Abstract
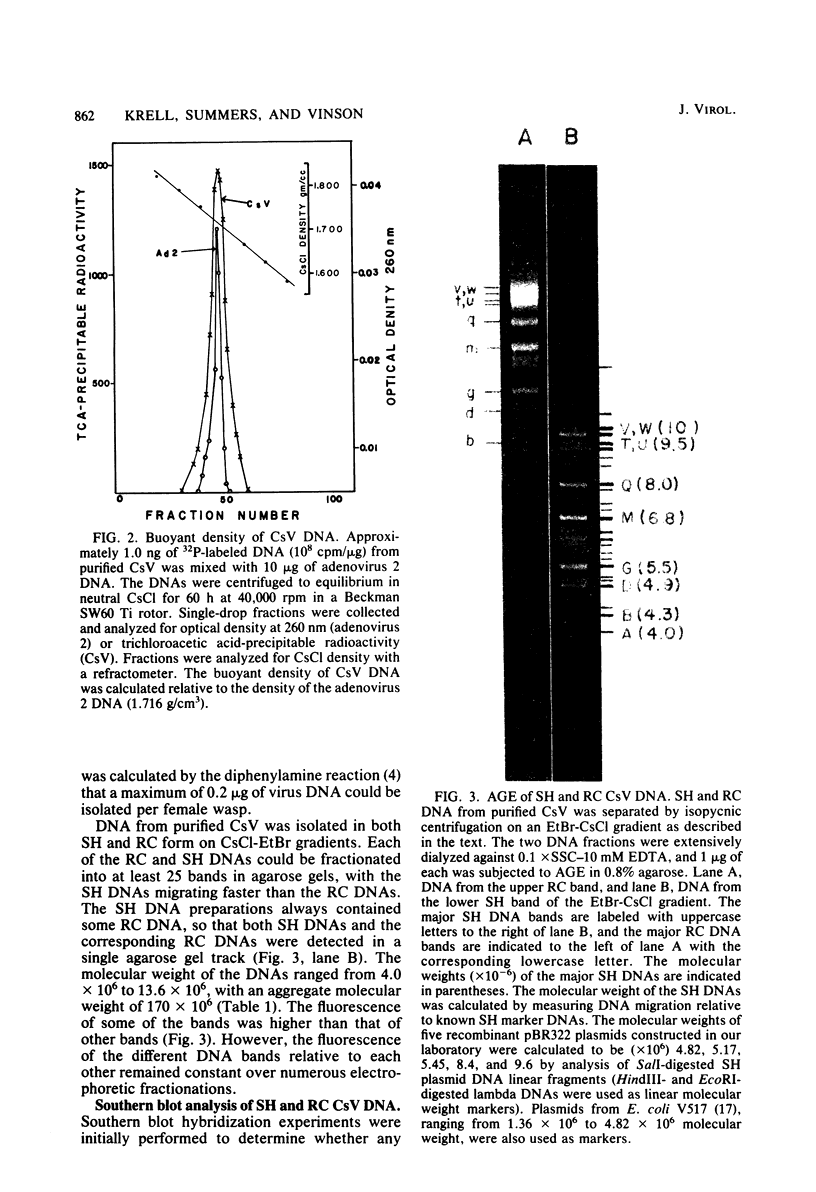
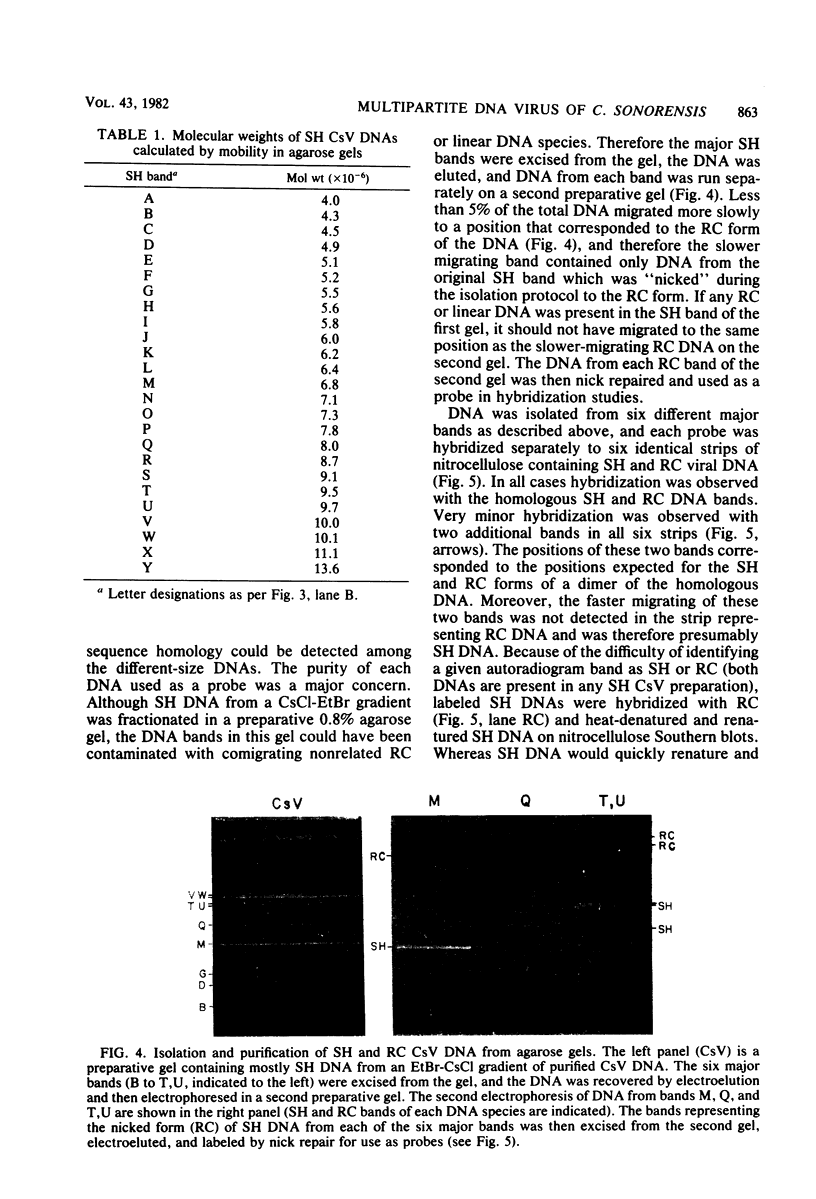
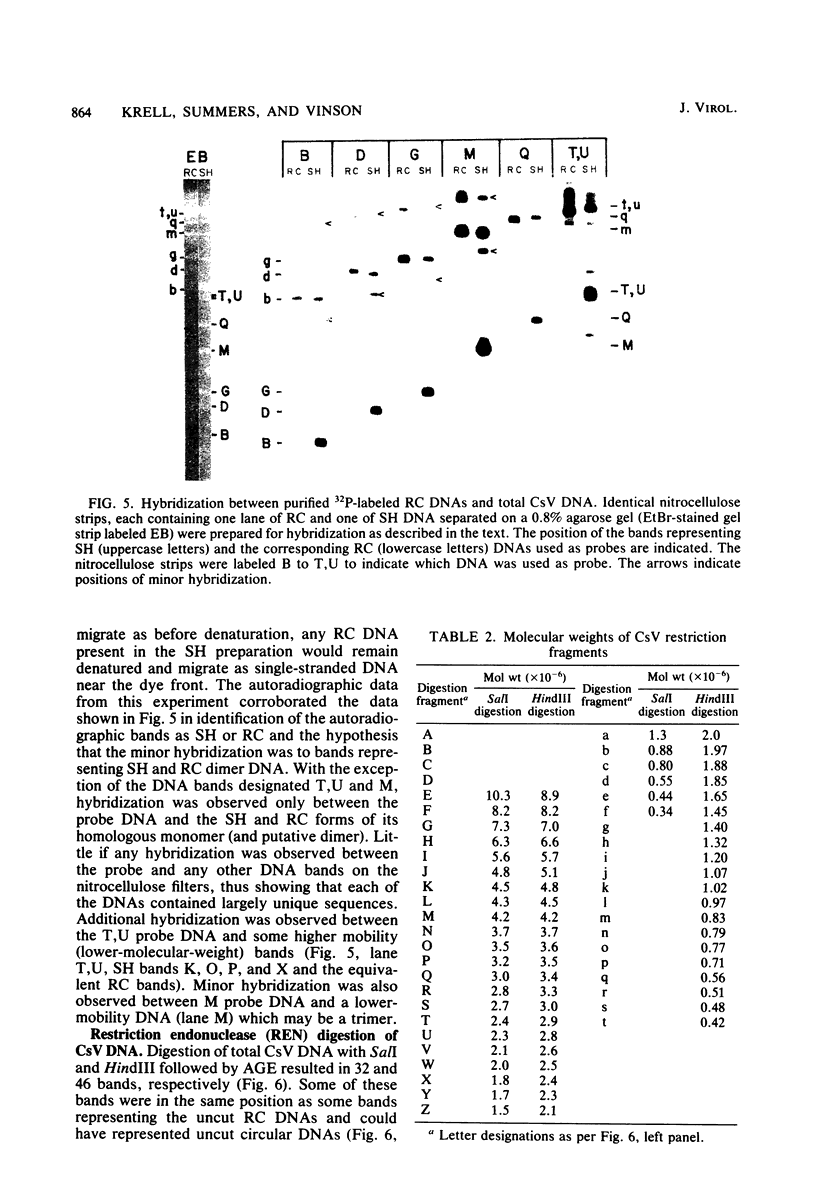
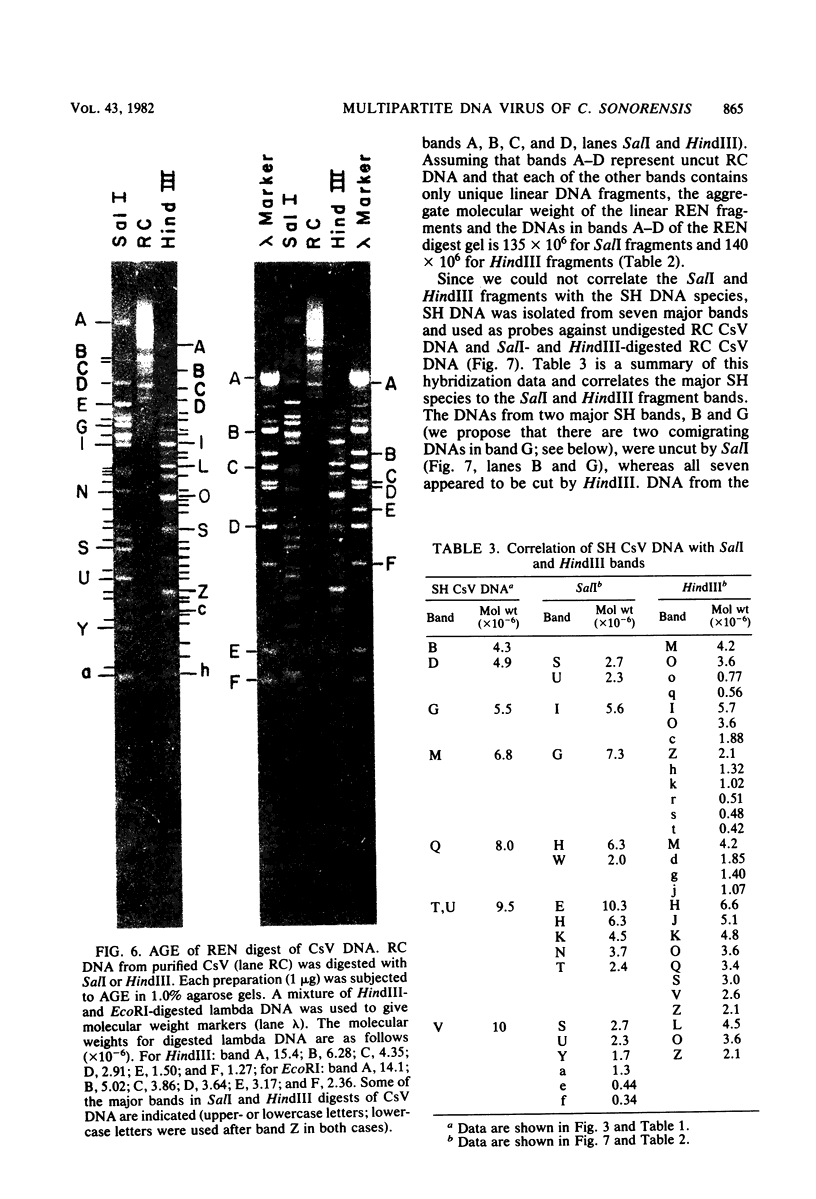
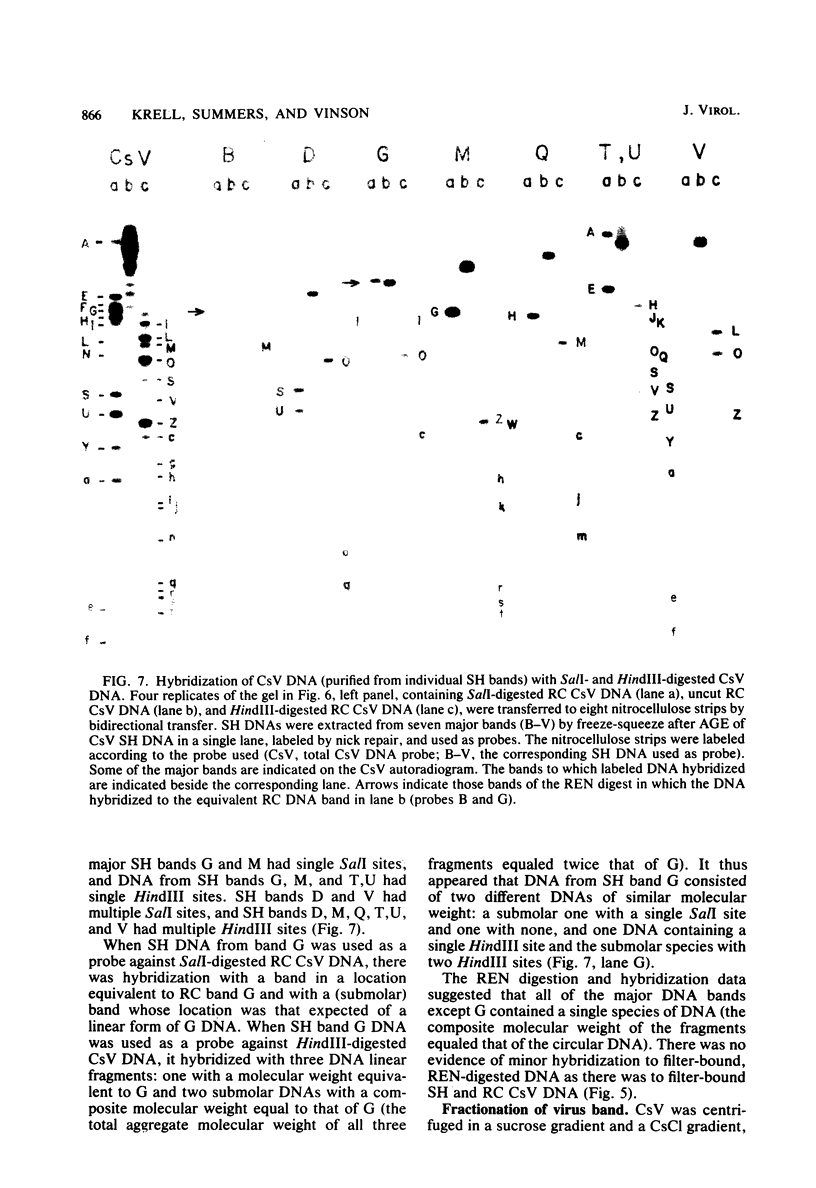
Virus was isolated from the lumen of the calyx region of ovaries in the parasitoid wasp Campoletis sonorensis (Hymenoptera: Ichneumonidae), and the nature of the viral DNA was analyzed. DNA purified from a homogeneous band of virus contained double-stranded superhelical molecules which were polydisperse in molecular weight. At least 25 different covalently closed circles were present, ranging in molecular weight from 4.0 × 106 to 13.6 × 106. The virus DNA was analyzed with restriction enzymes, and the nature of the genetic complexity was evaluated by Southern blot hybridization of native superhelical and relaxed circular virus DNA and of SalI- and HindIII-digested DNA. The data suggest that most of the variously sized covalently closed DNAs were composed primarily of nonhomologous sequences. The different size classes of covalently closed viral DNAs did not appear to exist in equimolar concentrations. However, there was no evidence from observation of virus particles in the electron microscope or from virus fractionation experiments that a mixture of viruses was present in the calyx fluid. The results from this study suggest' that the virus isolated from C. sonorensis, like those isolated from other endoparasitic hymenoptera, may belong to a new class of DNA viruses in which the genome is multipartite, with each DNA existing as a superhelical molecule.