Abstract
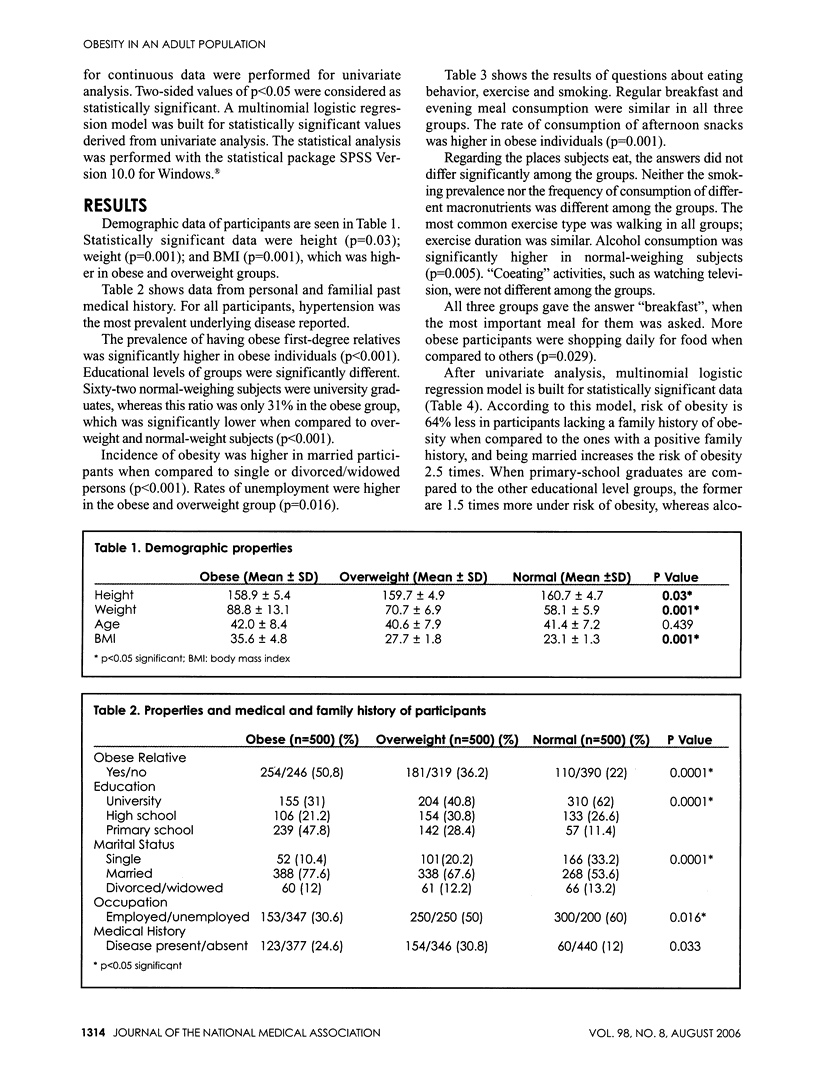
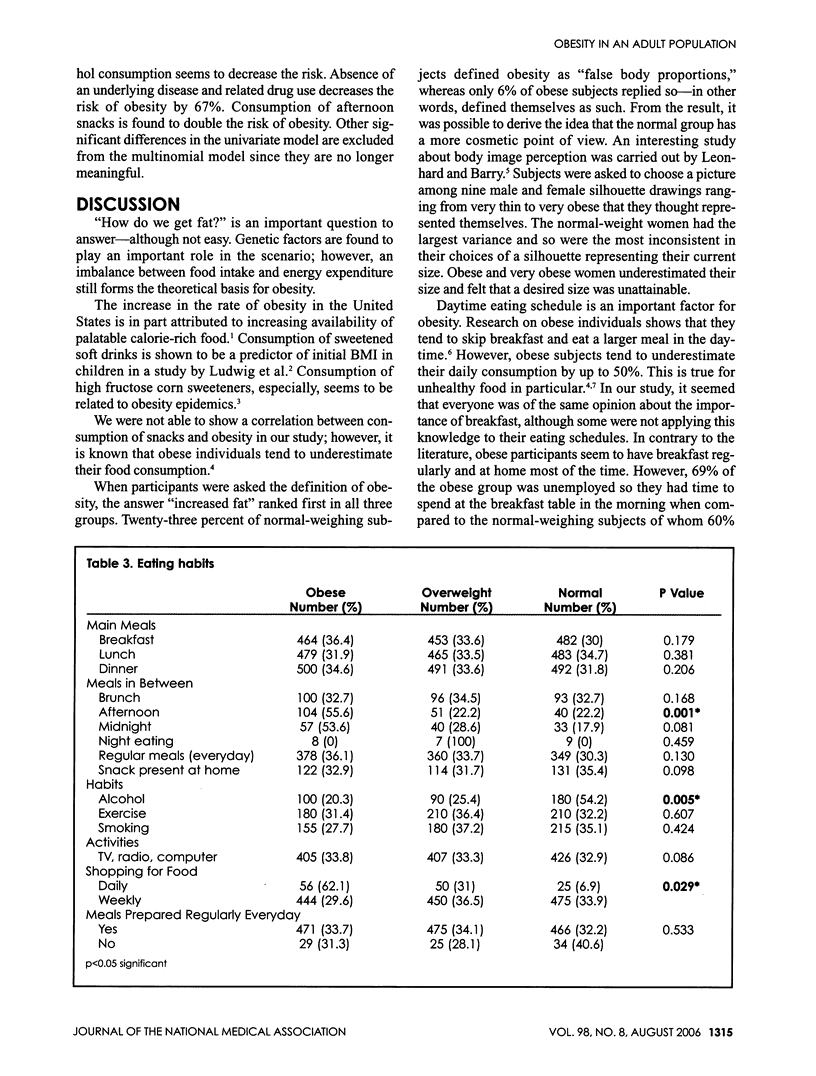
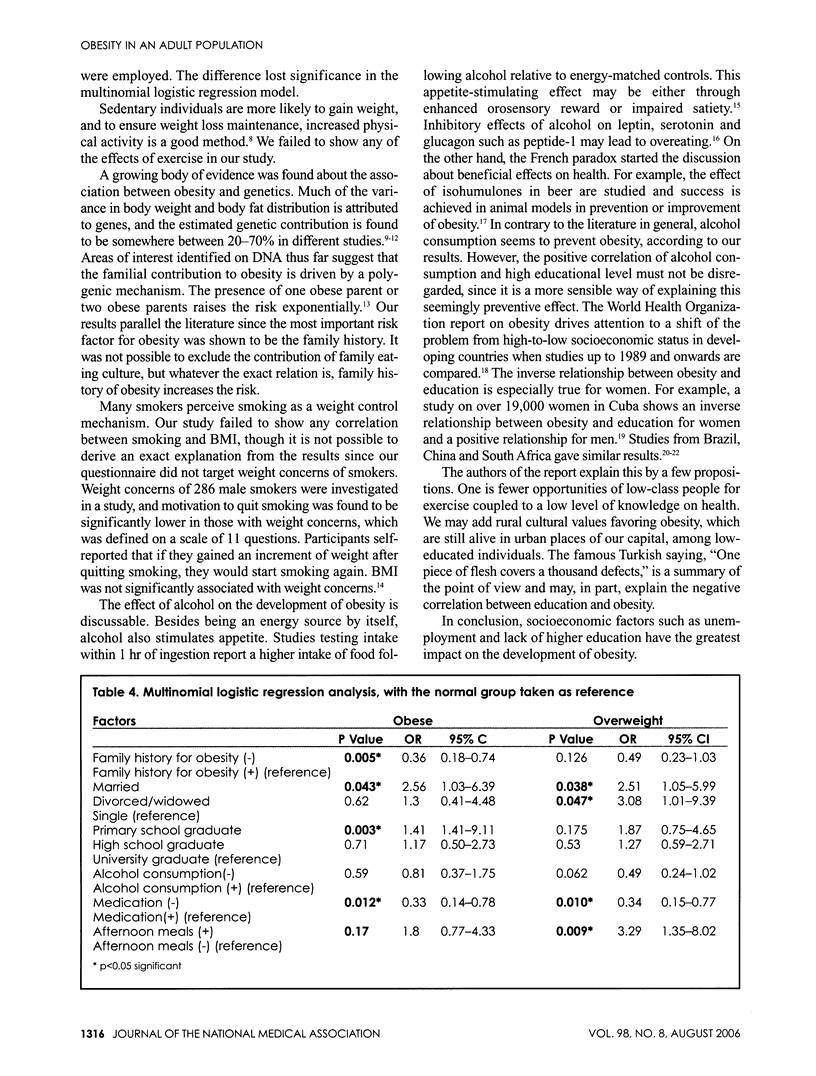
Obesity as a disease is a yet-unidentified sum of genetic and environmental factors. Risky eating behavior and lifestyle may bring the disease. The aim of the study was to find out risk factors for obesity factors influencing definition of obesity. Participants (n = 1500) who filled out a questionnaire about eating habits are grouped according to their body mass indices as normal weight, overweight and obese (n = 500 in each group). According to our results, the prevalence of having obese first-degree relatives is significantly higher in obese individuals (p < 0.001). Sixty-two of normal weighing subjects were university graduates, whereas this ratio was only 31% in the obese group (p < 0.001). Incidence of obesity was higher in married participants when compared to the single or divorced/widowed persons (p < 0.001). Multinomial logistic regression analysis gave the following results: risk of obesity was 57% less in participants lacking a family history of obesity when compared to the ones with a positive family history (p = 0.005). Being married increases the risk of obesity 2.5 times; being a primary school graduate increases the risk about 1.5 times. Lower educational level, unemployment and lack of counseling seem to be risk factors associated with obesity. Diverging patterns of sociodemographic features, lifestyles and perception were evident even between overweight and obese populations.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chagnon Yvon C., Rankinen Tuomo, Snyder Eric E., Weisnagel S. John, Pérusse Louis, Bouchard Claude. The human obesity gene map: the 2002 update. Obes Res. 2003 Mar;11(3):313–367. doi: 10.1038/oby.2003.47. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark Matthew M., Decker Paul A., Offord Kenneth P., Patten Christi A., Vickers Kristin S., Croghan Ivana T., Hays J. Taylor, Hurt Richard D., Dale Lowell C. Weight concerns among male smokers. Addict Behav. 