G. R., Burek J., Adam E., Kaufman R. H., Melnick J. L., Powell K. L., Purifoy D. J. Expression of herpesvirus-induced antigens in human cervical cancer. Nature. 1980 Feb 7;283(5747):591–593. doi: 10.1038/283591a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Oncogenic transformation of hamster embryo cells after exposure to inactivated herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1973 Aug;12(2):209–217. doi: 10.1128/jvi.12.2.209-217.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duff R., Rapp F. Properties of hamster embryo fibroblasts transformed in vitro after exposure to ultraviolet-irradiated herpes simplex virus type 2. J Virol. 1971 Oct;8(4):469–477. doi: 10.1128/jvi.8.4.469-477.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. Amino acid metabolism in mammalian cell cultures. Science. 1959 Aug 21;130(3373):432–437. doi: 10.1126/science.130.3373.432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberle R., Courtney R. J. Preparation and characterization of specific antisera to individual glycoprotein antigens comprising the major glycoprotein region of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):902–917. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.902-917.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flannery V. L., Courtney R. J., Schaffer P. A. Expression of an early, nonstructural antigen of herpes simplex virus in cell transformed in vitro by herpes simplex virus. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):284–291. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.284-291.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frenkel N., Locker H., Cox B., Roizman B., Rapp F. Herpes simplex virus DNA in transformed cells: sequence complexity in five hamster cell lines and one derived hamster tumor. J Virol. 1976 Jun;18(3):885–893. doi: 10.1128/jvi.18.3.885-893.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galloway D. A., Copple C. D., McDougall J. K. Analysis of viral DNA sequences in hamster cells transformed by herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Feb;77(2):880–884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.2.880. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman S. C., Docherty J. J., Clarke A., Rawls W. E. Reaction patterns of herpes simplex virus type 1 and type 2 proteins with sera of patients with uterine cervical carcinoma and matched controls. Cancer Res. 1980 Dec;40(12):4640–4647. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Lausch R. N., Hay K. A., Rapp F. Expression of type-common envelope antigens by herpes simplex virus type 2-transformed hamster cells. Intervirology. 1980;14(1):50–56. doi: 10.1159/000149162. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gupta P., Rapp F. Identification of virion polypeptides in hamster cells transformed by herpes simplex virus type 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):372–374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jariwalla R. J., Aurelian L., Ts'o P. O. Tumorigenic transformation induced by a specific fragment of DNA from herpes simplex virus type 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2279–2283. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2279. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimura S., Flannery V. L., Levy B., Schaffer P. A. Oncogenic transformation of primary hamster cells by herpes simplex virus type 2 (hsv-2) and an hsv-2 temperature-sensitive mutant. Int J Cancer. 1975 May 15;15(5):786–798. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910150510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera L. S., Gusdon J. P., Edwards I., Herbst G. Oncogenic transformation of rat embryo fibroblasts with photoinactivated herpes simplex virus: rapid in vitro cloning of transformed cells. J Gen Virol. 1977 Jun;35(3):473–485. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-35-3-473. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucera L. S., Gusdon J. P. Transformation of human embryonic fibroblasts by photodynamically inactivated herpes simplex virus, type 2 at supra-optimal temperature. J Gen Virol. 1976 Feb;30(2):257–261. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-30-2-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutinová L., Vonka V., Broucek J. Increased oncogenicity and synthesis of herpesvirus antigens in hamster cells exposed to herpes simplex type-2 virus. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Mar;50(3):759–766. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.3.759. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leiden J. M., Frenkel N., Rapp F. Identification of the herpes simplex virus DNA sequences present in six herpes simplex virus thymidine kinase-transformed mouse cell lines. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):272–285. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.272-285.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macnab J. C. Transformation of rat embryo cells by temperature-sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus. J Gen Virol. 1974 Jul;24(1):143–153. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-24-1-143. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss B., Rosenblum E. N. Hydroxylapatite chromatography of protein-sodium dodecyl sulfate complexes. A new method for the separation of polypeptide subunits. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 25;247(16):5194–5198. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed C. L., Cohen G. H., Rapp F. Detection of a virus-specific antigen on the surface of herpes simplex virus-transformed cells. J Virol. 1975 Mar;15(3):668–670. doi: 10.1128/jvi.15.3.668-670.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reyes G. R., LaFemina R., Hayward S. D., Hayward G. S. Morphological transformation by DNA fragments of human herpesviruses: evidence for two distinct transforming regions in herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2 and lack of correlation with biochemical transfer of the thymidine kinase gene. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1980;44(Pt 1):629–641. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1980.044.01.066. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruyechan W. T., Morse L. S., Knipe D. M., Roizman B. Molecular genetics of herpes simplex virus. II. Mapping of the major viral glycoproteins and of the genetic loci specifying the social behavior of infected cells. J Virol. 1979 Feb;29(2):677–697. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.2.677-697.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear P. G. Membrane proteins specified by herpes simplex viruses. I. Identification of four glycoprotein precursors and their products in type 1-infected cells. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):991–1008. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.991-1008.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takahashi M., Yamanishi K. Transformation of hamster embryo and human embryo cells by temperature sensitive mutants of herpes simplex virus type 2. Virology. 1974 Sep;61(1):306–311. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(74)90267-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]