Abstract
As a direct approach to visualize Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) binding to its cellular receptors and to learn more on the nature of this binding, virus preparations were conjugated to fluorescein isothiocyanate and used to detect EBV receptors on lymphoid cells. Different enzymatic and chemical treatments were also applied either to the virus or to target cells or to both, and the effect of these treatments on virus binding was then examined. The results obtained show that: (i) EBV can be fluoresceinated without affecting its infectivity or cell binding ability, and the fluoresceinated virus represents an important tool to investigate the biology and nature of EBV interactions with its cellular receptors; (ii) the two virus strains (P3HR-1 and B95-8) share common receptors on Raji cells; (iii) protease treatment of EBV or target cells abrogates virus binding; (iv) EBV receptors regenerate after removal of the protease, and this regeneration is inhibited by cycloheximide or sucrose; (v) EBV particles bear concanavalin A receptors, and this lectin hinders the interaction of the virus with its cellular receptors; (vi) neuraminidase treatment, various monosaccharides, ovalbumin, and glycopeptides derived from EBV or cell surface do not inhibit virus binding. Taken together, the above data also demonstrate that some cellular and viral surface (glyco-) proteins are required for EBV binding to its targets.
Full text
PDF


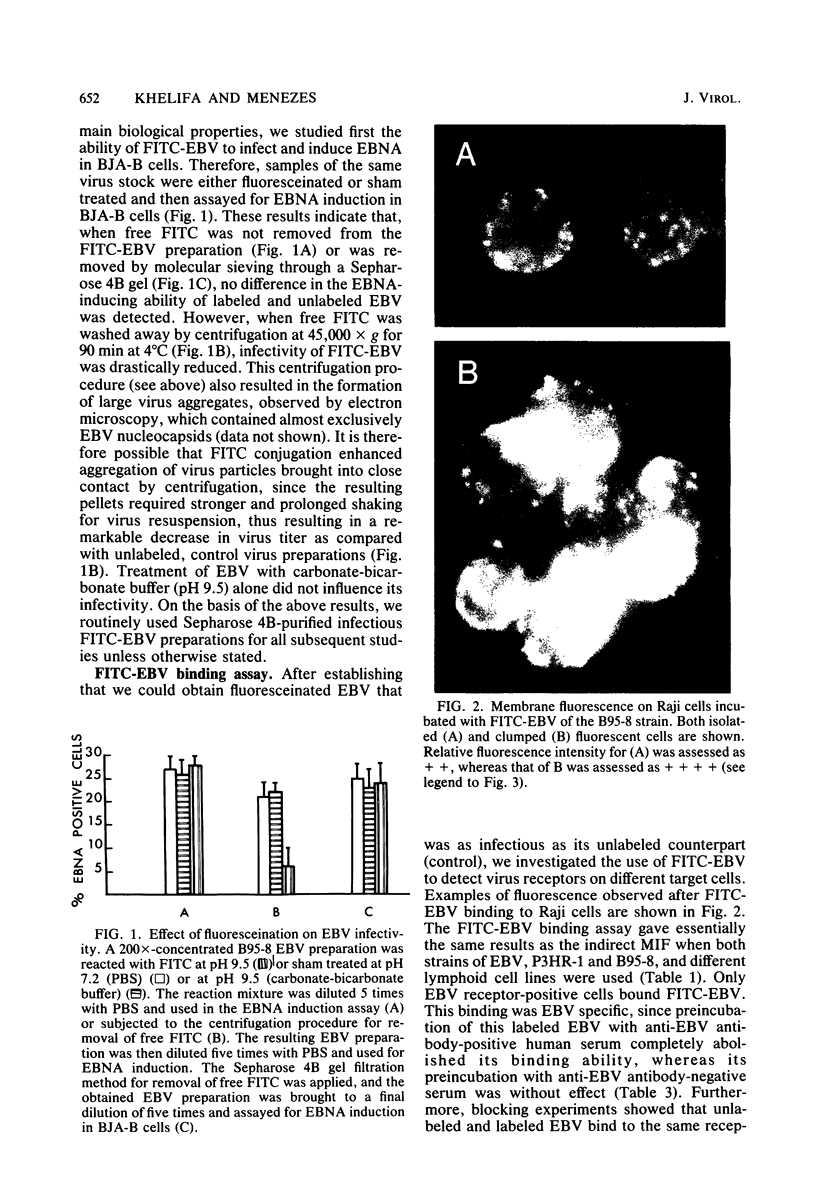
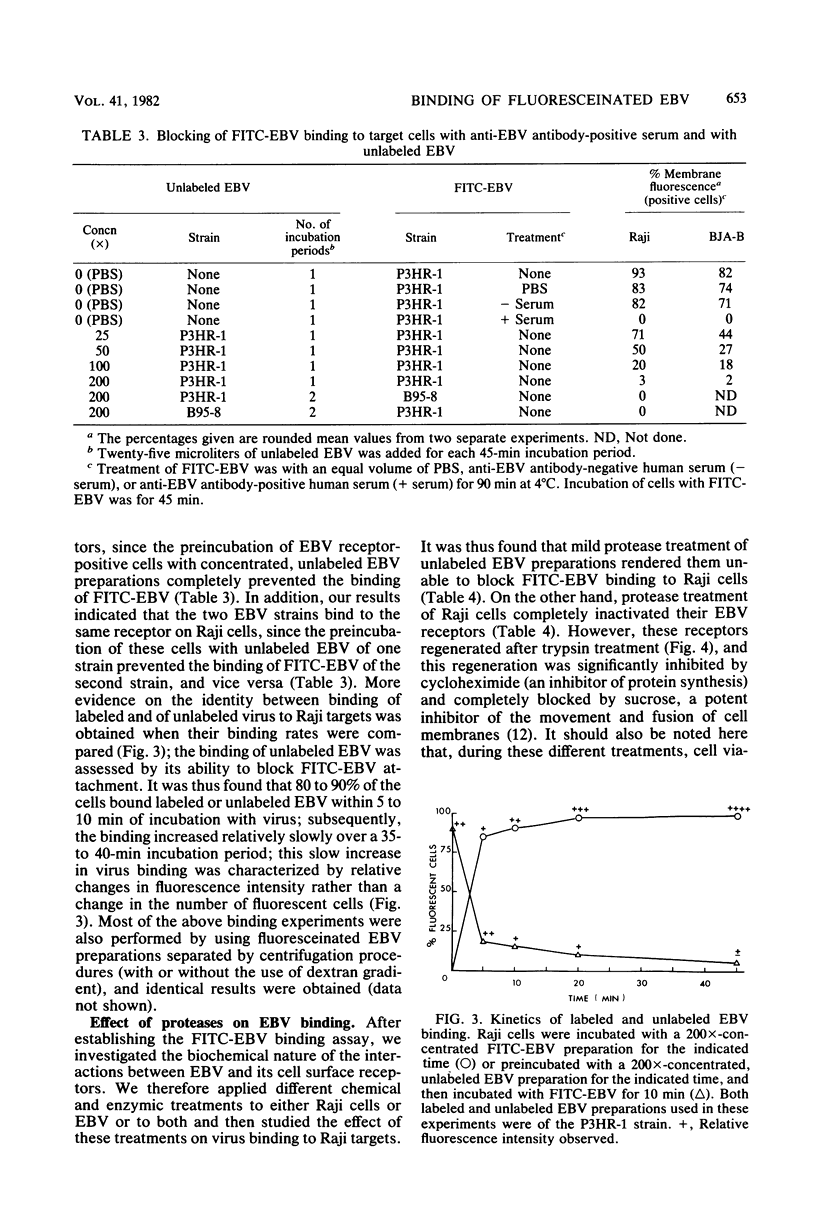
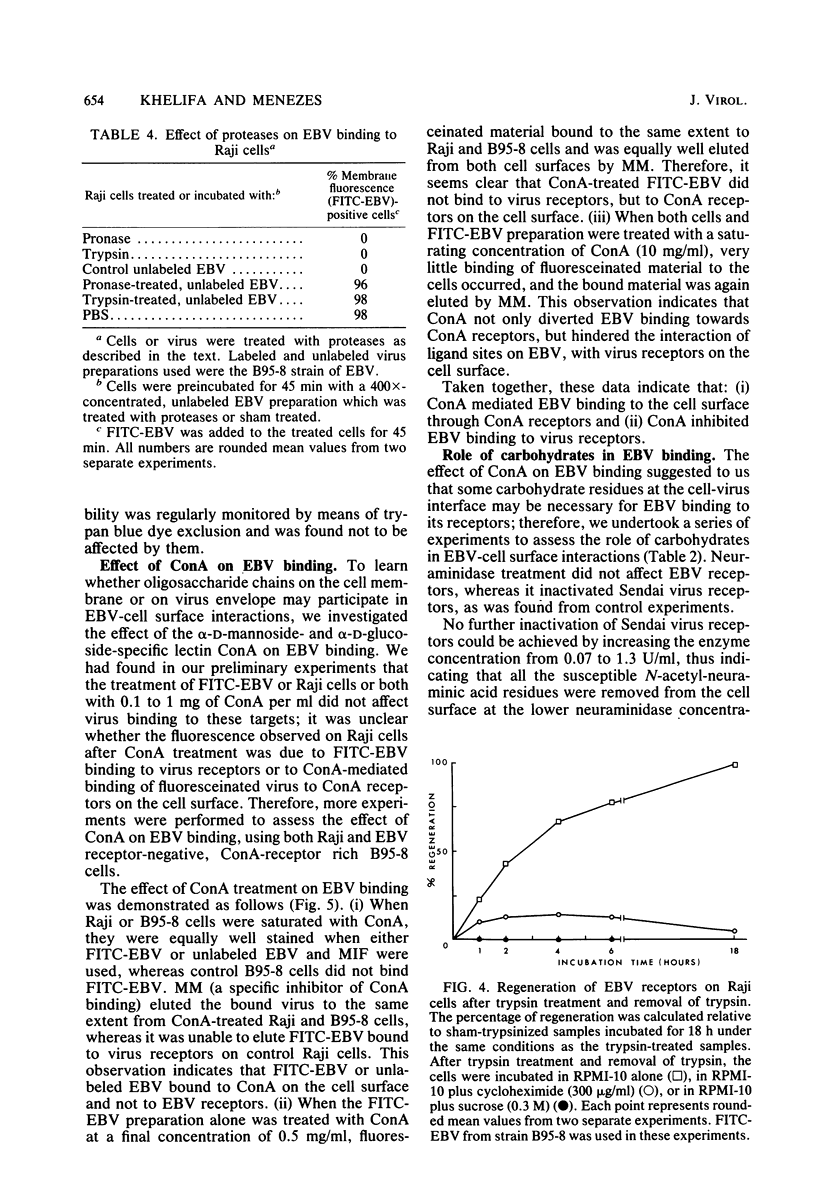

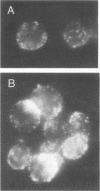
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baenziger J. U., Fiete D. Structural determinants of concanavalin A specificity for oligosaccharides. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 10;254(7):2400–2407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolyniuk M., Pritchett R., Kieff E. Proteins of Epstein-Barr virus. I. Analysis of the polypeptides of purified enveloped Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1976 Mar;17(3):935–949. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.3.935-949.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gervais F., Wills A., Leyritz M., Lebrun A., Joncas J. H. Relative lack of Epstein Barr virus (EBV) receptors on B cells from persistently EBV seronegative adults. J Immunol. 