2004 Nov;29(8):1637–1641. doi: 10.1016/j.addbeh.2004.02.034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damcott Coleen M., Sack Paul, Shuldiner Alan R. The genetics of obesity. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2003 Dec;32(4):761–786. doi: 10.1016/s0889-8529(03)00076-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drewnowski A. Nutrition transition and global dietary trends. Nutrition. 2000 Jul-Aug;16(7-8):486–487. doi: 10.1016/s0899-9007(00)00295-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du Shufa, Lu Bing, Zhai Fengying, Popkin Barry M. A new stage of the nutrition transition in China. Public Health Nutr. 2002 Feb;5(1A):169–174. doi: 10.1079/PHN2001290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo Keiji. Beer and health: preventive effects of beer components on lifestyle-related diseases. Biofactors. 2004;22(1-4):303–310. doi: 10.1002/biof.5520220160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lake J. K., Power C., Cole T. J. Child to adult body mass index in the 1958 British birth cohort: associations with parental obesity. Arch Dis Child. 1997 Nov;77(5):376–381. doi: 10.1136/adc.77.5.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonhard M. L., Barry N. J. Body image and obesity: effects of gender and weight on perceptual measures of body image. Addict Behav. 1998 Jan-Feb;23(1):31–34. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4603(97)00017-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lichtman S. W., Pisarska K., Berman E. R., Pestone M., Dowling H., Offenbacher E., Weisel H., Heshka S., Matthews D. E., Heymsfield S. B. Discrepancy between self-reported and actual caloric intake and exercise in obese subjects. N Engl J Med. 1992 Dec 31;327(27):1893–1898. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199212313272701. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loos R. J. F., Bouchard C. Obesity--is it a genetic disorder? J Intern Med. 2003 Nov;254(5):401–425. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2796.2003.01242.