Abstract
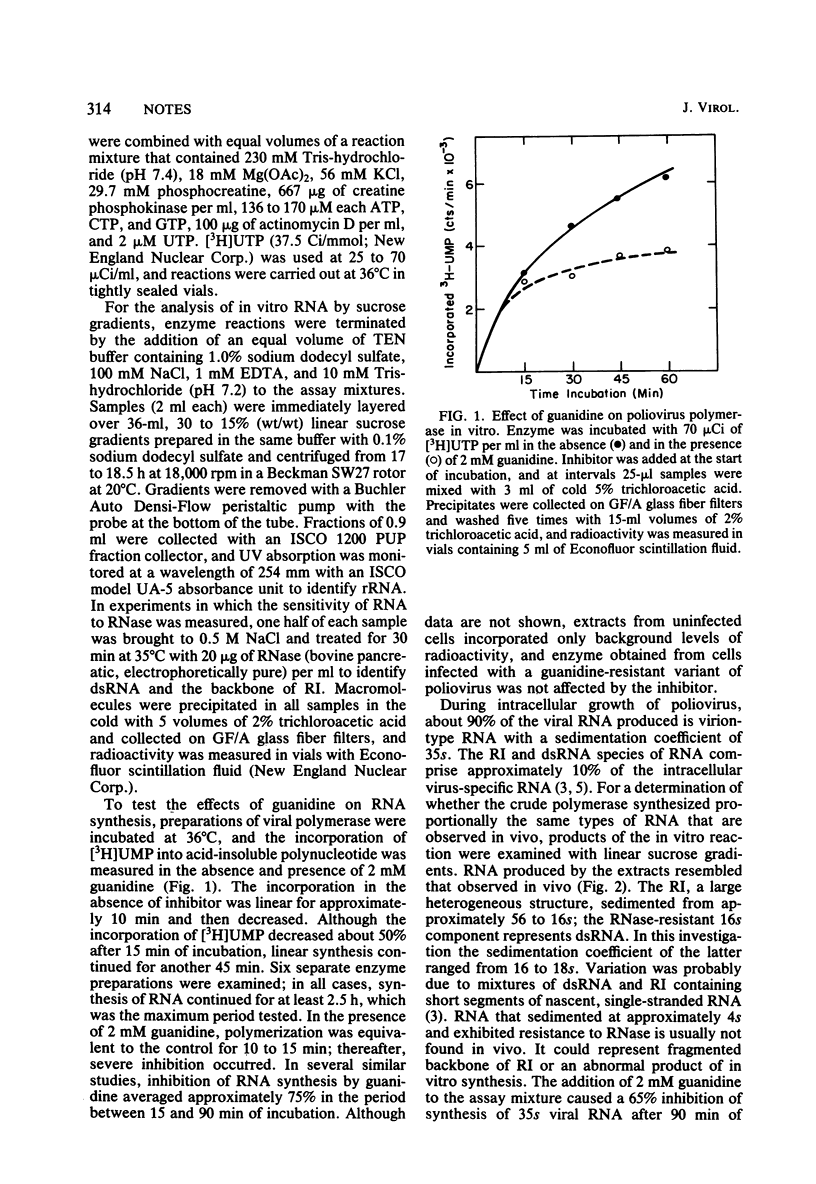
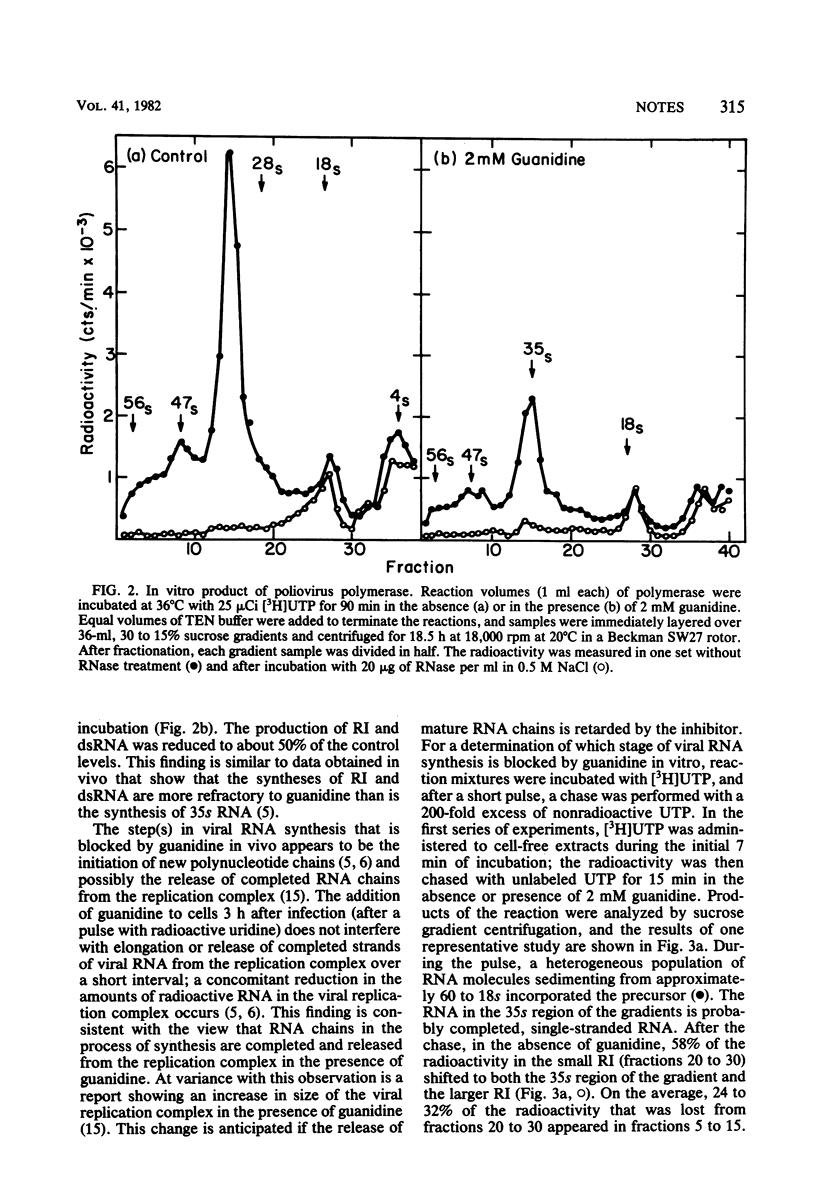
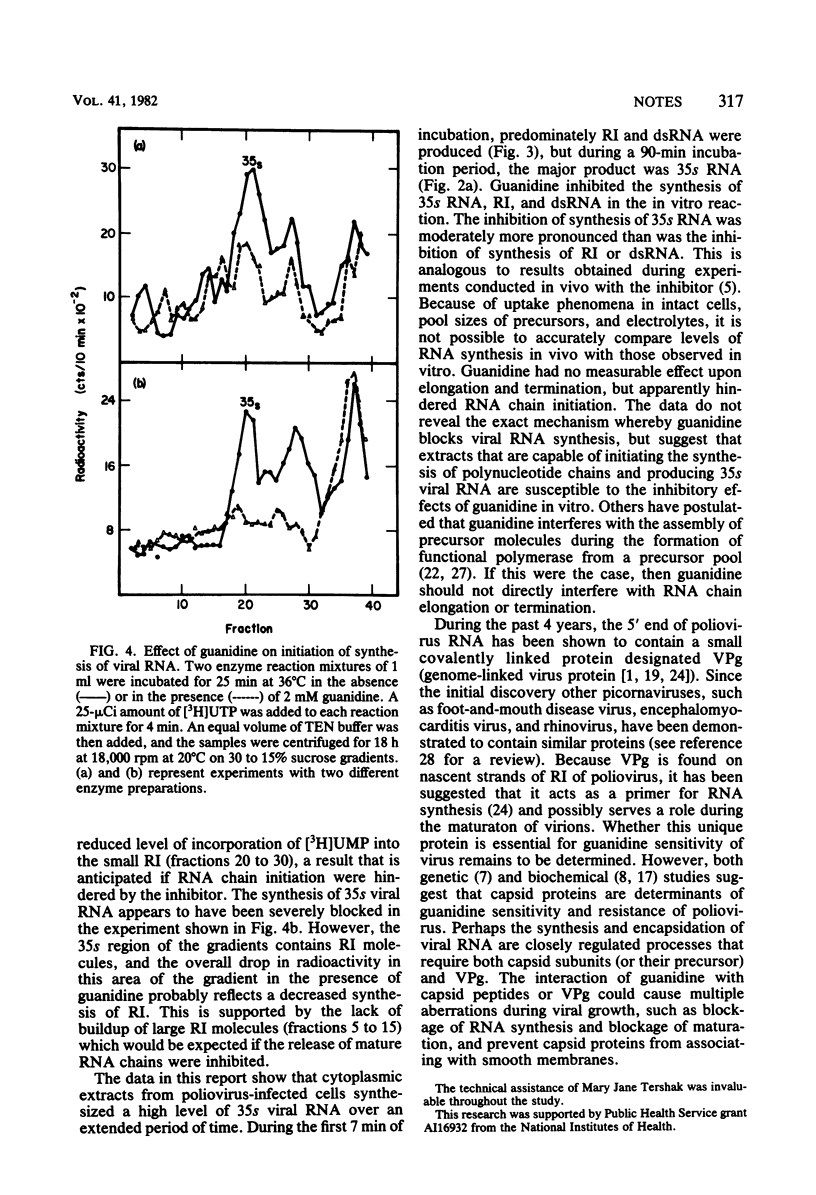
Extracts from poliovirus-infected HeLa cells synthesized 35s viral RNA, replicative intermediate, and double-stranded RNA in vitro. Guanidine inhibited the synthesis of all three species of RNA; production of 35s RNA was most sensitive to the inhibitor. Pulse-chase experiments with [3H]UTP indicated that guanidine had no detectable effect on elongation of polynucleotide chains or the release of completed RNA chains from the viral replication complex. Experiments in which short pulses of precursor were used suggest that guanidine blocked the initiation step of RNA synthesis in vitro.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ambros V., Baltimore D. Protein is linked to the 5' end of poliovirus RNA by a phosphodiester linkage to tyrosine. J Biol Chem. 1978 Aug 10;253(15):5263–5266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BALTIMORE D. IN VITRO SYNTHESIS OF VIRAL RNA BY THE POLIOVIRUS RNA POLYMERASE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Mar;51:450–456. doi: 10.1073/pnas.51.3.450. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baltimore D. Purification and properties of poliovirus double-stranded ribonucleic acid. J Mol Biol. 1966 Jul;18(3):421–428. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80034-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Compans R. W. The formation of poliovirus particles in association with the RNA replication complexes. J Gen Virol. 1973 Oct;21:99–108. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-21-1-99. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caliguiri L. A., Tamm I. Action of guanidine on the replication of poliovirus RNA. Virology. 1968 Jul;35(3):408–417. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90219-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper P. D., Wentworth B. B., McCahon D. Guanidine inhibition of poliovirus: a dependence of viral RNA synthesis on the configuration of structural protein. Virology. 1970 Mar;40(3):480–493. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90191-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dasgupta A., Baron M. H., Baltimore D. Poliovirus replicase: a soluble enzyme able to initiate copying of poliovirus RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2679–2683. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2679. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson W. O. Guanidine inhibits tobacco mosaic virus RNA synthesis at two stages. Intervirology. 1975;6(2):83–89. doi: 10.1159/000149459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Baltimore D. Poliovirus-specific primer-dependent RNA polymerase able to copy poly(A). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Sep;74(9):3677–3680. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.9.3677. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flanegan J. B., Van Dyke T. A. Isolation of a soluble and template-dependent poliovirus RNA polymerase that copies virion RNA in vitro. J Virol. 1979 Oct;32(1):155–161. doi: 10.1128/jvi.32.1.155-161.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedman R. M. Basis for variable response of arboviruses to guanidine treatment. J Virol. 1970 Nov;6(5):628–636. doi: 10.1128/jvi.6.5.628-636.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang A. S., Balitmore D. Initiation of polyribosome formation in poliovirus-infected HeLa cells. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 14;47(3):275–291. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90302-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobson M. F., Baltimore D. Morphogenesis of poliovirus. I. Association of the viral RNA with coat protein. J Mol Biol. 1968 Apr 28;33(2):369–378. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(68)90195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koschel K., Wecker E. Early functions of poliovirus. 3. The effect of guanidine on early functions. Z Naturforsch B. 1971 Sep;26(9):940–944. doi: 10.1515/znb-1971-0917. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. F., Nomoto A., Detjen B. M., Wimmer E. A protein covalently linked to poliovirus genome RNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):59–63. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.59. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee Y. S., Yajima Y., Nonoyama M. Mechanism of infection by Epstein-Barr virus. II. Comparison of viral DNA from HR-1 and superinfected Raji cells by restriction enzymes. Virology. 1977 Aug;81(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90054-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lund G. A., Scraba D. G. The isolation of Mengo virus stable non-capsid polypeptides from infected L cells and preliminary characterization of an RNA polymerase activity associated with polypeptide E. J Gen Virol. 1979 Aug;44(2):391–403. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-44-2-391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lundquist R. E., Maizel J. V., Jr Structural studies of the RNA component of the poliovirus replication complex. I. Purification and biochemical characterization. Virology. 1978 Apr;85(2):434–444. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(78)90450-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lwoff A. The specific effectors of viral development. Biochem J. 1965 Aug;96(2):289–301. doi: 10.1042/bj0960289. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McDonnell J. P., Levintow L. Kinetics of appearance of the products of poliovirus-induced RNA polymerase. Virology. 1970 Dec;42(4):999–1006. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(70)90348-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Detjen B., Pozzatti R., Wimmer E. The location of the polio genome protein in viral RNAs and its implication for RNA synthesis. Nature. 1977 Jul 21;268(5617):208–213. doi: 10.1038/268208a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penman S., Summers D. Effects on host cell metabolism following synchronous infection with poliovirus. Virology. 1965 Dec;27(4):614–620. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(65)90187-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RIGHTSEL W. A., DICE J. R., McALPINE R. J., TIMM E. A., McLEAN I. W., Jr, DIXON G. J., SCHABEL F. M., Jr Antiviral effect of guanidine. Science. 1961 Aug 25;134(3478):558–559. doi: 10.1126/science.134.3478.558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Röder A., Koschel K. Virus-specific proteins associated with the replication complex of poliovirus RNA. J Gen Virol. 1975 Jul;28(1):85–98. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-28-1-85. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sangar D. V. The replication of picornaviruses. J Gen Virol. 1979 Oct;45(1):1–13. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-45-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varma J. P. Inhibition of tobacco necrosis virus by guanidine carbonate. Virology. 1968 Oct;36(2):305–308. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(68)90149-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H. Involvement of viral procapsid in the RNA synthesis and maturation of poliovirus. Virology. 1977 Oct 15;82(2):299–307. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(77)90005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin F. H. Possible in vitro repair of viral RNA by ligase-like enzyme(s) in poliovirus-infected cells. J Virol. 1977 Jan;21(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/jvi.21.1.61-68.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