1981 Mar;126(3):897–900. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greaves M. F., Brown G. Epstein-Barr virus binding sites on lymphocyte subpopulations and the origin of lymphoblasts in cultured lymphoic cell lines and in the blood of patients with infectious mononucleosis. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1975 Mar;3(4):514–524. doi: 10.1016/0090-1229(75)90076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hinuma Y., Grace J. T., Jr Cloning of immunoglobulin-producing human leukemic and lymphoma cells in long-term cultures. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1967 Jan;124(1):107–111. doi: 10.3181/00379727-124-31677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G., Oldstone M. B., Bokish V., Yefenof E. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. VIII. Association between complement and Epstein-Barr virus receptors on human lymphoid cells. Scand J Immunol. 1976;5(4):401–410. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1976.tb00294.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jondal M., Klein G. Surface markers on human B and T lymphocytes. II. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors on B lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1973 Dec 1;138(6):1365–1378. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.6.1365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein E., Klein G., Nadkarni J. S., Nadkarni J. J., Wigzell H., Clifford P. Surface IgM-kappa specificity on a Burkitt lymphoma cell in vivo and in derived culture lines. Cancer Res. 1968 Jul;28(7):1300–1310. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Dombos L., Gothoskar B. Sensitivity of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) producer and non-producer human lymphoblastoid cell lines to superinfection with EB-virus. Int J Cancer. 1972 Jul 15;10(1):44–57. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910100108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein G., Hyman R., Trowbridge I. Correlated expression of a B-lymphocyte-specific glycoprotein (gp27/35) and the EBV receptor/C3 receptor complex in sublines from the same Burkitt lymphoma. Int J Cancer. 1979 Jan 15;23(1):37–41. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910230108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lozzio C. B., Lozzio B. B. Cytotoxicity of a factor isolated from human spleen. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1973 Feb;50(2):535–538. doi: 10.1093/jnci/50.2.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeda Y., Kim J., Koseki I., Mekada E., Shiokawa Y., Okada Y. Modification of cell membranes with viral envelopes during fusion of cells with HVJ (Sendai virus). III. Effects of mono- and di-saccharides on cell fusion and membrane movement of fused cells. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Aug;108(1):95–106. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(77)80014-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Jondal M., Leibold W., Dorval G. Epstein-Barr virus interactions with human lymphocyte subpopulations: virus adsorption, kinetics of expression of Epstein-Barr virus-associated nuclear antigen, and lymphocyte transformation. Infect Immun. 1976 Feb;13(2):303–310. doi: 10.1128/iai.13.2.303-310.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G. Biological differences between Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) strains with regard to lymphocyte transforming ability, superinfection and antigen induction. Exp Cell Res. 1975 May;92(2):478–484. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(75)90404-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Leibold W., Klein G., Clements G. Establishment and characterization of an Epstein-Barr virus (EBC)-negative lymphoblastoid B cell line (BJA-B) from an exceptional, EBV-genome-negative African Burkitt's lymphoma. Biomedicine. 1975 Jul;22(4):276–284. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Menezes J., Seigneurin J. M., Patel P., Bourkas A., Lenoir G. Presence of Epstein-Barr virus receptors, but absence of virus penetration, in cells of an Epstein-Barr virus genome-negative human lymphoblastoid T line (Molt 4). J Virol. 1977 Jun;22(3):816–821. doi: 10.1128/jvi.22.3.816-821.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller G., Lipman M. Release of infectious Epstein-Barr virus by transformed marmoset leukocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1973 Jan;70(1):190–194. doi: 10.1073/pnas.70.1.