Abstract
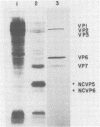
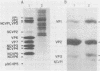
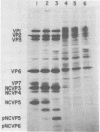
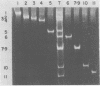
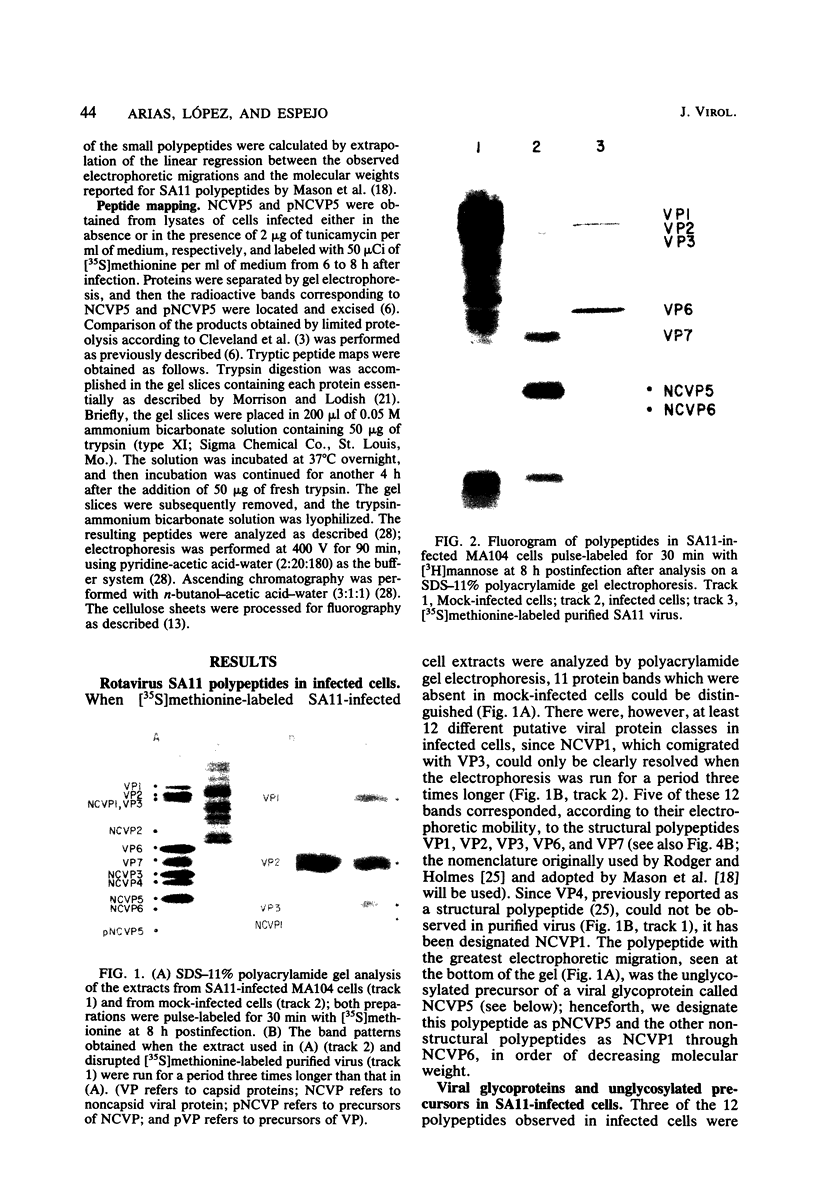
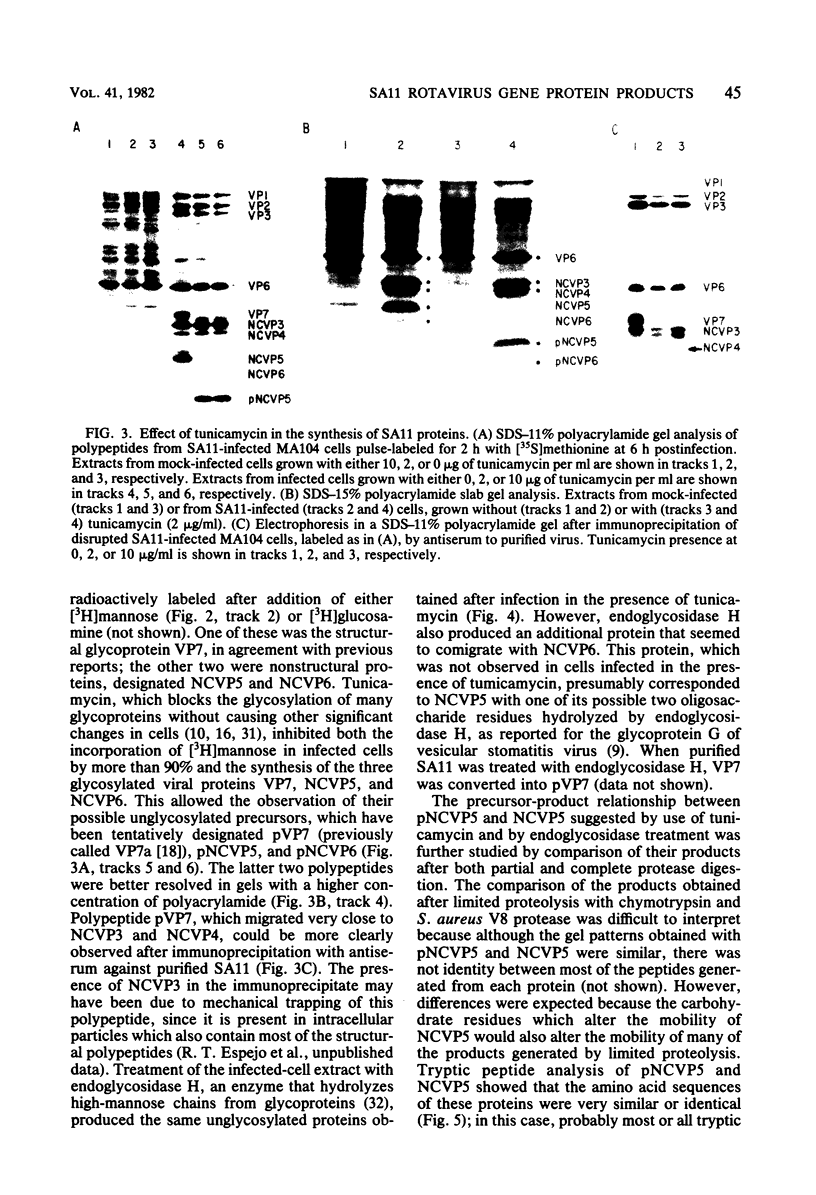
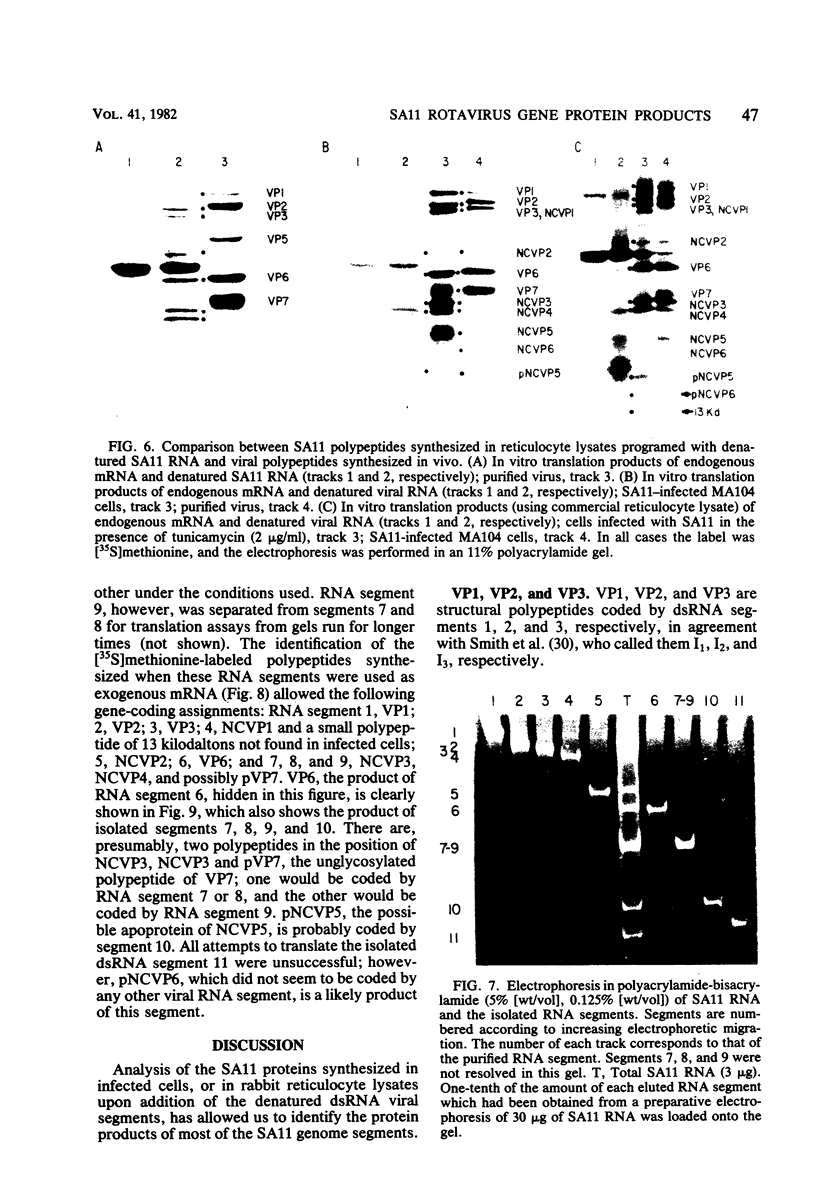
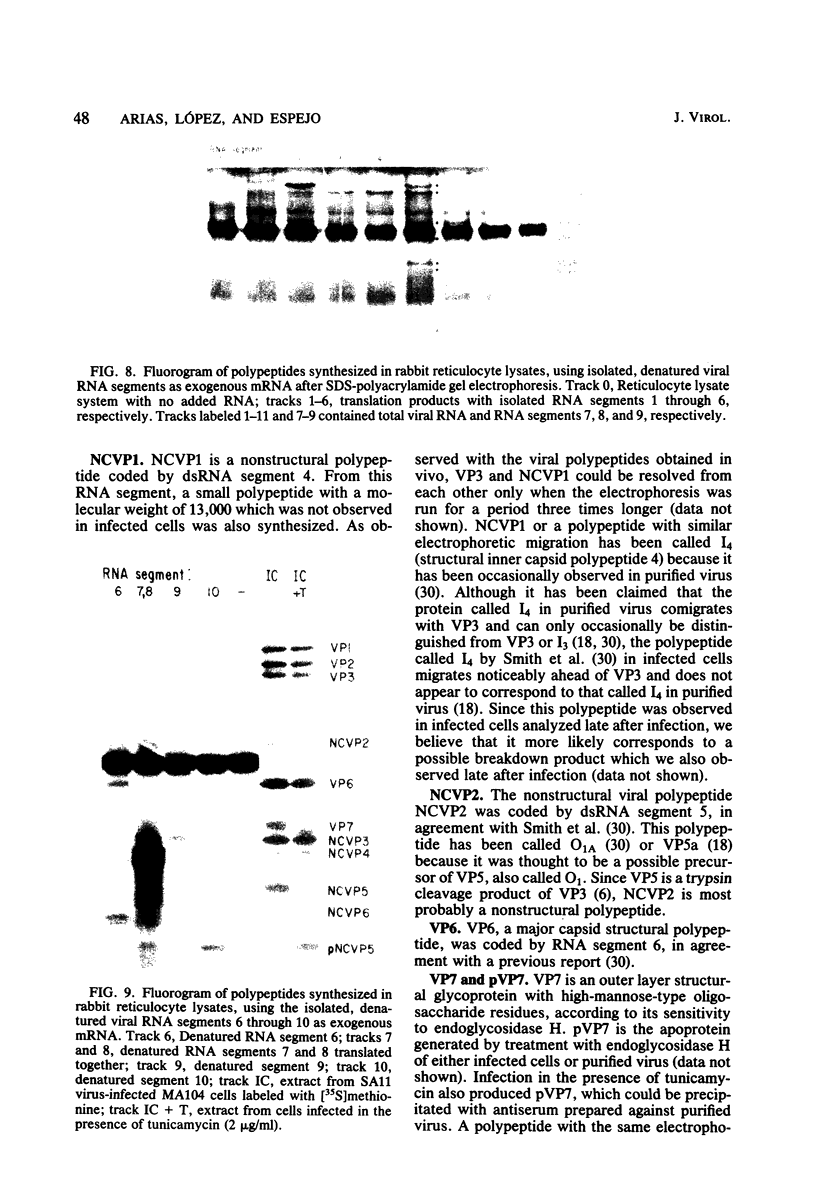
When MA104 cells were infected with SA11 rotavirus, 12 protein classes, absent in mock-infected cells, could be distinguished by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. At least two of these proteins were glycosylated, and their synthesis could be blocked with tunicamycin. The oligosaccharides of both glycoproteins were cleaved by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H, suggesting that they were residues of the "high-mannose" type. Of the 12 viral polypeptides observed in infected cells, 1 was probably the apoprotein of one of these glycoproteins; 5, including 1 glycoprotein, were structural components of the virions, whereas the other 6, including a second and possibly third glycoprotein, were nonstructural viral proteins. When the 11 double-stranded RNA genome segments of SA11 were translated, after denaturation, in an RNA-dependent cell-free translation system, at least 11 different polypeptides were synthesized. Ten of these polypeptides had electrophoretic migration patterns equal to those of viral proteins observed in tunicamycin-treated infected cells. Nine of the 11 double-stranded RNA genome segments were resolved by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis and were translated individually. Two were not resolved from each other and therefore were translated together. Correlation of each synthesized polypeptide with an individual RNA segment allowed us to make a probable gene-coding assignment for the different SA11 genome segments.