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abodeely R. A., Palmer E., Lawson L. A., Randall C. C. The proteins of enveloped and deenveloped equine abortion (herpes) virus and the separated envelope. Virology. 1971 Apr;44(1):146–152. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90161-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allington W. B., Cordry A. L., McCullough G. A., Mitchell D. E., Nelson J. W. Electrophoretic concentration of macromolecules. Anal Biochem. 1978 Mar;85(1):188–196. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90289-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bedwin O. The particulate basis of the resistance of a parasitoid to the defence reactions of its insect host. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1979 Aug 1;205(1159):267–270. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1979.0064. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahlman D. L., Vinson S. B. Trehalose and glucose levels in the hemolymph of Heliothis virescens parasitized by Microplitis croceipes or Cardiochiles nigriceps. Comp Biochem Physiol B. 1975 Dec 15;52(4):465–468. doi: 10.1016/0305-0491(75)90219-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edson K. M., Vinson S. B., Stoltz D. B., Summers M. D. Virus in a parasitoid wasp: suppression of the cellular immune response in the parasitoid's host. Science. 1981 Feb 6;211(4482):582–583. doi: 10.1126/science.7455695. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glossmann H., Neville D. M., Jr Glycoproteins of cell surfaces. A comparative study of three different cell surfaces of the rat. J Biol Chem. 1971 Oct 25;246(20):6339–6346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess H. Die Indikation und Kontraindikation zu Injektionsbehandlungen bei Sportverletzungen und Sportschäden. Unfallheilkunde. 