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PULVERTAFT J. V. A STUDY OF MALIGNANT TUMOURS IN NIGERIA BY SHORT-TERM TISSUE CULTURE. J Clin Pathol. 1965 May;18:261–273. doi: 10.1136/jcp.18.3.261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patel P., Menezes J. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV)-lymphoid cell interactions. I. Quantification of EBV particles required for the membrane immunofluorescence assay and the comparative expression of EBV receptors on different human B, T and null cell lines. J Gen Virol. 1981 Mar;53(Pt 1):1–11. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-53-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sairenji T., Hinuma Y. Modes of Epstein-Barr virus infection in human floating cell lines. Gan. 1973 Dec;64(6):583–590. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwaber J. F., Klein G., Ernberg I., Rosen A., Lazarus H., Rosen F. S. Deficiency of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) receptors on B lymphocytes from certain patients with common varied agammaglobulinemia. J Immunol. 1980 May;124(5):2191–2196. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sefton B. M., Keegstra K. Glycoproteins of Sindbis virus: priliminary characterization of the oligosaccharides. J Virol. 1974 Sep;14(3):522–530. doi: 10.1128/jvi.14.3.522-530.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volsky D. J., Shapiro I. M., Klein G. Transfer of Epstein-Barr virus receptors to receptor-negative cells permits virus penetration and antigen expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5453–5457. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5453. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Horoszewicz J. S. Some biophysical aspects of E-B virus adsorption to the surfaces of three types of mammalian cells. Int J Cancer. 1971 Jan 15;7(1):149–159. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910070117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yefenof E., Klein G. Membrane receptor stripping confirms the association between EBV receptors and complement receptors on the surface of human B lymphoma lines. Int J Cancer. 1977 Sep 15;20(3):347–352. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910200305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]