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig D. S., Peterson K. E., Gortmaker S. L. Relation between consumption of sugar-sweetened drinks and childhood obesity: a prospective, observational analysis. Lancet. 2001 Feb 17;357(9255):505–508. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)04041-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro C. A., Conde W. L., Popkin B. M. Independent effects of income and education on the risk of obesity in the Brazilian adult population. J Nutr. 2001 Mar;131(3):881S–886S. doi: 10.1093/jn/131.3.881S. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monteiro Carlos A., Moura Erly C., Conde Wolney L., Popkin Barry M. Socioeconomic status and obesity in adult populations of developing countries: a review. Bull World Health Organ. 2005 Jan 5;82(12):940–946. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morgan K. J., Zabik M. E., Stampley G. L. The role of breakfast in diet adequacy of the U.S. adult population. J Am Coll Nutr. 1986;5(6):551–563. doi: 10.1080/07315724.1986.10720156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pronk N. P., Wing R. R. Physical activity and long-term maintenance of weight loss. Obes Res. 1994 Nov;2(6):587–599. doi: 10.1002/j.1550-8528.1994.tb00110.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schoeller D. A. Limitations in the assessment of dietary energy intake by self-report. Metabolism. 1995 Feb;44(2 Suppl 2):18–22. doi: 10.1016/0026-0495(95)90204-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeomans Martin R., Caton Samantha, Hetherington Marion M. Alcohol and food intake. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2003 Nov;6(6):639–644. doi: 10.1097/00075197-200311000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeomans Martin R. Effects of alcohol on food and energy intake in human subjects: evidence for passive and active over-consumption of energy. Br J Nutr. 2004 Aug;92 (Suppl 1):S31–S34. doi: 10.1079/bjn20041139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemel M. B., Shi H., Greer B., Dirienzo D., Zemel P. C. Regulation of adiposity by dietary calcium. FASEB J. 2000 Jun;14(9):1132–1138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