1979 Apr;82(4):129–132. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaspars E. M. Plant viruses with a multipartite genome. Adv Virus Res. 1974;19:37–149. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60659-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krell P. J., Stoltz D. B. Unusual Baculovirus of the Parasitoid Wasp Apanteles melanoscelus: Isolation and Preliminary Characterization. J Virol. 1979 Mar;29(3):1118–1130. doi: 10.1128/jvi.29.3.1118-1130.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macrina F. L., Kopecko D. J., Jones K. R., Ayers D. J., McCowen S. M. A multiple plasmid-containing Escherichia coli strain: convenient source of size reference plasmid molecules. Plasmid. 1978 Jun;1(3):417–420. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(78)90056-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Norton W. N., Vinson S. B., Stoltz D. B. Nuclear secretory particles associated with the calyx cells of the ichneumonid parasitoid Campoletis sonorensis (Cameron). Cell Tissue Res. 1975 Sep 17;162(2):195–208. doi: 10.1007/BF00209207. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reijnders L. The origin of multicomponent small ribonucleoprotein viruses. Adv Virus Res. 1978;23:79–102. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60098-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rigby P. W., Dieckmann M., Rhodes C., Berg P. Labeling deoxyribonucleic acid to high specific activity in vitro by nick translation with DNA polymerase I. J Mol Biol. 1977 Jun 15;113(1):237–251. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90052-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. Restriction Maps of Five Autographa californica MNPV Variants, Trichoplusia ni MNPV, and Galleria mellonella MNPV DNAs with Endonucleases SmaI, KpnI, BamHI, SacI, XhoI, and EcoRI. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):828–838. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.828-838.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith G. E., Summers M. D. The bidirectional transfer of DNA and RNA to nitrocellulose or diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper. Anal Biochem. 1980 Nov 15;109(1):123–129. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90019-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B. A putative baculovirus in the ichneumonid parasitoid, Mesoleius tenthredinis. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jan;27(1):116–122. doi: 10.1139/m81-018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Faulkner G. Apparent replication of an unusual virus-like particle in both a parasitoid wasp and its host. Can J Microbiol. 1978 Dec;24(12):1509–1514. doi: 10.1139/m78-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Krell P. J., Vinson S. B. Polydisperse viral DNA's in ichneumonid ovaries: a survey. Can J Microbiol. 1981 Jan;27(1):123–130. doi: 10.1139/m81-019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Vinson S. B., MacKinnon E. A. Baculovirus-like particles in the reproductive tracts of female parasitoid wasps. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Jul;22(7):1013–1023. doi: 10.1139/m76-148. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Vinson S. B. Penetration into caterpillar cells of virus-like particles injected during oviposition by parasitoid ichneumonid wasps. Can J Microbiol. 1979 Feb;25(2):207–216. doi: 10.1139/m79-032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoltz D. B., Vinson S. B. Viruses and parasitism in insects. Adv Virus Res. 1979;24:125–171. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3527(08)60393-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Summers M. D., Smith G. E. Baculovirus structural polypeptides. Virology. 1978 Feb;84(2):390–402. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90257-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thuring R. W., Sanders J. P., Borst P. A freeze-squeeze method for recovering long DNA from agarose gels. Anal Biochem. 1975 May 26;66(1):213–220. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(75)90739-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vinson S. B. Microplitis croceipes: inhibitions of the Heliothis zea defense reaction to Cardiochiles nigriceps. Exp Parasitol. 1977 Feb;41(1):112–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4894(77)90136-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl G. M., Stern M., Stark G. R. Efficient transfer of large DNA fragments from agarose gels to diazobenzyloxymethyl-paper and rapid hybridization by using dextran sulfate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3683–3687. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3683. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood H. A. Viruses with double-stranded RNA genomes. J Gen Virol. 1973 Jun;20(Suppl):61–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-20-Supplement-61. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]