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Altenburg B. C., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. Ultrastructural study of rotavirus replication in cultured cells. J Gen Virol. 1980 Jan;46(1):75–85. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-46-1-75. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner W. M., Laskey R. A. A film detection method for tritium-labelled proteins and nucleic acids in polyacrylamide gels. Eur J Biochem. 1974 Jul 1;46(1):83–88. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1974.tb03599.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- England J. M., Bolognesi D. P., Dietzschold B., Halpern M. S. Evidence that a precursor glycoprotein is cleaved to yield the major glycoprotein of avian tumor virus. J Virol. 1977 Feb;21(2):810–814. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.2.810-814.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., Calderón E., González N., Salomon A., Martuscelli A., Romero P. Presence of two distinct types of rotavirus in infants and young children hospitalized with acute gastroenteritis in Mexico City, 1977. J Infect Dis. 1979 Apr;139(4):474–477. doi: 10.1093/infdis/139.4.474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Espejo R. T., López S., Arias C. Structural polypeptides of simian rotavirus SA11 and the effect of trypsin. J Virol. 1981 Jan;37(1):156–160. doi: 10.1128/jvi.37.1.156-160.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flewett T. H., Woode G. N. The rotaviruses. Arch Virol. 1978;57(1):1–23. doi: 10.1007/BF01315633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fries E., Rothman J. E. Transport of vesicular stomatitis virus glycoprotein in a cell-free extract. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3870–3874. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3870. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibson R., Leavitt R., Kornfeld S., Schlesinger S. Synthesis and infectivity of vesicular stomatitis virus containing nonglycosylated G protein. Cell. 1978 Apr;13(4):671–679. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90217-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes I. H. Viral gastroenteritis. Prog Med Virol. 1979;25:1–36. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kalica A. R., Theodore T. S. Polypeptides of simian rotavirus (SA-11) determined by a continuous polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis method. J Gen Virol. 1979 May;43(2):463–466. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-43-2-463. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kopchick J. J., Karshin W. L., Arlinghaus R. B. Tryptic peptide analysis of gag and gag-pol gene products of Rauscher murine leukemia virus. J Virol. 1979 May;30(2):610–623. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.2.610-623.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazarowitz S. G., Compans R. W., Choppin P. W. Influenza virus structural and nonstructural proteins in infected cells and their plasma membranes. Virology. 1971 Dec;46(3):830–843. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(71)90084-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leavitt R., Schlesinger S., Kornfeld S. Tunicamycin inhibits glycosylation and multiplication of Sindbis and vesicular stomatitis viruses. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):375–385. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.375-385.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malherbe H. H., Strickland-Cholmley M. Simian virus SA11 and the related O agent. Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1967;22(1):235–245. doi: 10.1007/BF01240518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mason B. B., Graham D. Y., Estes M. K. In vitro transcription and translation of simian rotavirus SA11 gene products. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):1111–1121. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.1111-1121.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuno S., Hasegawa A., Kalica A. R., Kono R. Isolation of a recombinant between simian and bovine rotaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1980 May;48(1):253–256. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-48-1-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCrae M. A., Joklik W. K. The nature of the polypeptide encoded by each of the 10 double-stranded RNA segments of reovirus type 3. Virology. 1978 Sep;89(2):578–593. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90199-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. G. Site of synthesis of membrane and nonmembrane proteins of vesicular stomatitis virus. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 10;250(17):6955–6962. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai Y., Klenk H. D. Activation of precursors to both glycoporteins of Newcastle disease virus by proteolytic cleavage. Virology. 1977 Mar;77(1):125–134. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90412-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Hubbard S. C., Turco S. J., Wirth D. F. Proposal for a common oligosaccharide intermediate in the synthesis of membrane glycoproteins. Cell. 1977 Dec;12(4):893–900. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(77)90153-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Holmes I. H. Comparison of the genomes of simian, bovine, and human rotaviruses by gel electrophoresis and detection of genomic variation among bovine isolates. J Virol. 1979 Jun;30(3):839–846. doi: 10.1128/jvi.30.3.839-846.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodger S. M., Schnagl R. D., Holmes I. H. Further biochemical characterization, including the detection of surface glycoproteins, of human, calf, and simian rotaviruses. J Virol. 1977 Oct;24(1):91–98. doi: 10.1128/jvi.24.1.91-98.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
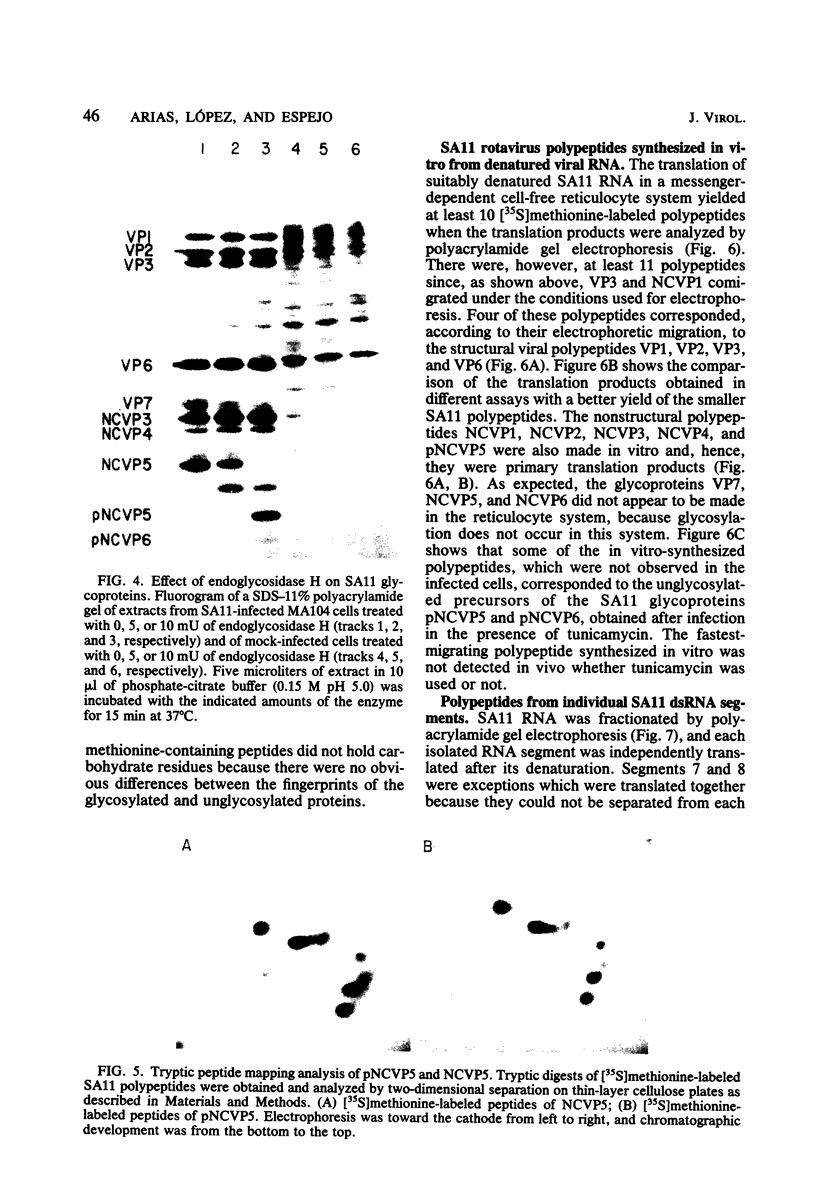
- Schlesinger S., Schlesinger M. J. Formation of Sindbis virus proteins: identification of a precursor for one of the envelope proteins. J Virol. 1972 Nov;10(5):925–932. doi: 10.1128/jvi.10.5.925-932.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott J. V., Stowring L., Haase A. T., Narayan O., Vigne R. Antigenic variation in visna virus. Cell. 1979 Oct;18(2):321–327. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90051-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver J., Schaffhausen B., Benjamin T. Tumor antigens induced by nontransforming mutants of polyoma virus. Cell. 1978 Oct;15(2):485–496. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90018-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith M. L., Lazdins I., Holmes I. H. Coding assignments of double-stranded RNA segments of SA 11 rotavirus established by in vitro translation. J Virol. 1980 Mar;33(3):976–982. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.3.976-982.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takatsuki A., Arima K., Tamura G. Tunicamycin, a new antibiotic. I. Isolation and characterization of tunicamycin. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1971 Apr;24(4):215–223. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.24.215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Maley F. Purification and properties of an endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Streptomyces griseus. J Biol Chem. 1974 Feb 10;249(3):811–817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thouless M. E. Rotavirus polypeptides. J Gen Virol. 1979 Jul;44(1):187–197. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-1-187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., McDowell M., Baltimore D., Lodish H. F. Translation of reovirus mRNA, poliovirus RNA and bacteriophage Qbeta RNA in cell-free extracts of mammalian cells. Methods Enzymol. 1974;30:709–723. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(74)30068-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]